Common distributed databases require users to set the database shard key. Users need to manually manage database shard rules. This brings a threshold for users to use distributed databases. Users need to have a clear understanding of the data distribution of the database and the structure of each table to make good use of distributed databases. PolarDB-X proposed the concept of transparent distribution. The details of distribution are transparent to users. Users only need to use distributed databases in the same way as stand-alone databases. This significantly reduces the threshold for users to use distributed databases.
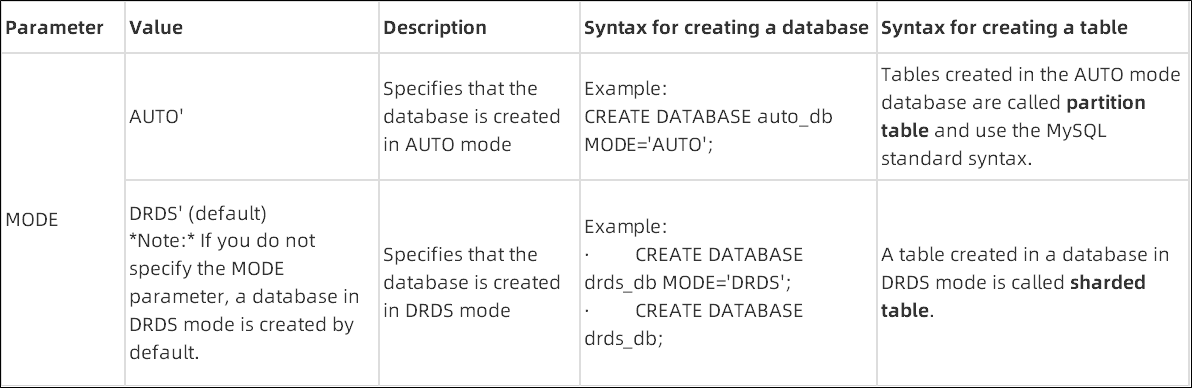
Databases in AUTO mode are supported in PolarDB-X5.4.13 and later versions and are also known as databases in automatic partitioning mode. Databases in AUTO mode support the automatic partitioning feature. When you create a table, you do not need to specify a partition key. Data in the table is automatically and evenly distributed among partitions. You can also use standard MySQL statements to partition the table. Databases in AUTO mode support features provided for distributed databases (such as transparent distribution, auto scaling, and partition management).
Databases earlier than PolarDB-X5.4.13 are called databases in DRDS mode. Databases in DRDS mode do not support automatic partitioning. When you create a table, you can use the sharding syntax dedicated to PolarDB-X to specify a database shard key and a table shard key. If no database shard key and table shard key are specified, a non-partitioned table is created.
PolarDB-X V5.4.13 and later versions support databases in AUTO mode and DRDS mode. A PolarDB-X instance can contain databases in AUTO mode and DRDS mode.
Note:
PolarDB-X introduces the MODE parameter when creating a database to determine whether the created database is in AUTO mode or DRDS mode. The following table describes how to specify the MODE parameter.
Note: After the database is created, the mode of the database cannot be changed.
You do not need to specify partitioning-related configuration items to configure automatic partitioning when you create a table, including a partition key or a partitioning policy. PolarDB-X can automatically select a partition key and perform horizontal partitioning on the table and its indexes. Only tables of databases in AUTO mode can be automatically partitioned. The automatic partitioning feature is unavailable for databases in DRDS mode.
