The intelligent baseline feature detects exceptions that prevent tasks on a baseline from completing on time and sends early warnings. This ensures that important data is generated within the expected time in scenarios with complex dependencies. This feature helps reduce configuration costs, prevent invalid alerts, and automatically monitor all important tasks.
Use cases
Manage task priorities.
When the number of tasks increases and resources are limited, resource preemption can occur. You can add important tasks to a baseline and set a high priority for the baseline to ensure that resources are allocated to these tasks first.
Calculate the estimated completion time of a task.
A task's execution is affected by resource availability and the status of its ancestor tasks. If you add a task to a baseline, DataWorks calculates its estimated daily or hourly completion time. This makes it easy to view the task's predicted completion time.
Ensure tasks finish before their committed time.
You can add a task to a baseline and set a committed time. If the system predicts that the task cannot finish before the committed time, or if an ancestor task fails or slows down, the system sends an alert. You can then use the alert information to resolve the issue promptly and ensure that the task completes on time.
Concepts
Baseline: After you add important tasks to a baseline and set a committed time, the system calculates the estimated completion time for the baseline tasks based on their execution status. If the system determines that a baseline task might not finish before the committed time, it triggers a baseline alert.
Committed time: The latest time by which a task must be successfully completed. For data applications, the task is guaranteed to be completed before this time. To reserve time for Operations and Maintenance (O&M) engineers to handle exceptions, you can set an Alert Margin for the baseline. The system then uses the formula
Committed time - Alert marginto calculate the alert time and determine if the task can be completed successfully before this time.Baseline task: A task that is added to a baseline.
Baseline instance: The system uses baseline instances to calculate the estimated completion time for each task run. A baseline instance can have one of the following statuses: Safe, Warning, or Breached.
Safe:
Estimated completion time < Alert time.Warning:
Alert time < Estimated completion time < Committed time.Breached:
Estimated completion time > Committed time.
Key path: The path with the longest execution time among all paths that affect a baseline task.
Event: An event is generated when a baseline task or its ancestor task fails, or when a task on the key path slows down. Events can affect the on-time completion of the baseline task.
Features
After you add important tasks to a baseline, DataWorks allocates resources to the baseline tasks based on the baseline's priority. It also determines the monitoring scope based on the upstream and downstream dependencies of the baseline tasks. A baseline alert or an event alert is triggered based on the execution status of tasks within this scope.

The monitoring scope is determined based on a baseline task K.
Ancestor nodes of the baseline task: All nodes that affect the output of task K are included in the monitoring scope:

Descendant nodes of the baseline task: These are not in the monitoring scope:

Key path: The longest path among all paths that affect task K:

Create a baseline:
Specify task K to be added to the baseline.
Set the baseline priority and alert policy parameters.
A baseline alert or an event alert is triggered based on the actual execution status of tasks within the monitoring scope.
As shown in the preceding figure, the main features of the intelligent baseline are as follows.
Create and manage baselines.
You can create and manage baselines on the Baseline Management page:
You can move tasks that require major event support to a baseline, set basic information such as the committed time, and configure the alert policy, including the alert method and recipients. The system then monitors and sends alerts for the tasks based on these settings.
You can also specify the priority of a baseline. The baseline priority determines the execution priority of its tasks. The higher the baseline priority, the higher the task priority. If schedule resources are limited, tasks with a higher priority are allocated resources first.
NoteThis priority is mapped to the priority of a MaxCompute computing task if the following two conditions are met:
The priority feature is enabled for the MaxCompute project.
The MaxCompute project uses subscription computing resources.
MaxCompute job priority = 9 - DataWorks baseline priority.
For more information about how to create and manage baselines, see Manage baselines.
Determine the monitoring scope.
DataWorks determines the monitoring scope based on the dependencies of tasks on a baseline. It monitors all tasks that might affect the data output of the baseline. For more information, see Core logic: Monitoring scope.
Trigger and send alerts
Baseline alerts.
DataWorks automatically triggers alerts based on the configured alert policy and the actual execution status of tasks. The system sends alert messages to the specified recipients in real time. If the system predicts that a task on the baseline cannot be completed before the committed time, it sends a baseline alert using the defined notification method. For more information, see Core logic: Baseline alerts.
Event alerts.
After the monitoring scope is determined, if a baseline task or its ancestor task fails, or if a task on the key path slows down, a corresponding event is generated and an event alert is sent. You can view the list of existing events on the Event Management page in DataWorks. For more information, see Event management.
Billing
Number of baseline instances: All enabled baselines generate baseline instances. DataWorks charges you based on the number of baseline instances generated by 23:59 on the current day. For more information, see Billing of intelligent baseline instances.
Number of alert text messages and phone calls: Baseline alerts incur fees for text messages and phone calls. For more information, see Billing of alert text messages and phone calls.
Limits
Only DataWorks Standard Edition and later versions support the intelligent baseline feature. If you are using an earlier version, you must upgrade to the Standard Edition or a later version to use this feature. For more information, see Features of different DataWorks editions.
Core logic: Monitoring scope
After a baseline is created and a task is added to it, the intelligent baseline feature does not monitor all upstream and downstream tasks of the baseline task. The monitoring scope for related upstream and downstream tasks is as follows:
Upstream tasks: Upstream tasks that affect the data output of a baseline task are included in the monitoring scope.
Downstream tasks: Downstream tasks are not included in the monitoring scope. This means that no alert is triggered if a downstream task of the baseline task or a downstream task on another branch of an ancestor task fails.

As shown in the preceding figure, assume that there are six task nodes in the DataWorks system. Tasks D and E are baseline tasks. Tasks A and B affect the data output of tasks D and E. Therefore, tasks A, B, D, and E are all included in the monitoring scope. Within this scope, if any task becomes abnormal, such as fails or slows down, the intelligent baseline feature automatically detects it. Tasks C and F are not monitored by the intelligent baseline.
Core logic: Baseline alerts
You can add important tasks to a baseline and set the Committed Time and Alert Margin:
DataWorks uses the formula
Committed time - Alert marginto calculate the Alert Time. It then combines the alert time with the historical average runtime of tasks in the monitoring scope. Using Baseline Instances, it calculates the latest completion time and latest start time for each task in the scope.During task execution, if the status of a task within the monitoring scope indicates that the baseline task might not be completed before the Alert Time, DataWorks triggers a baseline alert.
Core logic: Event alerts
After the monitoring scope is determined, if a task within the scope becomes abnormal, the intelligent monitoring system generates an event and triggers an alert based on its analysis. Task abnormalities include the following:
Failed: The task fails to run.
Slowed Down: The current runtime of the task is significantly longer than its average runtime over a previous period.
A task is considered to have slowed down and an event alert is triggered if its runtime exceeds 30 minutes and is 15 minutes longer than its historical average runtime.
If the same task first slows down and then fails, two events are generated.
You can go to the Event Management page to view the details of generated events.
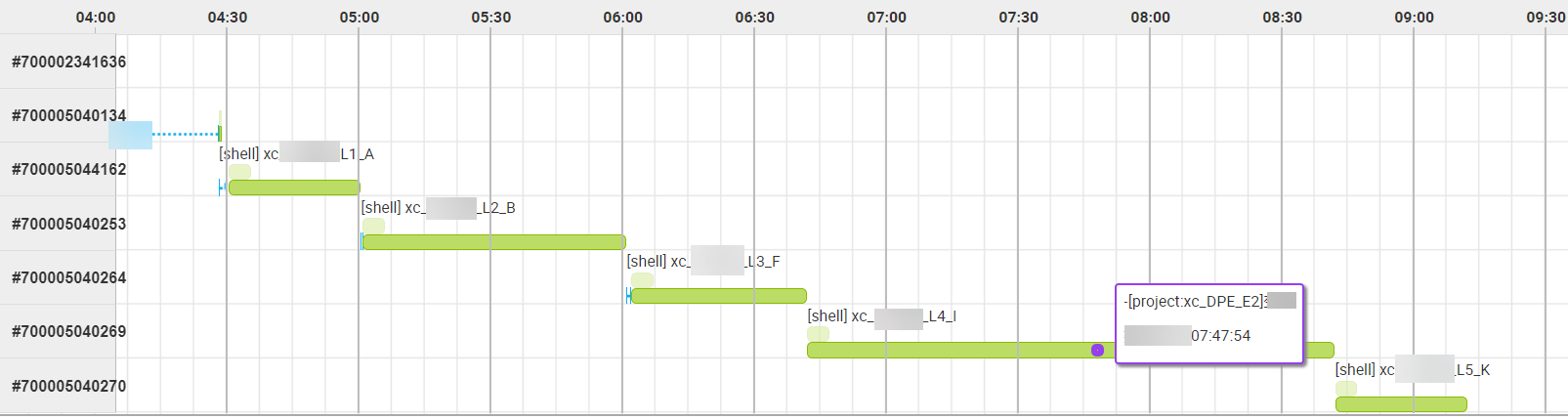
Core logic: Key path and key instances
The dependencies of tasks that must be guaranteed on a baseline can be complex. DataWorks provides a Gantt chart feature to help you quickly locate the key path and key instances that are blocking data output on the baseline. The key path of the baseline is the path with the longest runtime among the multiple paths that affect the output of a baseline task.

Example
Scenario: The current time is 6:40, and task F is still running.
Baseline warning:
YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss
Baseline XX warning, business time XX, margin: -10 min...
Event alert:
YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss
Event reminder, business time XX, task XX, status: Delayed...
A Gantt chart shows the key execution path of a target task. For the preceding example, the key path and exception catch time are shown as follows: