By Zhixin, OceanBase Technical Expert
OceanBase is a Distributed Relational Database Service (DRDS). As the size of ObServer clusters continues to expand, if you connect to the ObServer directly, the probability of stopping or machines going online or offline will also increase. As such, OBProxy was created to solve the problems of SQL routing and high availability in distributed database systems.
OBProxy (OceanBase Database Proxy) is a service proxy for OceanBase databases. Using OBProxy can mask the complexity brought about by the distribution of the backend ObServer cluster itself. It makes accessing a distributed database as simple as accessing a standalone database. To this end, we have planned a high-performance data access middleware: OBProxy topic, including nine articles. The topic will explain the deployment, principles, functions, architecture, troubleshooting, best practices, and other aspects of OBProxy at one time to help readers understand OBProxy.
Now, we will start a special series about OBProxy and learn OBProxy together. You will look at distributed system problems from the perspective of the full procedure and master important knowledge points, such as connection management, data routing, and high availability disaster recovery. You will understand SQL's experience from the ExecuteQuery interface call to return results so you can better control distributed databases!
This article offers a detailed explanation of OBProxy function modules and features to help you better understand what OBProxy is, its value, and how to use it.
Let's learn some terms for your follow-up reading.
| Terms | Description |
| ODP | Product name of the agent |
| Obproxy/ObProxy | ODP alias, ODP's binary, and process name |
| Obproxyd.sh | Daemon script for the obproxy process is responsible for ODP startup and health check. |
| ODP Console | Control center when using the sharding feature |
OceanBase Database Proxy is a service proxy for OceanBase databases. The user's SQL statement is sent to the ODP node first. ODP selects an appropriate ObServer (OceanBase database process name) to forward the SQL statement and returns the result to the user. First, let's take a look at OBProxy from the overall architecture.
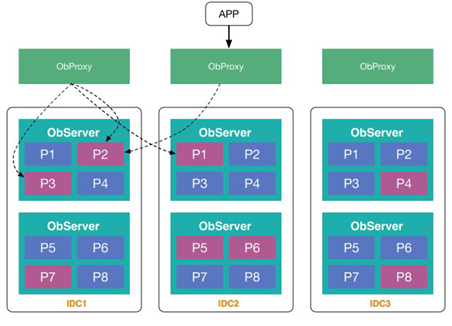
In the figure, APP represents a business process. There are three ObProxies in front of APP (the process name is Obproxy). In actual deployment, there is generally a Server Load Balancer between APP and ObProxy. For example, F5 distributes requests to multiple ObProxy, followed by ObServer. There are six ObServers in the figure. OBProxy knows the data distribution information in the ObServer and can efficiently forward user SQL to the machine where the data is located. The execution efficiency is higher than forwarding to a node without data. The data in table t1 is in P1, the data in table t2 is in P2, and the data in table t3 is in P3. Red indicates the primary replica, and blue indicates the secondary replica. For insert into t1 statements, OBProxy can send SQL to the ObServer machine that contains the primary replica P1 in IDC2.
Why does OBProxy need to send SQL statements to the node where the data resides? The SQL execution plan can be executed locally after the data is sent to the node where the data is located. The performance is better without remote RPC calls. In the actual production environment, in addition to data distribution, OBProxy considers the geographical distribution of machines to avoid requests across data centers and cities. There are many routing policies. We will also have special chapters to introduce to you later.
After deploying an OceanBase cluster (including OBProxy), users can use the database service. Let's use JDBC access database as an example:
final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:2883/test?useSSL=false&useServerPrepStmts=true";When establishing a connection, users must initialize the relevant connection information first. The preceding URL contains information, such as the IP address of the database, PORT, the name test of the accessed database, and connection attributes. The difference between using OBProxy access and direct connection to ObServer access is the difference between IP and PORT. Other information does not need to be changed. When used later, OBProxy is transparent to users.
Therefore, using OBProxy will make the problem simple. Users do not need to care about the distributed architecture of the database system. The benefits of this design include the following three aspects.
Reviewing the history of development can help us better understand why OBProxy is what it is from the perspectives of solution design, business requirements, and historical compatibility. Let's learn about the past and present of OBProxy together.
OBProxy products have been designed and developed since 2014 and have a history of nearly eight years. Its products are widely used in Ant Group, private cloud scenarios, and public cloud scenarios. They also play an important role in access links. The following is the development history:
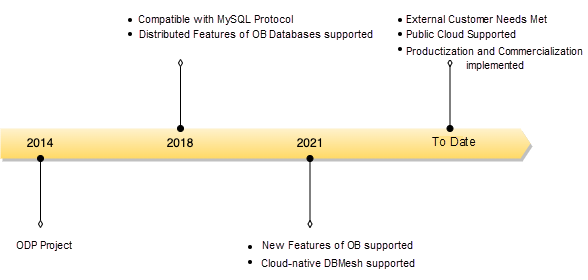
To sum up, the development history of OBProxy is listed below:
For middleware products, there are usually two types, SDK and proxy. Their respective advantages and disadvantages are listed below:
| Service Type | Advantage | Limit |
| SDK | Generally, it is integrated into the business code in the form of a library. Compared with the proxy mode, it has fewer hops, good performance, and short troubleshooting procedures. | It is tightly coupled and mutually interacted with business codes, and the O&M operations are perceived by the business sides. |
| Proxy | Decouple business logic and basic capabilities Enable faster version iteration and upgrade Support for multi-language drivers Upgrade O&M is less business-aware. |
This results in multiple or even two hops (Server Load Balancer) of the trace, which has a performance impact. Troubleshooting procedures are longer and more complex. Specialized O&M personnel is required. |
Currently, OBProxy products are provided in proxy form, and we will also provide SDK form in the future. The main challenge for OBProxy developers in supporting the SDK and proxy modes is how to reuse code. The solution is to wrap the underlying capabilities into library interfaces and make business code and OBProxy code call each other through process communication technology.