Example:
You can execute the following statement in standard MySQL syntax without specifying partitioning-related configuration items to create a table named tb:
CREATE TABLE tb(a INT, b INT, PRIMARY KEY(a));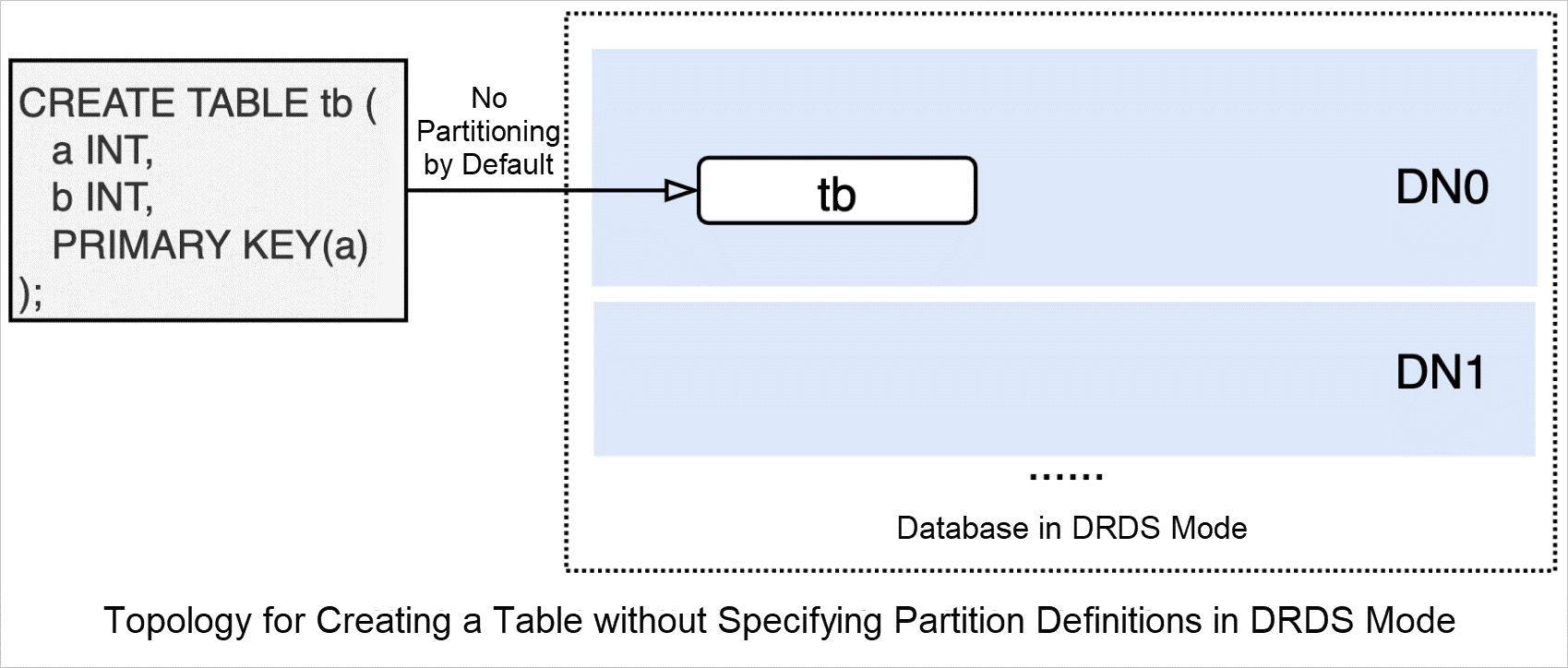
Execute the SHOW statement to view the complete CREATE TABLE statement:
SHOW FULL CREATE TABLE tb \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: tb
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `tb` (
`a` int(11) NOT NULL,
`b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`a`)
) ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4
1 row in set (0.02 sec)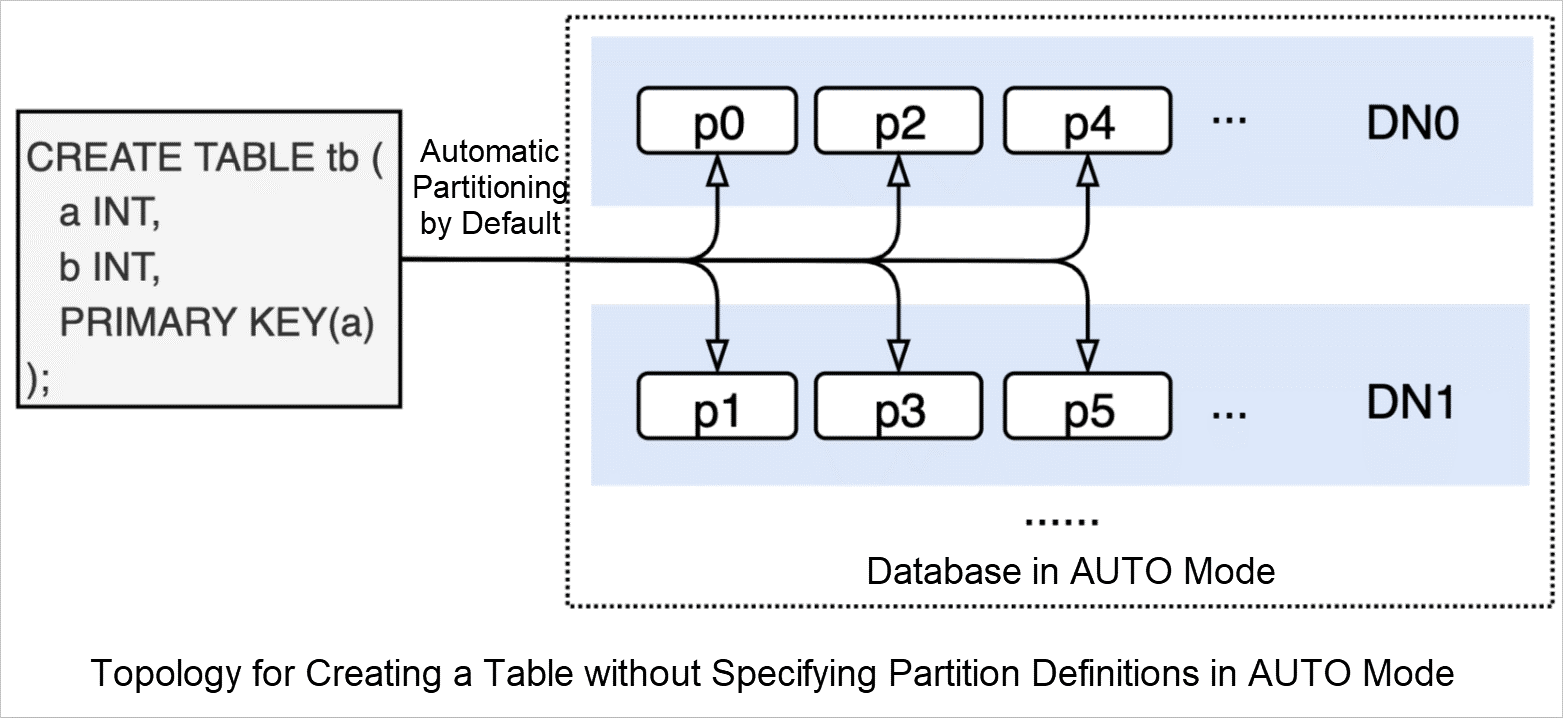
Execute the SHOW statement to view the complete CREATE TABLE statement:
SHOW FULL CREATE TABLE tb \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
TABLE: tb
CREATE TABLE: CREATE PARTITION TABLE `tb` (
`a` int(11) NOT NULL,
`b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`a`)
) ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4
PARTITION BY KEY(`a`)
PARTITIONS 16
1 row in set (0.01 sec)Therefore, in a database in AUTO mode, you only need to use the standard MySQL table creation syntax (including the index creation syntax) to create tables. The automatic partitioning feature of PolarDB-X allows applications to easily enjoy the benefits of distributed databases (such as Auto Scaling and partition management).
When you use the manual partitioning method to create a table, you need to specify partitioning-related configuration items (such as the partition key and partitioning policy). The syntax used to create a table in a database in AUTO mode is different from the syntax used to create a table in a database in DRDS mode.
In the following example, the PARTITION BY HASH(a) syntax is used, and the partition key a and the hash partitioning policy is used.
CREATE TABLE tb (a INT, b INT, PRIMARY KEY(a))
-> PARTITION by HASH(a) PARTITIONS 4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.83 sec)
SHOW FULL CREATE TABLE tb\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
TABLE: tb
CREATE TABLE: CREATE TABLE `tb` (
`a` int(11) NOT NULL,
`b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`a`)
) ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4
PARTITION BY KEY(`a`)
PARTITIONS 4
1 row in set (0.02 sec)In the following example, the DBPARTITION BY HASH(a) TBPARTITION BY HASH(a) syntax is used and the column a is used as the sharding key.
CREATE TABLE tb (a INT, b INT, PRIMARY KEY(a))
-> DBPARTITION by HASH(a)
-> TBPARTITION by HASH(a)
-> TBPARTITIONS 4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.16 sec)
SHOW FULL CREATE TABLE tb\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Table: tb
Create Table: CREATE TABLE `tb` (
`a` int(11) NOT NULL,
`b` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`a`)
) ENGINE = InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4 dbpartition by hash(`a`) tbpartition by hash(`a`) tbpartitions 4
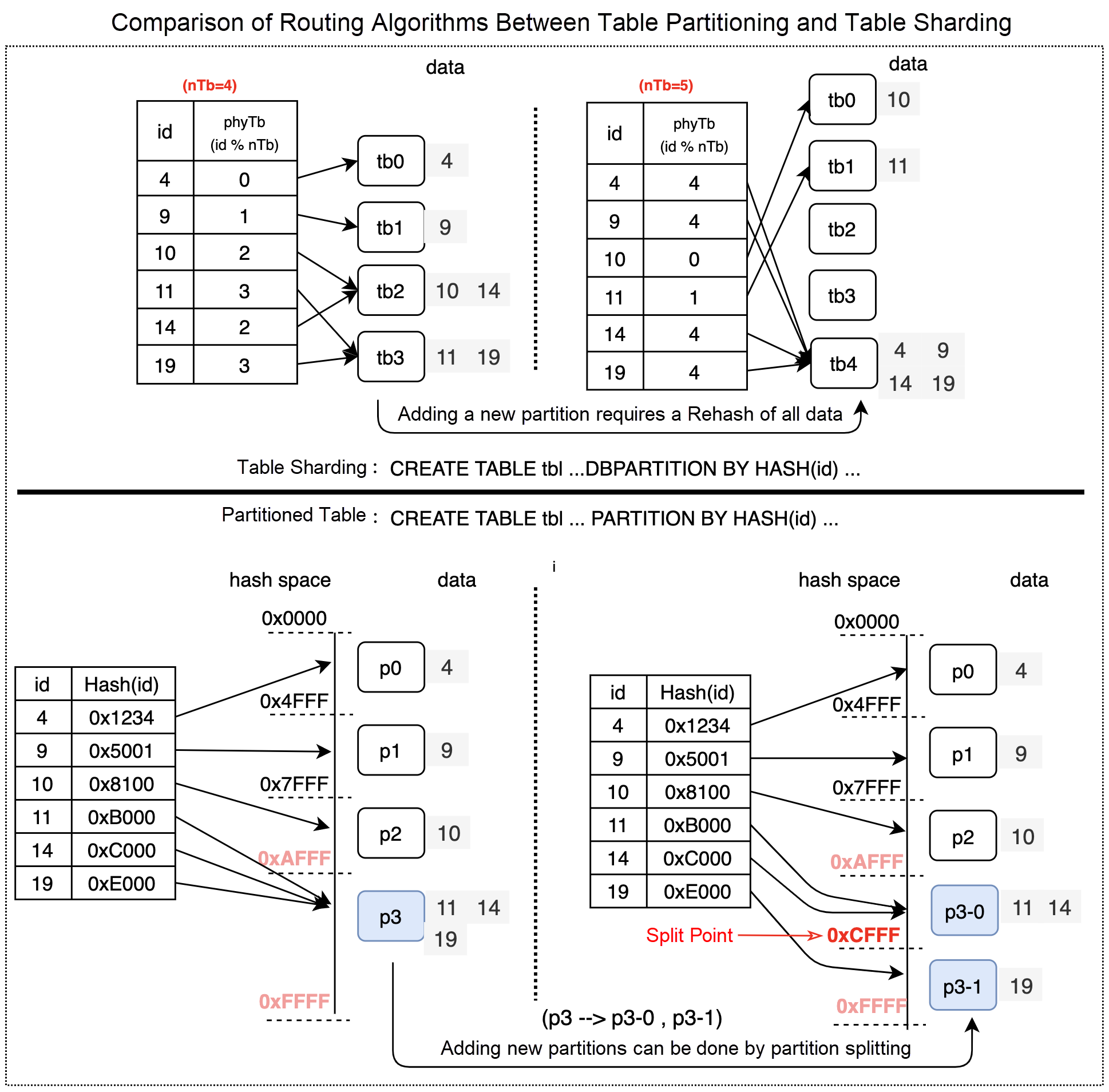
1 row in set (0.02 sec)The routing algorithm used for partitioned tables is different from the routing algorithm used for sharded tables. The following figure shows the difference between the routing algorithms.
PolarDB-X supports two processing methods for hot data:
ALTER TABLEGROUP #tgName EXTRACT to PARTITION #hotPartitionName BY HOT VALUE(#keyVal)ALTER TABLEGROUP #tgName MOVE PARTITIONS #hotPartitionName TO #dnALTER TABLEGROUP #tgName SPLIT INTO PARTITIONS #hotPartitionNamePrefix #N BY HOT VALUE(#keyVal);The preceding statement can be executed to split hot data into multiple partitions based on the value of the keyVal parameter, add the specified prefix to the partition names, and evenly distribute the partitions among different data nodes. This way, the hot data is linearly distributed among different data nodes. This helps you resolve issues related to hot data.
