Spark is a versatile, high-performance, and user-friendly engine for large-scale data analytics. You can use Spark to perform complex in-memory analysis and build large, low-latency data analytics applications. DataWorks provides EMR Spark nodes to help you develop and periodically schedule Spark tasks. This topic describes how to create an EMR Spark node and provides a detailed example.
Prerequisites
Before developing nodes, if you need to customize the component environment, you can create a custom image based on the official image
dataworks_emr_base_task_podand use the custom image in DataStudio.For example, you can replace Spark JAR packages or include specific
libraries,files, orJAR packageswhen creating the custom image.An EMR cluster is registered with DataWorks. For more information, see DataStudio (legacy version): Bind an EMR computing resource.
(Optional) If you use a Resource Access Management (RAM) user to develop tasks, you must add the user to the corresponding workspace and grant them the Development or Workspace Manager role. The Workspace Administrator role includes extensive permissions and must be granted with caution. For more information, see Add members to a workspace.
A resource group is purchased and configured. The configuration includes binding the workspace and configuring the network. For more information, see Use a Serverless resource group.
A business flow must be created. Because development operations for different engines in DataStudio are performed based on business flows, you must create a business flow before you create a node. For more information, see Create a business flow.
If your tasks require a specific development environment, you can use the custom image feature of DataWorks to build a component image for task execution. For more information, see Custom images.
Limitations
This type of node can be run only on a serverless resource group or an exclusive resource group for scheduling. We recommend that you use a serverless resource group. If you need to use an image in DataStudio, use a serverless computing resource group.
For DataLake or custom clusters, you must configure EMR-HOOK on the cluster to manage metadata in DataWorks. If EMR-HOOK is not configured, you cannot view metadata in real time, generate audit logs, view data lineage, or perform EMR-related data administration tasks in DataWorks. For more information about how to configure EMR-HOOK, see Configure EMR-HOOK for Spark SQL.
EMR on ACK Spark clusters do not support viewing data lineage. EMR Serverless Spark clusters support viewing data lineage.
EMR on ACK Spark clusters and EMR Serverless Spark clusters support only referencing OSS resources using OSS REF and uploading resources to OSS. They do not support uploading resources to HDFS.
DataLake clusters and custom clusters support referencing OSS resources using OSS REF, uploading resources to OSS, and uploading resources to HDFS.
Notes
If you enabled Ranger access control for Spark in the EMR cluster that is bound to the current workspace:
This feature is available by default when you run Spark tasks that use the default image.
To run Spark tasks that use a custom image, you must submit a ticket to upgrade the image to support this feature.
Preparations: Develop a Spark task and get the JAR package
Before you schedule an EMR Spark task in DataWorks, you must develop the Spark task code in EMR and compile it to generate a JAR package. For more information about how to develop an EMR Spark task, see Spark overview.
You must upload the task JAR package to DataWorks to periodically schedule the EMR Spark task.
Step 1: Create an EMR Spark node
Go to the DataStudio page.
Log on to the DataWorks console. In the top navigation bar, select the desired region. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select the desired workspace from the drop-down list and click Go to Data Development.
Create an EMR Spark node.
Right-click the target business flow and choose .
NoteYou can also hover over Create and choose .
In the Create Node dialog box, specify the Name, Engine Instance, Node Type, and Path, and then click Confirm.
NoteThe node name can contain uppercase letters, lowercase letters, Chinese characters, digits, underscores (_), and periods (.).
Step 2: Develop the Spark task
On the EMR Spark node editor page, double-click the created node to go to the task development page. Choose one of the following operations based on your scenario:
(Recommended) Upload a resource from your local machine to DataStudio and then reference the resource. For more information, see Scenario 1: Upload and then reference an EMR JAR resource.
Reference an OSS resource using OSS REF. For more information, see Scenario 2: Directly reference an OSS resource.
Scenario 1: Upload and then reference an EMR JAR resource
DataWorks lets you upload a resource from your local machine to DataStudio and then reference the resource. After you compile the EMR Spark task, obtain the compiled JAR package. We recommend that you store the JAR package resource based on its size.
You can upload the JAR package resource, create it as a DataWorks EMR resource, and then submit it. Alternatively, you can store it directly in the HDFS of EMR. EMR on ACK Spark clusters and EMR Serverless Spark clusters do not support uploading resources to HDFS.
