ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server supports the Linked Server feature, which lets you create linked servers between ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instances. You can also create a linked server to connect to an on-premises SQL Server instance if a network connection is established. This feature is useful for scenarios such as cross-region data access, data merging and analysis, and data migration and synchronization. This topic describes how to create a linked server on an ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instance over a VPN to connect to a self-managed SQL Server instance.
Prerequisites
Your ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instance must meet the following requirements:
RDS instances that run RDS Cluster Edition or RDS High-availability Edition. Instances that run RDS Basic Edition are not supported.
RDS instances that belong to the general-purpose or dedicated instance family. The shared instance family is not supported.
Subscription and pay-as-you-go RDS instances. Serverless RDS instances are not supported.
Before you deploy a VPN Gateway, plan your network:
Make sure that the private IP address range of the on-premises client and the private IP address range of the virtual private cloud (VPC) that you want to access do not overlap. Otherwise, communication will fail.
Make sure that the client can access the network.
Billing
Charges apply for using VPN Gateway. For more information, see Billing of VPN Gateway.
1. Use a VPN to establish a network connection between the VPC of the ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instance and the off-cloud machine
1.1. Create a VPN Gateway instance
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which you want to create a VPN gateway.
Make sure that the VPN gateway resides in the same region as the VPC that you want to associate with the VPN gateway.
On the VPN Gateways page, click Create VPN Gateway.
On the buy page, configure the parameters described in the following table, click Buy Now, and then complete the payment.
Parameter
Description
Instance Name
The name of the VPN gateway.
Resource Group Select the resource group to which the cluster belongs. You can use resource groups to manage resources within your Alibaba Cloud account by category and group. You can manage permissions, deploy resources, and monitor resources based on groups without the need to separately process each resource. Default Resource Group
The resource group to which the VPN gateway belongs.
If you leave this parameter empty, the VPN gateway belongs to the default resource group. You can manage the resource group to which the VPN gateway belongs and resource groups to which other cloud resources belong in the Resource Management console. For more information, see What is Resource Management?
Region
The region in which you want to create the VPN gateway.
Make sure that the VPN gateway and the VPC with which you want to associate the VPN gateway reside in the same region.
Gateway Type
The type of VPN gateway that you want to create. Default value: Standard.
Network Type
The network type of the VPN gateway. Valid values:
Public: The VPN gateway can be used to establish VPN connections over the Internet.
Private: The VPN gateway can be used to establish VPN connections over private networks.
NoteIf you want to establish a VPN connection over a private network, you recommend that you associate a router with the private IPsec-VPN connection. For more information, see Create multiple private IPsec-VPN connections to implement load balancing.
Tunnels
The tunnel mode of the VPN gateway. The system displays the tunnel modes that are supported in this region. Valid values:
Single-tunnel
Dual-tunnel
For more information about the tunnel mode, see [Upgrade notice] IPsec-VPN connections support the dual-tunnel mode.
VPC
The VPC with which you want to associate the VPN gateway.
vSwitch
The vSwitch with which you want to associate the VPN gateway. Select a vSwitch from the selected VPC.
If you select Single-tunnel, you need to specify only one vSwitch.
If you select Dual-tunnel, you need to specify two vSwitches.
After the IPsec-VPN feature is enabled, the system creates an elastic network interface (ENI) for each of the two vSwitches as an interface to communicate with the VPC over an IPsec-VPN connection. Each ENI occupies one IP address in the vSwitch.
NoteThe system selects a vSwitch by default. You can change or use the default vSwitch.
After a VPN gateway is created, you cannot modify the vSwitch associated with the VPN gateway. You can view the vSwitch associated with the VPN gateway, the zone to which the vSwitch belongs, and the ENI in the vSwitch on the details page of the VPN gateway.
vSwitch 2
The other vSwitch with which you want to associate the VPN gateway in the associated VPC if you select Dual-tunnel.
Specify two vSwitches in different zones in the associated VPC to implement disaster recovery across zones for IPsec-VPN connections.
For a region that supports only one zone, disaster recovery across zones is not supported. We recommend that you specify two vSwitches in the zone to implement high availability of IPsec-VPN connections. You can also select the same vSwitch as the first one.