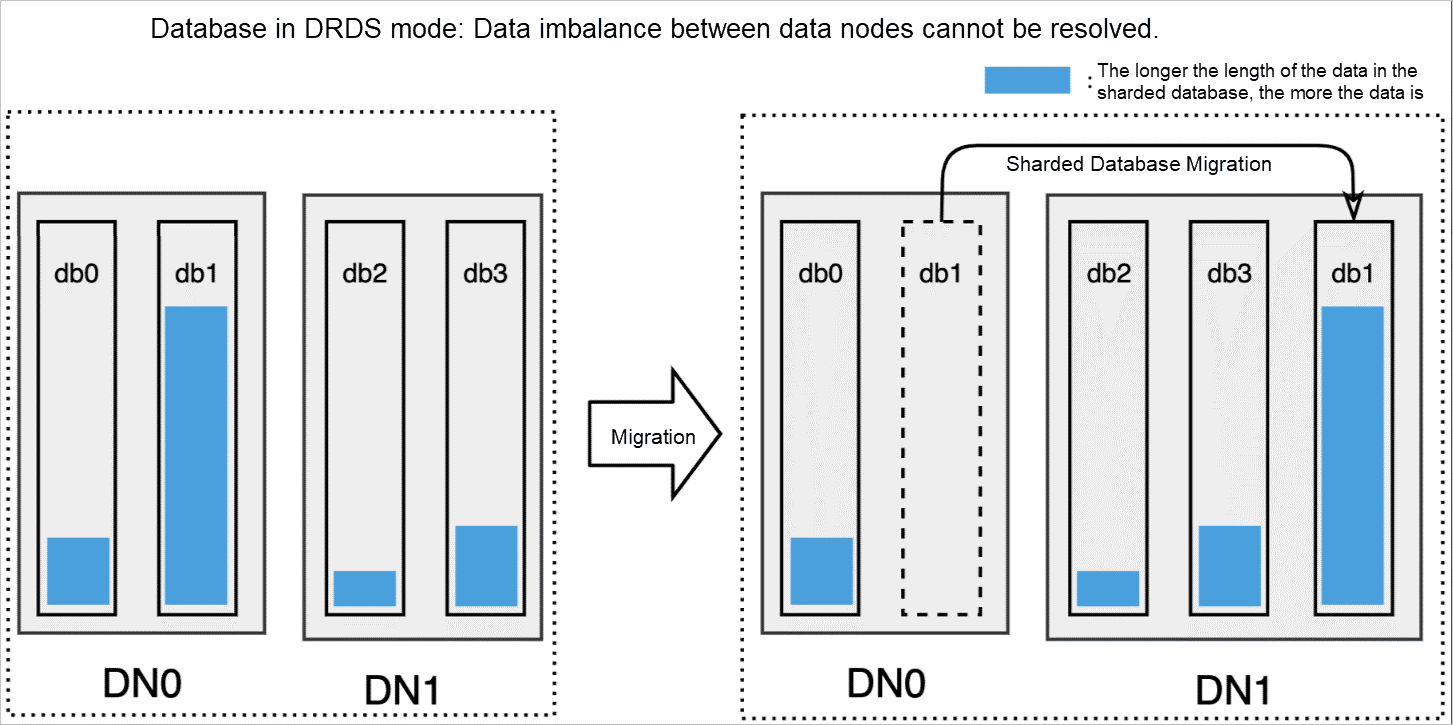
In DRDS mode, a modulo operation is performed based on hash values to implement sharding in databases. A table shard is associated with a specific database shard. For example, Database shard N includes Table shard M. You cannot modify the relationships between database shards and table shards. If you want to split, merge, or migrate a table shard, you need to recalculate hash values for all data in the table.
