This topic describes how to get started with AnalyticDB for MySQL Data Warehouse Edition. AnalyticDB for MySQL is an online analytical processing (OLAP) warehouse service that can process petabytes of highly concurrent data in real time. This topic walks you through the procedure of using an AnalyticDB for MySQL Data Warehouse Edition cluster.
Data Warehouse Edition is unavailable for purchase. You can purchase Enterprise Edition or Basic Edition clusters. If you have purchased Data Warehouse Edition clusters, you can refer to this topic to use the Data Warehouse Edition clusters.
Usage process
The first time you use AnalyticDB for MySQL Data Warehouse Edition, we recommend that you read the following topics:
Product introduction: describes the terms, benefits, and scenarios of AnalyticDB for MySQL.
Pricing: describes the prices and billing methods of AnalyticDB for MySQL.
Getting started (this topic): describes how to use an AnalyticDB for MySQL Data Warehouse Edition cluster.
The following figure shows the process of using AnalyticDB for MySQL Data Warehouse Edition:

Step 1: Create a database account
AnalyticDB for MySQL supports two types of database accounts: privileged accounts and standard accounts. For information about the differences between privileged accounts and standard accounts, see the "Account types" section of the Create a database account topic.
Create a privileged account
Log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console. In the upper-left corner of the console, select a region. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters. Find the cluster that you want to manage and click the cluster ID.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Accounts.
On the Accounts tab, click Create Privileged Account.
In the Create Account panel, configure the parameters that are described in the following table.
Parameter
Description
Database Account
The name of the privileged account. Enter a name that meets the on-screen requirements.
Account Type
The account type. For a Data Warehouse Edition cluster, this parameter is automatically set to Privileged Account.
New Password
The password of the privileged account. Enter a password that meets the on-screen requirements.
Confirm Password
Enter the password of the privileged account again.
Description
Optional. The description that is used to identify the account for future management.
Click OK.
Create and grant permissions to a standard account
The standard accounts created by executing SQL statements are not displayed in the console.
For information about how to create a database account, see CREATE USER.
For information about how to grant permissions to a database account, see GRANT.
For information about how to revoke permissions from a database account, see REVOKE.
For information about how to change the name of a database account, see RENAME USER.
For information about how to delete a database account, see DROP USER.
Step 2: Configure an IP address whitelist
The default IP address whitelist of an AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster contains only the default IP address 127.0.0.1, which indicates that no devices are allowed to access the cluster. You can configure an IP address whitelist to allow other devices to access the cluster. For example, you can specify 10.10.10.0/24 to allow all IP addresses in 10.10.10.x to access the cluster. If you want to add multiple IP addresses or CIDR blocks, separate multiple entries with commas (,). Do not add spaces before or after the commas. Example: 192.168.0.1,172.16.213.9.
WarningThe IP address 0.0.0.0 is not allowed in a whitelist.
If your public IP addresses change frequently and you want to allow all public IP addresses to access an AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster, contact technical support.
You can configure an IP address whitelist to enable fine-grained access control for your AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster. We recommend that you update the whitelist on a regular basis.
The whitelist configuration does not affect the running of your AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster. The modification to an IP address whitelist takes effect in 1 minute.
Procedure
Log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console. In the upper-left corner of the console, select a region. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters. Find the cluster that you want to manage and click the cluster ID.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Security.
On the Whitelist Settings tab, click Modify to the right of the default whitelist.
NoteYou can also click Create Whitelist to create an IP address whitelist.
In the Edit Whitelist panel, remove the default IP address 127.0.0.1 and enter the IP addresses or CIDR blocks that you want to allow. Then, click OK.
NoteTo add the egress IP address of the client to the IP address whitelist, query the IP address first. For more information, see Connections.
Step 3: Connect to an AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster
You can connect to an AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster by using Data Management (DMS), a business intelligence (BI) visualization tool, the MySQL command-line tool, or a MySQL client such as Navicat for MySQL, DBeaver, DbVisualizer, or SQL Workbench/J.AnalyticDB for MySQL You can also enter information such as the endpoint, port, and database account of an AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster in your application to connect to the cluster.
Use DMS to connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL
Log on to the AnalyticDB for MySQL console. In the upper-left corner of the console, select a region. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters. Find the cluster that you want to manage and click the cluster ID.
In the upper-right corner of the Cluster Information page, click Log On to Database.
In the dialog box that appears, configure the parameters that are described in the following table.
Parameter
Description
Database Type
The database type of the cluster. By default, AnalyticDB MySQL 3.0 is displayed.
Instance Region
The region of the cluster. By default, the region where the cluster resides is displayed.
Instance ID
The cluster ID. By default, the ID of the current cluster is displayed.
Database Account
The name of the database account used to connect to the cluster.
Database Password
The password of the database account used to log on to the cluster.
