By Yuanyi
Kubernetes is currently the industry standard for cloud-native computing, offering a robust ecosystem and cross-cloud capabilities. It abstracts the IaaS resource delivery standard, making it easier for users to access cloud resources. Meanwhile, users desire to focus more on their core businesses and achieve application-oriented delivery, giving rise to the concept of Serverless. But how can we leverage the native Kubernetes to deliver Serverless capabilities? And how can we achieve the on-demand utilization of heterogeneous resources such as GPUs? This article will introduce the development practices of ACK Serverless: On-Demand Use of Heterogeneous Resources.
To address these challenges, we adopt Knative + ASK as the Serverless architecture. After collecting the data, it is sent to ApsaraMQ Kafka for further processing. Upon receiving the event from the Kafka event source, the service gateway accesses the data processing service, which automatically scales up or down based on the incoming request volume.
• Kubernetes container developers.
• Serverless developers.
• AI audio and video encoding/decoding scenarios.
• Big data and AI intelligent recognition.
• Serverless Kubernetes (ASK): the ACK Serverless cluster is a serverless Kubernetes container service provided by Alibaba Cloud.
• Knative: Knative is a Kubernetes-based serverless framework. The purpose of Knative is to create a cloud-native and cross-platform orchestration standard for serverless applications. It implements this serverless standard by integrating the creation of containers (or functions), workload management (auto-scaling), and event models.
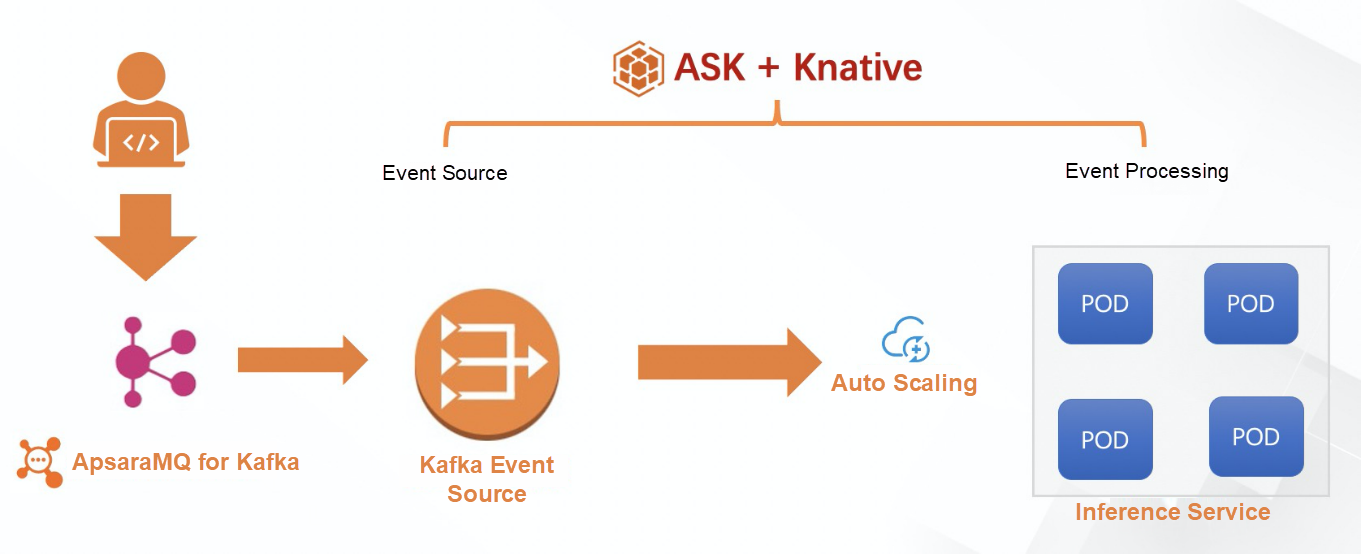
After the user collects the data and sends it to ApsaraMQ for Kafka, the Kafka event source in Knative receives the message and forwards it to the AI inference service, where the service performs intent recognition processing on the event.
For users aiming to use on-demand resources through Serverless technology to reduce resource usage costs, simplify O&M deployment, and those with business demands for heterogeneous resources such as GPU, the ASK + Knative solution can fulfill the usage requirements of heterogeneous resources like GPU, streamline application O&M and deployment (minimizing operations on resources such as k8s deployment/svc/ingress/hpa). Notably, IaaS resources are maintenance-free.
• A Container Service for Kubernetes Serverless (ACK Serverless) cluster is created.
• Knative Eventing is deployed.
• An event source KafkaSource is installed.
This service is used to receive events sent by Knative Eventing and perform auto-scaling based on the number of requests to process data. Before deployment, we should confirm that there are no workloads, which will facilitate the observation of the results after deployment.
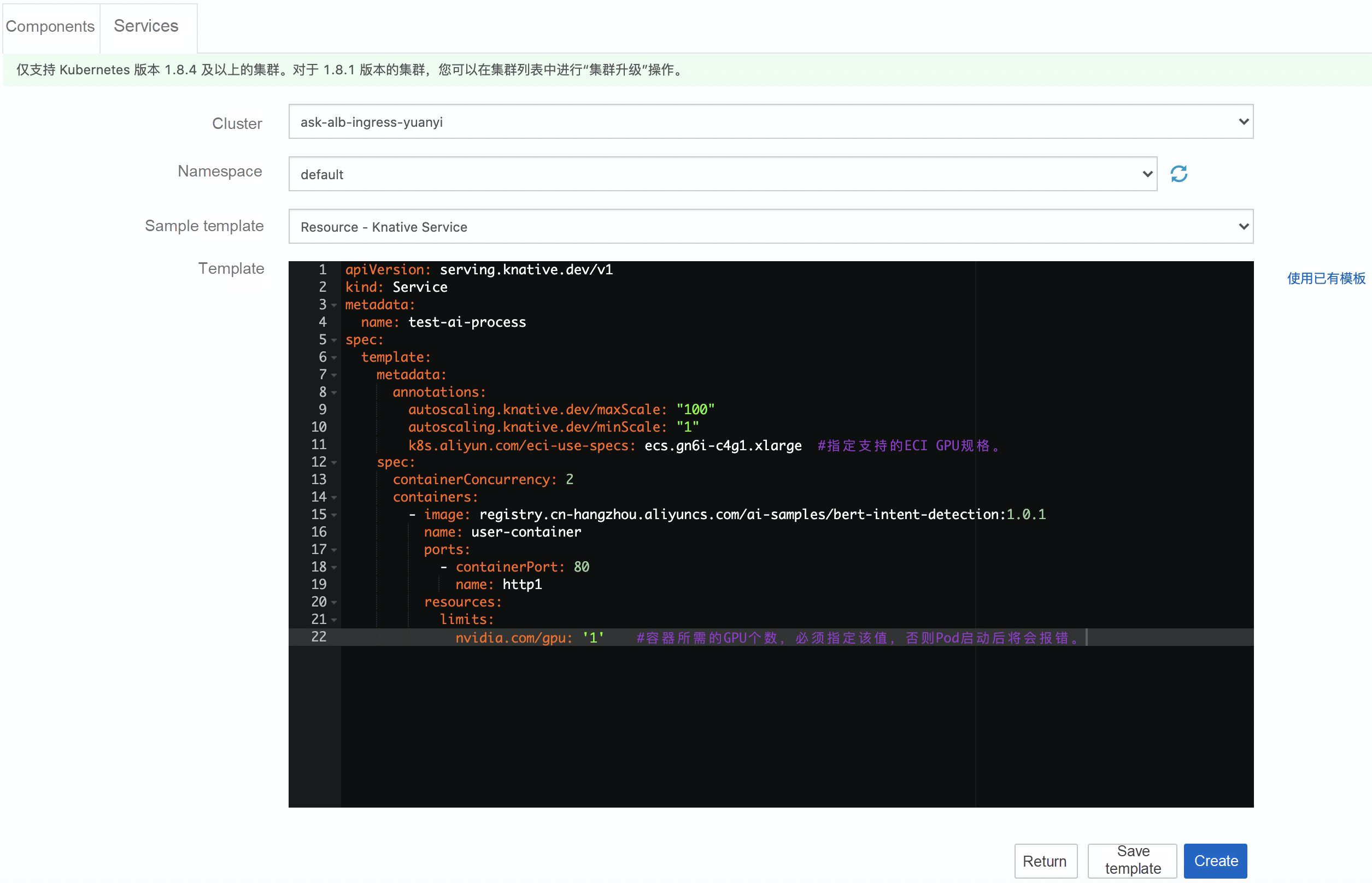
Then, use Knative to deploy inference processing to GPU-based workloads. Here, we use YAML to deploy it. The YAML content is as follows:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: test-ai-process
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
autoscaling.knative.dev/maxScale: "100"
autoscaling.knative.dev/minScale: "1"
k8s.aliyun.com/eci-use-specs: ecs.gn6i-c4g1.xlarge # Specify supported ECI GPU specifications.
spec:
containerConcurrency: 2
containers:
- image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/ai-samples/bert-intent-detection:1.0.1
name: user-container
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: http1
resources:
limits:
nvidia.com/gpu: '1' # Specify the number of GPUs that are required by the container. This field is required. If you do not specify this field, an error will be returned when the Pod is started.Parameter description:
• minScale and maxScale: indicate the minimum and maximum number of Pods configured for the service.
• containerConcurrency: indicates the maximum request parallelism of the configured Pods.
• k8s.aliyun.com/eci-use-specs: indicates the configured ECI specification.
Then we can deploy the service.
After the inference service is deployed, we can access the service as follows.
$ curl -H "host: test-ai-process.default.8829e4ebd8fe9967.app.alicontainer.com" "http://120.26.143.xx/predict?query=music" -vThe following result is returned:
* Trying 120.26.143.xx...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to 120.26.143.xx (120.26.143.xx) port 80 (#0)
> GET /predict?query=music HTTP/1.1
> Host: test-ai-process.knative-serving.8829e4ebd8fe9967.app.alicontainer.com
> User-Agent: curl/7.64.1
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Date: Thu, 17 Feb 2022 09:10:06 GMT
< Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
< Content-Length: 9
< Connection: keep-alive
<
* Connection #0 to host 120.26.143.xx left intact
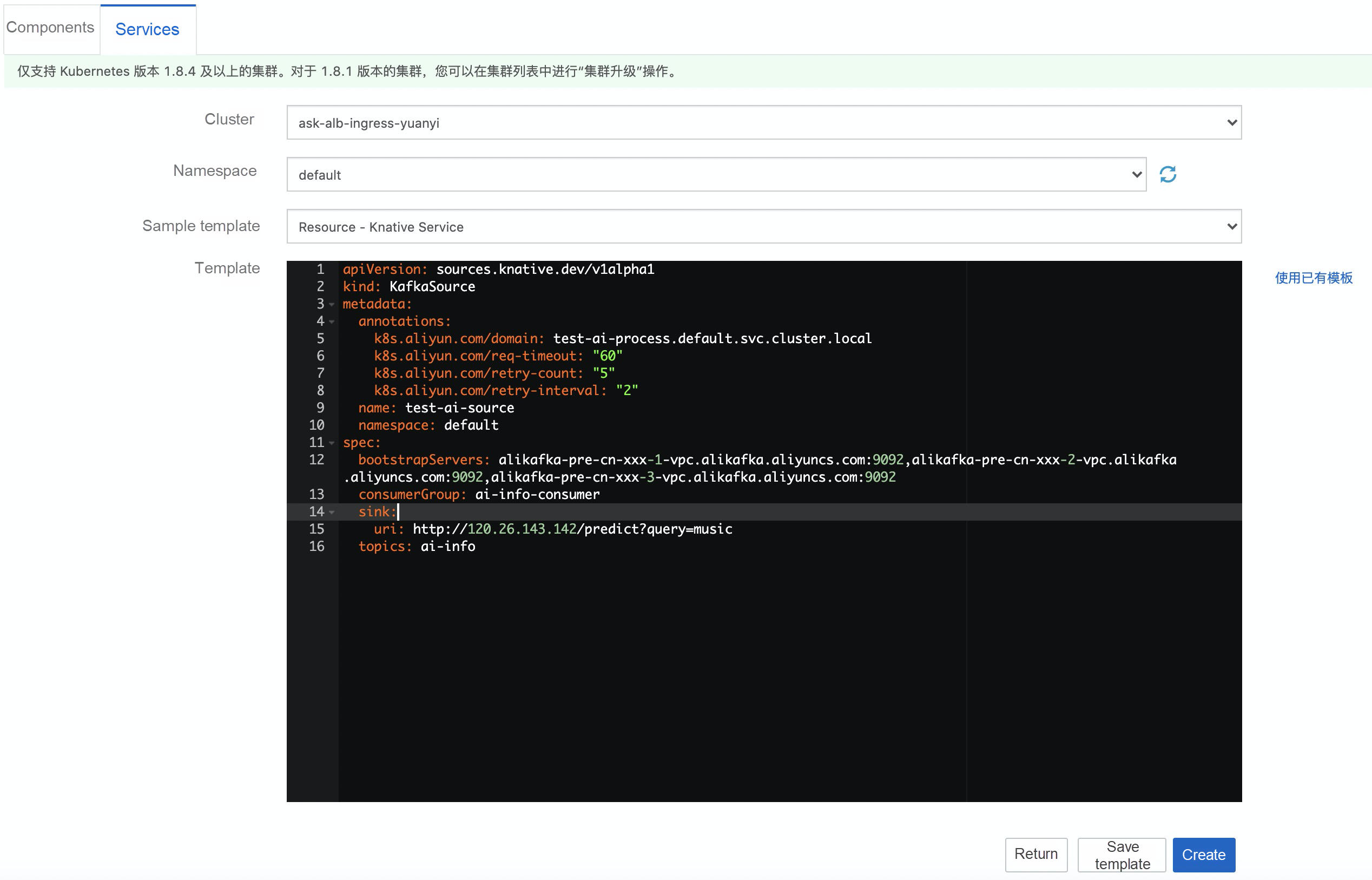
PlayMusic* # Intent recognition resultsWe can use Knative Eventing to receive, filter, and transfer events. Here, we use a Kafka event source as the event driver to receive events from Kafka and then send the events to message processing. We use YAML to deploy it. The YAML content is as follows:
apiVersion: sources.knative.dev/v1alpha1
kind: KafkaSource
metadata:
annotations:
k8s.aliyun.com/domain: test-ai-process.default.svc.cluster.local
k8s.aliyun.com/req-timeout: "60"
k8s.aliyun.com/retry-count: "5"
k8s.aliyun.com/retry-interval: "2"
name: test-ai-source
namespace: default
spec:
bootstrapServers: alikafka-pre-cn-xxx-1-vpc.alikafka.aliyuncs.com:9092,alikafka-pre-cn-7pp2kmoc7002-2-vpc.alikafka.aliyuncs.com:9092,alikafka-pre-cn-xx-3-vpc.alikafka.aliyuncs.com:9092
consumerGroup: ai-info-consumer
sink:
uri: http://120.26.143.xx/predict?query=music
topics: ai-infoParameter description:
Forward route:
k8s.aliyun.com/domain: test-ai-process.default.svc.cluster.local.http://120.26.143.xx/predict?query=music.Then we can deploy the service.
Next, we will simulate sending messages concurrently to perform automatic elastic verification. The Golang client sends a message to Kafka with the following codes:
package main
import (
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"strconv"
"time"
"github.com/Shopify/sarama"
)
var producer sarama.SyncProducer
func init() {
// Initialize the Kafka client.
// Set the username, password, and access certificate.
kafkaConfig := sarama.NewConfig()
kafkaConfig.Version = sarama.V0_10_2_0
kafkaConfig.Producer.Return.Successes = true
kafkaConfig.Net.SASL.Enable = true
kafkaConfig.Net.SASL.User = "alikafka_xxx"
kafkaConfig.Net.SASL.Password = "RpfoLE41hdX60ybxxxx"
kafkaConfig.Net.SASL.Handshake = true
certBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile("/Users/richard/common/demo/ca-cert")
clientCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
ok := clientCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(certBytes)
if !ok {
panic("kafka producer failed to parse root certificate")
}
kafkaConfig.Net.TLS.Config = &tls.Config{
//Certificates: []tls.Certificate{},
RootCAs: clientCertPool,
InsecureSkipVerify: true,
}
kafkaConfig.Net.TLS.Enable = true
if err = kafkaConfig.Validate(); err != nil {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Kafka producer config invalidate. err: %v", err)
fmt.Println(msg)
panic(msg)
}
// Set the endpoint of the Kafka instance.
producer, err = sarama.NewSyncProducer([]string{"alikafka-pre-cn-xxx-1.alikafka.aliyuncs.com:9093","alikafka-pre-cn-xxx-2.alikafka.aliyuncs.com:9093","alikafka-pre-cn-xxx-3.alikafka.aliyuncs.com:9093"}, kafkaConfig)
if err != nil {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Kafak producer create fail. err: %v", err)
fmt.Println(msg)
panic(msg)
}
}
func main() {
// Simulate 50 concurrent messages for 100s.
