This topic lists frequently asked questions (FAQs) about Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch (ES). The questions cover topics such as instance purchasing, unsubscription, configuration, access, queries, data writing, plug-ins, tokenizers, logs, restarts, load or status abnormalities, backup and recovery, and monitoring and alerts.
Overview of FAQ
Purchase or unsubscription issues
What do I do if I select an incorrect configuration when I purchase an ES instance?
What are the specific versions that correspond to the versions on the ES purchase page?
What do I do if no VPCs are available when I purchase an ES instance?
What do I do if resources are sold out when I purchase an instance?
Why should I upgrade my existing 1-core 2 GiB instance as soon as possible?
What do I do if an ES instance is always in the Creating state after purchase?
After an ES cluster is created, do I need to purchase a Kibana node separately?
What is the default account for the password I enter when I purchase an ES instance?
Product feature questions
Can I upgrade or downgrade the version of an Alibaba Cloud ES instance?
Can I log on to a cluster over SSH to modify its configuration?
When can I use the force restart feature for ES? What are the effects of using this feature?
How do I confirm that the Log4j2 vulnerability in ES is fixed?
How do I enable service interconnection between ES instances in different regions?
Do I need to purchase client nodes to enable the HTTPS protocol?
What is the maximum number of shards supported by a single ES node?
How are indexes that start with .monitoring-es generated and what are they used for?
What encryption algorithm is used for disk encryption on ES data disks?
Data migration and synchronization issues
Instance restart issues
Does enabling or disabling public network access for an ES instance trigger a restart?
Does changing the cluster access password trigger a cluster restart?
Does the absence of replica shards in an index affect a cluster restart?
How do I restart a role node (such as a Kibana node) or a single node?
Can I set up scheduled restarts for nodes in an ES instance?
Abnormal cluster load or status issues
Cluster query and write issues
Cluster configuration and change issues
How do I view the configuration parameters of an ES instance?
Does changing the cluster configuration affect the ES service?
After changing the number of nodes, does the cluster automatically rebalance the shards?
Does ES support changing other types of nodes into cold data nodes?
After upgrading the instance specifications, can I downgrade the configuration, and how?
When upgrading a cluster, a "UpgradeVersionMustFromConsole" prompt appears. What should I do?
An error or timeout occurs when upgrading a cluster. What should I do?
The cluster configuration cannot be changed. What should I do?
Will changing the disk type of an ES instance cause existing data to be lost?
Plug-in, tokenizer, and synonym issues
When using the IK tokenizer, how do I customize and extend the dictionary content?
When using the IK analysis plug-in, an "ik startOffset" error is reported. What should I do?
If the local IK dictionary file is lost, can it be recovered from the cluster management page?
Can custom plug-ins access external networks, for example, to read dictionary files from GitHub?
How is the analysis-aliws tokenizer configured, and what is the file format?
What are the differences among ES synonyms, IK tokenization, and AliNLP tokenization?
Which built-in Chinese tokenizers does Alibaba Cloud ES support?
Does the IK tokenizer used by Alibaba Cloud ES support remote dictionaries?
How do I install the vector search plug-in (aliyun-knn) on an Alibaba Cloud ES 7.10 instance?
Does restarting after installing a plug-in affect cluster services?
Log issues
Data backup and recovery issues
Cluster monitoring and alert issues
Cluster access issues
Index-related issues
Purchase or unsubscription issues
What do I do if I select an incorrect configuration when purchasing an ES instance?
If you find that the selected configuration does not meet your expectations after you purchase an ES instance, refer to the following table to find a solution based on your configuration.
Before you unsubscribe from or release your cluster, back up your data. For more information, see Manual backup and restoration. After the unsubscription or release, the data stored on the cluster is deleted and cannot be restored.
Configuration | Solution |
Billing method | If you purchased a pay-as-you-go instance, you can change its billing method to subscription. For more information, see Change the billing method of an instance from pay-as-you-go to subscription. |
Version | An instance must meet one of the following conditions to support a version change:
For information about how to upgrade the instance version, see Upgrade the version of an instance. If your version upgrade does not meet the preceding conditions, we recommend that you unsubscribe from or release your instance and purchase another instance of the desired version. |
Region | This cannot be changed. We recommend that you unsubscribe and purchase a new instance. |
Zone | You can migrate the zone. For more information, see Migrate and upgrade zones. Note When migrating zones, make sure the ES instance has been created successfully, meaning the instance status is Normal. |
Number of zones | This cannot be changed. We recommend that you unsubscribe and purchase a new instance. |
Instance type | You can change this setting. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster. |
Storage class | You can change this configuration. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster. |
Disk encryption | This cannot be changed. We recommend that you unsubscribe and purchase a new instance. |
Storage space per node | You can modify this configuration item. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster. |
Number of data nodes | You can change this setting. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster. |
Network type, virtual private cloud, virtual switch | These cannot be changed. We recommend that you unsubscribe and purchase a new instance. Note Only virtual private clouds are supported. |
Username | The default username is elastic. You cannot modify this configuration item. You can create a user in the Kibana console and grant the required permissions to the user. For more information, see Use the RBAC mechanism provided by Elasticsearch X-Pack to implement access control. |
Logon password | This can be changed. For details, see Reset instance access password. |
For configurations not mentioned in the preceding table, check the cluster upgrade or downgrade page. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster and Downgrade a cluster.
What are the specific versions that correspond to the versions on the ES purchase page?
Version on the purchase page | Specific version |
8.15 | 8.15.1 |
8.13 | 8.13.4 |
8.9 | 8.9.1 |
8.5 | 8.5.1 |
7.16 | 7.16.2 |
7.10 | 7.10.0 |
7.7 | 7.7.1 |
6.8 | 6.8.6 |
6.7 | 6.7.0 |
6.3 | 6.3.2 |
5.6 | 5.6.16 |
5.5 | 5.5.3 |
When you purchase an instance, if you already have a self-managed cluster, we recommend that you select a similar version, such as one with a similar minor version. If you do not have a self-managed cluster, we recommend that you select the latest version.
What do I do if no VPCs are available when I purchase an ES instance?
This issue occurs if the RAM user is not granted the permission to obtain the list of VPCs. Check whether the RAM user is granted the permission to obtain the list of VPCs. For more information, see View RAM user information. If the permission is not granted, grant the permission to the RAM user. For more information, see Create a custom policy.
When I purchase an ES instance, I have a VPC, but no virtual switches are available or the vSwitch list is empty, and the error "vSwitch: may not be empty" is reported. How do I fix this?
This issue occurs because no vSwitches are available in the zone that you selected. To resolve this issue, go to the vSwitch page in the VPC console and check whether vSwitches are available in the selected zone. If no vSwitches are available, you must create one. For more information, see Create a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR block.
If I unsubscribe from an instance and purchase a new one, does the endpoint of the new instance change?
After you purchase a new instance, we recommend modifying the client code before releasing the old one to prevent business interruptions.
How do I release or unsubscribe from an ES instance?
For information about how to release pay-as-you-go or expired subscription instances, see Release an instance.
For unexpired subscription instances:
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Management Console. In the top navigation bar, choose . In the left-side navigation pane of the Expenses and Costs console, click Unsubscribe. On the Unsubscribe page, perform cluster unsubscription or order cancellation. For more information, see Methods for unsubscribing resources.
Can I purchase a single-node ES instance?
No. You must select at least two data nodes when you purchase an instance. For more information, see Purchase page parameters.
What do I do if resources are sold out when I purchase an instance?
If resources are sold out when you try to create an instance, we recommend that you take the following measures:
Change the region
Change the zone
Change the resource configuration
If resources are still unavailable after you adjust your requirements, we recommend that you wait for a while before you try to purchase the instance again. Instance resources are dynamic. If resources are insufficient, Alibaba Cloud replenishes them as soon as possible, but this process takes some time.
Why should users of existing instances with 1-core 2 GiB specifications upgrade their instances as soon as possible?