NoteYou can select Remember Password This way, the next time you connect to the current AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster, you do not need to enter the name and password of the database account.
NoteThe first time you connect to an AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster by using DMS, the data in the cluster is managed in Flexible Management mode. You can modify the control mode by editing the cluster. For more information, see Modify database instances and Control modes.
After you configure the parameters, you can click Test Connection in the lower-left corner of the dialog box. If the connection fails, follow the instructions to check the information you entered, such as the Database Account or Database Password parameter.
The system automatically adds the IP addresses or CIDR blocks of the DMS server to an IP address whitelist of the cluster. If the IP addresses or CIDR blocks fail to be added, you must manually add the IP addresses or CIDR blocks. For more information, see the "Step 2: Configure an IP address whitelist" section of this topic and Add DMS IP addresses and CIDR blocks to security settings.
Click Login.
Use code to connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL during application development
Use the MySQL command-line tool to connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL
Use the MySQL command-line client to connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL
Use a client to connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL
Use a data visualization tool to connect to AnalyticDB for MySQL
Step 4: Create a database
You can create up to 2,048 databases for each AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
Select the INFORMATION_SCHEMA system database and enter CREATE DATABASE on the SQL Console tab.
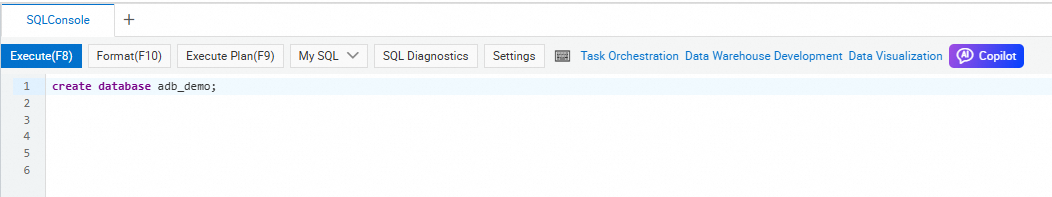
Syntax:
CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] $db_name.Parameter description: The
db_nameparameter specifies the name of the database that you want to create. The name can be up to 64 characters in length and can contain letters, digits, and underscores (_). The name must start with a lowercase letter and cannot contain consecutive underscores (_).NoteDo not use analyticdb as the database name. The name analyticdb is reserved for built-in databases.
Examples:
create database adb_demo;create database if not exists adb_demo2;
In the upper-left corner of the SQLConsole tab, click Execute. The database is created.
Step 5: Import and query data
Prerequisites
A directory is created in an Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket by performing the following operations to store data imported from an AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
Activate OSS. For more information, see Activate OSS.
Create an OSS bucket. For more information, see Create buckets.
ImportantMake sure that the OSS bucket resides in the same region as the AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster.
Create a directory. For more information, see the "Create a directory".section of the Manage directories topic.
Upload an object. For more information, see Upload objects.
In this example, the
oss_import_test_data.txtobject is uploaded to the<bucket-name>.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/adb/directory in OSS. The row delimiter is a line feed, and the column delimiter is a semicolon (;). The following code shows part of the data contained in this object:uid;other 12;hello_world_1 27;hello_world_2 28;hello_world_3 33;hello_world_4 37;hello_world_5 40;hello_world_6 ...
An AnalyticDB for MySQL cluster is created. An IP address whitelist is configured for the cluster. A database account and a database are created for the cluster. For more information, see Process of getting started with Data Warehouse Edition.
Procedure
Execute the CREATE TABLE statement to create an external table in the
adb_demodatabase. For information about how to create an OSS external table for an object that is in the CSV, Parquet, or TEXT format, see the "Syntax for creating an OSS external table" section of this topic.Query OSS data.
You can query the data of external tables in the same manner as you query the data of internal tables of AnalyticDB for MySQL . Example:
select uid, other from oss_import_test_external_table where uid < 100 limit 10;If an object is in the CSV or TEXT format and contains a large amount of data, we recommend that you import the object to AnalyticDB for MySQL before you query the data. Otherwise, the query performance may be compromised.
If an object is in the Parquet format, you can determine whether to directly query the data or import the object to AnalyticDB for MySQL before you query the data.
Execute the CREATE TABLE statement to create a destination table named
adb_oss_import_testin theadb_demodatabase to store the data imported from OSS.CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS adb_oss_import_test ( uid string, other string ) DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(uid);Execute an INSERT statement to import data from the OSS external table to AnalyticDB for MySQL.
ImportantBy default, the
INSERT INTOandINSERT OVERWRITE SELECTstatements import data synchronously. If hundreds of gigabytes of data is imported, the client must maintain a connection with the AnalyticDB for MySQL server for an extended period of time. During this process, the import may fail due to a network disconnection. Therefore, if you want to import a large amount of data, we recommend that you execute theSUBMIT JOB INSERT OVERWRITE SELECTstatement to import data asynchronously.Method 1: Execute the
INSERT INTOstatement to import data. If the primary key has duplicate values, data is not repeatedly inserted and the INSERT INTO statement is equivalent to theINSERT IGNORE INTOstatement. For more information, see INSERT INTO.INSERT INTO adb_oss_import_test SELECT * FROM oss_import_test_external_table;Method 2: Execute the INSERT OVERWRITE statement to import data. If the primary key has duplicate values, the original value is overwritten by the new value.
INSERT OVERWRITE adb_oss_import_test SELECT * FROM oss_import_test_external_table;Method 3: Execute the
INSERT OVERWRITEstatement to import data asynchronously. In most cases, theSUBMIT JOBstatement is used to submit an asynchronous job. You can add a hint (/*+ direct_batch_load=true*/) before the data import statement to accelerate the job. For more information, see the "Asynchronous writing" section of the INSERT OVERWRITE SELECT topic.SUBMIT JOB INSERT OVERWRITE adb_oss_import_test SELECT * FROM oss_import_test_external_table;Sample result:
+---------------------------------------+ | job_id | +---------------------------------------+ | 2020112122202917203100908203303****** |For information about how to submit asynchronous jobs, see Asynchronously submit an import job.
Execute the following statement to query the data of the
adb_oss_import_testtable:SELECT * FROM adb_oss_import_test;
Syntax for creating an OSS external table
Non-partitioned OSS external tables
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name
(column_name column_type[, …])
ENGINE='OSS'
TABLE_PROPERTIES='{
"endpoint":"endpoint",
"url":"OSS_LOCATION",
"accessid":"accesskey_id",
"accesskey":"accesskey_secret",
"format":"text|orc|parquet",
"delimiter":";",
"skip_header_line_count":1,
"charset":"utf-8"
}';Table format | Parameter | Required | Description |
CSV, Parquet, or ORC | ENGINE='OSS' | Yes | The table engine. Set the value to OSS. |
endpoint | The endpoint of the OSS bucket. AnalyticDB for MySQL can access OSS only by using a virtual private cloud (VPC). Note You can log on to the OSS console, find the bucket, and then obtain the endpoint on the Overview page. | ||
url | The path of the OSS object or directory. Valid values:
| ||
accessid | The AccessKey ID of the Alibaba Cloud account or the Resource Access Management (RAM) user that has permissions on OSS. For information about how to obtain an AccessKey ID, see Accounts and permissions. | ||
accesskey | The AccessKey secret of the Alibaba Cloud account or the RAM user that has permissions on OSS. For information about how to obtain an AccessKey secret, see Accounts and permissions. | ||
CSV | delimiter | The column delimiter of the CSV object. | |
Parquet or ORC | format | The format of the OSS object.
Note
| |
CSV | null_value | No | The Important This parameter is supported only for AnalyticDB for MySQL clusters of V3.1.4.2 or later. |
ossnull | The rule for defining the
Note The preceding examples are provided on the premise of | ||
skip_header_line_count | The number of header rows to skip when you import data. The first row of a CSV object is the table header. If you set this parameter to 1, the first row of the object is skipped when you import data. The default value of this parameter is 0, which specifies that no rows are skipped. | ||
oss_ignore_quote_and_escape | Specifies whether to ignore quotation marks (") and escape characters. The default value of this parameter is false, which specifies that quotation marks (") and escape characters are not ignored. Important This parameter is supported only for AnalyticDB for MySQL clusters of V3.1.4.2 or later. | ||
charset | The character set that is used by the OSS external table. Valid values:
Important This parameter is supported only for AnalyticDB for MySQL clusters of V3.1.10.4 or later. |
The column names used in the statement to create an external table must be the same as those in the Parquet or ORC file. Column names are case-insensitive. The sequence of the columns in the statement must be the same as that in the Parquet or ORC file.
When you create an external table, you can choose only specific columns in a Parquet or ORC file as the columns of the external table. Columns that are not selected in the Parquet or ORC file are not imported.
If the statement used to create an external table contains a column that is not in the Parquet or ORC file, NULL is returned for this column.
Data type mappings between Parquet, ORC, and AnalyticDB for MySQL
Data type mappings between Parquet and AnalyticDB for MySQL
Basic type in Parquet | Logical type in Parquet | Data type in AnalyticDB for MySQL |
BOOLEAN | N/A | BOOLEAN |
INT32 | INT_8 | TINYINT |
INT32 | INT_16 | SMALLINT |
INT32 | N/A | INT or INTEGER |
INT64 | N/A | BIGINT |
FLOAT | N/A | FLOAT |
DOUBLE | N/A | DOUBLE |
| DECIMAL | DECIMAL |
BINARY | UTF-8 |
|
INT32 | DATE | DATE |
INT64 | TIMESTAMP_MILLIS | TIMESTAMP or DATETIME |
INT96 | N/A | TIMESTAMP or DATETIME |
Parquet external tables that use columns of the STRUCT type cannot be created.
Data type mappings between ORC and AnalyticDB for MySQL
Data type in ORC | Data type in AnalyticDB for MySQL |
BOOLEAN | BOOLEAN |
BYTE | TINYINT |
SHORT | SMALLINT |
INT | INT or INTEGER |
LONG | BIGINT |
DECIMAL | DECIMAL |
FLOAT | FLOAT |
DOUBLE | DOUBLE |
|
|
TIMESTAMP | TIMESTAMP or DATETIME |
DATE | DATE |
ORC external tables that use the LIST, STRUCT, or UNION type cannot be created. ORC external tables that use the MAP type cab be created but cannot be queried.
AnalyticDB for MySQL allows you to read and write data of TEXT files in Hive by using OSS external tables in the CSV format. The following statement can be used to create an external table:
CREATE TABLE adb_csv_hive_format_oss (
a tinyint,
b smallint,
c int,
d bigint,
e boolean,
f float,
g double,
h varchar,
i varchar, -- binary
j timestamp,
k DECIMAL(10, 4),
l varchar, -- char(10)
m varchar, -- varchar(100)
n date
) ENGINE = 'OSS' TABLE_PROPERTIES='{
"format": "csv",
"endpoint":"oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com",
"accessid":"LTAI****************",
"accesskey":"yourAccessKeySecret",
"url":"oss://testBucketname/adb_data/",
"delimiter": "\\1",
"null_value": "\\\\N",
"oss_ignore_quote_and_escape": "true",
"ossnull": 2
}';When you create an OSS external table in the CSV format to read and write data of a TEXT file in Hive, take note of the following items:
The default column delimiter for the TEXT file in Hive is
\1. If you want to use the OSS external table to read and write data of the TEXT file in Hive, \1 must be escaped to\\1for thedelimiterparameter.By default, the
NULLvalue of the TEXT file in Hive is\N. If you want to use the OSS external table to read and write data of the TEXT file in Hive, \N must be escaped to\\\\Nfor thenull_valueparameter.The
BINARY,CHAR(N), andVARCHAR(N)types in Hive all correspond to theVARCHARtype in AnalyticDB for MySQL. Other basic data types in Hive such asBOOLEANare the same as those in AnalyticDB for MySQL.
Partitioned OSS external tables
A hierarchical directory is generated for OSS data that contains partitions. Example:
parquet_partition_classic/
├── p1=2020-01-01
│ ├── p2=4
│ │ ├── p3=SHANGHAI
│ │ │ ├── 000000_0
│ └── 000000_1
│ └── p3=SHENZHEN
│ │ └── 000000_0
│ └── p2=6
│ └── p3=SHENZHEN
│ └── 000000_0
├── p1=2020-01-02
│ └── p2=8
│ ├── p3=SHANGHAI
│ │ └── 000000_0
│ └── p3=SHENZHEN
│ └── 000000_0
└── p1=2020-01-03
└── p2=6
├── p2=HANGZHOU
└── p3=SHENZHEN
└── 000000_0In the preceding example, p1 indicates the level-1 partition, p2 indicates the level-2 partition, and p3 indicates the level-3 partition. If you want to query the data by partition, you must specify partition key columns in the statement used to create an OSS external table. The following statement shows how to create an OSS external table and specify partition key columns in the external table. In this example, a Parquet object is used.
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name
(column_name column_type[, ...])
ENGINE='OSS'
TABLE_PROPERTIES='{
"endpoint":"endpoint",
"url":"OSS_LOCATION",
"accessid":"accesskey_id",
"accesskey":"accesskey_secret",
"format":"parquet",
"partition_column":"p1, p2, p3"
}';The
partition_columnproperty in theTABLE_PROPERTIESparameter specifies the partition key columns (p1, p2, and p3 in the example). The partition key columns specified by thepartition_columnproperty must conform to the partition levels of the sample data.When you define columns in the statement, you must include the partition key columns (p1, p2, and p3 in the example) and their data types. The partition key columns must be placed at the end of the column definition.
The partition key columns defined in the statement must be in the same order as the partition key columns specified by the
partition_columnproperty.Partition key columns support the following data types:
BOOLEAN,TINYINT,SMALLINT,INT,INTEGER,BIGINT,FLOAT,DOUBLE,DECIMAL,VARCHAR,STRING,DATE, andTIMESTAMP.When you query data, partition key columns can be displayed and used in the same manner as other columns.
If you leave the format parameter empty, the CSV format is used.
For information about other parameters, see the parameter table in the "Non-partitioned OSS external tables" section of this topic.
References
For more information about how to import data to AnalyticDB for MySQL, see Supported data sources.