By Chenhui
Apache Kafka is a distributed streaming platform. It is a widely used, indispensable message component in the Internet field. Kafka is generally used as the core hub for message forwarding. The upstream and downstream systems use Kafka to implement asynchronous peak-load shifting. Kafka is also irreplaceable in the big data processing and real-time data processing fields.
Kafka is widely used in fields (such as log collection, big data processing, and database). Kafka has standardized modules to connect with upstream and downstream components. For example, log collection includes Flume, Filebeat, and Logstash, and big data processing includes Spark and Flink. At the same time, there are no ready-made tools for direct docking in some niche fields (such as docking a niche database or a user's customized system). At this time, the general docking method is to develop Kafka production and consumption program docking.
The following issues are commonly encountered when different systems are connected:
Based on the extensive use of Kafka and the diversity of upstream and downstream systems, Kafka provides a built-in framework for connecting upstream and downstream systems: Kafka Connect.
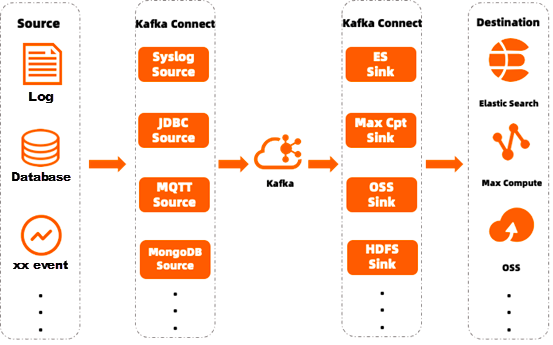
Kafka Connect is a framework for transferring data streams into and out of Kafka. The following describes some of the main concepts of connectors:
The connector in Kafka Connect defines where data should be copied from. A connector instance is a logical job that manages data replication between Kafka and another system.
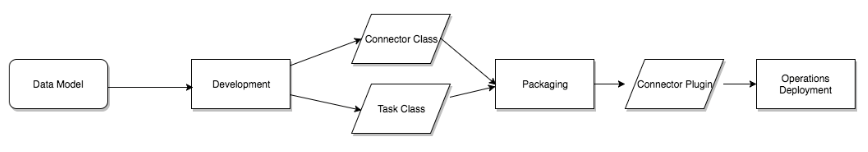
There are some open-source implementations of the connector. You can also write a new connector plug-in from scratch. The writing process generally works like this:
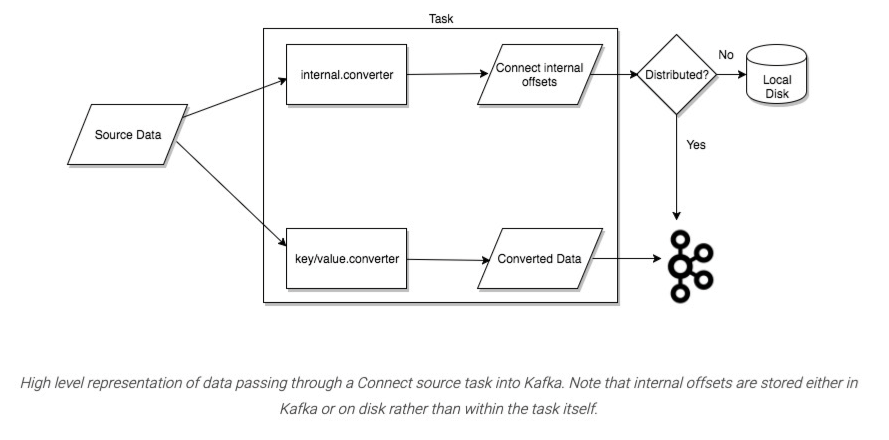
Task is the primary role in the Connect data model that deals with data. Each connector instance coordinates a set of tasks that replicate data. Kafka Connect provides built-in support for parallelism and scalable data replication with minimal configuration by allowing the connector to decompose a single job into multiple tasks. These tasks do not store any state. Task states are stored in special topic config.storage.topic and status.storage.topic in Kafka. Thus, tasks can be started, stopped, or restarted at any time to provide a flexible, scalable data pipeline.