Data nodes with 1 vCPU and 2 GiB of memory can affect the performance of Elasticsearch clusters. Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch no longer provides data nodes with these specifications since May 2021. Existing data nodes with these specifications can still be used. Data nodes with 1 vCPU and 2 GiB of memory are suitable only for online learning and are not suitable for production environments. The Service-Level Agreement (SLA) does not apply to clusters that contain these data nodes. Therefore, we recommend that you upgrade your data nodes with 1 vCPU and 2 GiB of memory as soon as possible. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster.
What do I do if an ES instance is always in the Creating state after purchase?
After an instance is created, it takes some time to become active. The time required depends on your cluster specifications, data structure, and data size, and is usually several hours.
After an ES cluster is created, do I need to purchase a Kibana node separately?
No. When you purchase an ES cluster, a Kibana node is enabled by default. This setting cannot be changed. You can and select the specifications for the Kibana node based on your requirements. For more information, see Create an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch instance.
For performance and stability, we recommend that you purchase Kibana nodes with specifications of 2 CPU cores and 4 GiB of memory or higher. Kibana nodes with 1 CPU core and 2 GiB of memory are free of charge but are recommended only for testing.
Why can't I find my created instance?
Check whether the selected region is correct. We recommend that you check the region selected at the top of the ES console. If the region is correct but the ES instance is still not found, we recommend that you clear your browser cache or try a different local network.
In what scenarios do I need to purchase dedicated master nodes and client nodes when purchasing an ES instance?
A dedicated master node performs cluster-level operations, such as creating or deleting indexes, tracking which nodes are part of the cluster, and deciding which shards to allocate to which nodes. The stability of dedicated master nodes is important for cluster health. We recommend that you purchase independent dedicated master nodes in the following scenarios:
The data nodes acting as primary nodes in the cluster are under high pressure.
For write-intensive scenarios.
This is ideal for scenarios that require high cluster stability.
Coordinating nodes primarily handle query and write requests by forwarding them to data nodes and merging the query results. We recommend purchasing dedicated coordinating nodes, especially for aggregation scenarios. As a best practice, add one coordinating node for every five data nodes (with a minimum of two), and ensure their specifications match those of the data nodes. For more information about specification and capacity assessment, see Specification and capacity assessment.
What is the default account for the password I enter when purchasing an ES instance?
The default username is elastic. You can also create custom users. For more information, see Use the RBAC mechanism provided by Elasticsearch X-Pack to implement access control.
Product feature questions
Can I upgrade or downgrade the version of an Alibaba Cloud ES instance?
Only some versions support direct version upgrades. These include upgrades from 5.5 to 5.6, 5.6 to 6.3, and 6.3 to 6.7.
To upgrade or downgrade between other versions, you must first purchase an ES instance of the target version, then migrate the data from the original instance to the target instance, and finally unsubscribe from or release the original instance.
Alibaba Cloud ES free trial instances support only versions 8.5 and 8.9, and cannot be modified after creation.
To upgrade the version directly, see Upgrade the version.
For information about how to create an Elasticsearch cluster, see Create an Alibaba Cloud ES instance.
For information about how to migrate data between Elasticsearch clusters, see Data migration between Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch clusters.
To unsubscribe from an unexpired subscription instance, see Refund policy. To release a pay-as-you-go instance, see Release an instance.
Can I log on to a cluster over SSH to modify its configuration?
No. For security purposes, you are not allowed to log on to your ES cluster over SSH. To modify your cluster configuration, use the cluster configuration feature of ES. For more information, see Cluster Configuration.
Is Logstash 6.7 compatible with ES 6.3?
Yes, it is. For more information, see Compatibility matrixes.
Does Quick BI support ES data sources?
You can use Quick BI to connect to ES over the public network, but you must add the Quick BI IP addresses to the ES public access whitelist.
Does ES support scoring plug-ins?
ES supports creating tokenizers from an index to search data and sort the results based on scores. For more information, see Basic Edition: From Instance Creation to Data Retrieval.
Does ES support LDAP?
Yes, Elasticsearch supports Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). If you want to use LDAP to authenticate the requests that are sent to your Elasticsearch cluster, you must deploy an on-premises Elasticsearch cluster of the same version to conduct an authentication test. If the test is successful, you can then configure the corresponding template in the ES console. For more information, see Best practices for integrating LDAP authentication with X-Pack.
Does ES have a Java SDK?
Yes, it does. Each ES version requires a corresponding SDK. For more information, see Java API.
Where can I view the kernel version of an ES instance?
By default, ES clusters use the kernel of the latest version. For more information about kernel versions, see Kernel Version Release Notes. If your cluster does not use the kernel of the latest version, the A New Kernel Patch Is Available message appears on the Basic Information page of your cluster. Click this message to view the current kernel version of your cluster.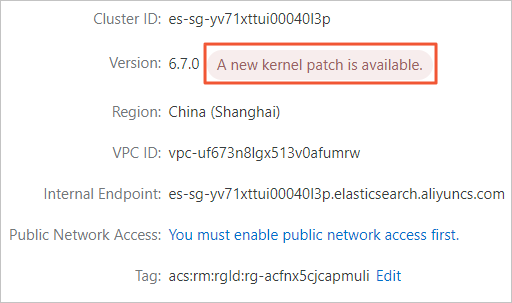
When can I use the force restart feature for ES? What are the effects of using this feature?
If the instance status is not Normal (yellow or red), the restart operation is not supported. In this case, you need to force a restart of the instance. Using this feature may cause service instability, data loss, or read/write failures during the restart phase. Proceed with caution.
How do I confirm that the Log4j2 vulnerability in ES is fixed?
The vulnerability is fixed after the cluster is successfully restarted. For more information, see [Vulnerability alert] Apache Log4j2 arbitrary code execution vulnerability.
Do I need to upgrade the ES version to fix the Log4j2 vulnerability?
No, you do not. You only need to follow the instructions in the remediation procedure to fix the vulnerability.
How do I enable service interconnection between ES instances in different regions?
You can enable service interconnection between ES instances in different regions in the following two ways:
Use a VPC peering connection. For more information, see Use a VPC peering connection to enable private connectivity between VPCs.
Use a Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) instance. For more information, see Connect network instances across regions using Cloud Enterprise Network.
How do I migrate data between Elasticsearch clusters?
You can migrate data to an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster from another Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster, a self-managed Elasticsearch cluster, or a third-party Elasticsearch source. The data migration solutions and tools vary based on the data migration scenario. For more information, see Select a data migration solution.
Do I need to purchase client nodes to enable the HTTPS protocol?
The following ES versions do not require you to purchase client nodes to enable HTTPS. Existing client nodes can be disabled.
7.16 and later versions.
For ES versions other than the preceding ones, you must enable client nodes to enable HTTPS. Client nodes cannot be unsubscribed from or disabled after purchase.
For security purposes, after you enable HTTPS for an Elasticsearch cluster, the system regularly maintains and updates the certificates on which the cluster depends. You cannot perform a rolling update for certificates installed on data nodes in Elasticsearch clusters of V7.10 or earlier. To reduce the impact of a node restart on online services during a certificate update, the system deploys the certificates on client nodes, which are used to forward requests. When you enable HTTPS for an Elasticsearch cluster that does not contain client nodes, the system displays a message to prompt you to purchase client nodes for the cluster. You must purchase client nodes for the cluster before you can enable HTTPS for the cluster. For more information, see Enable HTTPS.
What is the maximum number of shards supported by a single ES node?
Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch lets you allocate a maximum of 1,000 shards for indexes on a single data node in Elasticsearch V7.x clusters. The number of shards that can be allocated for indexes on a single data node is not limited for Elasticsearch clusters of other versions. You must configure shards for indexes on a single data node based on the specifications of the Elasticsearch cluster. For more information, see Evaluate specifications and storage capacity and Size your shards.
You can use the following command to temporarily modify the maximum number of shards for the cluster using the max_shards_per_node parameter:
PUT /_cluster/settings
{
"transient": {
"cluster": {
"max_shards_per_node":10000
}
}
}As a long-term solution, do not set this parameter to an excessively large value. Increase the number of nodes or decrease the number of shards in the cluster. Plan your shards properly to prevent cluster instability caused by excessive pressure.
How are indexes that start with .monitoring-es generated and what are they used for?
By default, the X-Pack monitoring client collects monitoring data from the cluster every 10s and stores the data in indexes that are prefixed with .monitoring-* in the corresponding Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch instance. For example, a v6.x instance has two primary types of indexes, .monitoring-es-6-* and .monitoring-kibana-6-*, which are rolled over daily. The collected data is stored in an index that is prefixed with .monitoring-es-6- and suffixed with the current date.
The .monitoring-es-6-* indexes consume a large amount of disk space. They primarily store information such as cluster status, cluster statistics, node statistics, and index statistics. For more information, see Configure monitoring indexes.
What encryption algorithm is used for disk encryption on ES data disks?
ES uses the industry-standard AES-256 encryption algorithm and Key Management Service (KMS) to encrypt disks. For more information, see Overview of disk encryption.
Does the Alibaba Cloud ES service support port 9300?
Only Alibaba Cloud ES 5.x versions support both port 9300 (for TCP) and port 9200 (for HTTP or HTTPS). Other versions support only port 9200.
Alibaba Cloud ES instances of version 6.0 and later do not support access using Transport Client on port 9300. To access port 9300, you must purchase a 5.x version instance.
Data migration and synchronization issues
How do I synchronize data from MongoDB to Alibaba Cloud ES?
You can use Monstache to sync MongoDB data to Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch in real time. For more information, see Use Monstache to sync MongoDB data to Elasticsearch in real time.
Instance restart issues
How long does it take to restart an ES instance or node?
When you restart an Elasticsearch cluster or node, the system displays an estimated time. The time is estimated based on the specifications, data structure, and data volume of the cluster or node. In most cases, a few hours are required to restart a cluster. For more information, see Restart an instance or a node.
Does enabling or disabling public network access for an ES instance trigger a restart?
No, it does not. However, the instance status briefly changes for the setting to take effect. This does not affect normal use.
Does changing the cluster access password trigger a cluster restart?
No, it does not. Changing the password only triggers a cluster reload, not a restart. For more information, see Reset the instance access password.
Does the absence of replica shards in an index affect a cluster restart?
Yes, it does. It may prevent the cluster from providing continuous service during the restart. If the overall cluster load is not high and the index has replica shards, the service can generally be provided continuously during a restart. However, in some scenarios, access timeouts may occur during the restart. For example, if the concurrency of a forced restart is high, the cluster load is very high and the cluster is already inaccessible, there are no replica shards, or there are many writes and queries during the restart or forced restart. We recommend that you design a retry mechanism on the client side and perform the operation during off-peak hours.
How do I restart a role node (such as a Kibana node) or a single node?
Restart a role node
On the Basic Information page of the instance, click Restart. Select Role Node Restart for Operation Type and select the corresponding role node. For more information, see Restart an instance or a node.
Restart a single node
You can restart a single node in one of the following two ways:
On the Basic Information page of the instance, click Restart, set Operation Type to Node Restart, and select the node that you want to restart. For more information, see Restart an instance or a node.
In the Node Visualization section of the Basic Information page of the instance, move the pointer over the node that you want to restart. In the popover that appears, click Restart. For more information, see View the cluster status and node information.
What do I do if an instance restart gets stuck?
We recommend that you first view the details of the instance change task in the task list. For versions other than 7.16, instance restarts take hours. For more information, see View instance task progress. If the change progress remains unchanged for a long time, you can refer to the following instructions to troubleshoot the issue.
Possible cause | Solution |
A plug-in issue prevents the node from starting. | Delete the corresponding plug-in. |
Shards cannot be allocated due to high disk usage. Note You can view the disk usage of the cluster in cluster monitoring. For more information, see View metrics and handle exceptions. | Delete the index or temporarily set the number of replicas for the index to 0. |
Shards cannot be allocated due to a cluster parameter setting issue. | Run the |
The number of replicas is greater than the number of nodes. | Reset the number of replicas. |
The cluster specifications are too small, causing an out-of-memory (OOM) error. |
Can I set up scheduled restarts for nodes in an ES instance?
No, you cannot. Periodically restarting nodes is not supported. If you have this requirement, you can call the RestartInstance API operation. However, you must write a scheduled task and configure the corresponding node information.
Abnormal cluster load or status issues
When using ES, the CPU and load of some nodes are normal, while others are idle. What should I do?
This issue is caused by unbalanced loads on the cluster. Unbalanced loads may be caused by several reasons, which include inappropriate shard settings, uneven segment sizes, unseparated hot and cold data, and persistent connections that are used for Server Load Balancer (SLB) instances and multi-zone architecture. Resolve the issue based on the actual scenario. For more information, see Unbalanced loads on a cluster.
Before you troubleshoot, check your cluster specifications. If your cluster has 1 CPU core and 2 GiB of memory (learning specifications), upgrade it to 2 CPU cores and 4 GiB of memory or higher. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster.
The 1-core 2 GiB specification is suitable only for learning scenarios and not for production environments. It is not covered by the product Service-Level Agreement (SLA). Due to its weak stability, this specification is no longer available for purchase. We recommend that you upgrade your 1-core 2 GiB instances to higher specifications as soon as possible.
The 2-core 4 GiB specification is recommended for use in test environments. For production environments, we recommend that you use higher specifications.
What do I do if the ES cluster status is yellow?
Cause
When the number of replicas you set for an index is greater than the current number of nodes minus 1, the cluster status becomes yellow.
Solution
Run the
GET _cat/indices?vcommand to view the distribution of index shards, locate the index with a yellow status, and set its number of replica shards to 0. After the cluster returns to normal, set the number of replica shards for the corresponding index back to its original value.WarningAfter you set the number of replica shards to 0, data may be lost if a node goes offline. Proceed with caution. After the cluster returns to normal (in about 1 minute), restore the number of replica shards to its original value as soon as possible.
PUT test/_settings { "index" : { "number_of_replicas":"0" } }
What do I do if the ES cluster status turns red due to high load?
An abnormality in the node where the primary shard is located causes the cluster to turn red. You can run the GET /_cat/indices?v command to view the distribution of index shards, locate the red index, and troubleshoot based on the following common causes and solutions.
Common cause | Solution |
Insufficient cluster resources due to unbalanced load. | Change the total number of primary and replica shards to an integer multiple of the number of data nodes in the cluster to balance loads on nodes. For more information, see How do I adjust uneven shard distribution?. |
The cluster contains useless index data. | Clear unnecessary indexes on a regular basis, such as monitoring indexes whose names start with .monitor. For more information, see Configure monitoring indexes. |
Unassigned shards. | Run the |
Cache causes resource consumption. | We recommend that you use the |
A cluster change operation, such as an upgrade, is in progress. | We recommend that you interrupt the current change and select Force Change on the upgrade page. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster. |
The instance specifications are low and resources are insufficient, such as 1-core 2 GiB or 2-core 4 GiB specifications. | Upgrade the cluster. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster. Note
|
The disk usage exceeds 85% | We recommend that you delete the historical data you no longer require or expand the capacity of disks. For more information, see High disk usage and read-only indexes. |
I see from monitoring or receive an alert that the cluster's CPU utilization is too high. What should I do?
The common causes and their corresponding solutions are as follows.
Common Causes | Solution |
an increase in write or query QPS leads to an increase in CPU usage. | You can reduce the concurrent write volume, lower the write and query QPS, or scale out the cluster. We recommend that you perform stress testing in your production environment to select the appropriate specifications. |
The index cache is consuming excessive resources. | We recommend that you run the |
The cluster has insufficient resources. | Upgrade the cluster. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster. |
The CPU usage is high and the load is unbalanced on a single node. | You can change the total number of primary and replica shards to an integer multiple of the number of data nodes in the cluster to balance the load across the nodes. For more information, see What do I do if shards are not evenly distributed on nodes in an Elasticsearch cluster?. |
What do I do if the ES disk usage is too high?
We recommend running the DELETE /index_name command to delete unnecessary indexes. After the disk usage drops below 75%, you can upgrade the disk capacity and specifications of the cluster in the console. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster. If the disk usage on a single node is too high, you also need to optimize shards. For more information, see What do I do if shards are not evenly distributed on nodes in an Elasticsearch cluster?.
To prevent high disk usage from affecting the Elasticsearch service, we recommend enabling disk usage monitoring and alerting. Check alert notifications promptly and take preventive measures. For more information, see View metrics and handle exceptions. When the disk usage of a node exceeds specific thresholds, the cluster is affected in the following ways:
Exceeds 85%: New shards cannot be allocated.
Exceeds 90%: ES attempts to migrate shards from the corresponding node to other data nodes with lower disk usage.
If disk usage exceeds 95%, the system forcefully sets the read_only_allow_delete attribute on all indexes in the Elasticsearch cluster. As a result, data cannot be written to the indexes. You can only read from or delete the indexes.
I see from monitoring or receive an alert that the ES memory usage is too high. What should I do?
The common causes and their corresponding solutions are as follows.
Common cause | Solution |
The cluster cache is consuming memory. | In the short term, you can run the |
The write activity is excessive. | Stop read and write operations, install a rate-limiting plugin, and enable cluster rate limiting. For detailed instructions, see Use the cluster rate-limiting plugin (aliyun-qos). |
Unnecessary indexes are consuming memory. | Delete unnecessary indexes to release resources. You can set a retention period for monitoring indexes, especially those with the .monitoring-* prefix. For more information, see Configure Monitoring logs. |
A single node has high memory usage and uneven shard distribution. | Optimize the shard load. Set the total number of primary and replica shards to an integer multiple of the number of data nodes in the cluster. For more information, see What do I do if shards are unevenly distributed?. |
Abnormal queries, such as queries that contain a long string of special characters from a client application. | To obtain information about a time-consuming query task, you can run the |
How do I adjust uneven shard distribution?
We recommend that you reassign and properly plan your shards. Ensure that the total number of primary and replica shards is an integer multiple of the number of data nodes in the cluster. This practice distributes data evenly across each data node and prevents high loads on a single node caused by uneven distribution. The following are examples of primary and replica shard allocation:
If a cluster has 3 data nodes, you can set the number of primary shards to 3 and the number of replica shards to 1. This configuration results in a total of 6 shards.
If a cluster has 8 data nodes, you can set the number of primary shards to 4 and the number of replica shards to 1, for a total of 8 shards. Alternatively, you can set the number of primary shards to 8 and the number of replica shards to 1, for a total of 16 shards.
After you adjust the number of shards, you must reindex your indices during off-peak hours to apply the changes to existing data. Although increasing the number of replica shards improves the availability and query performance of an Elasticsearch cluster, it also increases the cluster's memory usage.
The number of shards and the size of each shard both contribute to the stability and performance of an Elasticsearch cluster. You must properly plan the shards for all indexes in an Elasticsearch cluster. This prevents an excessive number of shards from degrading cluster performance, which can be an issue in complex business scenarios. For more information about shard planning, see Shard evaluation.
Uneven shard distribution can lead to unbalanced cluster loads. You can check for uneven shard distribution in the following ways:
Refer to Metric descriptions and troubleshooting suggestions. If the CPU, memory, or disk load on a node is high, this indicates that shards are not evenly distributed.
Run the
GET _cat/shards?vcommand to view the shard information of the index. If many of an index's shards are on nodes with high loads, this indicates an uneven shard distribution.
The cluster load is high, and the primary log reports a "java.lang.StackOverflowError for the entire cluster" error. What should I do?
This stack overflow error occurs because the amount of data written to the stack by Lucene exceeds the limit. This issue is caused by regular expression-based queries and fuzzy matching. This issue is fixed in Elasticsearch V6.0 and later. We recommend that you upgrade your cluster version or optimize your queries as soon as possible. For more information, see java.lang.StackOverflowError for the entire cluster.
How do I query the actual amount of memory allocated by the JVM configuration?
You can run the GET _nodes/stats/jvm?pretty command to view this value. By default, this value is half of the cluster's memory and cannot be modified.
Cluster query and write issues
How do I adjust the queue size?
You can adjust the queue size by setting the thread_pool.write.queue_size parameter in the YML configuration. For more information, see Configure YML parameters. Before you adjust this parameter, you can run the GET /_cat/thread_pool?v command to check the current queue usage.
For Elasticsearch clusters that are earlier than version 6.0, you must use the thread_pool.index.queue_size parameter.
How do I query or export data from a specific time period?
To query data from a specific time period in Elasticsearch, you can use a range query. For more information, see Range query.
To export data from a specific time period, you can use Logstash to filter the data. For more information, see Logstash configuration files.
Are there any quantity limits for ES bulk insert operations?
By default, the data volume of a bulk submission cannot exceed 100 MB (for more information, see HTTP settings). If you exceed this limit, you can adjust the amount of data that you write in each request. The data volume of each write request is the number of documents multiplied by the size of a single document. However, the number of documents alone is not an accurate way to estimate the data volume because the volume also depends on the size and complexity of each document. If your individual documents are large, you can reduce the number of documents in each request. We recommend that you start testing with a data volume of 5 MB to 15 MB per write request. For specific tuning methods, see the Using and Sizing Bulk Requests documentation.
There is a time difference between Elasticsearch query results and the actual time. What should I do?
By default, Elasticsearch uses Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which may differ from your local time zone. Because Elasticsearch does not support time zone adjustments, you must manually handle time conversions. You can use one of the following methods to resolve the time difference:
When you query date-type data, you can specify a time zone or use a timestamp. For more information, see Parameters for <field>.
When you write time data, you can specify the time zone. For example,
"time" : "2022-07-15T12:58:17.136+0800"(UTC+8).You can use Kibana to display data. When Kibana retrieves a date-type field from Elasticsearch, it uses JavaScript to determine the browser's local time zone. It then converts the time values in the field from UTC to the browser's time zone and displays the results. For more information, see How do I change the time zone for data visualization in the Kibana console?.
If you are synchronizing data with Logstash and there is an 8-hour time difference, you must manually add the corresponding time offset to the pipeline configuration. For example:
filter{ ruby{ code => "event.set('update_time', event.get('update_time').time.localtime + 8*60*60)" } }.
An ES cluster query returns results after a long time, or does not return results at all. What should I do?
A query that takes a long time to return results or fails to return any results is considered a slow query. You can view slow query logs in the console to investigate. For more information, see Slow Query Log. To identify the cause, refer to View metrics and handle exceptions. The following table describes common causes and their solutions.
Common causes | Solution |
Unbalanced shard load. | You can optimize the shard load by ensuring that the total number of primary and replica shards is an integer multiple of the number of data nodes in the cluster. For more information, see What do I do if shards are not evenly distributed on nodes in an Elasticsearch cluster?. |
The cluster has insufficient resources. | If you run resource-intensive queries on the cluster, we recommend that you optimize the query statements or upgrade the cluster configuration. Examples include aggregate, term, script, and fuzzy match queries. For more information about upgrading an Elasticsearch cluster, see Upgrade a cluster. Note The health of an Elasticsearch cluster affects its query performance. Performance is optimal when memory usage is below 80% and node loads are balanced. |
A "Data too large... which is larger than the limit of" error is reported when writing to the cluster. What should I do?
Cause
The write volume is too high, which triggers the circuit breaker. The cluster resources are insufficient to handle the current volume of write requests.
Solution
ImportantIf you cannot perform the following operations, you need to stop all query and write operations, and then force a restart of the cluster. After the cluster returns to a normal state, perform the required operations.
Run the
POST /index_name/_cache/clear?fielddata=truecommand to clear the index cache. If this does not solve the problem, proceed to the next step.Run the
GET /_cat/indices?vcommand to check if shards are unevenly distributed across the nodes in the cluster. For more information, see What do I do if shards are not evenly distributed on nodes in an Elasticsearch cluster?. If the issue persists, proceed to the next step.Reduce concurrent writes, delete unnecessary indexes to release resources, and reduce the use of Kibana monitoring.
To disable Kibana monitoring, run the following command:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent": { "xpack.monitoring.collection.enabled": false } }If this does not solve the problem, proceed to the next step.
Increase the cluster capacity by upgrading the cluster.
Does ES support deleting indexes in batches?
Yes, you can. You must configure a YML parameter by setting Index Naming Rule For Deletion to Allow Wildcards. After the cluster is restarted, you can use wildcard characters to batch delete indexes. For more information, see Configure YML parameters.
Deleted indexes cannot be recovered. Use this configuration with caution.
When creating a new index, an "index uuid conflicted" error occasionally occurs, and index documents cannot be written. What should I do?
This is a known issue. To resolve this issue, upgrade the kernel version of the instance to 1.5.0 or later. For more information, see Upgrade the version of an instance.
How do I modify index.max_result_window (the maximum number of documents for a paged query)?
The default value of the ES index.max_result_window parameter is 10000. This parameter specifies the maximum number of documents (`from` + `size`) that can be returned for a paged query. If a query exceeds this value, the following error is reported: Result window is too large, from + size must be less than or equal to: [10000].
For search scenarios that require deep paging, you may need to increase the value of the index.max_result_window parameter. You can run the following command to change the value of index.max_result_window based on your requirements. The value in the command is for reference only. This parameter setting persists after an Elasticsearch cluster restart.
PUT /my_index/_settings
{
"index": {
"max_result_window": 50000
}
}If a query returns many results, we recommend that you do not use the from and size parameters to perform deep paging because this operation consumes a large amount of CPU and memory resources. For deep paging scenarios, we recommend that you use scroll or search after instead.
An error is reported when updating ES data: "Rejecting mapping update to [] as the final mapping would have more than 1 type". What should I do?
This error occurs when the type specified in an update operation differs from the type of the original index. Because an ES index cannot have more than one type, you must use the same type as the original index when updating data.
In Elasticsearch 7.0 and later, type definitions are removed from mappings and the type is set to _doc.
How do I query the detailed content of documents in an index?
You can log on to the Kibana console and run the following command:
GET _search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}You can also use the Discover tool in Kibana to view documents after you create an index pattern. For more information, see Kibana Guide.
Cluster configuration and change issues
Before using ES, how do I properly plan the cluster's resources and specifications, along with the shard size and quantity?
You can also refer to Evaluate specifications and storage capacity.
How do I view the configuration parameters of an ES instance?
You can view the configuration parameters on the Basic Information page of the instance. For more information, see View the basic information of an instance.
When you use Transport Client to access an ES instance, set the cluster.name parameter to the instance ID. For more information, see Transport Client (5.x).
Does changing the cluster configuration affect the ES service?
Modifying the cluster configuration triggers a rolling restart. If the cluster status is Normal (green), each index has at least one replica, and resource utilization is not excessive, the cluster can continue to provide services during the restart. You can view the resource utilization on the Cluster Monitoring page. For example, resource utilization is not considered excessive if node CPU utilization is around 80%, node heap memory utilization is around 50%, and the load_1m of a node is lower than the number of CPU cores of the data node. However, we recommend that you modify the cluster configuration during off-peak hours.
After changing the number of nodes, does the cluster automatically rebalance the shards?
Yes, it does. When the number of nodes in an Elasticsearch cluster changes, the system automatically reallocates shards. However, this reallocation process does not guarantee an even distribution of shards across the nodes. Factors such as index size, the number of shards, and the number of nodes can cause data to remain unevenly distributed. For more information about troubleshooting and resolving unbalanced cluster loads, see Unbalanced loads on a cluster.
Does an ES instance support changing the disk type?
Yes. When you downgrade a disk, the supported storage performance path is from enterprise SSD to standard SSD, and then to ultra disk. When you upgrade a disk, the path is from ultra disk to standard SSD, and then to enterprise SSD.
Does ES support changing other types of nodes into cold data nodes?
No, it does not. This action can cause your instance to become unstable. For more information, see “Hot-Warm” Architecture in Elasticsearch 5.x.
After upgrading the instance specifications, can I downgrade the configuration, and how?
Yes, you can downgrade the configuration. For more information, see Scale in the data nodes of a cluster or Downgrade a cluster.
If there is a temporary surge in business volume, how do I change the cluster configuration to ensure normal business operations?
If a temporary surge in business volume occurs, we recommend that you first scale out the nodes (Upgrade a cluster) and then scale in the data nodes (Scale in the data nodes of a cluster). These changes require a cluster restart to take effect. Before the restart, ensure that the following conditions are met:
The instance status is normal (green).
Each index has at least one replica and resource utilization is not excessively high. You can verify this on the cluster monitoring page. For example, node CPU utilization should be approximately 80%, node heap memory utilization should be approximately 50%, and the node load_1m should be lower than the number of CPU cores on the data node.
When upgrading a cluster, a "UpgradeVersionMustFromConsole" prompt appears. What should I do?
This issue occurs because the upgrade path is not supported. Alibaba Cloud ES supports upgrades only from version 5.5.3 to 5.6.16, from 5.6.16 to 6.3.2, and from 6.3.2 to 6.7.0.
How long does it take to upgrade the ES version?
The time required for an upgrade depends on the data size, data structure, and cluster specifications. The process typically takes about one hour.
Does upgrading the ES version affect cluster services?
When you upgrade an Elasticsearch cluster, you can still read from and write to the cluster, but you cannot make other changes. We recommend that you perform the upgrade during off-peak hours. For more information about the upgrade procedure and precautions, see Upgrade the version of a cluster.
An error or timeout occurs when upgrading a cluster. What should I do?
This issue usually occurs because the cluster is in an abnormal state. In this case, stop all query and write operations, and troubleshoot the issue by following the instructions in What do I do if an Elasticsearch cluster is in a state indicated by the color red due to heavy loads?. After the cluster recovers to a normal state, try upgrading the configuration again. Alternatively, you can ignore the cluster's health status and perform a forced upgrade. However, a forced upgrade may disrupt the ES service. Proceed with caution.
For other upgrade issues, you need to troubleshoot and resolve them based on the error message.
The cluster configuration cannot be changed. What should I do?
To troubleshoot this issue, perform the following steps:
Check whether your cluster nodes use local disks. Configuration changes are not supported for nodes that use local disks. To upgrade the node specifications, you must first change the disk type.
If the frontend validation indicates insufficient inventory, try the configuration change in a different zone or wait for other users to release instances in the current zone.
If the frontend validation indicates that the cluster status is unhealthy, check for any indexes in the closed state and temporarily change their status to open. If the cluster status is red, check for issues such as offline nodes or unassigned shards, and resolve these cluster issues first.
Check whether the cluster meets the following conditions for a downgrade:
The CPU and memory of the target node specifications for the downgrade must be at least half of the current specifications. You cannot downgrade node specifications to 1-core 2 GiB, 2-core 2 GiB, 2-core 4 GiB, or 4-core 4 GiB.
NoteTo downgrade to a 2-core 4 GiB or 4-core 4 GiB instance, create a new instance with the desired specifications and migrate the data to it using a data migration method, such as Logstash.
You can downgrade a cluster only if its load meets the requirements. For more information about downgrade limits and precautions, see Downgrade a cluster.
You cannot reduce the disk capacity during a downgrade.
Can I adjust the http.max_content_length and discovery.zen.ping_timeout values in the cluster's YML file configuration?
No, you cannot configure these parameters. You can configure only the parameters that are provided by Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch. For more information, see Configure YML parameters.
The discovery.zen.ping_timeout, discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout, discovery.zen.fd.ping_interval, and discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries parameters usually do not need to be adjusted.
Can I switch the VPC of an ES instance?
You cannot switch the VPC for an ES instance. As a workaround, you can purchase a new ES instance in the desired VPC, migrate your data, and then release the original instance.
Will changing the disk type of an ES instance cause existing data to be lost?
No, your existing data will not be lost. However, new data written to the cluster during the upgrade may be lost. We recommend that you perform the upgrade during off-peak hours or after you stop writing data to the cluster. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster.
When upgrading a cluster, a "cluster unhealthy" prompt appears, but the cluster status is confirmed as Green. What should I do?
This issue can occur if some indexes in the cluster are in the close state. You can run the POST /<index_name>/_open command to temporarily open the indexes. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster.
Can ES directly upgrade the CPU to avoid data migration?
No, it cannot. Upgrading or downgrading the CPU triggers a blue-green change, which migrates data from the old nodes to new nodes and changes the node IP addresses.
Why can't cold data nodes be downgraded?
You can downgrade a cluster only if specific conditions are met. For example, the CPU and memory of the selected target specifications must be at least half of the current specifications, and you cannot downgrade the node specifications to 1 core and 2 GiB of memory, 2 cores and 2 GiB of memory, 4 cores and 4 GiB of memory, or 2 cores and 4 GiB of memory. For more information, see Downgrade a cluster.
If the conditions for a configuration downgrade are not met, you can create a new instance, migrate the data, and then release the original cluster. For more information, see Select a data migration solution.
When scaling in cluster data nodes, an error "This operation will cause the current cluster resources (Disk/CPU/Memory) to be insufficient or cause shard allocation abnormalities" is reported. What should I do?
Possible cause | Solution |
Insufficient cluster resources. After a scale-in operation, the cluster has insufficient resources, such as disk, memory, and CPU, to handle the current system data or load. | You can run the |
Shard allocation error. Based on Lucene principles, Elasticsearch does not allocate multiple replica shards of the same index to a single data node. Consequently, if a scale-in operation results in the number of replicas for an index being greater than or equal to the number of remaining data nodes, a shard allocation error occurs. | You can run the |
When scaling in cluster data nodes, an error "The cluster is currently in an abnormal state or has unfinished tasks" is reported. What should I do?
You can use the Cluster Diagnosis feature to diagnose the cluster and troubleshoot the issue based on the provided diagnostic results and suggestions. For more information, see Perform a diagnostic on an Elasticsearch cluster.
When scaling in cluster data nodes, an error "The number of reserved nodes must be greater than 2" is reported. What should I do?
To ensure cluster reliability and stability, at least two data nodes must remain after a scale-in operation. For a multi-zone cluster, each zone must also retain at least two data nodes, and all zones must have the same number of remaining data nodes. If your scale-in plan does not meet these requirements, you must adjust the number of nodes to remove, or upgrade the cluster.
When scaling in cluster data nodes, an error "The current ES cluster configuration does not support this operation" is reported. What should I do?
Run the GET _cluster/settings command to view the cluster configuration and check for the setting that disallows data allocation: "cluster.routing.allocation.enable" : "none". If this setting is present, you can temporarily change it to "cluster.routing.allocation.enable" : "all". If this configuration affects other operations, you must revert it after the scale-in is complete.
Using an auto_expand_replicas index causes data migration or node scale-in to fail. What should I do?
Cause
This issue can occur if you use the permission management feature of X-Pack. In earlier versions, the corresponding .security index uses the
"index.auto_expand_replicas" : "0-all"configuration by default, which causes data migration or node scale-in to fail.Solution
View the index configuration.
GET .security/_settingsThe following output is returned:
{ ".security-6" : { "settings" : { "index" : { "number_of_shards" : "1", "auto_expand_replicas" : "0-all", "provided_name" : ".security-6", "format" : "6", "creation_date" : "1555142250367", "priority" : "1000", "number_of_replicas" : "9", "uuid" : "9t2hotc7S5OpPuKEIJ****", "version" : { "created" : "6070099" } } } } }Modify the configuration using one of the following methods:
Method 1
PUT .security/_settings { "index" : { "auto_expand_replicas" : "0-1" } }Method 2
PUT .security/_settings { "index" : { "auto_expand_replicas" : "false", "number_of_replicas" : "1" } }ImportantThe number_of_replicas parameter specifies the number of replicas for an index. You can configure this parameter as needed. Make sure that the value is greater than or equal to 1 and no more than the number of available data nodes.
How do I clear the ES cache?
You can log on to the Kibana console and run the following commands:
Clear the cache for a specific index
POST /<index_name>/_cache/clear?fielddata=trueClear all caches
POST /_cache/clear
How do I change the zone of an ES cluster?
For the procedure, refer to Migrate Elasticsearch nodes in a zone or upgrade the deployment mode of an Elasticsearch cluster.
Does an ES cluster support independent disk expansion?
Yes, this is supported. For more information, see Upgrade a cluster.
Scaling out triggers a rolling restart of the cluster. We recommend that you perform this operation during off-peak hours.
Does ES support modifying JVM parameters?
Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch uses the JVM parameter settings recommended by official Elasticsearch. These settings cannot be modified. By default, the heap size is set to half of the cluster memory, up to a maximum of 32 GB. For more information, see Heap size settings.
Plug-in, tokenizer, and synonym issues
When using the IK tokenizer, how do I customize and extend the dictionary content?
You can add or delete words in the dictionary using the cold and hot update features of the IK analysis plug-in for Alibaba Cloud ES. For more information, see Use the analysis-ik plug-in.
When using the IK analysis plug-in, an "ik startOffset" error is reported. What should I do?
This error is caused by a bug in ES 6.7. To resolve it, restart your cluster. For more information, see Restart an instance or a node.
If the local IK dictionary file is lost, can it be recovered from the cluster management page?
No, you cannot. You can only delete or update dictionary files on the cluster management page. We recommend that you download the official main and stopword dictionary files, replace the main tokens and stopwords in the files with the nouns from your system dictionary, and then re-upload the files.
After updating the IK tokenizer dictionary, how do I make the new dictionary effective for existing data?
You must perform a reindex operation. By default, an updated IK tokenizer dictionary applies only to new data. To apply the dictionary updates to existing data in an index, you must perform a reindex operation. For more information, see Configure a reindex whitelist.
Is there a standard value for FullGC?
To determine if a FullGC (cleaning the entire heap space) event is problematic, you must analyze business latency and compare historical with current conditions. The CMS collector starts garbage collection when memory usage reaches 75%. This leaves sufficient headroom to handle sudden traffic spikes.
Can unused plug-ins be uninstalled?
Only some plug-ins can be uninstalled. You can view which plug-ins can be uninstalled on the Built-in Plug-ins tab of the Plug-ins page for your Elasticsearch cluster. A plug-in can be uninstalled if Remove is displayed in the Actions column. For more information, see Install and remove a built-in plug-in.
Are the dictionaries of the Alibaba Cloud ES IK analysis plug-in and the open source IK plug-in the same?
Yes, they are. The built-in dictionaries for the Alibaba Cloud ES IK analysis plugin are the same as those for the corresponding version of the open-source IK analysis plugin. For more information, see IK Analysis for Elasticsearch.
Can custom plug-ins access external networks, for example, to read dictionary files from GitHub?
Custom plugins cannot access external networks. To access external files, you can upload them to OSS and read them from there.
Do custom plug-ins support hot updates?
No, they do not. However, you can enable this feature by configuring the plug-in to use the same hot update method as the IK dictionary. For more information, see IK Analysis for Elasticsearch.
How is the analysis-aliws tokenizer configured, and what is the file format?
For more information, see Use the AliNLP tokenizer plugin (analysis-aliws).
The dictionary file requirements are as follows:
File name: Must be aliws_ext_dict.txt.
File format: Must be UTF-8.
Content: One word per line, with no leading or trailing whitespace. Use UNIX or Linux line feeds (\n). If the file is generated in Windows, use the dos2unix tool on a Linux machine to convert the dictionary file before uploading.
What are the differences among ES synonyms, IK tokenization, and AliNLP tokenization?
Tokenizer type | Usage | Feature description | Supported file type | Tokenizer or analyzer |
Synonym | Upload a synonym file in the cluster configuration module to use. | Write several synonyms in a file. When you query one of them, the others will also be displayed. | UTF-8 encoded TXT file | Custom |
IK tokenization | Via the analysis-ik plug-in. | The system splits a paragraph based on the main.dic file. If you send a query that contains one or more words split from the paragraph, the system returns the entire paragraph in the query result. The system also uses the stop.dic stopword file. After the paragraph is split, words found in the stop.dic file are filtered out. You can view these dictionary files in the official documentation. | UTF-8 encoded DIC file | Tokenizers:
|
AliNLP tokenization | Via the analysis-aliws plug-in. | Similar to IK tokenization, but does not include a separate stopword file. Stopwords are integrated into the main dictionary file: aliws_ext_dict.txt, and the dictionary is not publicly available. Custom stopwords are not currently supported. | File name must be: aliws_ext_dict.txt, UTF-8 encoded |
|
Where is the ES IK tokenization mode configured?
The analysis-ik plug-in is a built-in IK analyzer provided by Alibaba Cloud ES and cannot be removed. You can use the standard or rolling update method to update the plug-in's built-in main dictionary and stopword list. You can then use the updated dictionary and stopword list when you configure mappings for an index. For more information about how to use the analysis-ik plug-in, see Use the analysis-ik plug-in.
Which built-in Chinese tokenizers does Alibaba Cloud ES support?
Alibaba Cloud ES supports two built-in Chinese tokenizers: analysis-ik and analysis-aliws. You can use these tokenizers after configuring their corresponding dictionaries.
When hot-updating a dictionary file via OSS, if the content of the dictionary file on the OSS side changes, will the ES side update automatically?
No, it will not. Alibaba Cloud ES does not currently support automatic hot updates for dictionary files from OSS. After the content of an OSS file changes, you must manually reconfigure and upload it for the changes to take effect. For indexes that are already configured with IK tokenization, synonyms, or AliNLP tokenization, the dictionary update applies only to new data. To apply the changes to all data, you must reindex.
Does the IK tokenizer used by Alibaba Cloud ES support remote dictionaries?
No, it does not. The IK tokenizer provided by Alibaba Cloud ES lets you upload or update dictionaries. For more information, see Use the IK analysis plugin (analysis-ik). However, it does not support remote dictionaries or related configurations, such as IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml.
How do I install the vector search plug-in (aliyun-knn) on an Alibaba Cloud ES 7.10 instance?
On Alibaba Cloud ES 7.10 instances, the aliyun-knn plug-in is integrated into the built-in apack plug-in. Therefore, to install or uninstall the aliyun-knn plug-in, you must perform the operations on the apack plug-in. For more information, see Use the physical replication feature of the apack plug-in. For installation instructions for other versions, see Use the vector search plugin (aliyun-knn).
If the minor engine version of the instance is 1.4.0 or later, the apack plug-in is already the latest version and does not need to be updated. You can run the GET _cat/plugins?v command to retrieve the plug-in version.
Does restarting after installing a plug-in affect cluster services?
If the overall cluster load is low and the index has replica shards, services can generally remain available during a restart. However, in some scenarios, access timeouts may occur during a restart. For example, timeouts may occur if there is high concurrency during a forced restart, the cluster load is extremely high, the index has no replica shards, or there is a high volume of write and query operations during the restart. We recommend that you implement a retry mechanism on the client and perform the operation during off-peak hours.
Log issues
Does ES support setting a retention period for .security logs?
Yes, you can configure this using index lifecycle management (ILM). For detailed instructions, see Manage Heartbeat data using an index lifecycle.
The .security index stores information related to the elastic account. Periodically deleting this index may prevent you from logging on to ES.
How do I save ES logs locally?
You can call the ListSearchLog API. For more information, see ListSearchLog.
I cannot see the query and update logs for ES. What should I do?
You can configure slow logs and reduce the timestamp precision of log entries. For more information, see References.
How do I configure and view slow logs for an ES instance?
By default, the slow log for an ES instance records read and write operations that take 5 to 10 seconds. You can log on to the Kibana console of the instance and run commands to lower the time threshold for logging. This lets you capture more logs. For more information, see the referenced document.
Modifying the slow log format is not supported.
How do I programmatically pull slow logs from an ES instance on a regular basis?
You can call the ListSearchLog API operation to pull slow logs from your ES instance on a regular basis. For more information, see ListSearchLog.
How do I find out which clients are using an ES instance?
You can view the access logs or audit logs of your ES instance:
To view information about operations on an instance, such as add, delete, modify, and query, you need to enable audit logs.
Enable access logs to view information such as the cluster node and its IP address, the client IP address, bodySize, request content, request time, and uri.
For more information about limits, precautions, and enabling access logs and audit logs, see Query logs.
Data backup and recovery issues
Can snapshots of an ES instance be restored to an instance of a different version?
For automatic backups, you can restore snapshots only to the original instance, or you can use the cross-cluster snapshot restoration feature. For more information, see Automatic backup and restoration and Configure a cross-cluster OSS repository.
For manual snapshots, you can directly restore data from the snapshots to other clusters. We recommend using a destination cluster with the same version as the original cluster to avoid potential compatibility issues. For more information, see Manual backup and restoration.
How can I resolve an unhealthy cluster status when backing up ES data for a version upgrade in the Alibaba Cloud ES console?
If the ES cluster status is unhealthy, you cannot trigger a snapshot backup. We recommend that you first restore the cluster status to green.
I have enabled automatic backups but have not configured OSS. Does this mean the backup was unsuccessful?
Alibaba Cloud ES provides an OSS bucket by default. To retrieve data from automatic backups, Log on to the Kibana console and run the GET _snapshot/aliyun_auto_snapshot/_all command in Kibana.
When migrating (restoring) data via snapshot, the destination shows a shard abnormality. The shard recovery command POST /_cluster/reroute?retry_failed=true is still unsuccessful, and the corresponding index shows an abnormality. What should I do?
When you migrate (restore) data from a snapshot, the following issue may occur:
Delete the problematic index, and then call the _restore API to restore it. Add the max_restore_bytes_per_sec parameter to the restore command to limit the node recovery speed. The default value is 40 MB per second.
POST /_snapshot/aliyun_snapshot_from_instanceId/es-cn-instanceId_datetime/_restore
{
"indices": "myIndex",
"settings": {
"max_restore_bytes_per_sec" : "150mb"
}
}You can also specify other parameters, such as:
compress: Specifies whether to enable data compression. The default value is true.
max_snapshot_bytes_per_sec: Specifies the snapshot rate for each node. The default value is 40 MB per second.
Can data in ES be exported to a local machine?
Yes. Alibaba Cloud ES provides a data backup feature. For more information, see Data backup. You can back up your data to OSS and then download it to a local machine by following the instructions in Download objects.
How do I restore a snapshot across clusters?
You can use a shared OSS repository to restore the data. For more information about the operations, conditions, and precautions, see Configure a shared OSS repository. If you want to migrate data between clusters that belong to the same Alibaba Cloud account but reside in different regions, you can use Snapshot backup and recovery commands. For more information about available data migration solutions, see Select a data migration solution.
What data backup solutions does Alibaba Cloud ES offer?
For information about data backup solutions for Alibaba Cloud ES, including their use scenarios and limitations, see Data Backup.
Cluster monitoring and alert issues
How do I configure X-Pack Watcher alerts?
For information about how to configure a DingTalk or WeCom robot to receive X-Pack Watcher alerts, see Configure a DingTalk robot to receive X-Pack Watcher alerts and Configure a WeCom robot to receive X-Pack Watcher alerts.
With X-Pack Watcher in Alibaba Cloud ES, you can perform operations when specific conditions are met. For example, you can configure a trigger to automatically send a DingTalk message when an error log appears in the logs index. X-Pack Watcher is a monitoring and alert service based on ES.
An alert for "GC memory allocation failed" appears. What should I do?
Possible causes include a high cluster load, a high number of queries per second (QPS), or a large amount of data being written. Troubleshoot and resolve the issue as follows:
High cluster load: For more information, see Troubleshoot high cluster disk usage and read-only issues.
High QPS or a large amount of data to write: You can install the cluster throttling plug-in (aliyun-qos) on your cluster to implement read and write throttling. For more information, see Use the cluster throttling plug-in (aliyun-qos).
NoteFor image retrieval, you can install the aliyun-knn plug-in and plan your cluster and indexes. For more information, see Use the aliyun-knn plug-in.
What do the cluster status metric values mean?
The ClusterStatus(value) metric indicates the health of a cluster. A value of 0.00 indicates that the cluster is healthy. The following table describes the values of the ClusterStatus(value) metric. For more information, see View metrics and handle exceptions.
Value | Meaning |
0.00 | The cluster status is normal. |
1.00 | The cluster is in a sub-healthy state. The replica shards of one or more indexes in the current cluster are lost, which does not affect continued use. |
2.00 | The cluster status is abnormal. The primary shards of one or more indexes in the current cluster are lost (unassigned), which affects the normal use of the cluster and needs to be fixed as soon as possible. |
How do I view the disk usage of ES?
You can view ES disk usage in the console or using X-Pack monitoring in Kibana. For more information, see View metrics and handle exceptions and Configure Monitoring logs.
What do I do if a "promotion failed" error is reported during CMS GC?
A "promotion failed" error may occur in Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch when you use the Concurrent Mark Sweep (CMS) garbage collector. This error usually indicates that the old generation space is insufficient, which prevents objects from being promoted to the old generation space. If you encounter this CMS garbage collection issue, consider the following solutions:
Monitoring and log analysis:
View the garbage collection (GC) logs to obtain detailed information. Analyze the logs to determine if frequent CMS GC or Full GC operations are occurring and to confirm if the
CMS GC promotion failederror is caused by insufficient old generation space.Log on to the Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch log query page. Search for log records that contain
promotion failedto better understand the cause of the issue.
Adjust heap memory size and garbage collector settings:
If your Elasticsearch version is 6.7.0 or later and the data node memory is 32 GB or greater, we recommend that you switch the garbage collector to G1 to optimize garbage collection performance.
Evaluate whether to increase the instance memory based on your cluster's resource utilization and business requirements.
Tuning recommendations:
If memory-related issues persist, you may need to evaluate the overall index data volume, query load, and cluster resource configuration. If necessary, contact Alibaba Cloud technical support for professional tuning guidance.
What do I do if no data is displayed for basic monitoring?
Description: No data is displayed for the monitoring metrics on the basic monitoring page of an Elasticsearch instance. To go to the basic monitoring page and view metric details, see View cluster monitoring details.
Cause: No data is displayed for monitoring metrics. This may be caused by an abnormal backend monitoring service, an abnormal cluster status, or a manually disabled monitoring feature.
Solution: Check whether the X-Pack monitoring feature is enabled and whether its data collection behavior is as expected.
NoteIf Elasticsearch detects that the amount of data in a request exceeds a preset resource limit (such as insufficient memory or resource limits on query or indexing operations), a
Data too large... which is larger than the limit oferror may be reported. To prevent the circuit breaker from being triggered due to insufficient cluster resources, some users may disable the X-Pack monitoring feature.Use the following code to view the cluster configuration information.
GET /_cluster/settings?prettyEnable the X-Pack monitoring feature.
If the X-Pack monitoring feature is disabled, which means the X-Pack configuration is
xpack.monitoring.collection.enabled: false, you can run the following command to enable it.PUT _cluster/settings # Enable data collection for the X-Pack monitoring feature. Persistent indicates a persistent setting, which means the configuration is retained even after a cluster restart. { "persistent": { "xpack.monitoring.collection.enabled": true } }
true: The monitoring feature is enabled.
false: The monitoring feature is disabled.
If no data is displayed for basic monitoring after you perform the preceding steps, submit a ticket to contact technical support.
Cluster access issues
How do I use a client to connect to an Alibaba Cloud ES cluster, and how does it differ from open source ES?
You can connect to an Alibaba Cloud ES cluster using its internal or public endpoint. This endpoint is the equivalent of the cluster endpoint for an open source Elasticsearch cluster. For more information, see Use a client to access an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster.
Can I disable Basic Auth (security authentication) when accessing an ES instance with a client?
No, you cannot. ES instances include the X-Pack feature, which provides Basic Auth as an authentication mechanism for Kibana. Therefore, you cannot disable Basic Auth.
An Alibaba Cloud ECS instance and an ES instance are in the same VPC but different zones. Can the ECS instance access the ES instance over the internal network?
Yes, it can. Instances in the same VPC can access each other over the internal network, regardless of their zones.
How do I configure a public or private access whitelist for ES?
To access an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch instance over the Internet or a VPC, you must add the IP address of your device to the public or private IP address whitelist for the instance. For more information, see Configure a public or private IP address whitelist for an instance. Before you configure an IP address whitelist, note the following:
When you configure a public access whitelist, you must first enable the public endpoint switch, which is disabled by default.
You can add a maximum of 50 IP addresses or IP address ranges to the whitelist.
If you add an IP address range to the whitelist, the IP address that you enter must be the first IP address of the subnet after the mask is applied.
You cannot add 0.0.0.0/0 to the whitelist at the same time as other specific IP addresses or IP address ranges. This action will cause an error. To add 0.0.0.0/0 for testing purposes, you must add it to the whitelist by itself.
How do I connect to an ES instance from the internet?
You can access an Elasticsearch instance over the internet using its public endpoint. However, you must first configure a public IP address whitelist for the instance. For more information, see Configure a public or private IP address whitelist for an instance. To connect, you must provide parameters such as the endpoint, username, and password. For more information, see Access an Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch cluster using a client.
Unable to access ES: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno 61] Connection refused
The following are possible causes and solutions.
Possible cause | Solution |
Public network access is unavailable. | If you access the ES cluster using a public domain name, perform the following steps to troubleshoot the issue:
|
Private network access is unavailable. | If you access the ES cluster using a private domain name, perform the following steps to troubleshoot the issue:
|
The cluster is unhealthy. | If you cannot access the ES cluster even though the network connection is normal, check the status of the cluster and resolve the issue based on the results:
|
Does resetting the password affect ES access?
If you reset the password for the elastic account of an Elasticsearch cluster in the Elasticsearch console, only access to the cluster with that account is affected. Access with other accounts is not affected. We recommend that you use a custom account to access the Elasticsearch cluster. The custom account must be assigned a role with the required permissions. For more information, see Use the RBAC mechanism provided by Elasticsearch X-Pack to implement access control.
Changing the password does not trigger an instance restart.
The Elasticsearch-Head plug-in version 5.0.0 cannot access Alibaba Cloud ES (all versions). What should I do?
This issue is usually caused by Chrome's cross-domain restrictions. The following method resolves this issue for Chrome on a Mac. For other operating systems, refer to the documentation for Chrome's cross-domain configuration.
Create an empty folder.
Open the terminal and enter the following command.
open -n /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/ --args --disable-web-security --user-data-dir=path_to_new_empty_folder
The Elasticsearch-Head plugin is no longer maintained for Elasticsearch versions 5.x and later. We recommend using Cerebro to access your Alibaba Cloud ES cluster. For more information, see Connect to a cluster using Cerebro.
Index-related issues
How do I close an index?
After an ES index is closed, it no longer supports queries or writes.
POST /<index_name>/_open #Set the index status to open
POST /<index_name>/_close #Set the index status to close