If the JAR package is smaller than 500 MB
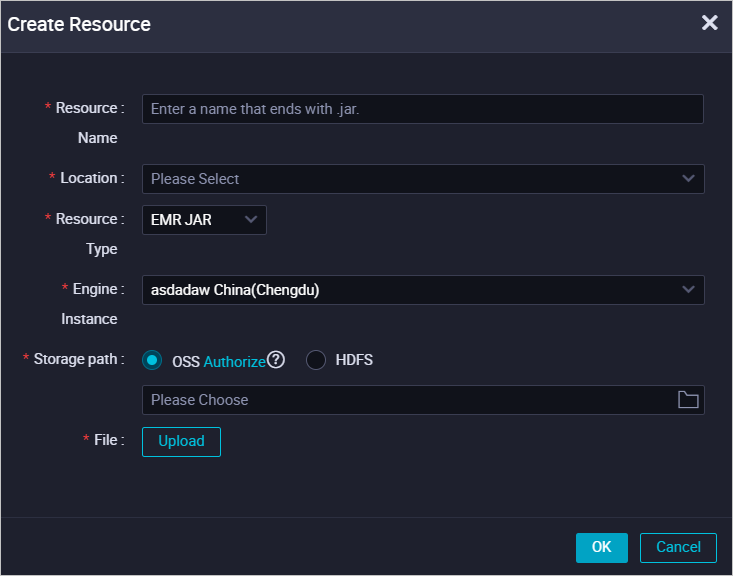
Create an EMR JAR resource.
If the JAR package is smaller than 500 MB, you can upload it from your local machine as a DataWorks EMR JAR resource. This method makes it easier to manage the resource in the DataWorks console. After you create the resource, you must submit it. For more information, see Create and use EMR resources.
 Note
NoteWhen you create an EMR resource for the first time, if you want to store the uploaded JAR package in OSS, you must first perform authorization as prompted on the page.
Reference the EMR JAR resource.
Double-click the EMR Spark node to open its code editor.
In the node, find the EMR JAR resource that you uploaded. Right-click the resource and select Insert Resource Path.
After you select the resource, a resource reference code is automatically added to the editor page of the current EMR Spark node. The following code is an example.
##@resource_reference{"spark-examples_2.12-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-shaded.jar"} spark-examples_2.12-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-shaded.jarIf the preceding reference code is automatically added, the resource is referenced. In the code, spark-examples_2.12-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT-shaded.jar is the name of the EMR JAR resource that you uploaded.
Modify the code of the EMR Spark node to add the spark-submit command. The following code is an example.
NoteThe EMR Spark node editor does not support comments. Make sure that you modify the task code as shown in the following example. Do not add comments. Otherwise, an error occurs when you run the node.
##@resource_reference{"spark-examples_2.11-2.4.0.jar"} spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi --master yarn spark-examples_2.11-2.4.0.jar 100Where:
org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi: The main class of the task in the compiled JAR package.
spark-examples_2.11-2.4.0.jar: The name of the EMR JAR resource that you uploaded.
For the other parameters, you can use the values from the preceding example or execute the following command to view the help documentation for
spark-submitand modify thespark-submitcommand as needed.NoteTo use simplified parameters for the
spark-submitcommand in the Spark node, you must add them to the code. For example,--executor-memory 2G.Spark nodes support submitting jobs only in the cluster mode of YARN.
For tasks submitted using
spark-submit, we recommend that you set the deploy-mode to cluster instead of client.
spark-submit --help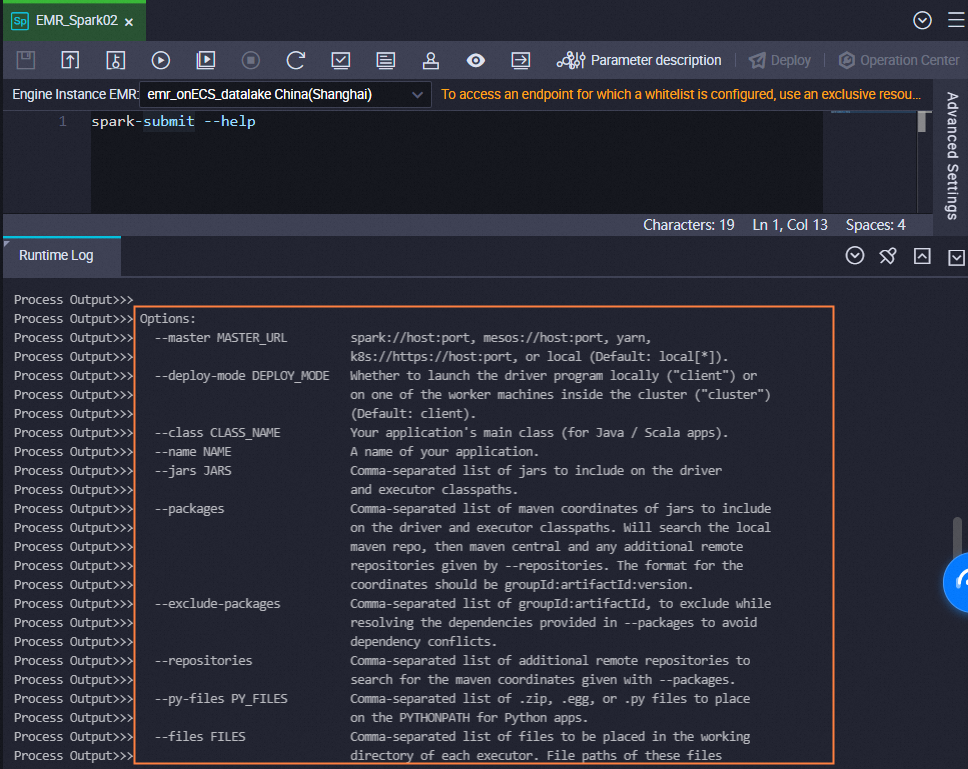
If the JAR package is 500 MB or larger
Create an EMR JAR resource.
If the JAR package is 500 MB or larger, you cannot upload it as a DataWorks resource from your local machine. We recommend that you store the JAR package in the HDFS of EMR and record its storage path. You must use this path to reference the package when you schedule the Spark task in DataWorks.
Reference the EMR JAR resource.
If the JAR package is stored in HDFS, you can reference it in the EMR Spark node by specifying its path in the code.
Double-click the EMR Spark node to open its code editor.
Write the spark-submit command. The following code is an example.
spark-submit --master yarn --deploy-mode cluster --name SparkPi --driver-memory 4G --driver-cores 1 --num-executors 5 --executor-memory 4G --executor-cores 1 --class org.apache.spark.examples.JavaSparkPi hdfs:///tmp/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.4.8.jar 100Where:
hdfs:///tmp/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.4.8.jar: The actual path of the JAR package in HDFS.
org.apache.spark.examples.JavaSparkPi: The main class of the task in the compiled JAR package.
The other parameters are for the actual EMR cluster and must be configured as needed. You can also run the following command to view the help information for spark-submit and modify the command as needed.
ImportantTo use simplified parameters for the Spark-submit command in the Spark node, you must add them to the code. For example,
--executor-memory 2G.Spark nodes support submitting jobs only in the cluster mode of YARN.
For tasks submitted using spark-submit, we recommend that you set the deploy-mode to cluster instead of client.
spark-submit --help
Scenario 2: Directly reference an OSS resource
(Optional) Configure advanced parameters
You can configure Spark-specific property parameters in the Advanced Settings of the node. For more information about Spark property parameters, see Spark Configuration. The available advanced parameters vary based on the EMR cluster type, as shown in the following tables.
DataLake cluster/Custom cluster: EMR on ECS
Advanced parameter | Configuration description |
queue | The scheduling queue for submitting jobs. The default queue is `default`. If you configured a workspace-level YARN Resource Queue when you registered the EMR cluster with the DataWorks workspace:
For more information about EMR YARN, see Basic queue configuration. For more information about queue configuration during EMR cluster registration, see Set a global YARN resource queue. |
priority | The priority. The default value is 1. |
FLOW_SKIP_SQL_ANALYZE | The execution mode for SQL statements. Valid values:
Note This parameter can be used only for testing and running flows in the development environment. |
Other |
|
EMR Serverless Spark cluster
For more information about parameter settings, see Set parameters for submitting a Spark task.
Advanced parameter | Configuration description |
queue | The scheduling queue for submitting jobs. The default queue is `dev_queue`. |
priority | The priority. The default value is 1. |
FLOW_SKIP_SQL_ANALYZE | The execution mode for SQL statements. Valid values:
Note This parameter can be used only for testing and running flows in the development environment. |
SERVERLESS_RELEASE_VERSION | The Spark engine version. By default, the Default Engine Version configured for the cluster in Cluster Management of the SettingCenter is used. To set different engine versions for different tasks, you can set them here. |
SERVERLESS_QUEUE_NAME | Specifies a resource queue. By default, the Default Resource Queue configured for the cluster in Cluster Management of the SettingCenter is used. If you have resource isolation and management requirements, you can add a queue. For more information, see Manage resource queues. |
Other |
|
Spark cluster: EMR ON ACK
Advanced parameter | Configuration description |
queue | Not supported. |
priority | Not supported. |
FLOW_SKIP_SQL_ANALYZE | The execution mode for SQL statements. Valid values:
Note This parameter can be used only for testing and running flows in the development environment. |
Other |
|
Hadoop cluster: EMR on ECS
Advanced parameter | Configuration description |
queue | The scheduling queue for submitting jobs. The default queue is `default`. If you configured a workspace-level YARN Resource Queue when you registered the EMR cluster with the DataWorks workspace:
For more information about EMR YARN, see Basic queue configuration. For more information about queue configuration during EMR cluster registration, see Set a global YARN resource queue. |
priority | The priority. The default value is 1. |
FLOW_SKIP_SQL_ANALYZE | The execution mode for SQL statements. Valid values:
Note This parameter can be used only for testing and running flows in the development environment. |
USE_GATEWAY | Specifies whether to submit the job through a Gateway cluster. Valid values:
Note If the cluster where this node resides is not associated with a Gateway cluster, the EMR job fails to be submitted if you set this parameter to |
Other |
|
Run the SQL task
In the toolbar, click the
 icon. In the Parameters dialog box, select the scheduling resource group that you created and click Run.Note
icon. In the Parameters dialog box, select the scheduling resource group that you created and click Run.NoteTo access computing resources in a public network or a VPC, you must use a scheduling resource group that has passed the network connectivity test with the computing resources. For more information, see Network connectivity solutions.
To change the resource group for a task, click the Run With Parameters
 icon and select the target resource group.
icon and select the target resource group.When you use an EMR Spark node to query data, a maximum of 10,000 data records can be returned, and the total data size cannot exceed 10 MB.
Click the
 icon to save the SQL statement.
icon to save the SQL statement.(Optional) Perform smoke testing.
If you want to perform smoke testing in the development environment, you can do so when you submit the node or after the node is submitted. For more information, see Perform smoke testing.
Step 3: Configure node scheduling
If you want the system to periodically run a task on the node, you can click Properties in the right-side navigation pane on the configuration tab of the node to configure task scheduling properties based on your business requirements. For more information, see Overview.
You must configure the Rerun and Parent Nodes parameters on the Properties tab before you commit the task.
If you need to customize the component environment, you can create a custom image based on the official image
dataworks_emr_base_task_podand use the custom image in DataStudio.For example, you can replace Spark JAR packages or include specific
libraries,files, orJAR packageswhen creating the custom image.
Step 4: Publish the node task
After a task on a node is configured, you must commit and deploy the task. After you commit and deploy the task, the system runs the task on a regular basis based on scheduling configurations.
Click the
 icon in the top toolbar to save the task.
icon in the top toolbar to save the task. Click the
 icon in the top toolbar to commit the task.
icon in the top toolbar to commit the task. In the Submit dialog box, configure the Change description parameter. Then, determine whether to review task code after you commit the task based on your business requirements.
NoteYou must configure the Rerun and Parent Nodes parameters on the Properties tab before you commit the task.
You can use the code review feature to ensure the code quality of tasks and prevent task execution errors caused by invalid task code. If you enable the code review feature, the task code that is committed can be deployed only after the task code passes the code review. For more information, see Code review.
If you use a workspace in standard mode, you must deploy the task in the production environment after you commit the task. To deploy a task on a node, click Deploy in the upper-right corner of the configuration tab of the node. For more information, see Deploy nodes.
More operations
After you commit and deploy the task, the task is periodically run based on the scheduling configurations. You can click Operation Center in the upper-right corner of the configuration tab of the corresponding node to go to Operation Center and view the scheduling status of the task. For more information, see View and manage auto triggered tasks.
FAQ
Q: Why does a connection timeout occur when I run a node?
A: Ensure network connectivity between the resource group and the cluster. Go to the computing resource list page to initialize the resource. In the dialog box that appears, click Re-initialize and verify that the initialization is successful.


 icon. Select the Serverless resource group that you created to run the EMR Spark node. After the task is complete, record the
icon. Select the Serverless resource group that you created to run the EMR Spark node. After the task is complete, record the