Next, we will interpret the OBProxy function module to help you systematically understand the implementation and functions of OBProxy. The following figure divides the functions of OBProxy into three layers:
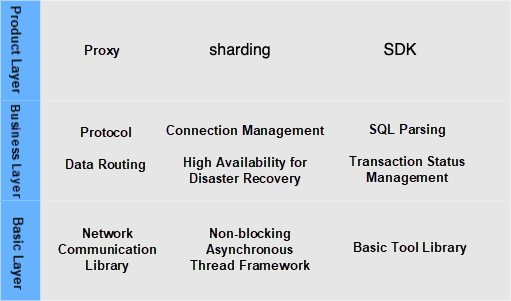
The basic layer implements basic frameworks and basic tool libraries (such as network communication and thread management) and provides support for upper layers.
The network communication library supports TCP protocol, SSL protocol, and RDMA communication and encapsulates easy-to-use interfaces for upper-layer use. The asynchronous event framework completes thread creation, management, task distribution, and scheduling. The basic library encapsulates some basic capabilities and provides easy-to-use interfaces for writing code.
In continuous development, OBProxy productizes some capabilities to provide external services. Its product forms are mainly proxy mode and SDK mode. Sharding is a database and table sharding capability supported by OBProxy in the unitized architecture of Ant Group. We are also exploring more useful features and enriching product functions.
After understanding the functional modules, we look at the execution process of OBProxy from SQL requests.
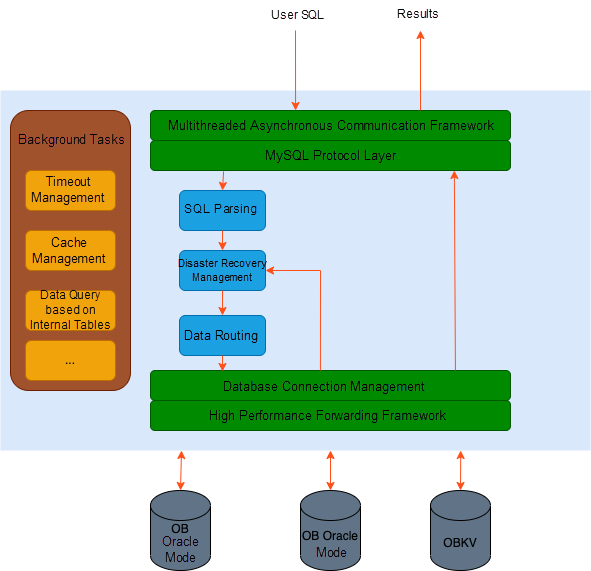
The execution process is listed below:
The preceding process does not describe disaster recovery management under abnormal conditions. You can refer to the preceding figure. In addition to requesting the main process, OBProxy has many background tasks, which are also important. We will introduce it in subsequent articles on this topic.
We learned about the functional modules of OBProxy in 5.1. We learned about the main work of OBProxy when executing an SQL statement in 5.2. To sum up, the main key features of OBProxy are listed below:
Hopefully, readers have better understanding of OBProxy after reading this article. How will OBProxy plan for the future? We will continue to meet the demands of customers and create good products.
OBProxy originated from Ant Group and served more customers. We believe the main future directions include:
The future is full of opportunities and challenges. OBProxy will continuously forge forward together with the OceanBase database kernel to provide good products, documents, and services for everyone.
OBProxy is not very much noticeable to users. However, when it comes to some advanced features and the distribution of OceanBase databases, the principle of OBProxy is an unavoidable topic. Later, we will provide more interesting content, such as data routing, full trace troubleshooting, connection stability, and the high availability of distributed systems. These contents will also help you understand the OceanBase database. I hope you can learn and grow through this series of articles!
OceanBase Rewriting Series: Group By Equivalent Transformation Method - Grouping Down
An Interpretation of the Source Code of OceanBase (2): Life of SQL
Alibaba Cloud Community - August 26, 2022
oceanbaseworld - November 29, 2019
Alibaba Cloud Native - April 10, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - April 20, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - August 14, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - April 10, 2020
 ApsaraDB for OceanBase
ApsaraDB for OceanBase
A financial-grade distributed relational database that features high stability, high scalability, and high performance.
Learn More Database for FinTech Solution
Database for FinTech Solution
Leverage cloud-native database solutions dedicated for FinTech.
Learn More Oracle Database Migration Solution
Oracle Database Migration Solution
Migrate your legacy Oracle databases to Alibaba Cloud to save on long-term costs and take advantage of improved scalability, reliability, robust security, high performance, and cloud-native features.
Learn More Database Migration Solution
Database Migration Solution
Migrating to fully managed cloud databases brings a host of benefits including scalability, reliability, and cost efficiency.
Learn MoreMore Posts by OceanBase