for i := 1; i <= 100; i++ {
for j := 0; j < 50; j++ {
key := strconv.FormatInt(time.Now().UTC().UnixNano()+int64(j), 10)
value := `{"id":12182,"template_name":"template_media/videos/templates/8f3a5f293149095aa62958029e208501_1606889936.zip","width":360,"height":640}`
go produce("demo", key, value)
}
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}
// The function for sending messages from Kafka.
func produce(topic string, key string, content string) error {
msg := &sarama.ProducerMessage{
Topic: topic,
Key: sarama.StringEncoder(key),
Value: sarama.StringEncoder(content),
Timestamp: time.Now(),
}
_, _, err := producer.SendMessage(msg)
if err != nil {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Send Error topic: %v. key: %v. content: %v", topic, key, content)
fmt.Println(msg)
return err
}
fmt.Printf("Send OK topic:%s key:%s value:%s\n", topic, key, content)
return nil
}We can see the automatic elastic scale-out as follows:
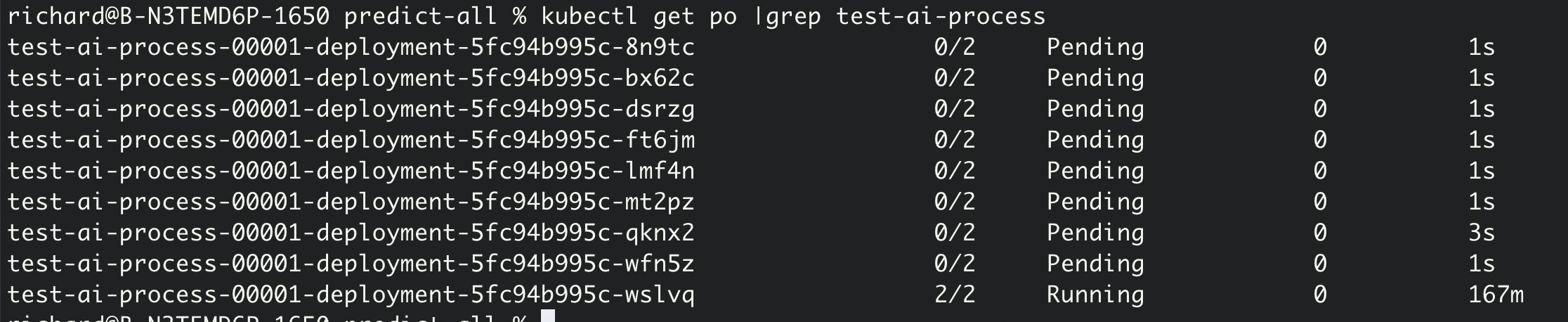
Based on Kubernetes, the ACK Serverless provides serverless capabilities, such as on-demand use, node O&M-free, heterogeneous resources, and Knative Eventing, so that developers can truly implement serverless application programming through Kubernetes standardized APIs.
Pod fails to be created when deploying the inference service (test-ai-process).
You can view the event exception information of the Pod:
The Kafka instance must belong to the same VPC as the ACK Serverless cluster, and the Kafka instance whitelist must be set to 0.0.0.0/0.
ACK Cloud Native AI Suite | Training and Inference of Open-Source Large Models on Kubernetes

223 posts | 33 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Indonesia - February 22, 2024
Alibaba Developer - February 7, 2022
Alibaba Container Service - November 15, 2024
Alibaba Developer - September 22, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - July 15, 2020
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - March 14, 2022

223 posts | 33 followers
Follow Function Compute
Function Compute
Alibaba Cloud Function Compute is a fully-managed event-driven compute service. It allows you to focus on writing and uploading code without the need to manage infrastructure such as servers.
Learn More ACK One
ACK One
Provides a control plane to allow users to manage Kubernetes clusters that run based on different infrastructure resources
Learn More Container Service for Kubernetes
Container Service for Kubernetes
Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes is a fully managed cloud container management service that supports native Kubernetes and integrates with other Alibaba Cloud products.
Learn More Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Accelerate and secure the development, deployment, and management of containerized applications cost-effectively.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Container Service