The Alarm feature allows you to configure custom alert rules to monitor the status and resource usage of nodes. This feature also allows you to configure intelligent baselines to ensure that the data you want to obtain is generated as expected in scenarios where dependencies between nodes are complex. In addition, you can configure custom O&M rules for resource groups based on your business requirements to implement automated O&M for node instances that are run on the resource groups.
Modules
The following table describes the modules that are provided by the Alarm feature.
Module | Description |
A baseline enables DataWorks to identify an exception that prevents a node in the baseline from being completed on schedule and send you an alert notification about the exception at the earliest opportunity. This ensures that the data you want to obtain is generated as expected in scenarios where dependencies between nodes in the baseline are complex. On the Smart Baseline page, you can perform the following operations:
| |
In the left-side navigation pane of the Operation Center page, choose . On the page that appears, you can manage global alert rules and configure custom alert rules based on your business requirements.
| |
In the left-side navigation pane of the Operation Center page, choose . On the page that appears, you can view alerts, including alerts that are generated based on custom alert rules, alerts that are generated based on global alert rules, and baseline alerts. | |
In the left-side navigation pane of the Operation Center page, choose . On the page that appears, you can configure a custom shift schedule. When you specify a notification method for an alert rule, you can select the shift schedule. This way, alert notifications can be sent to the on-duty engineer based on the shift schedule. Note You can configure both primary and secondary on-duty engineers in a shift schedule. By default, an alert notification is sent to the primary on-duty engineer. If the primary on-duty engineer does not handle the alert after the alert notification is sent twice, the subsequent alert notifications are sent to both the primary and secondary on-duty engineers. | |
You can create O&M rules for exclusive resource groups and associate the O&M rules with created alert rules based on your business requirements. If an associated alert rule is triggered, DataWorks performs automated O&M on the node instances that are run on the specified exclusive resource groups and that meet the specified filter conditions. Note You can associate O&M rules only with the alert rules configured for exclusive resource groups for scheduling. |
Node status monitoring
Monitored objects
You can configure custom alert rules and intelligent baselines to monitor resource usage and the status of auto triggered nodes, auto triggered node instances, and real-time computing nodes.
Status of auto triggered nodes
DataWorks generates auto triggered node instances that are scheduled to run on the next day for an auto triggered node every night. DataWorks provides built-in global alert rules to periodically monitor auto triggered nodes and ensure that instances are generated and scheduled for the auto triggered nodes as expected. If an exception occurs, DataWorks sends an alert notification. The built-in global alert rules are not workspace-level alert rules. These rules include alert rules for isolated nodes and alert rules for nodes that form a loop.
Rule type
Monitored object
Trigger condition
Description
Global alert rule
Isolated nodes: This type of node does not depend on other nodes.
An alert notification is automatically sent when an isolated node is generated. We recommend that you handle the alert at the earliest opportunity.
NoteIn DataWorks, except the root node in your workspace, each auto triggered node that you created must have ancestor nodes. If no ancestor nodes are configured for an auto triggered node, the auto triggered node cannot be scheduled. Isolated nodes cannot be automatically scheduled to run. If an isolated node has a large number of descendant nodes, serious consequences may occur.
DataWorks scans the status of auto triggered nodes at 09:00:00, 12:00:00, and 16:00:00 every day. If an isolated node or a node dependency loop is detected, DataWorks sends an alert notification by using the specified method. However, exceptions that are generated within the 10 minutes before a scan are not included in the current scanning cycle. These exceptions are included in the subsequent scanning cycle.
Global alert rules are built-in rules that are automatically created in DataWorks. If an alert is triggered based on a global alert rule, an alert notification is sent to a node owner by text message or email by default. You can change the alert contact for global alert rules on the Rule Management page.
You can disable global alert rules on the Rule Management page.
Nodes that form a loop: This type of node depends on their descendant nodes and forms a dependency loop with their descendant nodes.
An alert notification is automatically sent after a node dependency loop is formed. We recommend that you handle the alert at the earliest opportunity.
NoteThis type of node cannot be automatically scheduled to run.
Status of auto triggered node instances
In DataWorks, auto triggered node instances are generated when an auto triggered node is periodically scheduled. You can configure custom alert rules for auto triggered nodes to monitor the status of the instances of the auto triggered nodes. You can configure a custom alert rule for a specified object and configure an intelligent baseline for important nodes.
Rule type
Monitored object
Trigger condition
Nodes of the Node, Baseline, Workspace, or Workflow object type
An alert notification is sent if a node of a specified object type is in one of the following states: Completed, Uncompleted, Error, Uncompleted in Cycle, Overtime, and The error persists after the node automatically reruns.
An alert notification is sent if the object type of a node is Workspace and the node is in one of the following states and the preceding states: Instance Generated and Fluctuation of Instance Number.
Nodes in a baseline and the ancestor nodes that affect data generation of the nodes in a baseline
NoteYou can specify a priority for a baseline to ensure that nodes in the baseline are scheduled and data of the nodes is generated as expected.
If an auto triggered node is important and the dependencies between the auto triggered node and its ancestor nodes are complex, you can move the auto triggered node to a specific baseline.
Baseline alerts:
If DataWorks predicts that nodes in a baseline cannot finish running before the committed completion time, DataWorks sends you a baseline alert notification by using the specified notification method. For more information, see Core logic: baseline alert.
Event alerts:
When an error is reported for a node in a baseline, an error is reported for an ancestor node of the node in the baseline, or a node in the key path slows down, an event is generated and DataWorks sends you an event alert notification. For more information, see Manage events.
Status of real-time computing nodes
Rule type: custom alert rule
Monitored objects: real-time computing nodes
Trigger condition: An alert is reported if an error occurs on a real-time computing node.
Resource usage
Rule type: custom alert rule
Monitored objects: exclusive resource groups for scheduling and exclusive resource groups for Data Integration
Trigger conditions:
If the value of the Resource Group Usage parameter is greater than a specific percentage for a specific period of time, an alert is reported.
If the value of the Number of instances Waiting for Resources in Resource Group parameter is greater than a specific number for a specific period of time, an alert is reported.
Notification methods
After you configure alert rules, when DataWorks detects that an alert rule is triggered, DataWorks sends you an alert notification by using the notification method that you specified, such as email, text message, phone call, or DingTalk message. This way, you can identify and troubleshoot issues at the earliest opportunity.
Rule type | Notification method | Alerting frequency control |
Custom alert rule, global alert rule, and intelligent baseline |
| You can use the following parameters to control alerting frequency: Maximum Alerts, Minimum Alert Interval, and Quiet Hours. Note
|
Automated O&M on node instances that are run on exclusive resource groups for scheduling
The automated O&M feature enables DataWorks to perform O&M operations on node instances that are run on exclusive resource groups for scheduling. DataWorks performs O&M operations based on the O&M rules that you created and the alert rules that are associated with the O&M rules.
Trigger condition: Associated alert rules are triggered.
NoteThe resource usage of a resource group and the number of node instances that are waiting for resources in a resource group are monitored.
Automated O&M can be performed only on node instances that are run on exclusive resource groups for scheduling.
Node instances on which automated O&M can be performed: You can specify the following filter conditions to search for desired node instances: Instance Type, Scheduling Cycle, Priority, Status, and Workspace.
O&M operation: Terminate node instances that are running.
NoteA maximum of 2,000 node instances can be terminated at a time.
View alert information
You can view information about alerts that are generated for a specified node instance in the directed acyclic graph (DAG) of the node instance or on the Intelligent Diagnosis page.
View alert information in the DAG of a node instance
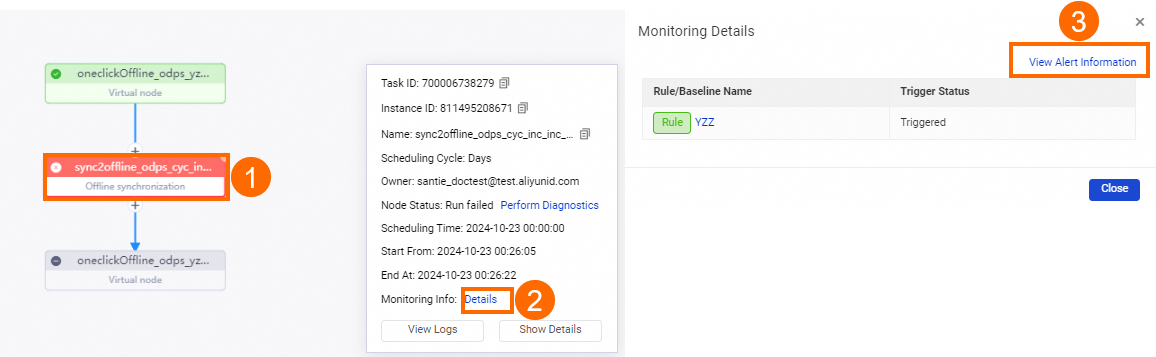
For a node instance for which alert rules are configured and alerts are generated within 24 hours from the current point in time, you can perform the following operations to view alert information: In the left-side navigation pane of the Operation Center page, choose . On the page that appears, find the node instance and open the DAG of the node instance. On the DAG page, click the red dot in the upper-right corner of the node instance. In the Monitoring details pane, view the rules or baselines to which the monitored node that generates the instance is added and view the status of each rule or baseline. The red dot is displayed in the area marked with 2 in the following figure. You can also click View alarm information in the upper-right corner of the Monitoring details pane to go to the Alert Management page and view alert details on this page. In addition, you can click the name of a rule in the Rule/Baseline Name column to go to the Rule Management page and view the configuration details of the rule.
NoteYou can select the Nodes that generated alarms in the past 24 hours check box in the area marked with 1 in the following figure to search for desired node instances.
View alert information on the Intelligent Diagnosis page
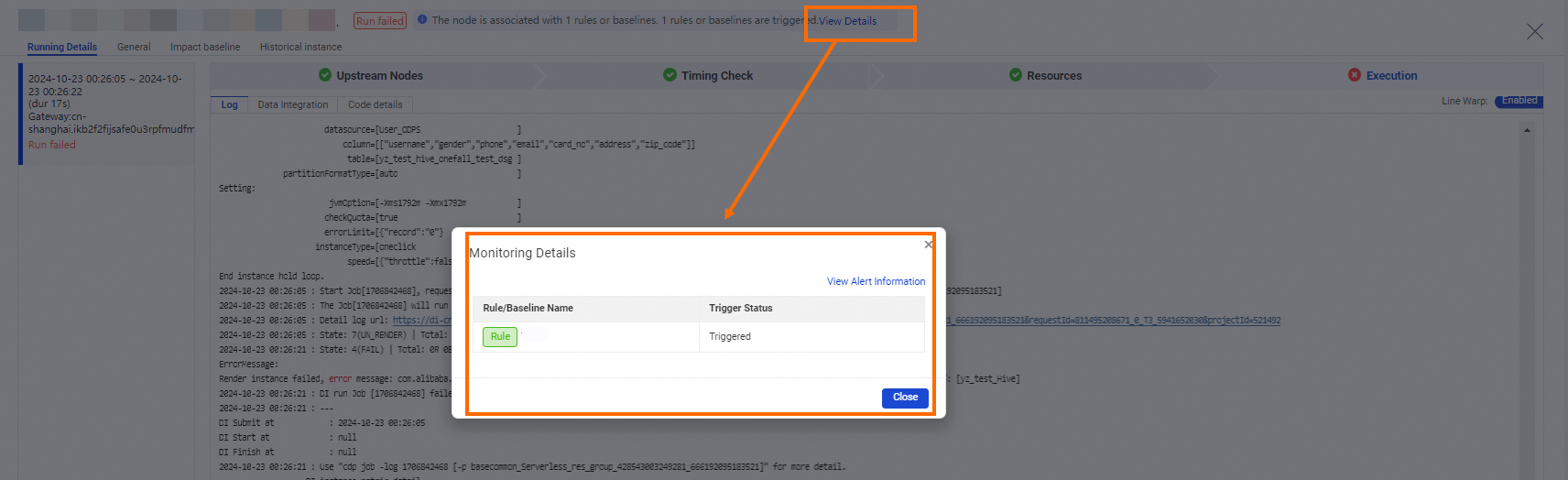
For a node for which alert rules are configured, you can perform the following operations to view alert information about an instance that is generated for the node: Go to the Intelligent Diagnosis page. Find the desired node instance and click the node instance. On the End-to-end Diagnostics tab of the page that appears, click View details next to the prompt message. In the Monitoring details pane, view the rules or baselines to which the monitored node that generates the instance is added and view the status of each rule or baseline. You can also click View alarm information in the upper-right corner of the Monitoring details pane to go to the Alert Management page and view alert details on this page. In addition, you can click the name of a rule in the Rule/Baseline Name column to go to the Rule Management page and view the configuration details of the rule.
View alert information on the Alert Management page
You can view all generated alerts on the Alert Management page and view the details of an alert on the Alarm details page, including the alert rule that triggers the alert, the trigger condition, and the alert cause. For more information, see View alert details.
