You can use Global Traffic Manager 3.0 to configure a primary/backup disaster recovery plan. If the primary service address fails, DNS queries automatically switch to the backup address. After the primary address is restored, a predefined policy determines whether to switch traffic back. This ensures high availability for your services.
Solution architecture
This topic uses a primary/backup disaster recovery scenario as an example. In this scenario, the service is deployed in two data centers: a primary data center that handles daily traffic and a backup data center for disaster recovery. If the primary data center becomes unavailable due to network issues or a service interruption, traffic is automatically switched to the backup data center to reduce downtime.

The workflow is as follows:
Health check: Global Traffic Manager (GTM) continuously performs health checks on the service addresses in the
Primary-DCandBackup-DCaddress pools to monitor their availability.DNS query: A user initiates a network request. The local DNS then sends a DNS query for the service domain name to GTM.
Traffic scheduling:
If the primary address pool is healthy, GTM returns the IP address of the primary address pool based on the configured sequence policy.
If the primary address pool fails, GTM determines that it is unavailable and automatically returns the IP address of the backup address pool.
Fault recovery: After the primary address pool is restored, GTM determines whether to switch traffic back to the primary address pool or keep it at the backup address pool based on the configured Preemptive Mode or Non-Preemptive Mode.
Prerequisites
Prepare a domain name: You must have an Access Domain hosted by Public Zone. Ensure that the domain name has at least one DNS Server IP Address with a Available status in Public Zone.
Deploy services: The primary and backup services must be deployed and have service addresses. For example, the Shanghai data center uses
121.21.*.*and the Hangzhou data center uses139.3.*.*.
Procedure
1. Create Access Domain
Go to the Alibaba Cloud DNS-Global Traffic Manager console.
On the Access Domain tab, click the Create Access Domain button.
In the dialog box that appears, select Custom Scenario.
On the Access Domain configuration page, click the access domain name icon and select Basic Configuration.
Complete the form configuration.
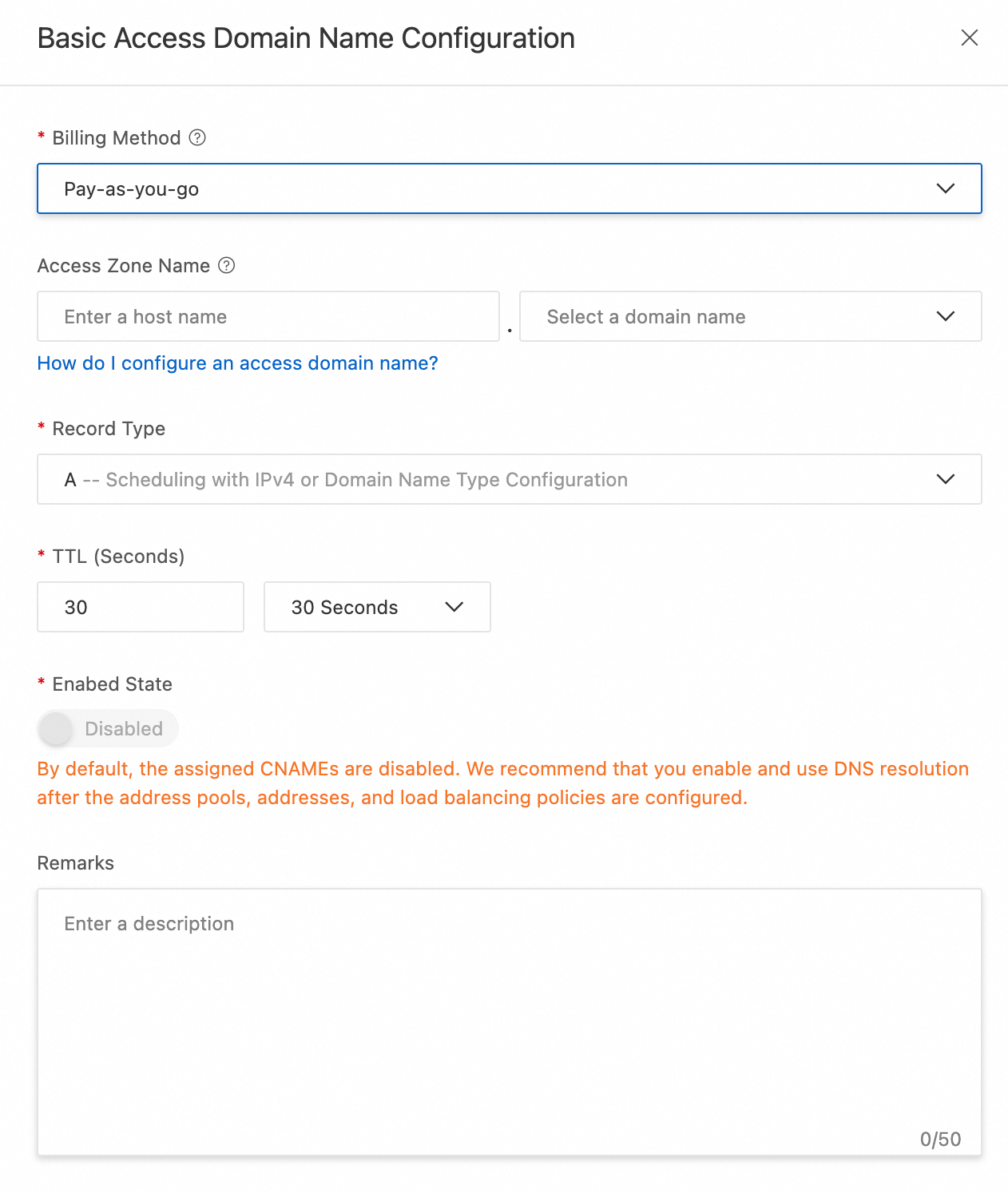
Access Domain: Set the access domain name, for example,
gtm.your-domain.com. If the drop-down list is empty, purchase a domain name or go to Public Zone to add a third-party domain name.Billing Method: For this solution, select Pay-as-you-go.