Peak Bandwidth
The maximum bandwidth of the VPN gateway. Unit: Mbit/s.
Traffic
The metering method of the VPN gateway. Default value: Pay-by-data-transfer.
IPsec-VPN
Specifies whether to enable the IPsec-VPN feature for the VPN gateway. Default value: Enable.
You must enable this feature if you want to establish an IPsec-VPN connection.
SSL-VPN
Specifies whether to enable the SSL-VPN feature for the VPN gateway. Default value: Disable.
You do not need to enable this feature for the VPN gateway to establish an IPsec-VPN connection.
Billing Cycle
The billing cycle of the VPN gateway. Default value: By Hour.
Service-linked Role
Click Create Service-linked Role and the system automatically creates the service-linked role AliyunServiceRoleForVpn.
VPN Gateway assumes this role to access other cloud resources. For more information, see AliyunServiceRoleForVpn.
If Created is displayed, the service-linked role is created and you do not need to create it again.
After the VPN gateway is created, the system assigns an IP address to the VPN gateway to establish an IPsec-VPN connection with the on-premises data center.
What to do next
After the VPN gateway is created, you must also create a customer gateway before you can establish an IPsec-VPN connection. The customer gateway is used to register the information about the gateway device of your data center with Alibaba Cloud. The information includes the IP address and autonomous system number (ASN) of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). For more information, see Create and manage a customer gateway.
1.2. Create an SSL server
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region of the SSL server.
The SSL server and VPN gateway must reside in the same region.
On the SSL Servers page, click Create SSL Server.
In the Create SSL Server panel, set the following parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the SSL server.
Resource Group
The resource group to which the VPN gateway belongs.
The resource group to which the SSL server belongs must be the same as the resource group to which the VPN gateway belongs.
VPN Gateway
Select the VPN gateway that you want to associate with the SSL server.
Make sure that SSL-VPN is enabled for the VPN gateway.
Local Network
The local CIDR block that your client needs to access by using an SSL-VPN connection.
The CIDR block can be the CIDR block of a virtual private cloud (VPC), a vSwitch, a cloud service such as Object Storage Service (OSS) or ApsaraDB RDS, or a data center that is connected to a VPC over an Express Connect circuit.
You can click Add Local Network to add up to five local CIDR blocks. You cannot specify the following CIDR blocks as the local CIDR blocks:
127.0.0.0~127.255.255.255
169.254.0.0~169.254.255.255
224.0.0.0~239.255.255.255
255.0.0.0~255.255.255.255
NoteThe subnet mask of the specified local CIDR block must be 8 to 32 bits in length.
Client CIDR Block
The CIDR block from which an IP address is assigned to the virtual network interface controller (NIC) of the client. Do not enter the private CIDR block of the client. If the client accesses the SSL server over an SSL-VPN connection, the VPN gateway assigns an IP address from the specified client CIDR block to the client. The client uses the assigned IP address to access cloud resources.
Make sure that the number of IP addresses in the client CIDR block is at least four times the maximum number of SSL-VPN connections supported by the VPN gateway.
ImportantThe subnet mask of the client CIDR block must be 16 to 29 bits in length.
Make sure that the client CIDR block does not overlap with the local CIDR block, the VPC CIDR block, or route CIDR blocks associated with the client.
We recommend that you use 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16, or one of their subnets as the client CIDR block. If you want to specify a public CIDR block as the client CIDR block, you must specify the public CIDR block as the user CIDR block of a VPC. This way, the VPC can access the public CIDR block. For more information, see the FAQs and FAQs sections of the "FAQ" topic.
After you create an SSL server, the system automatically adds routes that point to the client CIDR block to the VPC route table. Do not add routes that point to the client CIDR block to the VPC route table again. Otherwise, SSL-VPN connections cannot work as expected.
Advanced Configuration
Protocol
The protocol that is used by the SSL-VPN connection. Default value: TCP(Recommended). Valid values:
UDP
TCP(Recommended)
Port
The port that is used by the SSL server. Valid values are in the range of 1 to 65535. Default value: 1194.
NoteThe following ports are not supported: 22, 2222, 22222, 9000, 9001, 9002, 7505, 80, 443, 53, 68, 123, 4510, 4560, 500, and 4500.
Encryption Algorithm
The encryption algorithm that is used by an SSL-VPN connection.
If the client uses Tunnelblick or OpenVPN V2.4.0 or later, the SSL server dynamically negotiates with the client about the encryption algorithm and uses the most secure encryption algorithm that is supported by the SSL server and the client. The encryption algorithm that you specify for the SSL server does not take effect.
If the client uses OpenVPN of a version that is earlier than 2.4.0, the SSL server and the client use the encryption algorithm that you specify for the SSL server. You can specify one of the following encryption algorithms for the SSL server:
AES-128-CBC
AES-192-CBC
AES-256-CBC
none
A value of none indicates that no encryption algorithm is used.
Compressed
Specifies whether to compress the data that is transmitted over the SSL-VPN connection. Default value: No. Valid values:
Yes
No (default)
Two-factor Authentication
Specifies whether to enable two-factor authentication for the VPN gateway. By default, two-factor authentication is disabled.
Two-factor authentication verifies the identity of a client by using the default SSL client certificate and the username and password of IDaaS EIAM before an SSL-VPN connection is established. The client must pass both authentications before the connection can be created. Two-factor authentication helps prevent user identity theft and unauthorized SSL-VPN connections. It efficiently improves the security of SSL-VPN connections and protects sensitive data in VPCs against data breaches. For more information, see SSL-VPN two-factor authentication.
After two-factor authentication is enabled, you can select the IDaaS EIAM instance and IDaaS application ID used for authentication.
NoteIf you use the two-factor authentication feature for the first time, you must first authorize VPN to access cloud resources.
When you create an SSL server in the UAE (Dubai) region, we recommend that you associate the SSL server with an IDaaS EIAM 2.0 instance in Singapore to reduce latency.
You can no longer purchase IDaaS EIAM 1.0 instances. If your Alibaba Cloud account has an IDaaS EIAM 1.0 instance, you can still specify the IDaaS EIAM 1.0 instance after you enable the two-factor authentication feature.
If your Alibaba Cloud account has no IDaaS EIAM 1.0 instance, you can specify only an IDaaS EIAM 2.0 instance after you enable the two-factor authentication feature.
You may need to update the VPN gateway to associate it with an IDaaS EIAM 2.0 instance. For more information, see Announcement on the change of supporting IDaaS EIAM 2.0 instances for two-factor authentication of SSL-VPN connections.
1.3. Create an SSL client certificate
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
- In the top navigation bar, select the region of the SSL client.
On the SSL Clients page, click Create SSL Client.
In the Create SSL Client panel, configure the parameters that are described in the following table and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the SSL client certificate.
Resource Group
The resource group to which the SSL client certificate belongs.
The resource group to which the SSL client certificate belongs must be the same as the resource group to which the SSL server belongs.
SSL Server
The SSL server with which you want to associate the SSL client certificate.
1.4. Download the SSL client certificate
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
- In the top navigation bar, select the region of the SSL client.
On the SSL Clients page, find the SSL client certificate that you want to download and click Download Certificate in the Actions column.
1.5. Configure the client
Download and install the OpenVPN client.
Decompress the downloaded certificate and copy it to the config folder in the OpenVPN installation directory.
Click Connect to initiate a connection.
1.6. Test the connection
Create an ECS instance in the same VPC.
In the OpenVPN client, run the
pingcommand to test the connectivity to the ECS instance.NoteMake sure that the security group rules for the ECS instance allow remote connections from the client. The authorization object must be the client CIDR block that is specified in the SSL server configuration. You must also specify the service port of the local database that you want to access. For more information, see Security group configuration examples.
If the connection fails, a firewall may be enabled on the local host. You must configure the firewall to allow remote connections.
2. Create a linked server on the ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instance
Method 1: Create a linked server after you connect to the RDS instance using SSMS
Connect to an ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instance using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
In SSMS, run the following SQL command to create a linked server:
DECLARE @linked_server_name sysname = N'yangzhao_slb', -- The name of the linked server. This name is used to identify the remote server. @data_source sysname = N'****.sqlserver.rds.aliyuncs.com,3888 ', -- The IP address and port number of the self-managed SQL Server database. Format: <IP address>,<Port number>. Example: 10.1.10.1,1433. @user_name sysname = N'ay15', -- The username of the self-managed SQL Server database. This username is used to connect to the remote database. @password nvarchar(128) = N'******', -- The password that corresponds to the username of the self-managed SQL Server database. -- Other options for the linked server, provided in XML format. @link_server_options xml = N' <rds_linked_server> <config option="data access">true</config> <config option="rpc">true</config> <config option="rpc out">true</config> </rds_linked_server>' ; -- Call the sp_rds_add_linked_server stored procedure to create the linked server. EXEC sp_rds_add_linked_server @linked_server_name, @data_source, @user_name, @password, @link_server_options;Run the following SQL command to view the list of configured linked servers:
SELECT * FROM [myTestLinkedServer].master.sys.servers;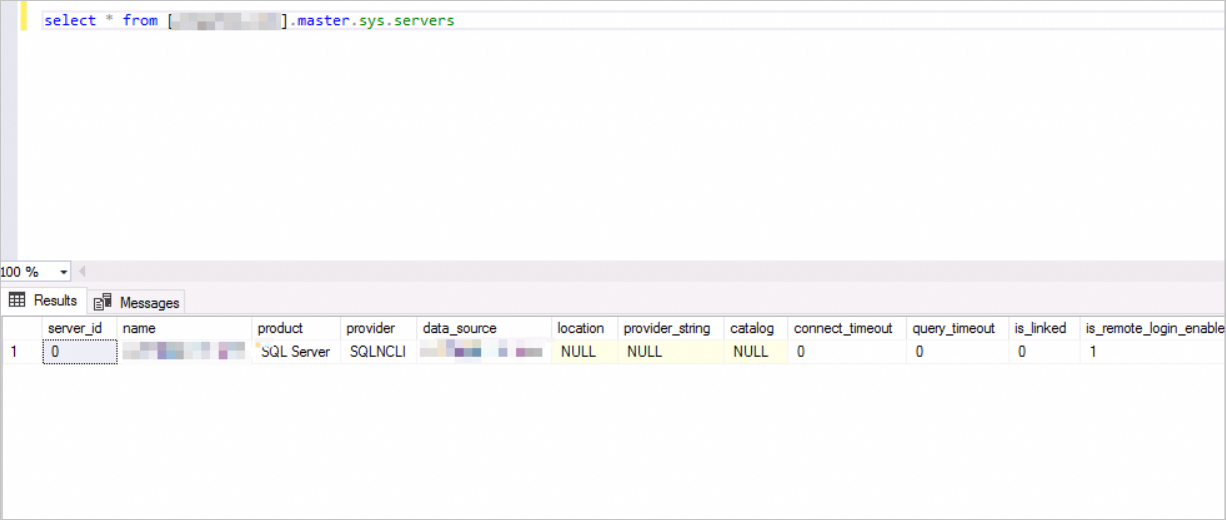
Method 2: Create a linked server after you connect to the RDS instance using DMS
Connect to an ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instance using DMS.
In DMS, run the following SQL command to create a linked server:
-- Call the sp_rds_add_linked_server stored procedure to create the linked server. EXEC sp_rds_add_linked_server @linked_server_name = N'yangzhao_slb', -- The name of the linked server. This name is used to identify the remote server. @data_source = N'rm-***.sqlserver.rds.aliyuncs.com,1433', -- The IP address and port number of the self-managed SQL Server database. Format: <IP address>,<Port number>. Example: 10.1.10.1,1433. @user_name = N'ay15', -- The username of the self-managed SQL Server database. This username is used to connect to the remote database. @password = N'******', -- The password that corresponds to the username of the self-managed SQL Server database. -- Other options for the linked server, provided in XML format. @link_server_options = N' <rds_linked_server> <config option="data access">true</config> <config option="rpc">true</config> <config option="rpc out">true</config> </rds_linked_server>' ;Run the following SQL command to view the list of configured linked servers:
SELECT * FROM [myTestLinkedServer].master.sys.servers;