You can only migrate database shards to a data node because table shards cannot be migrated to other data nodes. If you migrate a database shard that stores a large volume of data, data among data nodes cannot be balanced. The following figure shows the issue:
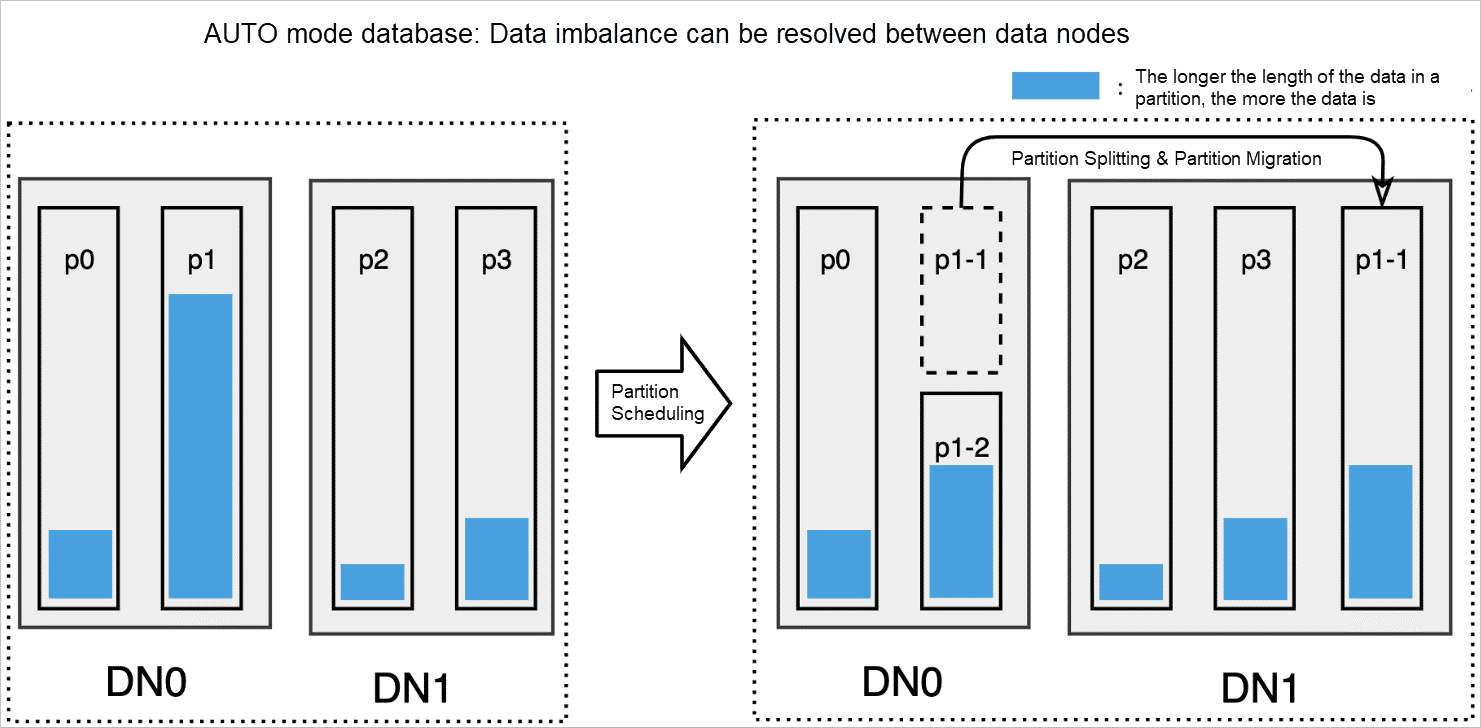
In AUTO mode, the consistent hashing routing algorithm is used for table partitioning. This way, you can merge, split, and migrate partitions in a flexible manner. For example, you can migrate your partitions to specified data nodes based on your business requirements. This operation does not affect irrelevant data in partitions. PolarDB-X can evenly distribute data to each data node by combining operations (such as partition merging and partition splitting with partition scheduling), as shown in the following figure. This balances data among data nodes.
In specific business scenarios, the volume of business data may increase in a short period, and the frequency at which business data is queried may decrease over a period. As such, if data is always stored in PolarDB-X, it occupies storage space and reduces the efficiency of normal business queries. In this scenario, many businesses choose to archive historical data and delete it in PolarDB-X. This allows customers to quickly delete historical data without affecting existing businesses.
If PolarDB-X can delete historical data through DDL, the speed of data cleansing is significantly improved. PolarDB-X developed the TTL feature in AUTO mode to quickly delete historical data.
If you include statements that are used to configure the TTL feature in the CREATE TABLE statement, a TTL table is created after the CREATE TABLE statement is executed. The following sample statement can be executed to create a table named t_order. The t_order table is partitioned based on the values in the gmt_modified column. One partition is added each month. Each partition expires 12 months after the partition is created. Three partitions are created when the table is created.
CREATE TABLE t_order (
id bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
gmt_modified DATETIME NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id, gmt_modified)
)
PARTITION BY HASH(id)
PARTITIONS 16
-- The following sample code provides an example of the TTL syntax
LOCAL PARTITION BY RANGE (gmt_modified) -- The table is partitioned based on the values in the gmt_modified column.
INTERVAL 1 MONTH -- One partition is added each month.
EXPIRE AFTER 12 -- Each partition expires 12 months after the partition is created.
PRE ALLOCATE 3; -- Three partitions are created when the table is created.The LOCALITY attribute is supported for databases in AUTO mode to allow you to specify locations based on multiple dimensions. You can use this attribute to specify the location where you want to store data.