Record Type: Select A. This is because the service addresses in this solution are IPv4 addresses.
TTL (Seconds): The default value is 30. A shorter TTL helps speed up DNS failover but increases the number of DNS queries.
Enabed State: Keep the default disabled status. Enable it after you complete all configurations.
Remarks: Enter a description.
2. Add primary and backup address pools
An address pool is a collection of service addresses. For this solution, you need to create a primary and a backup address pool that correspond to the two data centers.
Click the Access Domain icon, and then click Add Address Pool.
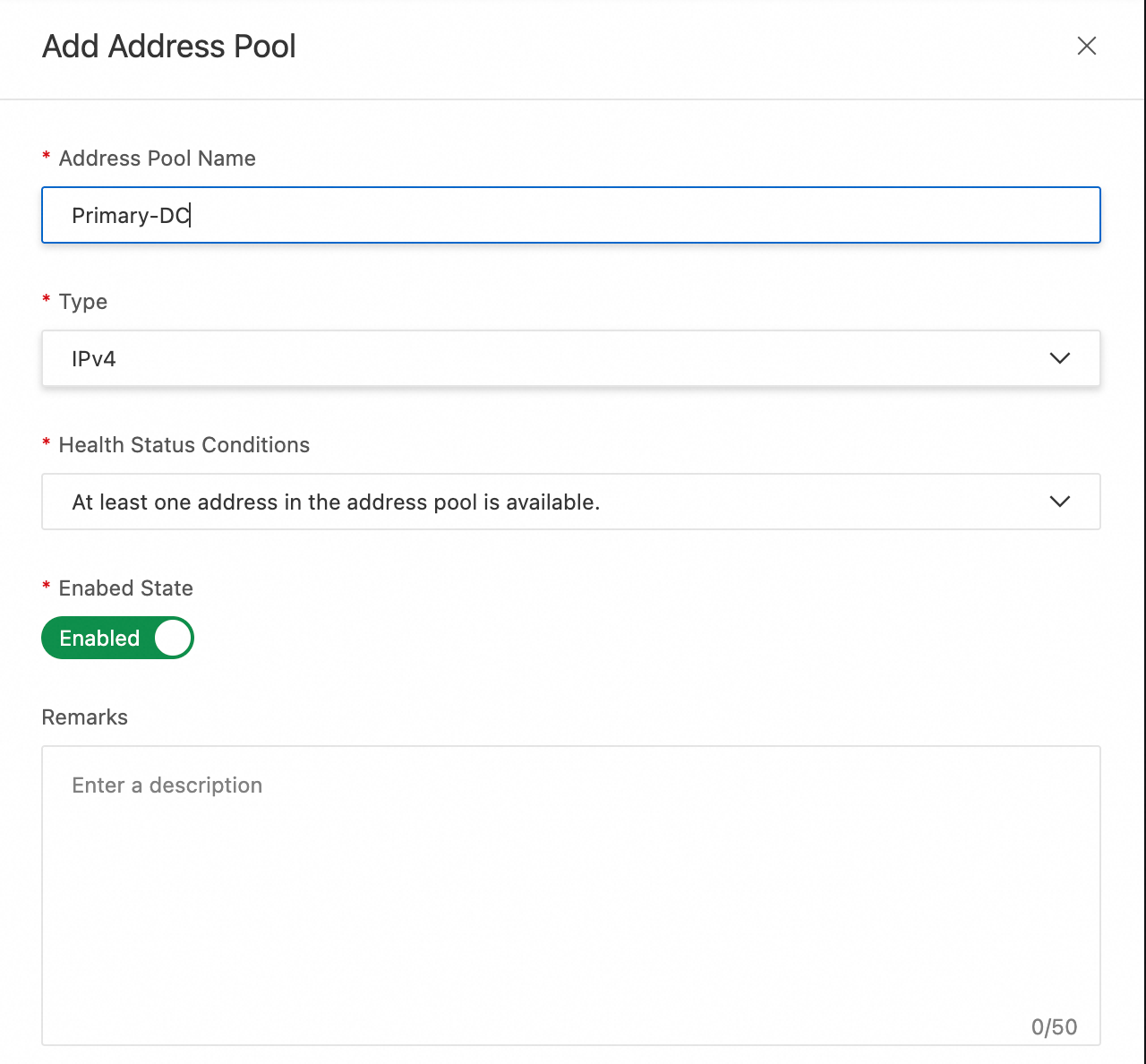
Fill out the form. For more information about the parameters, see Address pool configuration.
Address Pool Name:
Primary-DCType: IPv4
Health Status Conditions: Select At least one address in the address pool is available.. This means the pool is considered available if at least one address in it is healthy.
Enabed State: Enable
Follow the same steps to create the backup address pool
Backup-DC.
3. Add Address
Click the icon for the address pool that you just added, and then click Add Address.
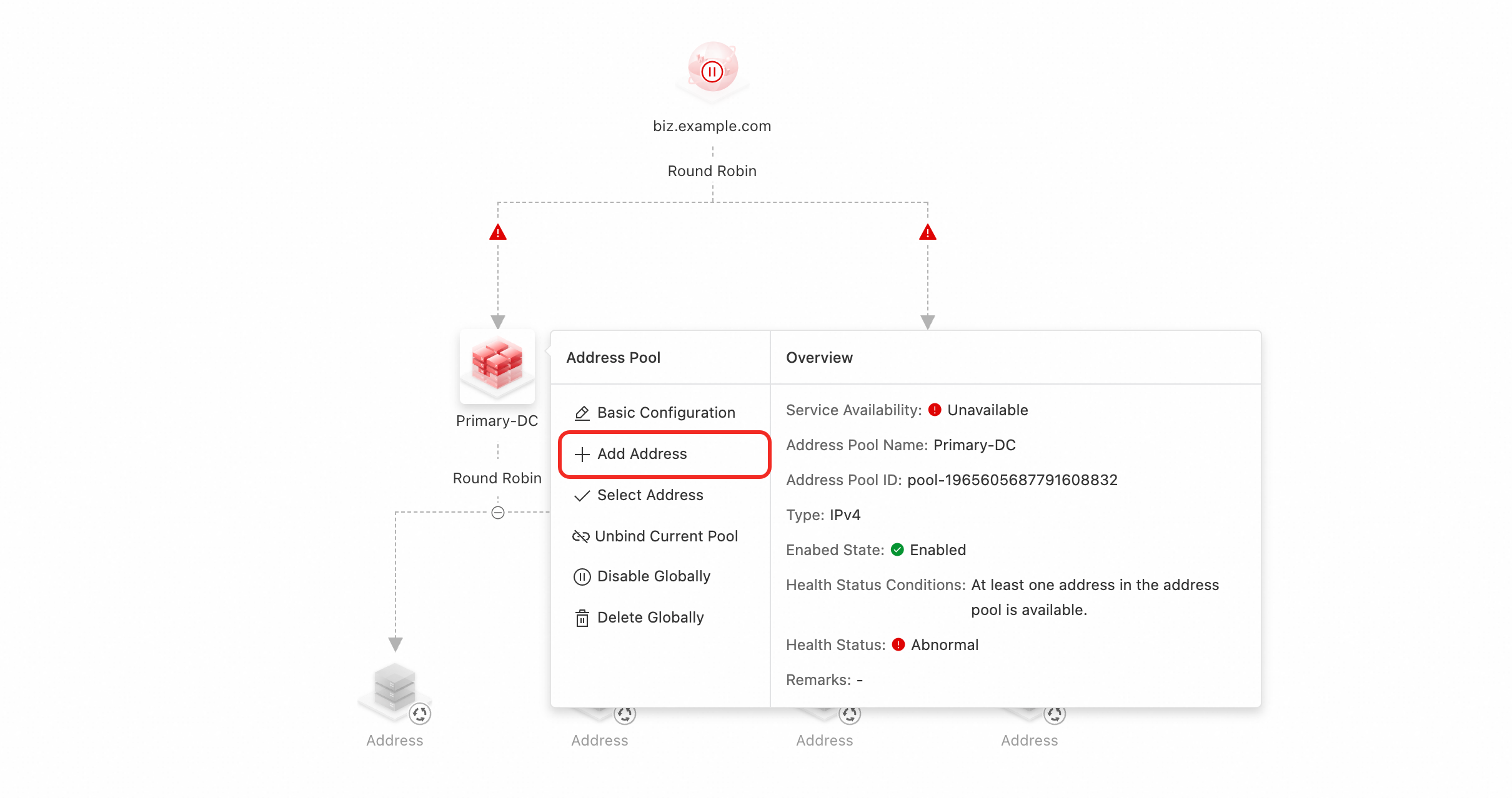
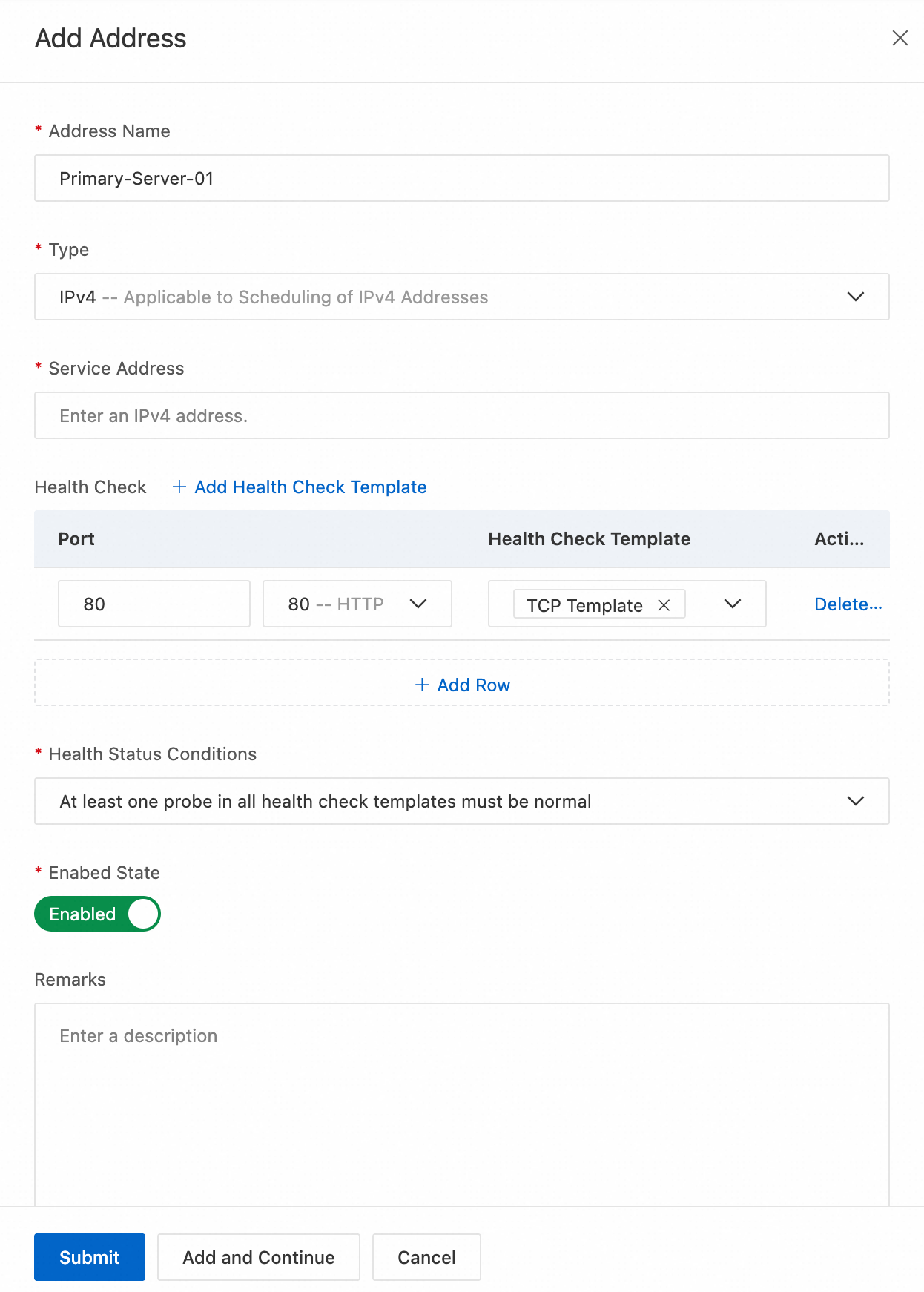
Complete the form configuration. For more information, see Address configuration.
Address Name:
Primary-Server-01Type: IPv4
Type: Enter the public IP address of the server in the primary data center.
Health Check: Enable this option. Configure the probe protocol, such as HTTP/HTTPS, the path, such as
/health, and the expected response code. GTM uses this configuration to determine whether the service is normal.
Follow the same steps to add a service address to the backup address pool
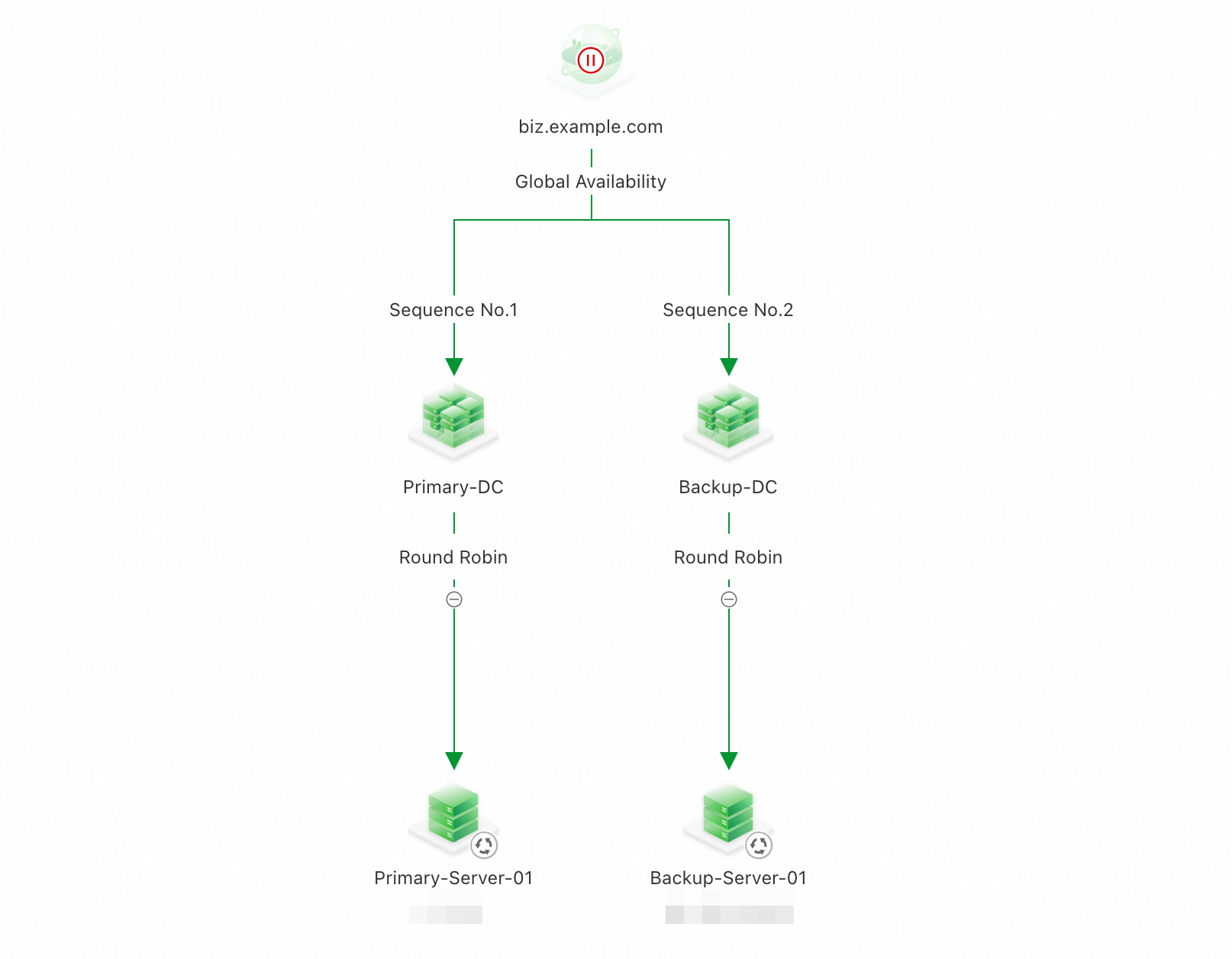
Backup-DC. The result is shown in the following figure.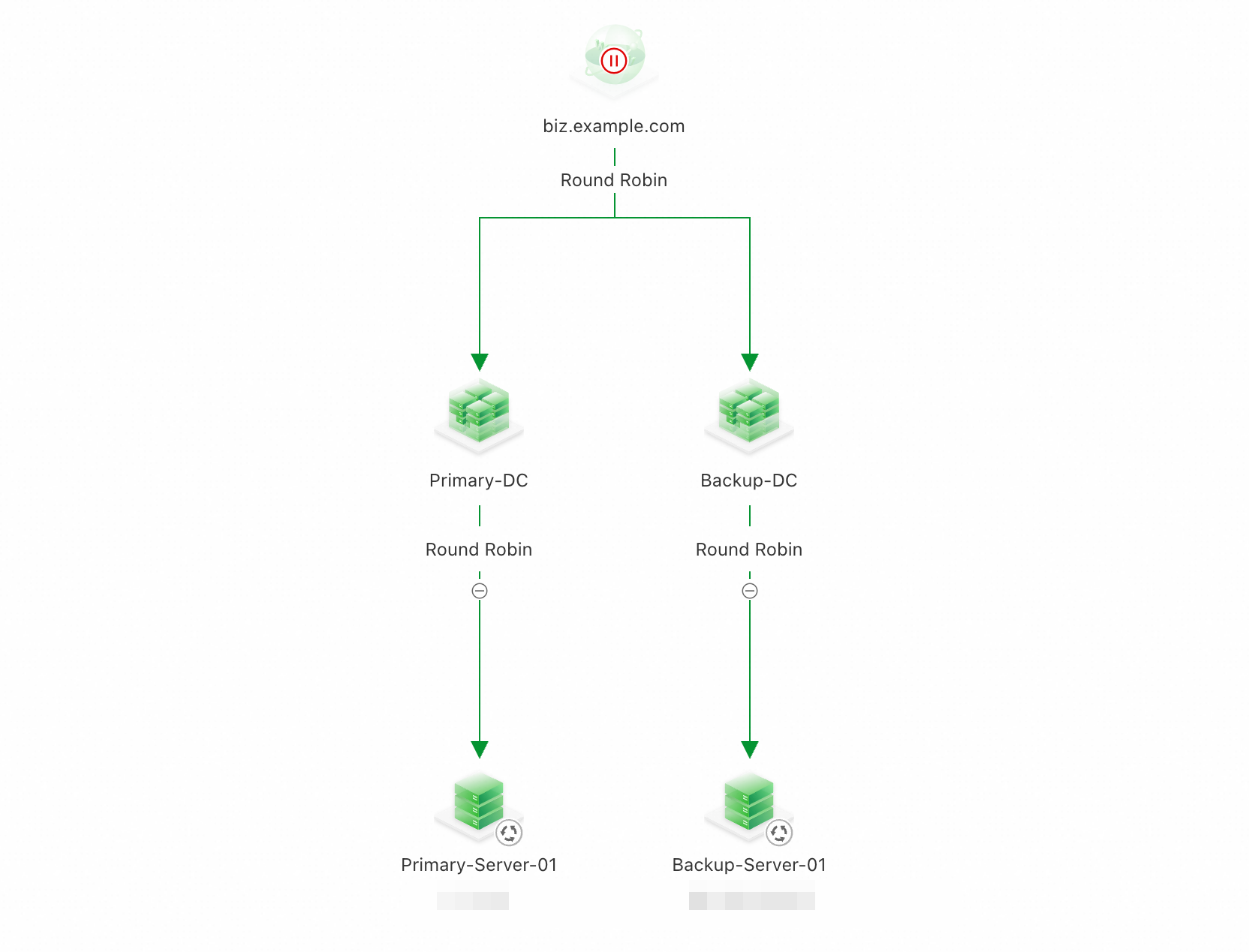
4. Load Balancing Policy
The access policy involves two layers of scheduling: a load balancing policy between address pools and a load balancing policy among addresses within a single address pool. The system applies the pool-level policy first, then the address-level policy, and returns the final resolution result.
Configure the load balancing policy between address pools
Click the policy above the address pools and select Load Balancing Policy.
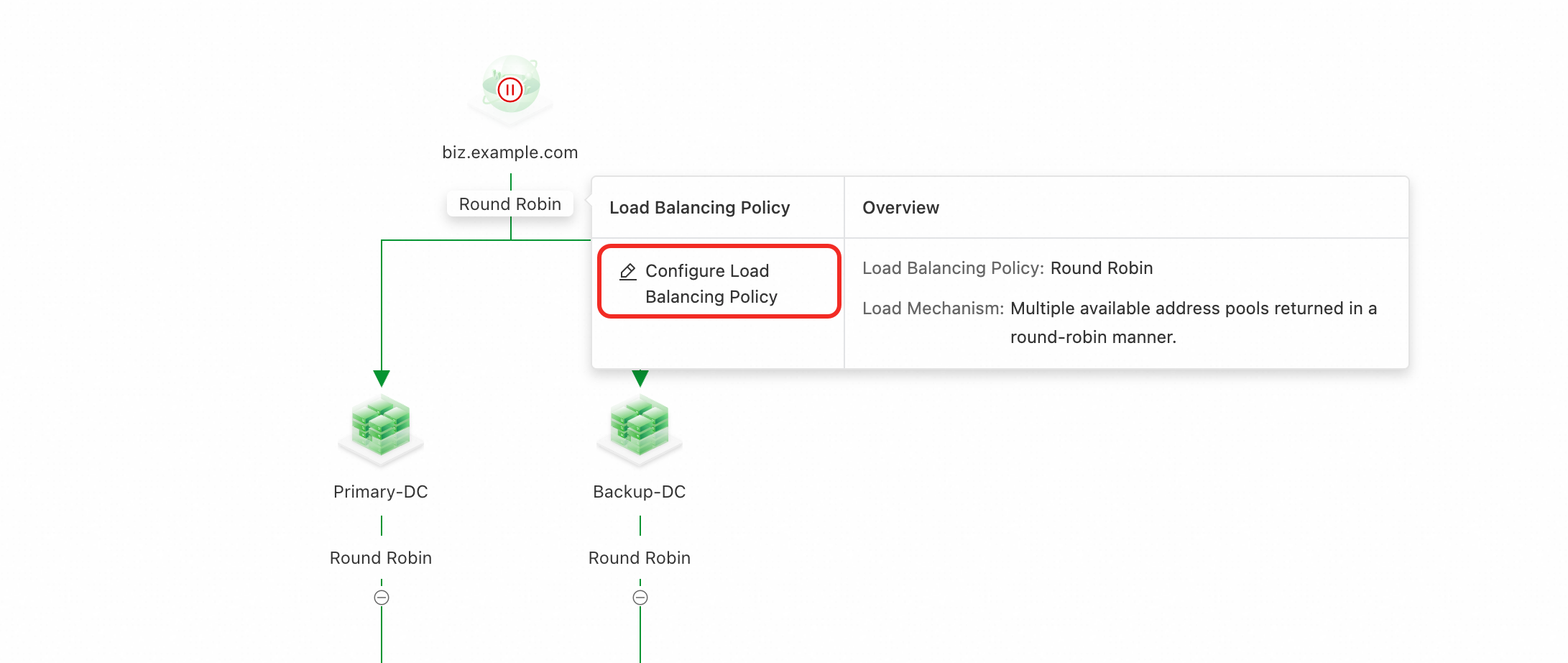
Complete the form configuration.
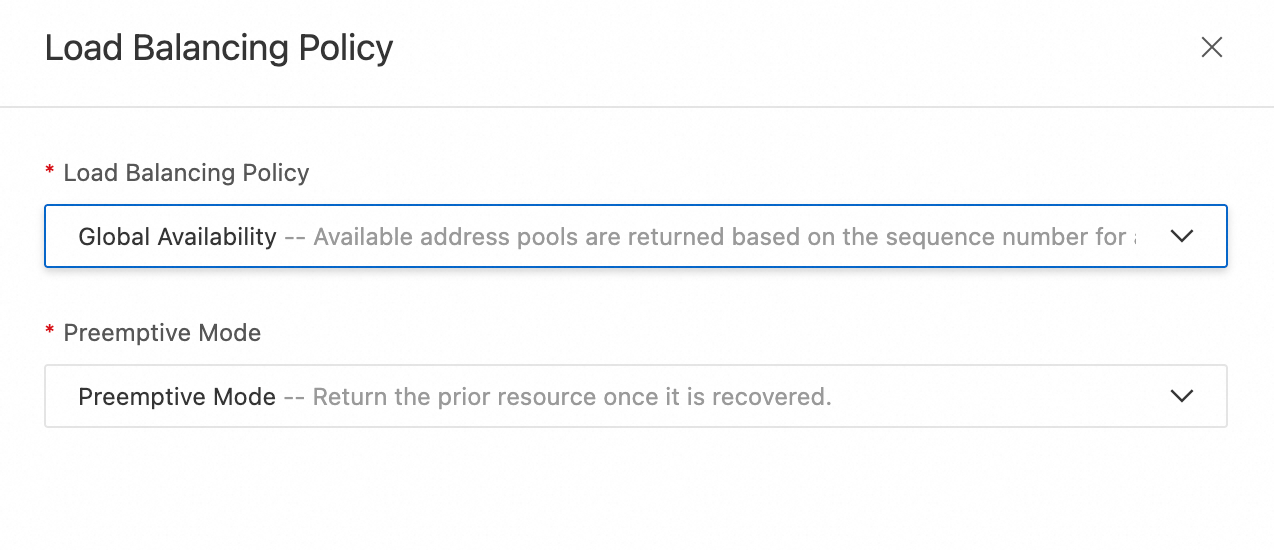
Load Balancing Policy: Global Availability
Preemptive Mode: Preemptive Mode
Click Sequence No. > Adjust Sequence Number.
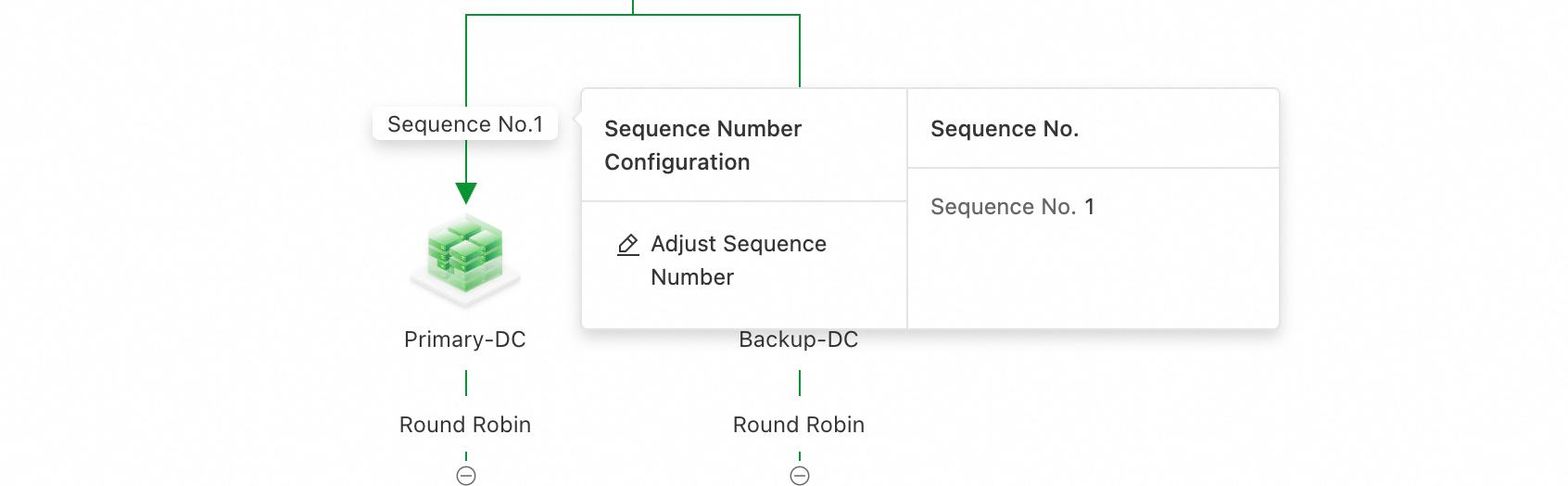
Drag the address pools to sort them. Place the primary address pool first.
Configure the load balancing policy within an address pool
In this solution, each address pool has only one service address. Therefore, you can keep the default Round Robin policy for load balancing within the address pool.
5. Enable the access domain name
By default, a newly configured access domain name instance is disabled and cannot provide external services. After you complete the configuration, you must manually enable the access domain name.
Make sure the health status of the service is normal. If you see any red or orange alert metrics, troubleshoot the address health check before you enable the service.


Click the access domain name icon and select Enable.
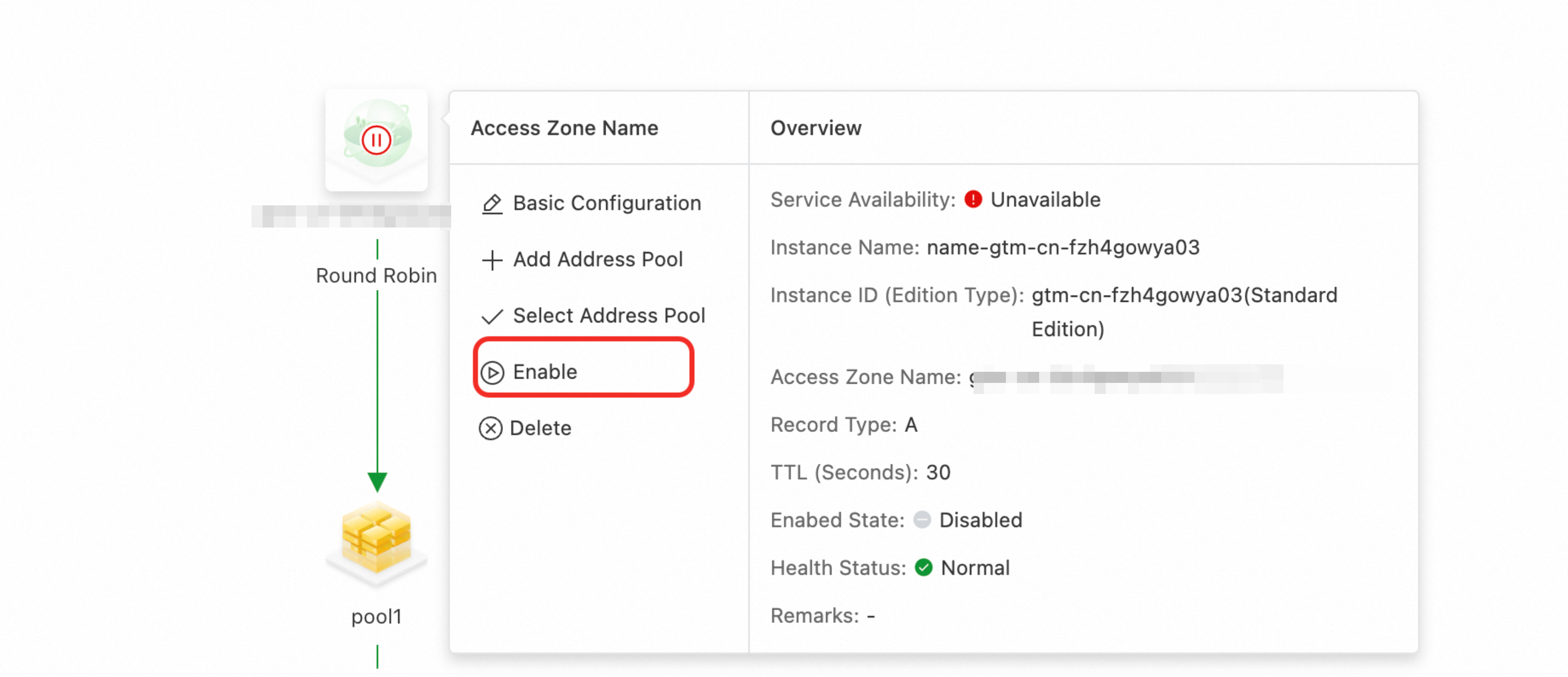
In the confirmation dialog box, review your settings and submit the configuration.
Wait for the access domain name configuration to take effect. This process takes about 10 minutes. You can use the Network Probe Tool. Enter the access domain name and check whether the DNS returns the expected IP address. You can also test with the following commands:
nslookup gtm.your-domain.comdig gtm.your-domain.com
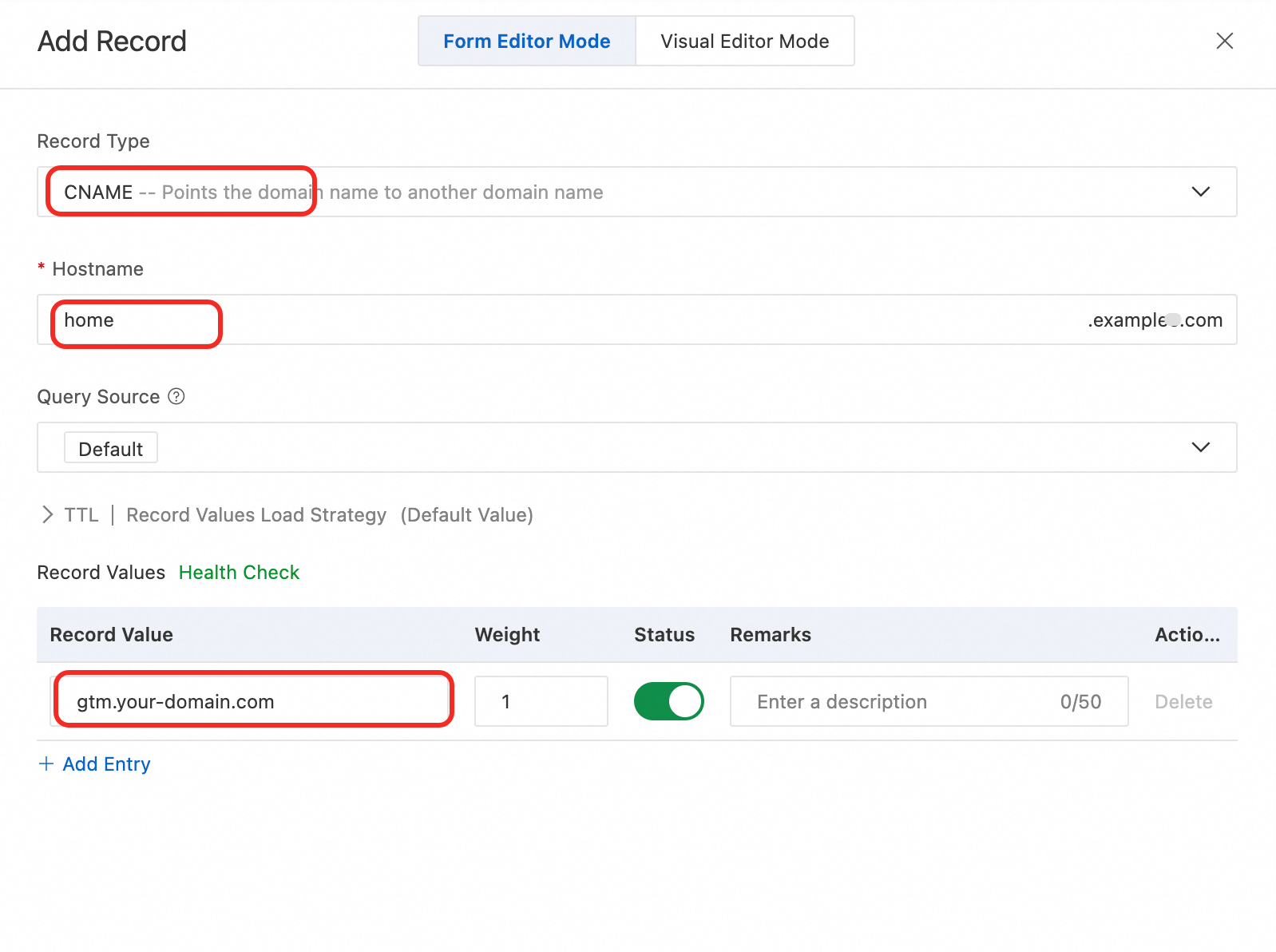
6. Configure a CNAME record for traffic steering
Configure a CNAME record for your service domain name to point to the Access Domain. For example: home.example.com CNAME gtm.your-domain.com
This topic uses a service domain name hosted by Public Zone as an example. If your service domain name is hosted by another DNS provider, configure the CNAME record with that provider.
Go to the Alibaba Cloud DNS - Public DNS console. Find the target domain name and click Settings.
Click Add Record.
Record Type: CNAME
Host: Enter the host record for traffic steering.
Value: Enter the configured access domain name.
 Important
ImportantIf the service domain name already has other types of DNS records, such as A or AAAA, adding a
CNAMErecord will cause a conflict. For more information about conflict rules, see DNS record conflict rules. You can resolve the conflict as follows:When you add the
CNAMErecord, create it in a disabled state.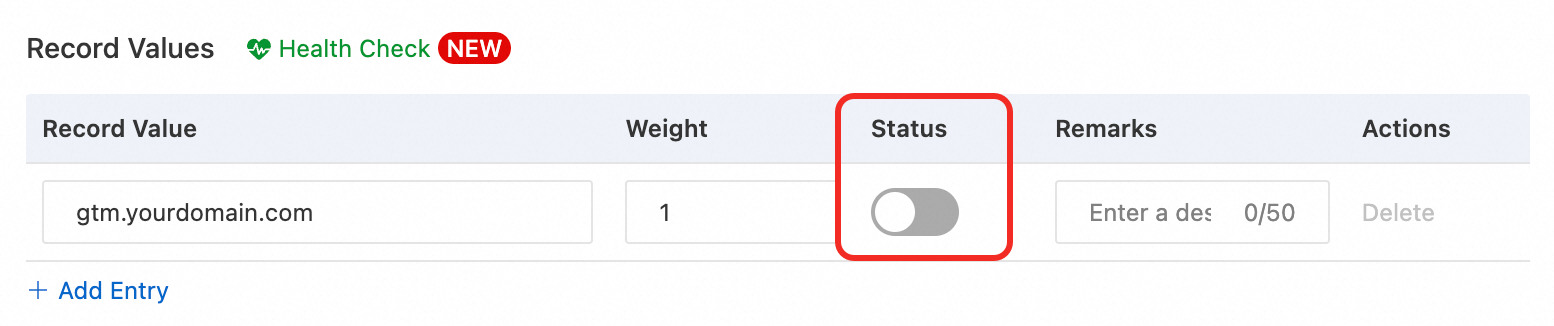
During off-peak hours, disable the existing DNS records of other types, such as A or AAAA.
Enable the
CNAMErecord.
Billing
For more information, see Product Billing.
Related reading
For more information, see FAQ.
If you want to learn about more scenarios, see Best practices.