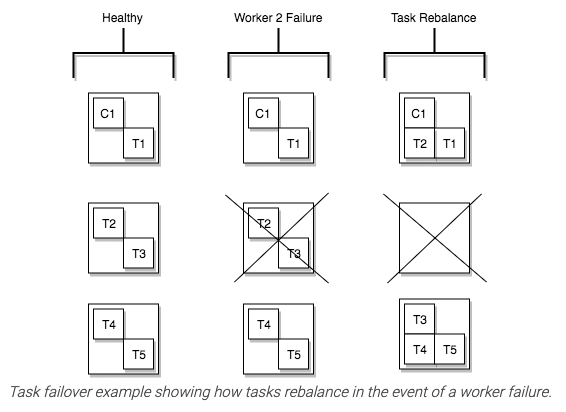
When a connector is first submitted to the cluster, workers rebalance all the connectors in the cluster and their tasks so each worker has roughly the same amount of work. The same rebalancing process is used when connectors increase or decrease the number of tasks they require or when the configuration of a connector is changed. When a worker fails, tasks are rebalanced among the active workers. When a task fails, rebalancing is not triggered because the task failure is considered an exception. Therefore, failed tasks are not automatically restarted by the framework and should be restarted via the REST API.
Converter is required for Kafka Connect to support specific data formats when writing to or reading data from Kafka. Task uses a converter to change data format from bytes to concatenate internal data format and vice versa.
The following converters are provided by default:
The converters are decoupled from the connectors themselves, so the converters are naturally reused between connectors.
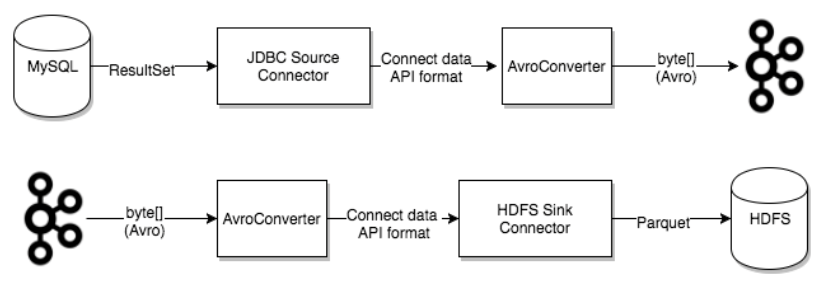
The connector can configure transformations to make simple and lightweight modifications to individual messages. This is convenient for small data adjustments and event routing, and multiple transformations can be chained together in a connector configuration.
When Kafka Connect is deployed separately offline, the design is good. When it is provided as a cloud service, there are still many problems, mainly reflected in the following points.
Based on the various problems of Kafka Connect deployment on the cloud, the Message Queue for Apache Kafka Team re-implemented the Kafka Connect module in a cloud-native manner while being compatible with the native Kafka Connect framework.
The architecture design separates the control plane from the running plane and performs task distribution and module communication through the database and Etcd. The underlying runtime environment uses Kubernetes clusters to better control the granularity and isolation of resources. The overall architecture diagram is listed below:
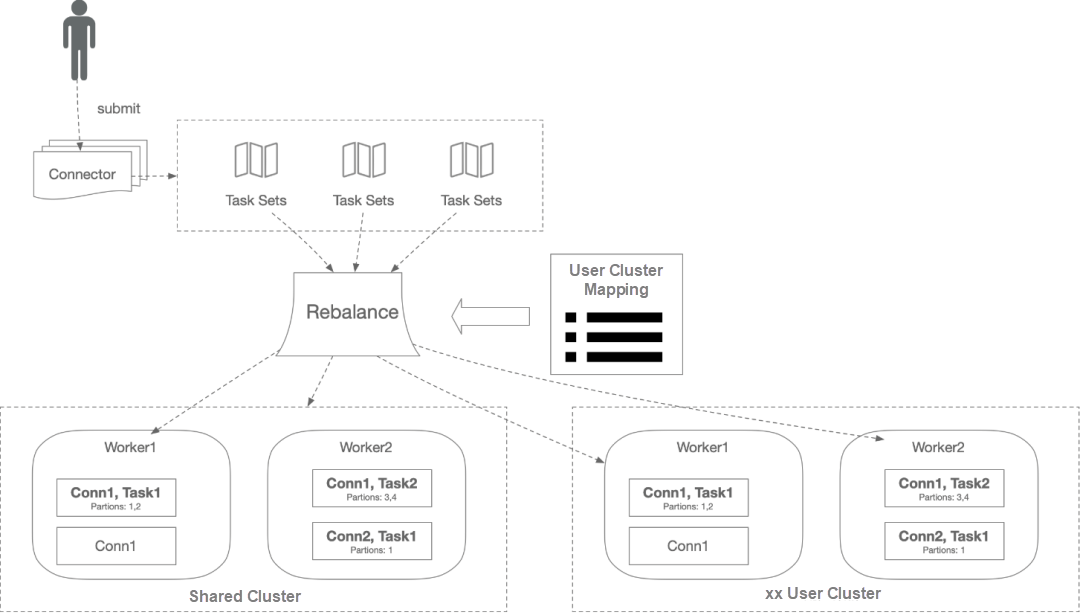
This architecture solves the problems encountered by Apache Kafka Connect modules on the cloud.
Alibaba Cloud Message Queue for Apache Kafka Connect can be implemented in the following ways:
The sections below detail how Connect is implemented:
Backups between databases generally do not use Kafka. MySQL → Kafka is generally used to distribute data to downstream subscriptions and make alerts or other responses when MySQL data changes. Link MySQL → Kafka → subscriptions → alerts/changes to other systems.
MaxCompute is commonly used in data warehouses on Alibaba Cloud. Tasks are characterized by high throughput and also require data cleaning. The general process is Kafka → MaxCompute, and then MaxCompute internal tasks perform data conversion. You can also clean data before it is transferred to MaxCompute. Generally, the link is Kafka → Flink → MaxCompute. You can use Function Compute to replace Flink on tasks with simple data conversion or small data volume. The link is Kafka → FC → MaxCompute.
Common data retrieval and reports are generally performed through ES, and data needs to be cleaned before being passed into ES. The suitable path is Kafka → Flink → ES/Kafka → FC → ES.
In the alert system, the general process of Kafka is used as the pre-module → Kafka → subscription → alert module. The best way is to use the pre-module → Kafka → FC → alert.
Some data may need to be archived regularly for long-term storage. OSS is a good medium. In this scenario, only the original data needs to be saved, so a good way may be Kafka → OSS. If data needs to be processed, you can use Kafka → FC → OSS links.
The connections currently supported by Message Queue for Apache Kafka are all developed independently using the self-developed new architecture, which has good coverage for mainstream usage scenarios. However, we can see Kafka ecology is developing rapidly, and Kafka usage scenarios are also increasing. Open-source Kafka Connect is also developing continuously. Next, Message Queue for Apache Kafka will connect to open-source Kafka Connect, so open-source Kafka Connect can seamlessly run on the self-developed architecture without modification.
Kafka has occupied an important position in Internet architecture and is also actively expanding upstream and downstream. In addition to Kafka Connect, Kafka Streams, Ksql, Kafka Rest Proxy, and other modules are continuously improving and maturing. I believe Kafka will play a more important role in the software architecture in the subsequent development.
Continuous Performance Profiling Practice Analysis: Locate Performance Problems at Any Time
Implementation and Practice of KubeAI: A Cloud-Native AI Platform of Dewu

212 posts | 13 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native - August 14, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Community - June 14, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Community - May 17, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Indonesia - June 3, 2024
Alibaba Container Service - July 22, 2024
Alibaba EMR - October 12, 2021

212 posts | 13 followers
Follow Message Queue for Apache Kafka
Message Queue for Apache Kafka
A fully-managed Apache Kafka service to help you quickly build data pipelines for your big data analytics.
Learn More Realtime Compute for Apache Flink
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink offers a highly integrated platform for real-time data processing, which optimizes the computing of Apache Flink.
Learn More ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ
ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ
ApsaraMQ for RocketMQ is a distributed message queue service that supports reliable message-based asynchronous communication among microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications.
Learn More MaxCompute
MaxCompute
Conduct large-scale data warehousing with MaxCompute
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native