As the most popular container cluster management platform, Kubernetes needs to coordinate the overall resource usage of a cluster and allocate appropriate resources to containers in pods. It must ensure that resources are fully utilized to maximize resource utilization, and that important containers in operation are allocated sufficient resources for stable operation.
The most basic resource metrics for a pod are CPU and memory.
Kubernetes provides requests and limits to pre-allocate resources and limit resource usage, respectively.
Limits restrict the resource usage of a pod as follows:
Deploy a stress testing container in a pod and allocate a memory of 250 MiB for stress testing. The memory limit of the pod is 100 MiB.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: memory-demo
namespace: example
spec:
containers:
- name: memory-demo-2-ctr
image: polinux/stress
resources:
requests:
memory: "50Mi"
limits:
memory: "100Mi"
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "250M", "--vm-hang", "1"]After deployment, check the pod status. We can see that it is OOM killed.
kubectl -n example get po
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
memory-demo 0/1 OOMKilled 1 11sapiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: cpu-demo
namespace: example
spec:
containers:
- name: cpu-demo-ctr
image: vish/stress
resources:
limits:
cpu: "1"
requests:
cpu: "0.5"
args:
- -cpus
- "2"Check the container information. Although the pod is not killed, its CPU usage is restricted to 1,000 millicpu.
kubectl -n example top po cpu-demo
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
cpu-demo 1000m 0MiKubernetes manages the quality of service (QoS). Based on resource allocation for containers, pods are divided into three QoS levels: Guaranteed, Burstable, and BestEffort. If resources are insufficient, scheduling and eviction strategies are determined based on the QoS level. The three QoS levels are described as follows:
Code for querying QoS: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/master/pkg/apis/core/helper/qos/qos.go
Kubernetes sets the oom_score_adj parameter based on the QoS level. The oom_killer mechanism calculates the OOM score of each pod based on its memory usage and comprehensively evaluates each pod in combination with the oom_score_adj parameter. Pods with higher process scores are preferentially killed when OOM occurs.
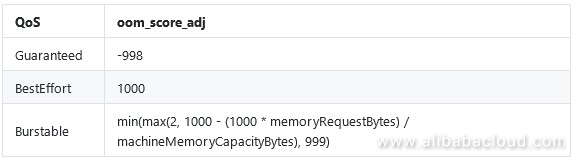
If the memory resources of a node are insufficient, pods whose QoS level is Guaranteed are killed in the end. Pods whose QoS level is BestEffort are preferentially killed. For pods whose QoS level is Burstable, the oom_score_adj parameter value ranges from 2 to 999. According to the formula, if the memory request is larger, the oom_score_adj parameter value is smaller and such pods are more likely to be protected during OOM.
Node information:
# kubectl describe no cn-beijing.i-2zeavb11mttnqnnicwj9 | grep -A 3 Capacity
Capacity:
cpu: 4
memory: 8010196Ki
pods: 110
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: memory-demo-qos-1
namespace: example
spec:
containers:
- name: memory-demo-qos-1
image: polinux/stress
resources:
requests:
memory: "200Mi"
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "50M", "--vm-hang", "1"]
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: memory-demo-qos-2
namespace: example
spec:
containers:
- name: memory-demo-qos-2
image: polinux/stress
resources:
requests:
memory: "400Mi"
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "50M", "--vm-hang", "1"]
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: memory-demo-qos-3
namespace: example
spec:
containers:
- name: memory-demo-qos-3
image: polinux/stress
resources:
requests:
memory: "200Mi"
cpu: "2"
limits:
memory: "200Mi"
cpu: "2"
command: ["stress"]
args: ["--vm", "1", "--vm-bytes", "50M", "--vm-hang", "1"]Each node can be allocated a memory of 8,010,196 KiB, which is about 7,822.45 MiB.
According to the formula for the QoS level at Burstable:
request 200Mi: (1000 ¨C 1000 x 200/7822.45) = About 975
request 400Mi: (1000 ¨C 1000 x 400/7822.45) = About 950The oom_score_adj parameter values of these three pods are as follows:
// request 200Mi
kubectl -n example exec memory-demo-qos-1 cat /proc/1/oom_score_adj
975
// request 400Mi?
kubectl -n example exec memory-demo-qos-2 cat /proc/1/oom_score_adj
949
// Guaranteed
kubectl -n example exec memory-demo-qos-3 cat /proc/1/oom_score_adj
-998Code for setting OOM rules: https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/master/pkg/kubelet/qos/policy.go
If the memory and CPU resources of a node are insufficient and this node starts to evict its pods, the QoS level also affects the eviction priority as follows:
Kubernetes provides the ResourceQuota object to set constraints on the number of Kubernetes objects by type and the amount of resources (CPU and memory) in a namespace.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: mem-cpu-demo
namespace: example
spec:
hard:
requests.cpu: "3"
requests.memory: 1Gi
limits.cpu: "5"
limits.memory: 2Gi
pods: "5"The LimitRange object is used to set the default resource requests and limits as well as minimum and maximum constraints for each pod in a namespace.
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange
metadata:
name: mem-limit-range
namespace: example
spec:
limits:
- default: # default limit
memory: 512Mi
cpu: 2
defaultRequest: # default request
memory: 256Mi
cpu: 0.5
max: # max limit
memory: 800Mi
cpu: 3
min: # min request
memory: 100Mi
cpu: 0.3
maxLimitRequestRatio: # max value for limit / request
memory: 2
cpu: 2
type: Container # limit type, support: Container / Pod / PersistentVolumeClaimThe LimitRange object supports the following parameters:
Kubernetes sets requests and limits for container resources. To maximize resource utilization, Kubernetes determines scheduling strategies based on pod requests to oversell node resources.
Kubernetes restricts the resource usage of pods based on preset limits. If the memory usage of a pod exceeds the memory limit, this pod is OOM killed. The CPU usage of a pod cannot exceed the CPU limit.
Based on requests and limits of each pod, Kubernetes determines the QoS level and divides pods into three QoS levels: Guaranteed, Burstable, and BestEffort. If node resources are insufficient and pods are to be evicted or OOM killed, the kubelet preferentially protects pods whose QoS level is Guaranteed, and then pods whose QoS level is Burstable (where pods whose QoS level is Burstable with larger requests but less resource usage are preferentially protected). The kubelet preferentially evicts pods whose QoS level is BestEffort.
Kubernetes provides the RequestQuota and LimitRange objects to set constraints on pod resources and the number of pods in a namespace. The RequestQuota object is used to set the number of various objects by type and the amount of resources (CPU and memory). The LimitRange object is used to set the default requests and limits, minimum and maximum requests and limits, and oversold ratio for each pod or container.
Reasonable and consistent pod limits and requests must be set for some important online applications. Then, if resources are insufficient, Kubernetes can preferentially guarantee the stable operation of such pods. This helps improve resource usage.
Pod requests can be appropriately reduced for some non-core applications that occasionally occupy resources. In this case, such pods can be allocated to nodes with fewer resources during scheduling to maximize resource utilization. However, if node resources become insufficient, such pods are still preferentially evicted or OOM killed.
To learn more about Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes, visit https://www.alibabacloud.com/product/kubernetes

228 posts | 33 followers
FollowAlibaba Container Service - May 13, 2019
Alibaba Container Service - November 21, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native - March 28, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native - May 23, 2022
Alibaba Container Service - April 20, 2020
Xi Ning Wang(王夕宁) - December 16, 2020

228 posts | 33 followers
Follow Backup and Archive Solution
Backup and Archive Solution
Alibaba Cloud provides products and services to help you properly plan and execute data backup, massive data archiving, and storage-level disaster recovery.
Learn More Drive and Photo Service
Drive and Photo Service
A low-code, high-availability, and secure platform for enterprise file management and application
Learn More Architecture and Structure Design
Architecture and Structure Design
Customized infrastructure to ensure high availability, scalability and high-performance
Learn More Sensitive Data Discovery and Protection
Sensitive Data Discovery and Protection
SDDP automatically discovers sensitive data in a large amount of user-authorized data, and detects, records, and analyzes sensitive data consumption activities.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Container Service