CREATE DATABASE db1 MODE='AUTO' LOCALITY='dn=pxc-xdb-s-pxcexample'CREATE TABLE tb (a INT, b INT, PRIMARY KEY(a)) LOCALITY='dn=pxc-xdb-s-pxcexample'CREATE TABLE orders_region(
id int,
country varchar(64),
city varchar(64),
order_time datetime not null)
PARTITION BY LIST COLUMNS(country,city)
(
PARTITION p1 VALUES IN (('China','Hangzhou'), ('China','Beijing')) LOCALITY='dn=pxc-xdb-s-pxcexample1',
PARTITION p2 VALUES IN (('United States','NewYork'),('United States','Chicago')) LOCALITY='dn=pxc-xdb-s-pxcexample2',
PARTITION p3 VALUES IN (('Russian','Moscow')) LOCALITY='dn=pxc-xdb-s-pxcexample3'
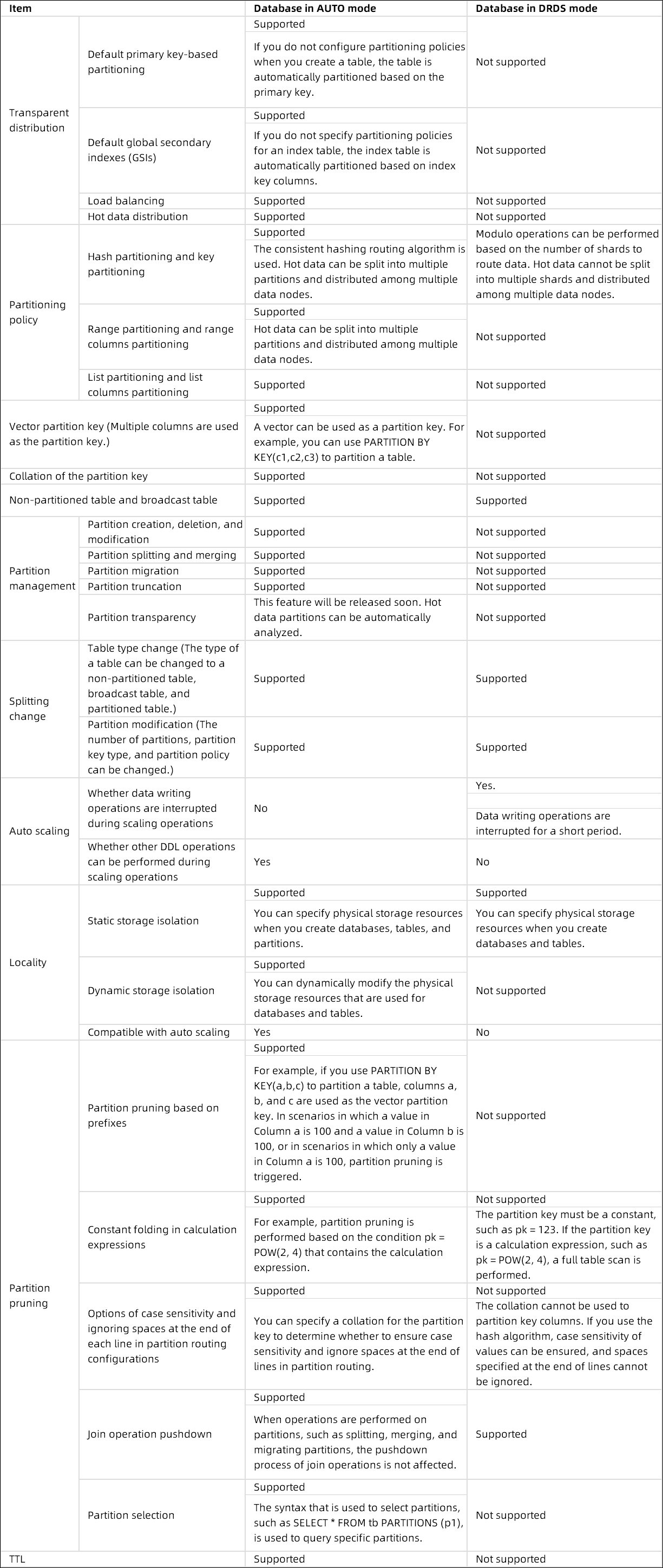
);Compared with databases in DRDS mode, databases in AUTO mode support new features (such as automatic partitioning, hot data splitting, partition scheduling, and time to live (TTL) tables). The distribution feature provided for databases in AUTO mode is also optimized based on various dimensions (such as partition management and partition modification).
