The O&M Dashboard page in Operation Center displays the O&M stability assessment information, key O&M metrics, and scheduling resource usage overview of auto triggered nodes and the running details of manually triggered nodes. This page also displays information about data synchronization nodes in Data Integration. This helps you quickly understand the overall information about nodes in your workspace, identify and handle exceptions at the earliest opportunity, and improve O&M efficiency.
Usage notes
The O&M Dashboard page allows you to view the overall O&M information about your auto triggered nodes, manually triggered nodes, and data synchronization nodes in Data Integration from the following perspectives. For more information about O&M on auto triggered nodes, manually triggered nodes, and data synchronization nodes in Data Integration, see View O&M information about auto triggered nodes, View O&M information about manually triggered nodes, and View O&M information about data synchronization nodes in Data Integration.
Specified workspace: You can view O&M information about a specified workspace, including the overall O&M information about the auto triggered nodes and manually triggered nodes in the workspace, and the O&M information about data synchronization nodes in the workspace.
All workspaces: You can view the overall O&M information about all workspaces within your current account. You cannot separately view the O&M information about data synchronization nodes in Data Integration.
Limits
The development environment of Operation Center in workspaces in standard mode does not support the O&M Dashboard feature. For information about workspaces in standard mode, see Differences between workspaces in basic mode and workspaces in standard mode.
NoteYou can switch between the production environment and the development environment in the top navigation bar of the Operation Center page.
Auto Triggered Node: This tab displays only O&M information about auto triggered nodes and instances.
Manually Triggered Node: This tab displays only O&M information about manually triggered workflows and manually triggered nodes and instances in the workflows.
Data Integration: This tab displays only O&M information about batch synchronization nodes and real-time synchronization nodes in Data Integration.
Go to the O&M Dashboard page
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Operation Center.
View O&M information about auto triggered nodes
On the Auto Triggered Node tab, you can view the O&M stability assessment information about auto triggered nodes, the items that need to be focused on, the distribution of auto triggered nodes in different O&M states, the completion status of auto triggered instances, and the resource usage of different resource groups for scheduling.
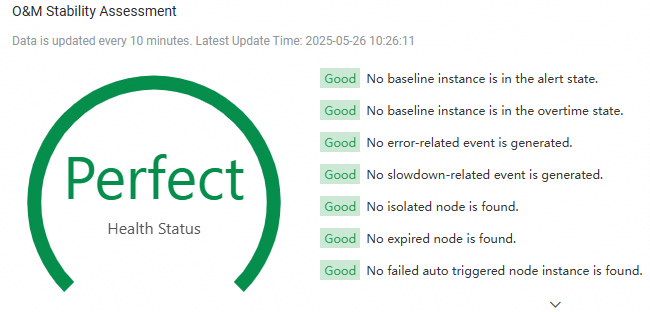
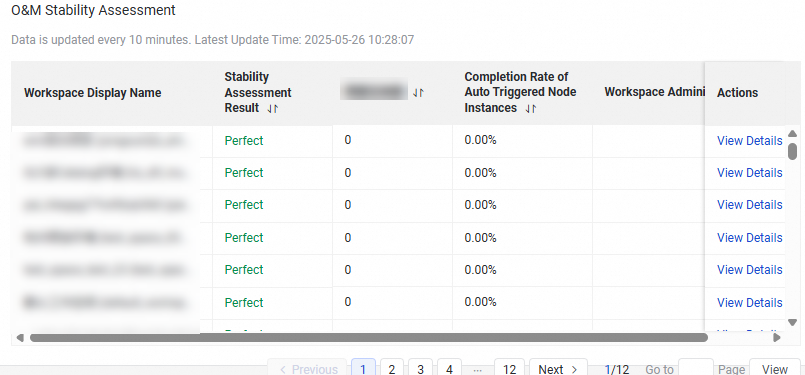
View information in the O&M Stability Assessment section
In the O&M Stability Assessment section, the O&M stability of your workspace is assessed based on the overall running details of nodes in your workspace.
Assessment scope | Single workspace | All your workspaces |
Illustration |
|
|
Stability description | The health status for O&M stability can be excellent, good, medium, or poor. If high-risk or low-risk items are displayed, the health status of the workspace is poor. You must handle the risky items and optimize the performance of the workspace at the earliest opportunity. |
|
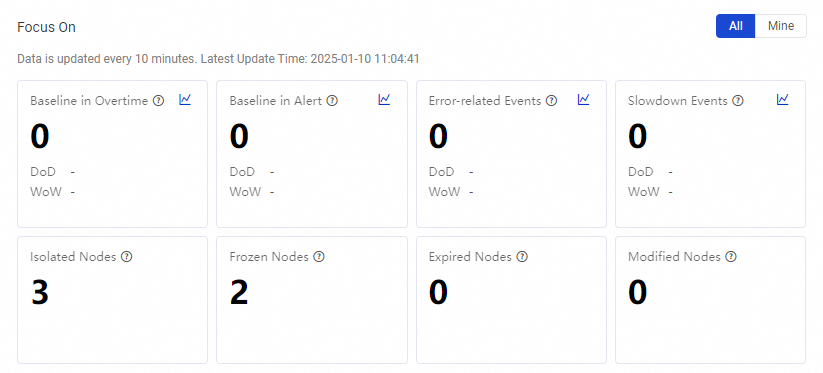
View information in the Focus On section
The Focus On section displays the O&M exceptions from the workspace and individual perspectives based on exception statistics of intelligent baselines and auto triggered nodes. You can view the overall information in your workspace or view only the information about nodes of which you are the owner to identify and handle exceptions at the earliest opportunity and ensure that your business is not affected.
Exception type | Description | References | Illustration |
Baseline in Overtime | Counts the number of baseline instances that are in the overtime state on the current day. If a node in a baseline is still running when the committed completion time of the baseline arrives, an instance that is generated for the node enters the overtime state. |
| |
Baseline in Alert | Counts the number of baseline instances that are in the alert state on the current day. You can specify an alert margin threshold to ensure that important data is generated as expected in scenarios in which dependencies between nodes in the baseline are complex. If the alert margin threshold is exceeded, nodes may fail to finish running as expected and exceptions may occur. | ||
Error-related Events | Counts the number of error-related events that are generated on the current day. An error-related event is generated if a node in a baseline fails. In this case, the running of descendant nodes of the node may be blocked. You must handle the error at the earliest opportunity to prevent the node from affecting the running of its descendant nodes. | ||
Slowdown Events | Counts the number of slowdown events that are generated on the current day. A slowdown event is generated if the running duration of a node in a baseline is significantly longer than the average running duration of the node in the historical periods of time. | ||
Isolated Nodes | Counts the number of isolated nodes on the current day. If an auto triggered node does not have an ancestor node, the auto triggered node becomes an isolated node. In this case, the node cannot be automatically scheduled to run. | ||
Frozen Nodes | Counts the number of auto triggered nodes that are frozen on the current day. If an auto triggered node is frozen, instances that are generated for the node are also frozen. Frozen instances are not automatically scheduled, and the descendant instances of the frozen instances are blocked from running. | ||
Expired Nodes | Counts the number of auto triggered nodes for which the effective period of scheduling expires. The system generates instances for an auto triggered node and runs the instances within the effective period of scheduling of the node. If the effective period of scheduling expires, the system does not generate or schedule auto triggered instances of the node. | None | |
Modified Nodes | Counts the number of auto triggered nodes whose configurations are modified on the current day.
Note If you select Mine in the upper-right corner of the Focus On section, only the number of modified nodes of which you are the owner is counted. | None |
View O&M information about auto triggered nodes and auto triggered instances
The following table lists the sections in which you can view O&M information about auto triggered nodes and auto triggered instances.
Section | Description | Illustration |
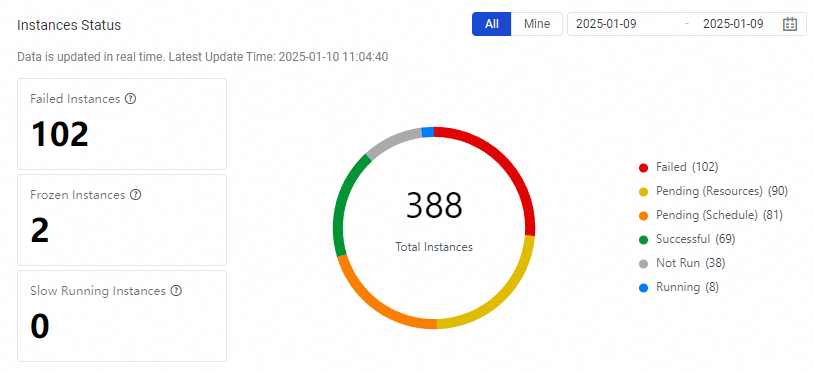
Instances Status |
Note Only statistics on normal nodes are collected. Statistics on dry-run nodes and frozen nodes are not collected. |
|
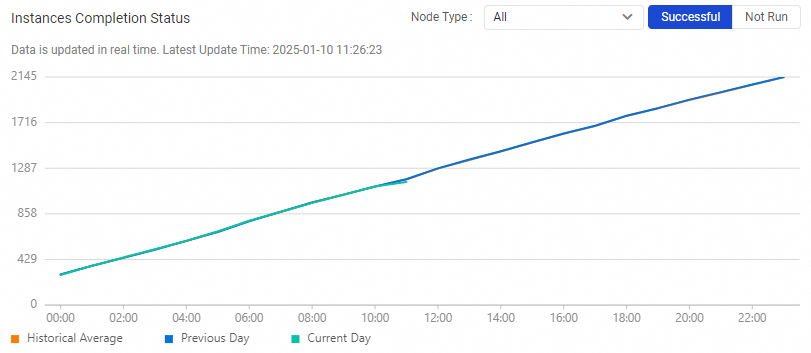
Instances Completion Status |
|
|
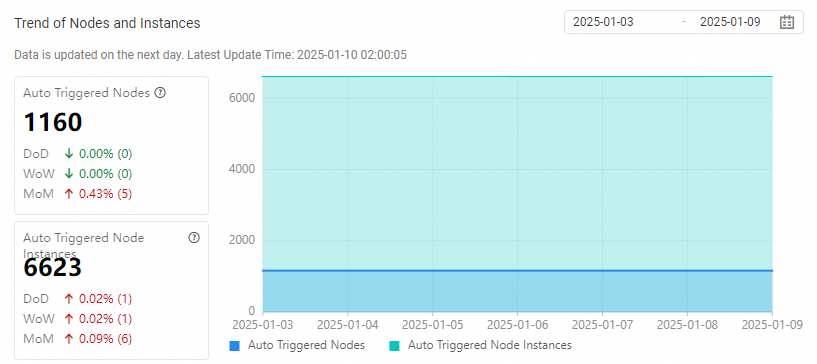
Trend of Nodes and Instances | Statistical scope: This section displays the changing trends of the numbers of auto triggered nodes and auto triggered instances in the production environment within a specific period of time. You can specify a period of time within the previous 12 months in the upper-right corner of this section. Note |
|
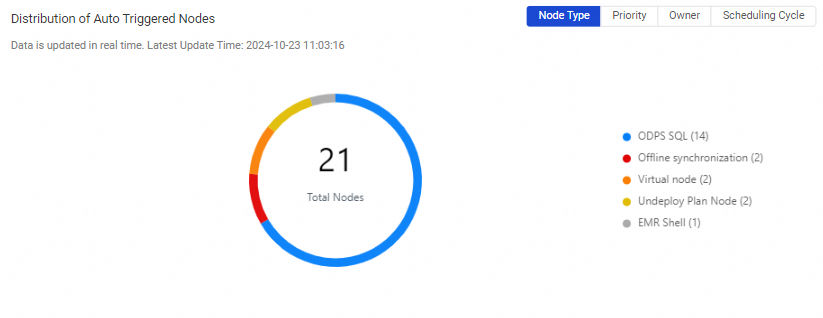
Distribution of Auto Triggered Nodes |
Note If you select All My Workspaces in the top navigation bar of the Operation Center page, you can view the distribution of auto triggered nodes by workspace in this section. |
|
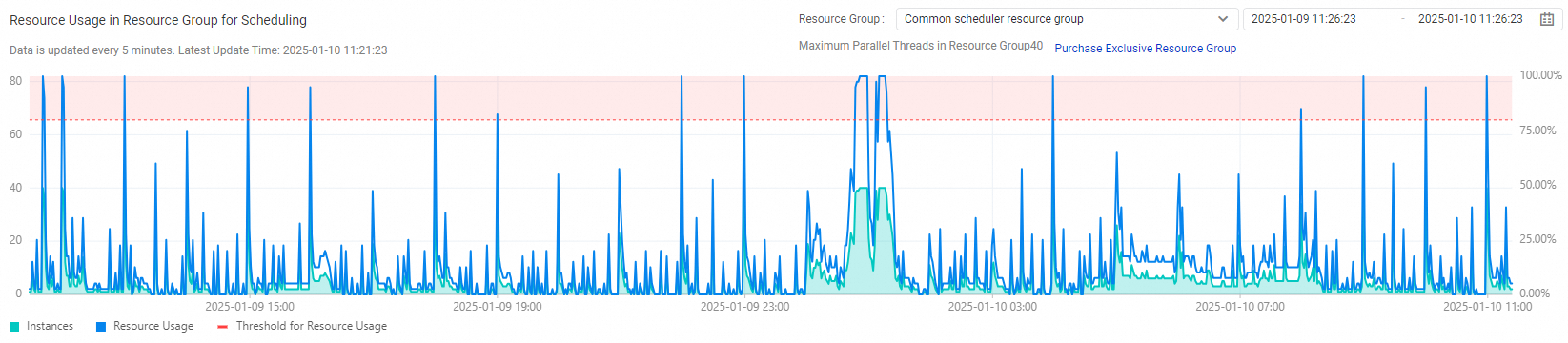
View information in the Resource Usage in Resource Group for Scheduling section
This section displays the resource usage of a resource group for scheduling and the changing trend of the number of instances that are run on the resource group over a specific period of time. The chart in this section shows the percentage of resources used by the instances that are run on the specified resource group.
This section displays statistics for a maximum of seven days.
If the resource usage of a resource group exceeds 80%, we recommend that you scale out the resource group to prevent insufficient resources from affecting the running of nodes.
The resource usage and the number of instances that are run on the resource group are collected at a level of resource group. For example, if multiple workspaces share the exclusive resource group for scheduling that you use, this section displays the resource usage and the changing trend of the number of instances that are run on the resource group in all the workspaces.
View the ranking of auto triggered instances on the previous day and the ranking of auto triggered instances with the highest error rate in the recent month

Ranking of Instances on Previous Day
This section ranks auto triggered instances based on their running duration, time spent in waiting for resources, and slow running duration on the previous day. Only the
top 30auto triggered instances are displayed. You can identify a time-consuming node based on the ranking, click the ID of the instance that is generated for the node to go to the instance details page, and then perform diagnostics on the instance to view the running situation of the instance.NoteSlow Running: The difference between the running duration of an instance on the previous day and the average running duration of the instance over a historical period is collected. Instances are sorted by the difference in descending order.
Ranking of Auto Triggered Node Instances with Highest Error Rate in Recent Month
This section ranks nodes on which errors occurred within the recent month and displays the
top 30nodes. You can identify a node with a high error rate in the recent month, view the running details of the node, and then identify the cause of the error.
View O&M information about manually triggered nodes
On the Manually Triggered Node tab, you can view the O&M information about manually triggered workflows and instances in the workflows.
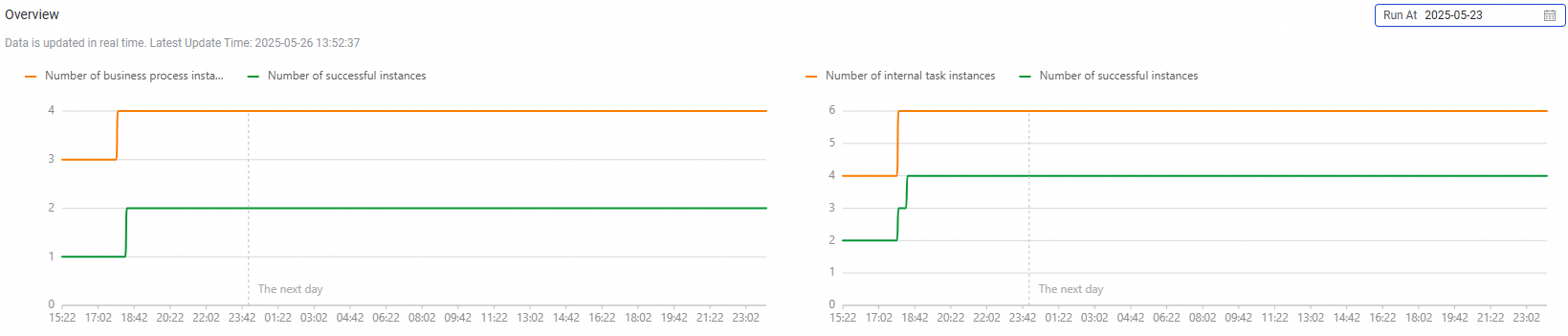
Overview
This section displays the numbers of manually triggered workflows and instances generated for manually triggered nodes in the workflows that are run on a specified date, and the proportion of auto triggered instances that are successfully run.
View information in the Business Process Instance State Distribution and Workflow Ranking sections
Section | Description | Illustration |
Business Process Instance State Distribution | In this section, a donut chart is used to display the distribution of instances that are generated for manually triggered nodes and in different states in manually triggered workflows.
|
|
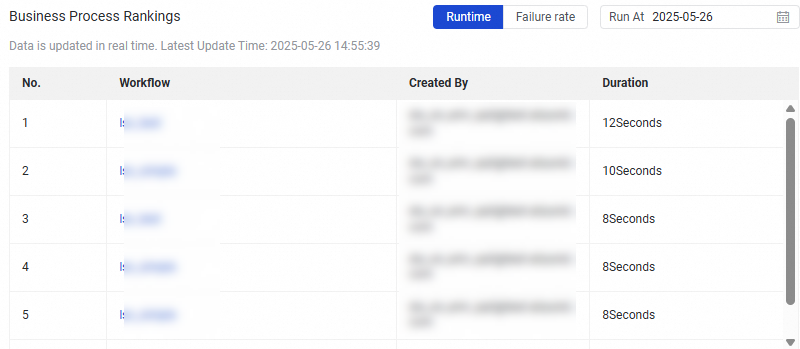
Workflow Ranking | This section displays the ranking of Top 30 workflows with the longest running durations and highest failure rates on a specific date.
|
|
View information in the Internal Task Distribution and Internal task leaderboard sections
Section | Description | Illustration |
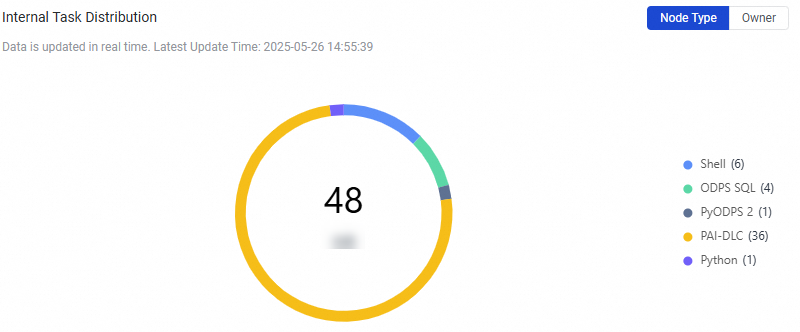
Internal Task Distribution | In this section, a donut chart is used to display the distribution of the number of nodes in Operation Center in real time. You can view the statistics from the Node Type or Owner dimension. |
|
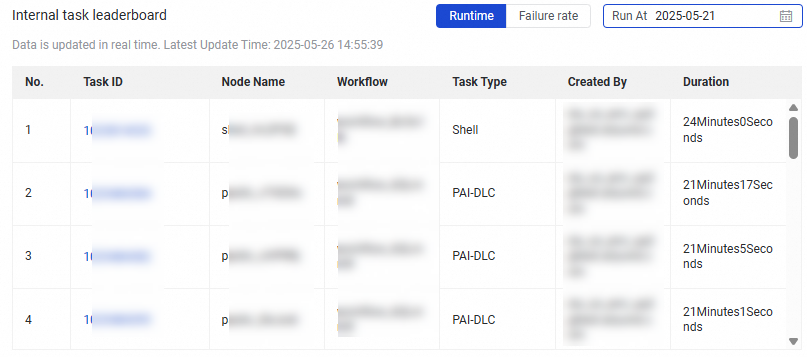
Internal task leaderboard | This section displays the ranking of Top 30 nodes with the longest running durations and highest failure rates in manually triggered workflows on a specific date.
|
|
View O&M information about data synchronization nodes in Data Integration
On the Data Integration tab, you can view the overview information about data synchronization nodes in Data Integration and the resource usage situations of resource groups for Data Integration on the previous day and current day.
View the resource usage situations of resource groups for Data Integration
The Status of Resource Group for Data Integration section displays the resource usage situations of resource groups for Data Integration used by all data synchronization nodes in the current workspace. The resource usage situations include the number of nodes that are running on and are waiting for resources in each resource group for Data Integration, and the resource usage and expiration time of each resource group for Data Integration. You can determine whether you need to scale in or out a resource group for Data Integration based on the number of nodes that are running on and waiting for resources in and the resource usage of the resource group. This can facilitate reasonable resource allocation.
For information about the operations that you can perform on an exclusive resource group for Data Integration, see Exclusive resource groups for Data Integration.
For information about the operations that you can perform on a serverless resource group, see the topics in the Use serverless resource groups directory.
The Data Integration tab of the O&M Dashboard page collects O&M statistics only on exclusive resource groups for Data Integration.
View the distribution of data synchronization nodes created in Data Integration by status
The Running Status Distribution section displays the distribution of data synchronization nodes by status in the current workspace in a donut chart. You can click a sector to go to the details page of the nodes in a specific state. On the details page, you can view details of the nodes and handle exceptions that occur on the nodes. You must take note of the nodes that are in the Abnormal and Running Failed states. The nodes in these states block the running of their descendant nodes.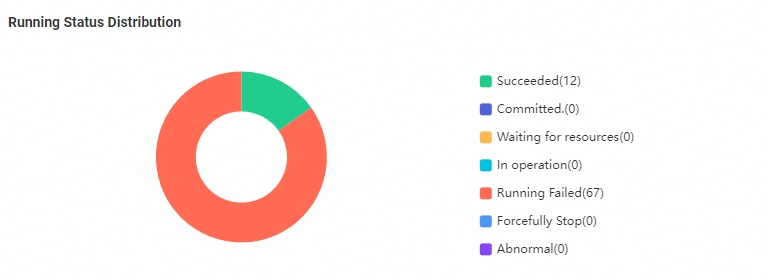
View the statistics on batch synchronization nodes
The following table lists the sections in which you can view the statistics on batch synchronization nodes.
Section | Description | Illustration |
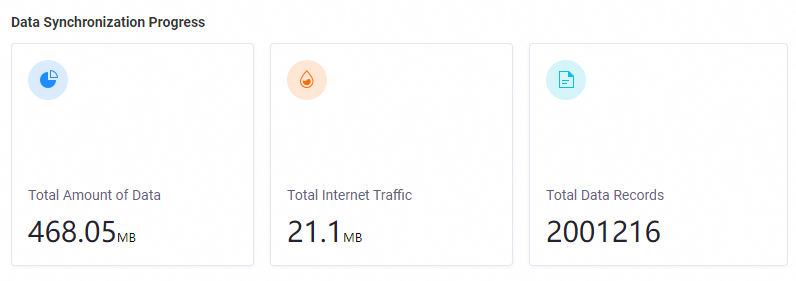
Data Synchronization Progress | This section displays information about the data that is involved in batch synchronization within a specified period of time. The metrics include Total Amount of Data, Total Internet Traffic, and Total Data Records. |
|
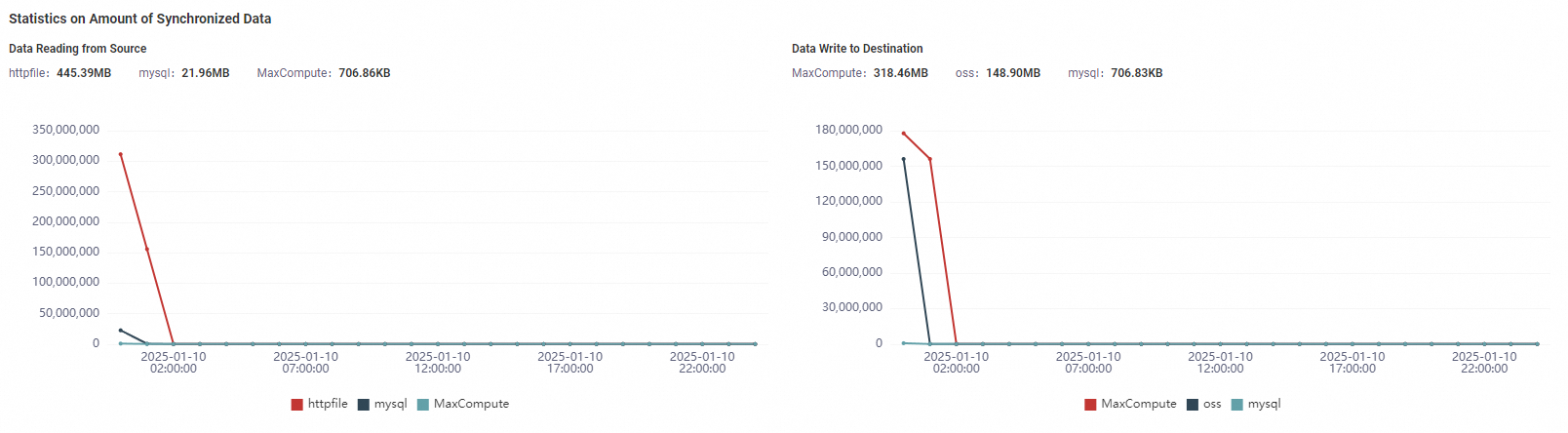
Statistics on Amount of Synchronized Data | This section displays the curves of the data that is read from or written to different data sources within a specified period of time. In this section, you can view the nodes of a specific type of compute engine that are run to synchronize a large amount of data. You can allocate an excess of resources for the nodes. |
|
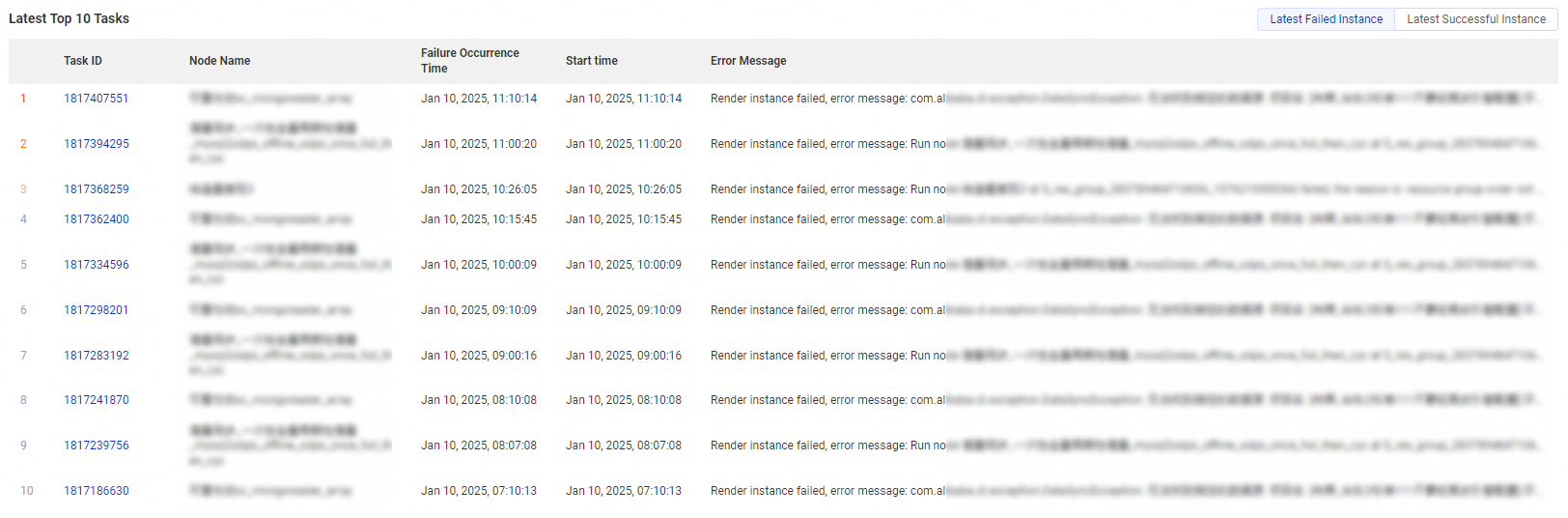
Latest Top 10 Tasks | This section displays the latest 10 instances that failed to run and the latest 10 instances that are successfully run. The statistics provide you with an overview of the latest instance status. You can quickly identify the cause of an instance failure and fix the error based on the error message. |
|
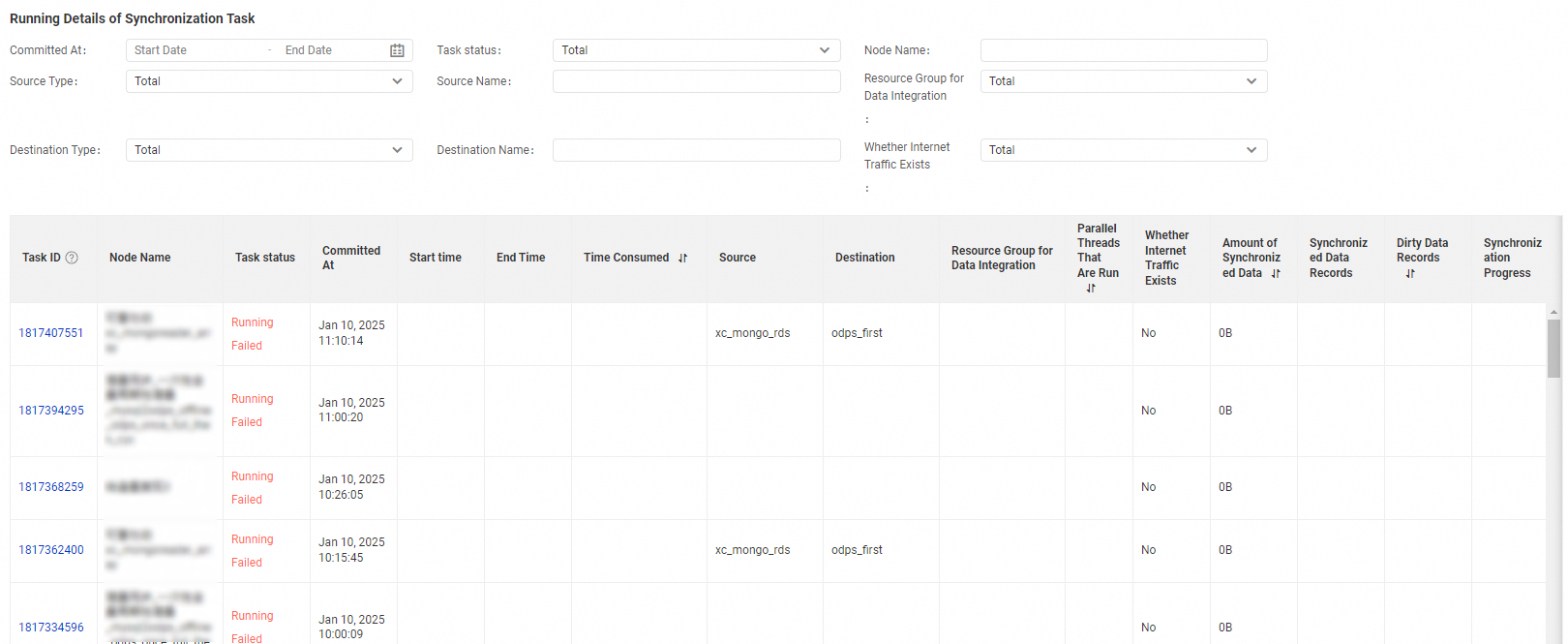
Running Details of Synchronization Task | This section allows you to specify filter conditions to search for nodes. The filter conditions include Committed At, Task Status, and Node Name. You can click the ID of a node to view the details of the node. |
|
View the statistics on real-time synchronization nodes
The following table lists the sections in which you can view the statistics on real-time synchronization nodes.
Section | Description | Illustration |
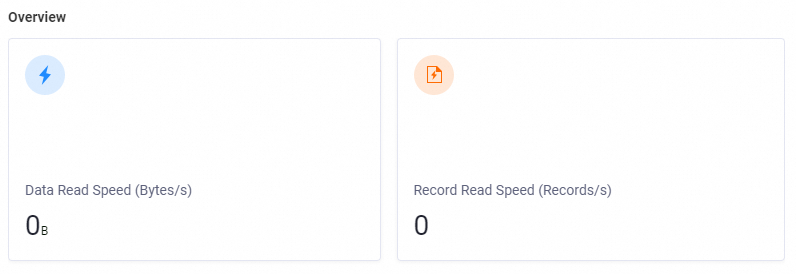
Overview | This section displays the total data transmission speed and total recording speed of all real-time synchronization nodes in the current workspace. |
|
Top 10 Tasks with Highest Latency | This section displays the top 10 nodes that have the highest latency. In this section, you can quickly identify nodes that have high latency and optimize the performance of the nodes at the earliest opportunity. |
|
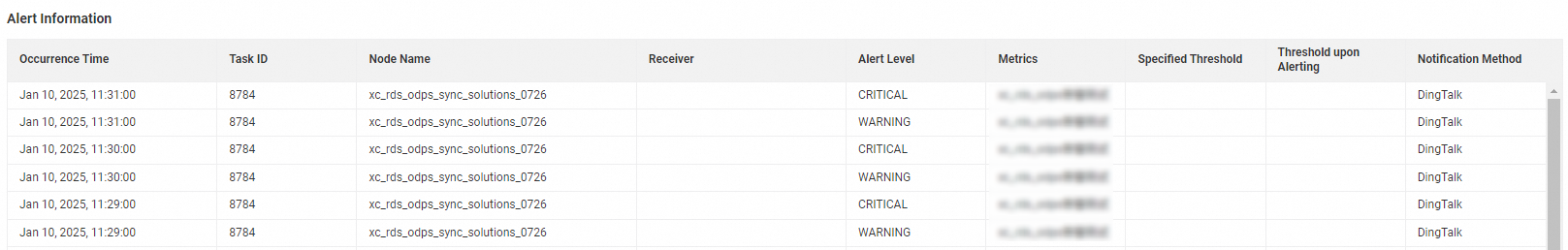
Alert Information | This section displays information about the latest alerts. This section allows you to quickly identify exceptions and handle the exceptions at the earliest opportunity. |
|
Failover Information | This section displays information about |
|