The following table describes the differences between the features provided for databases in AUTO mode and DRDS mode:
The DRDS mode table sharding uses different routing algorithms from the AUTO mode table partitioning. In order to evaluate the performance difference between the two routing algorithms, Sysbench is used to benchmark PolarDB-X and observe their throughput (in QPS) in different Sysbench test scenarios.
PolarDB-X Instance Types: polarx.x4.2xlarge.2e
Table partitioning settings and table sharding settings:
Table partitioning:
Table sharding:
The following list describes the scenarios in which Sysbench tests are performed:
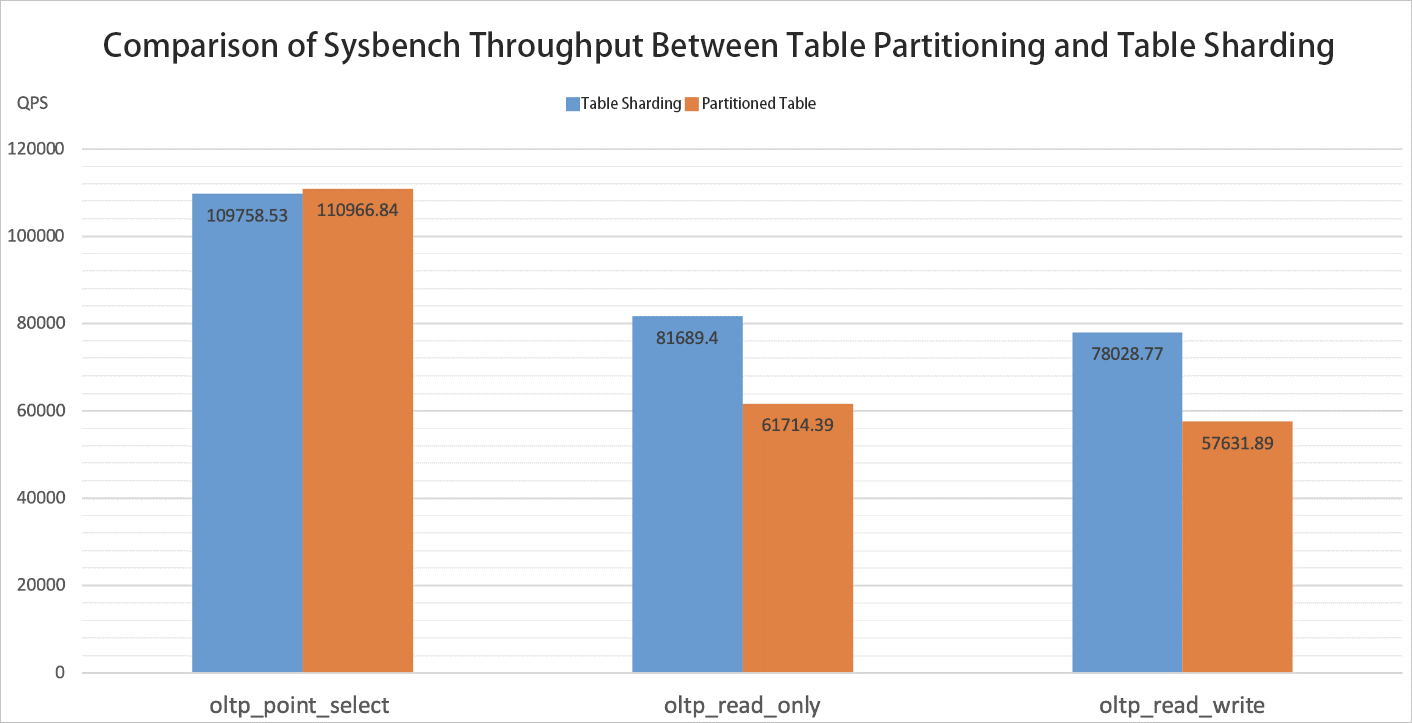
The following analysis results are obtained based on the preceding test results:
PolarDB-X Practice Series – Part 3 (1): How to Select an Application Connection
[Infographic] Highlights | Database New Feature in March 2023
ApsaraDB - February 21, 2023
ApsaraDB - April 20, 2023
ApsaraDB - August 15, 2024
ApsaraDB - April 10, 2024
ApsaraDB - August 13, 2024
ApsaraDB - January 23, 2024
 PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More PolarDB for Xscale
PolarDB for Xscale
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for Xscale (PolarDB-X) is a cloud-native high-performance distributed database service independently developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn More ApsaraDB for OceanBase
ApsaraDB for OceanBase
A financial-grade distributed relational database that features high stability, high scalability, and high performance.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB