The Domain Name System (DNS) records vary across different scenarios. Alibaba CLoud DNS supports various types of DNS records. This topic describes how to add a DNS record on the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.
Preparations
You must check the following items before configuring DNS settings to prevent DNS resolution issues:
Types of records
Types of DNS records supported by Alibaba Cloud DNS and their common application scenarios:
Type | Description and scenarios |
A record | A record that points a domain name to a specified IPv4 address. It is used to resolve the domain name for website. |
Canonical name (CNAME) record | A record that points a domain name to another domain name. It is used for website resolution, accelerated domain name, enterprise email, Global Traffic Manager (GTM) access, etc. |
Mail exchanger (MX) record | A record that specifies the mail server of a domain name and sorts the DNS records by priority. |
AAAA record | A record that points a domain name to a specified IPv6 address. It is used for accessing websites through an IPv6 address. |
Text (TXT) record | Identifies and describes a domain name. It is used for digital certificates, SPF records (anti-spam), domain name retrieval, etc. |
Explicit or implicit URL forwarding record | A record that points a domain name to another existing site, supporting explicit and implicit URL forwarding. |
Name server (NS) record | Specifies a particular DNS server to configure the DNS settings for a domain name. It is used for delegating subdomain resolution to other DNS service providers. |
Service (SRV) record | Identifies a server that uses a specific service, commonly used in directory management of Microsoft systems. |
Certification Authority Authorization (CAA) record | Specifies the authorized certification authority (CA) to issue HTTPS certificates for a domain name, preventing incorrect issuance of HTTPS certificates and enhancing website security. |
Pointer (PTR) record | A record that maps an IP address to a domain name. It can be used to verify whether a specific IP address is pointed to a domain name. |
Service Binding (SVCB) record | A record is provided to improve service discovery, provide protocol and endpoint information, optimize client connection decisions, and enhance performance and security. |
HTTPS record | HTTPS record is a specialized version of SVCB record, specifically used to describe HTTPS services. |
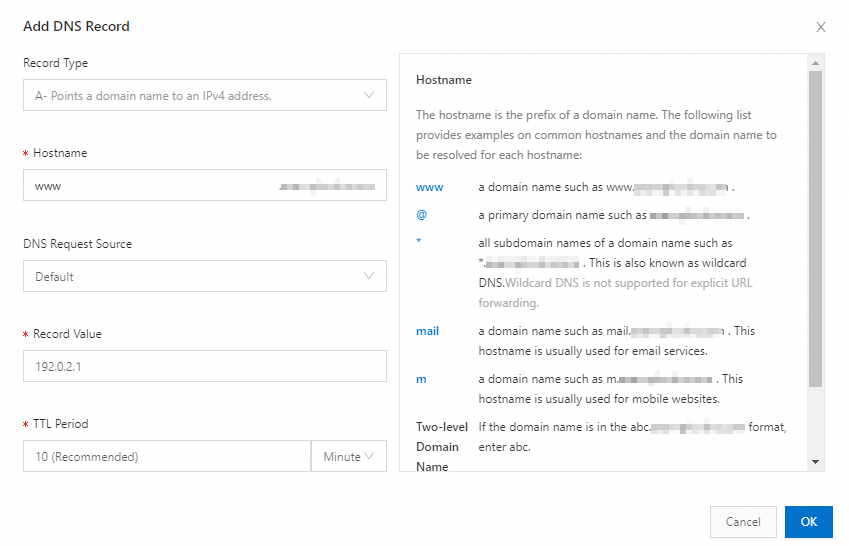
A record
Scenarios
To map a domain name to an IP address, you can add an A record for the domain name. A record is used to resolve the domain name of a website. If you want visitors to access your website by using a domain name, you can add an A record that maps the domain name to the IP address of your website.
Limits
The public IPv4 address of the server to which the domain name is mappped is available. For example: 192.0.2.1.
If your website is hosted on an Alibaba Cloud Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, log on to the ECS console to obtain the public IP address.
If your website is hosted on a third-party service provider, contact them to obtain the public IP address.
If the hostname is not @, A records and NS, CNAME, or URL records that have the same host record and resolution line conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add an A record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
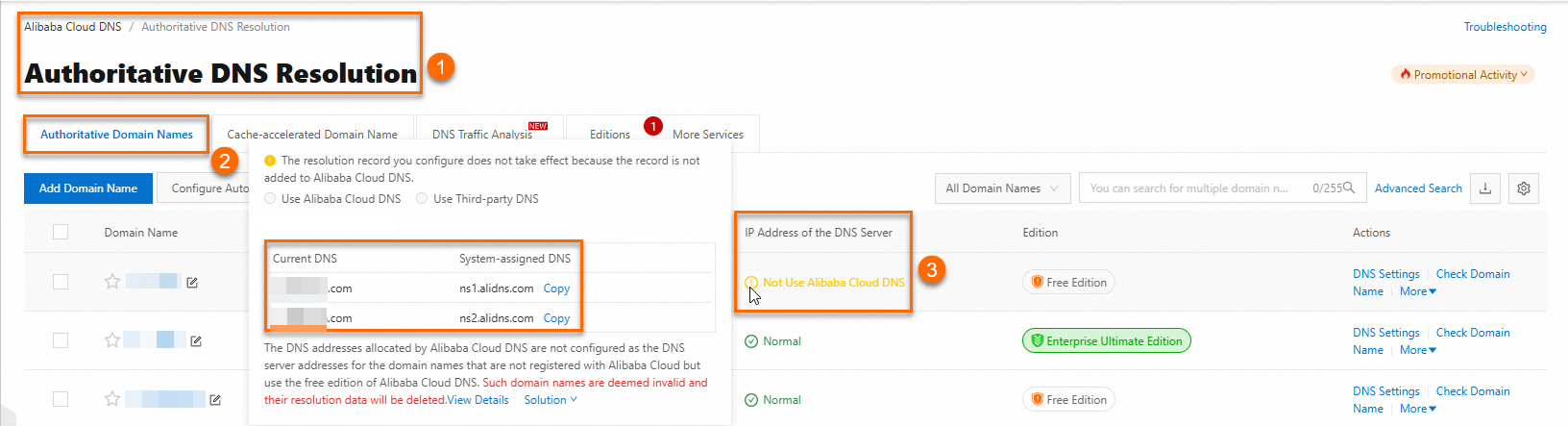
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
CNAME record
Scenarios
To map a domain name to another domain name that is mapped to an IP address, you can add a CNAME record. CNAME records apply if you use Alibaba Cloud CDN, Alibaba Mail, and GTM.
Limits
If you add a CNAME record that contains the default line and add an A record and an AAAA record that contain non-default lines, inaccurate intelligent DNS resolution may occur. For more information, see the Check whether a CNAME record that contains the default line is cached section of the "Solutions to inaccurate intelligent DNS resolution" topic.
If the hostname is not @, CNAME records and other types of DNS records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add a CNAME record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
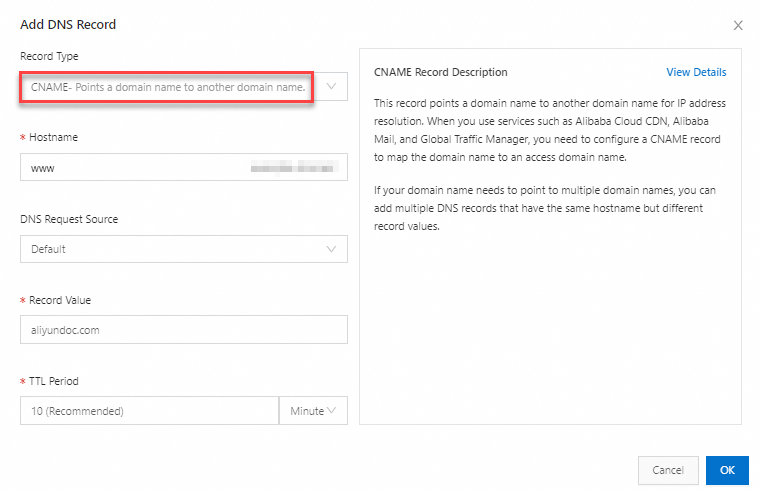
| Record Type: Select CNAME; Hostname: Enter the prefix of the subdomain name. For example: If you want to create a CNAME record for the subdomain name www.example.com, enter www. If you want to create a CNAME record for the domain name example.com, enter @.
DNS Request Source: specifies the source from which DNS queries are sent. In most cases, Default is selected. If you want to return different IP addresses for DNS requests from different sources, you can add other DNS request sources, such as ISP lines and lines for regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Intelligent DNS resolution.
Important Be sure to set a DNS record with the request source configured as Default for fallback resolution. This prevents resolution failures when some DNS requests do not match the DNS records with the satisfied request sources. Record Value: Enter the domain name to which the CNAME record is mapped. Example: aliyundoc.com;
Note If your domain name needs to point to multiple IPv6 addresses, you can add multiple DNS records that have the same hostname but different record values. The round-robin mode is selected by default. For information about how to return different DNS records based on the preset weights of IP addresses, see Set weights. TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
MX record
Scenarios
To ensure that your mailbox can receive emails, you must add an MX record for the mailbox. An MX record specifies the mail server that receives emails based on the email address suffix. For example, if a user sends an email to vincen@example.com, the system resolves the domain name example.com by using the MX record. The system forwards the email to the email server that corresponds to the resolved email address based on the priority of the MX record. if you want to add DNS records for mailboxes, see Add DNS records for mailbox.
Limits
You must deploy a server for the mailbox and obtain the domain name address from the mailbox provider.
If the hostname is not @, MX records and NS, or CNAME records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add an MX record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
An email address that is registered with Alibaba Mail is used in this example. Specify the following parameters:
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
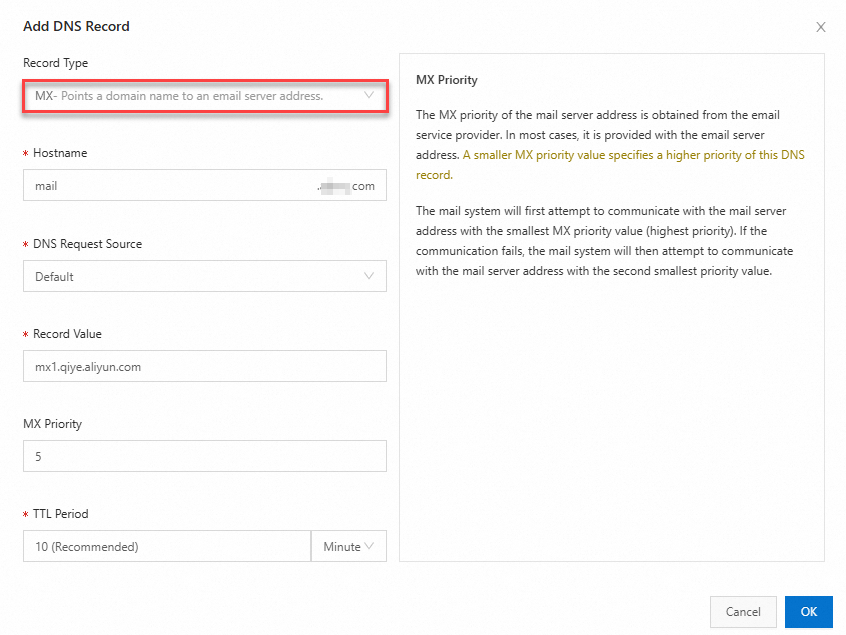
| Record Type: Select MX; Hostname: Enter the prefix of the subdomain name. For example: If the email address is mail.example.com, enter mail. If the email address is example.com, enter @.
DNS Request Source: specifies the source from which DNS queries are sent. In most cases, Default is selected. If you want to return different IP addresses for DNS requests from different sources, you can add other DNS request sources, such as ISP lines and lines for regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Intelligent DNS resolution.
Important Be sure to set a DNS record with the request source configured as Default for fallback resolution. This prevents resolution failures when some DNS requests do not match the DNS records with the satisfied request sources. Record Value: Enter the MX record value that is obtained from the email service provider. In this example, the MX record value provided by Alibaba Mail is mx1.qiye.aliyun.com; MX Priority: Enter the MX record priority that is obtained from the email service provider. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. The following figure shows how to configure the MX record. For example, the system attempts to forward an email tomx1.qiye.aliyun.com, which has an MX priority of 5. If the attempt fails, the system forwards the email to mx2.qiye.aliyun.com, which has an MX priority of 10; 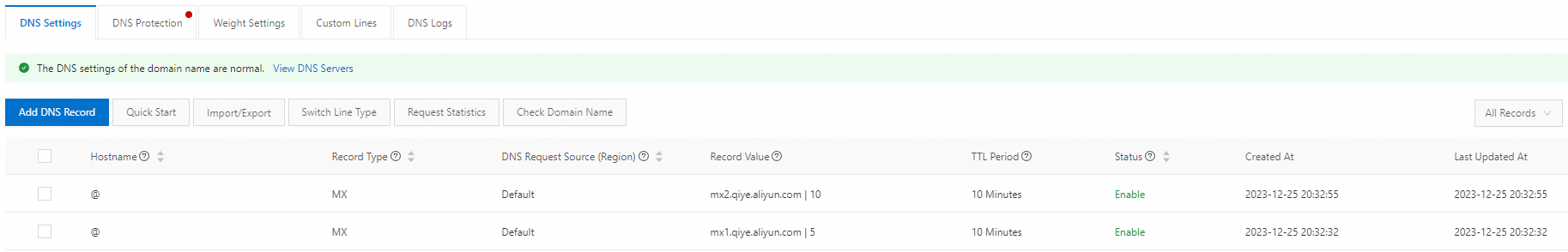
TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
Important The preceding example only shows how to add an MX record. To create a mailbox, you must also add CNAME and TXT records. For more information about the required DNS records, contact your email service provider. For more information about how to add DNS records for Alibaba Cloud mailboxes, see Add DNS records for mailbox.
|
AAAA record
Scenarios
If you want visitors to access your website by using IPv6 addresses, you can create an AAAA record for the domain name of your website.
Limits
You must obtain the IPv6 address of the server to which the domain name is mapped. Example: ff03:0:0:0:0:0:0:c1.
If the hostname is not @, AAAA records and NS, CNAME, or URL records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add an AAAA record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
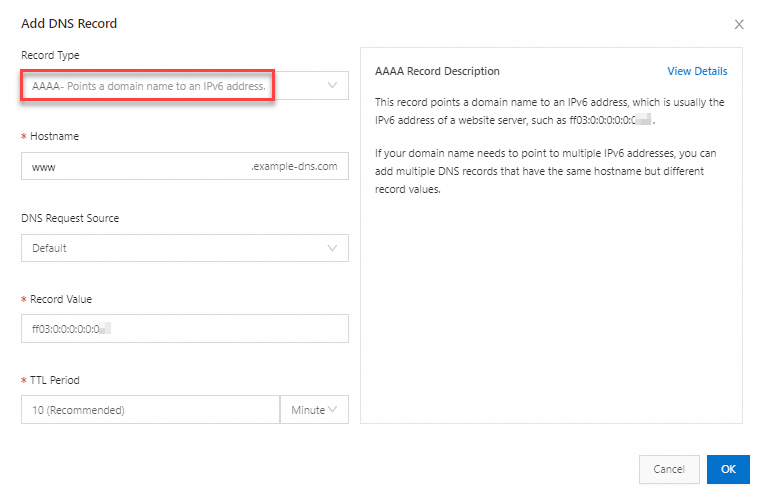
| Record Type: Select AAAA; Hostname: Enter the prefix of a subdomain name. For example: If you want to create an AAAA record for the subdomain name www.example.com, enter www. If you want to create an AAAA record for the domain name example.com, enter @.
DNS Request Source: specifies the source from which DNS queries are sent. In most cases, Default is selected. If you want to return different IP addresses for DNS requests from different sources, you can add other DNS request sources, such as ISP lines and lines for regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Intelligent DNS resolution.
Important Be sure to set a DNS record with the request source configured as Default for fallback resolution. This prevents resolution failures when some DNS requests do not match the DNS records with the satisfied request sources. Record Value: Enter the IPv6 address to which the domain name is mapped. Example: ff03:0:0:0:0:0:0:c1.
Note If your domain name needs to point to multiple IPv6 addresses, you can add multiple DNS records that have the same hostname but different record values. The round-robin mode is selected by default. For information about how to return different DNS records based on the preset weights of IP addresses, see Set weights. TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
TXT record
Scenarios
To identify and describe a domain name, you can add a TXT record for the domain name. In most cases, a TXT record is used as a digital authentication certificate or a Sender Policy Framework (SPF) record to prevent email spam.
Limits
If the hostname is not @, TXT records and NS, or CNAME records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add a TXT record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
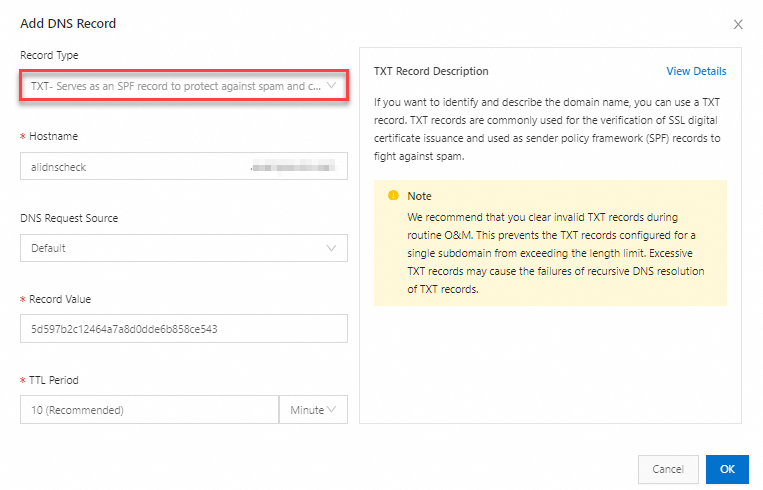
| Record Type: Select TXT; Hostname: Enter the prefix of a subdomain name. For example: If you want to create a TXT record for the subdomain name alidnscheck.example.com, enter alidnscheck. If you want to create a TXT record for the domain name example.com, enter @.
DNS Request Source: specifies the source from which DNS queries are sent. In most cases, Default is selected. If you want to return different IP addresses for DNS requests from different sources, you can add other DNS request sources, such as ISP lines and lines for regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Intelligent DNS resolution.
Important Be sure to set a DNS record with the request source configured as Default for fallback resolution. This prevents resolution failures when some DNS requests do not match the DNS records with the satisfied request sources. Record Value: In most cases, a TXT record is used for verification. For example, to host a subdomain name, you must add a TXT record. Enter 5d597b2c12464a7a8d0dde6b858ce543 for this example.; TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
FAQ
Why is there a text (TXT) record in my DNS records?
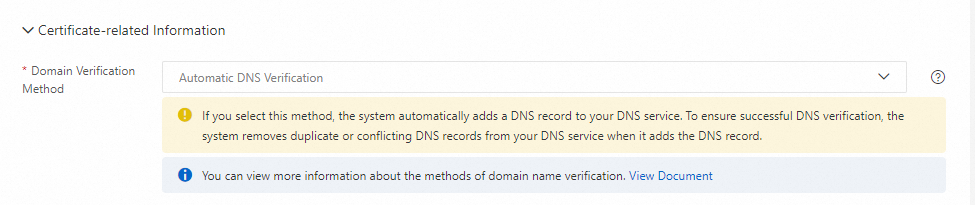
An additional TXT record may be added automatically for domain validation when using certain Alibaba Cloud products. For instance, if you choose Automatic DNS Verification under Domain Verification Method in the Certificate-related Information section on the SSL Certificate Service buy page, Alibaba Cloud will add a TXT record for you. For more information, see How do I select a method for domain name ownership verificatioN?
Add an explicit or implicit URL forwarding record
Warning URL forwarding record guarantees no availability for resolution services in the Service Level Agreement (SLA). To obtain a high availability, you can create a URL forwarding server for forwarding domain names. For more information, see Create a URL forwarding server by using Nginx.
Scenarios
To redirect requests for a domain name to another domain name of an existing website, you can create a URL forwarding record. After you add a URL forwarding record for a domain name, Alibaba Cloud DNS automatically adds an A record in which your domain name is mapped to the address of the URL forwarding server that Alibaba Cloud DNS provides. In this case, after you run the dig command, the A record and the IP address 203.107.XX.XX are displayed in the output. However, the record value that you specify in the console is a URL. The difference is a common occurrence.
Prerequisites
A URL forwarding record is used to map your domain name before URL forwarding to the address of an Alibaba Cloud URL forwarding server which forwards the requests for the domain name to the destination URL. The URL forwarding servers of Alibaba Cloud are deployed in the Chinese mainland. Therefore, an Internet Content Provider (ICP) filing must be complete for the domain name used before URL forwarding. You can apply for an ICP filing for the domain name in another filing system other than the Alibaba Cloud ICP Filing system. For information about applying for an ICP filing in Alibaba Cloud Filing system, see ICP filing process.
Limits
The record value in a URL forwarding record cannot be an IP address.
Domain names used before URL forwarding cannot contain underscores (_).
URL forwarding does not support wildcard DNS resolution.
Chinese domain names cannot be used as destination domain names.
Domain names used before URL forwarding support HTTP but do not support HTTPS. Destination domain names support both HTTP and HTTPS.
If the hostname is not @,URL records and NS, CNAME, A, AAAA or URL records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add a URL record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
URL forwarding is a special feature of Alibaba Cloud DNS. Alibaba Cloud DNS does not provide the attack defense service for this feature. URL forwarding becomes unavailable if blackhole filtering is triggered due to DDoS attacks. In this case, you can add an A or CNAME record to point the desired domain name to the destination IP address or the destination domain name. Alternatively, you can implement URL forwarding by using NGINX. For more information, see Create a URL forwarding server by using Nginx.
Procedure
Example: Redirect requests for http://example.com to http://www.aliyundoc.com:80/.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
Implicit URL forwarding
The inline frame (iframe) technology instead of the redirection technology is used.
Expected results
After a user enters http://example.com in the address bar of a browser and presses Enter, the page that corresponds to http://www.aliyundoc.com:80/ appears but http://example.com is still displayed in the address bar.
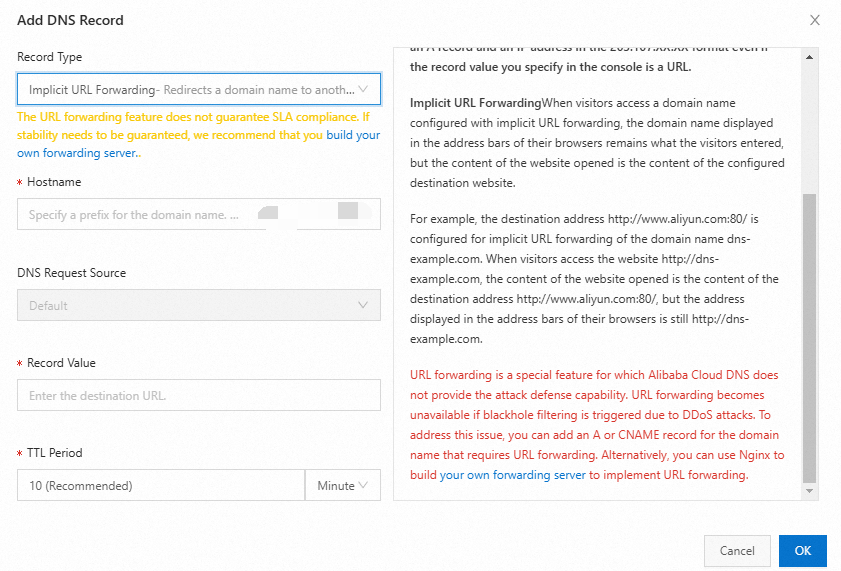
| Record Type: Select Implicit URL Forwarding; Hostname: Enter the prefix of the subdomain name. For example: If you want to create an Implicit URL Forwarding record for the subdomain name www.example.com, enter www. If you want to create an Implicit URL Forwarding record for the domain name example.com, enter @.
DNS Request Source:Select Default. Record Value: Enter http://www.aliyundoc.com:80/; TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
Explicit URL forwarding
Expected results
After a user enters http://example.com in the address bar of a browser and presses Enter, the page that corresponds to http://www.aliyundoc.com:80/ appears but http://www.aliyundoc.com:80/ is still displayed in the address bar.
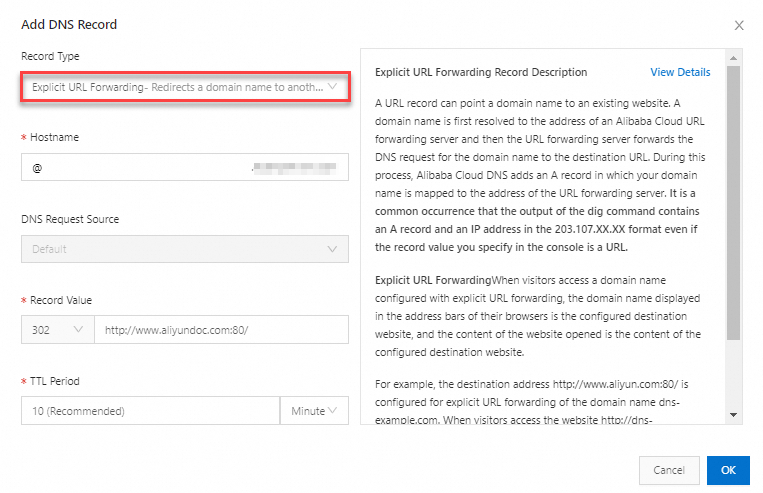
| Record Type: Explicit URL Forwarding; Hostname: Enter the prefix of a subdomain name. For example: If you want to create an Explicit URL Forwarding record for the subdomain name www.example.com, enter www; If you want to create an Explicit URL Forwarding record for the domain name example.com, enter @.
DNS Request Source: Select Default. Record Value: Permanent redirects (301 redirects) and temporary redirects (302 redirects) are supported. Example: 302http://www.aliyundoc.com:80/;
Note 301 indicates that the resource at the old address A has been permanently removed (this resource is no longer accessible). While crawling new content, search engines also replace the old URL with the redirected URL; 302 indicates that the resource at the old address A is still there (still accessible). This redirect is only temporarily redirecting from the old address A to the new address B. Search engines will crawl the new content while keeping the old URL.
TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
NS record
Scenarios
If you want the subdomain name to be resolved by another DNS service provider, you can add an DNS record. For more information about how to host subdomain names, see Subdomain Management.
Limits
You must obtain the DNS server address from your DNS service provider where the subdomain name is hosted.
You cannot set the hostname to an at sign (@) for an NS record. If you want to delegate your primary domain to another DNS service provider, change the DNS server at your domain name registrar.
If the hostname is not @, NS records and other types of DNS records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add an NS record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
For example, Alibaba Cloud DNS is used to resolve example.com. If you want to delegate the subdomain name www.example.com from Alibaba Cloud DNS to Tencent Cloud DNSPod, specify the following parameters to add an NS record.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
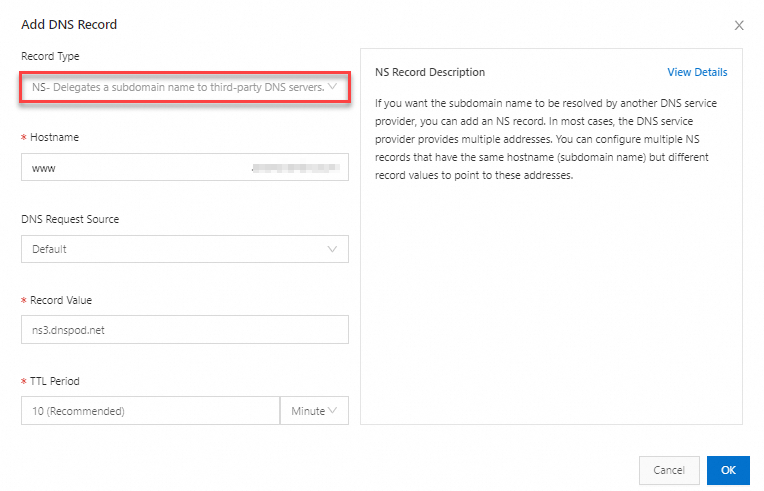
| Record Type: Select NS; Hostname: Enter the prefix of a subdomain name. If the subdomain name is www.example.com and you want to delegate the subdomain name to Tencent Cloud DNSPod, enter www. DNS Request Source: specifies the source from which DNS queries are sent. In most cases, Default is selected. If you want to return different IP addresses for DNS requests from different sources, you can add other DNS request sources, such as ISP lines and lines for regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Intelligent DNS resolution.
Important Be sure to set a DNS record with the request source configured as Default for fallback resolution. This prevents resolution failures when some DNS requests do not match the DNS records with the satisfied request sources. Record Value: Enter the domain name of the DNS server to which you want to delegate the subdomain name. For example, the domain name of the DNS server that is provided by Tencent Cloud DNSPod is ns3.dnspod.net;
Note You can configure multiple NS records that have the same hostname (subdomain name) but different record values to point to these addresses. TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
SRV record
Scenarios
An SRV record is used to specify a server that hosts a specific service. SRV records are commonly used in directory management for Microsoft operating systems.
Limits
If the hostname is not @, SRV records and NS or CNAME records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add an SRV record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
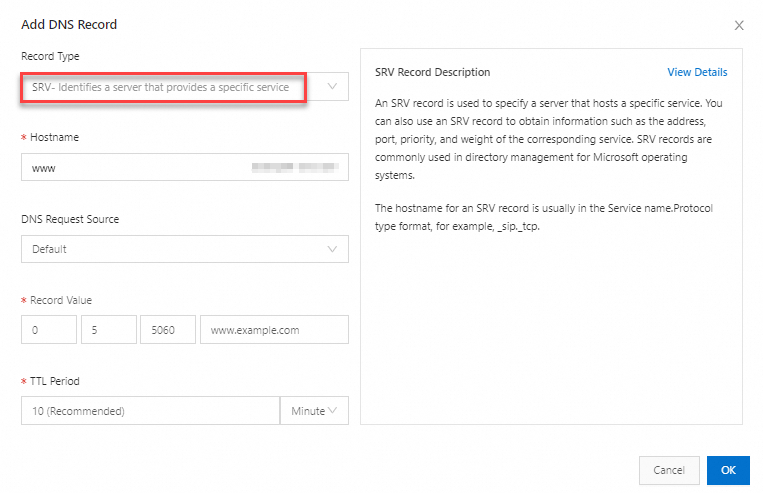
| Record Type: Select SRV; Hostname: Enter a hostname in the format of Service name.Protocol type. Example: _sip._tcp; DNS Request Source: specifies the source from which DNS queries are sent. In most cases, Default is selected. If you want to return different IP addresses for DNS requests from different sources, you can add other DNS request sources, such as ISP lines and lines for regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Intelligent DNS resolution.
Important Be sure to set a DNS record with the request source configured as Default for fallback resolution. This prevents resolution failures when some DNS requests do not match the DNS records with the satisfied request sources. Record Value: Enter a record value in the format of Priority Weight Port Destination domain name. Example: 0 5 5060 www.example.com; TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
CAA record
Scenarios
CAA stands for Certificate Authority Authorization. Certificate Authority Authorization record allows website domain owner to declare which certificate authorities (CAs) are allowed to issue certificates for their domain names. This prevents unauthorized third parties from attempting to obtain SSL or TSL certificates for the domain names by registering with other CAs.
When you add a CAA record for the domain name of your website, you can authorize a specific CA to issue certificates for the domain name. This prevents HTTPS certificates from being issued by unauthorized CAs and improves website security.
Limits
If the hostname is not @, CAA records and NS or CNAME records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add a CAA record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
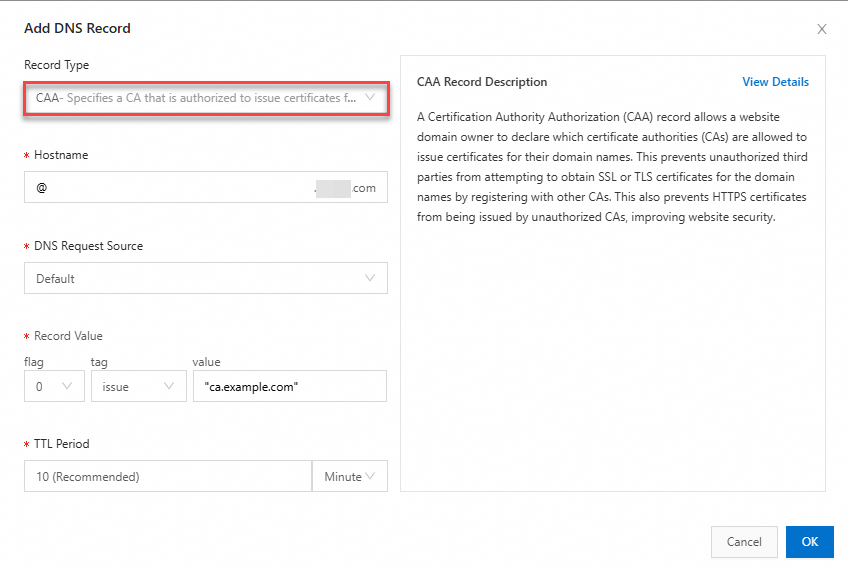
| Record Type: Select CAA; Hostname: Enter the prefix of a subdomain name. For example: If you want to create a CAA record for the subdomain name www.aliyundoc.com, enter www; If you want to create a CAA record for the domain name aliyundoc.com, enter @.
DNS Request Source: specifies the source from which DNS queries are sent. In most cases, Default is selected. If you want to return different IP addresses for DNS requests from different sources, you can add other DNS request sources, such as ISP lines and lines for regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Intelligent DNS resolution.
Important Be sure to set a DNS record with the request source configured as Default for fallback resolution. This prevents resolution failures when some DNS requests do not match the DNS records with the satisfied request sources. Record Value: The record value is in the format of [flag] [tag] [value]. The record value consists of a [flag] byte and a property that is a [tag]-[value] pair. You can add multiple CAA records for a domain name. Example: 0 issue "ca.example.com"; TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
PTR record
Reverse DNS lookup is a process of mapping an IP address to a domain name, which is the reverse of forward DNS lookup where an A record or AAAA record maps a domain name to an IP address. You can use a pointer (PTR) record to verify that a specific IP address is mapped to a designated domain name.
Configuration Method: To use this feature, contact your data center or host service provider. If your servers are provided by Alibaba Cloud, you can submit a ticket. The after-sales support engineers of Alibaba Cloud can help you add PTR records resolution.
SVCB record
Scenarios
SVCB records are designed to improve service discovery and to inform clients about additional parameters of services, such as supported protocols and details of service endpoints, before the clients attempt to access the services. SVCB records can be used for different transfer protocols and are closely related to HTTPS records.
SVCB records enable DNS systems to provide more flexible and detailed configuration information, and allow clients to make more informed decisions about service requests before the clients establish connections with services. This not only improves performance and security, but also optimizes user experience.
Limits
If the hostname is not @, SVCB records and NS or CNAME records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other, and SVCB records in alias mode and in service mode conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add an SVCB record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
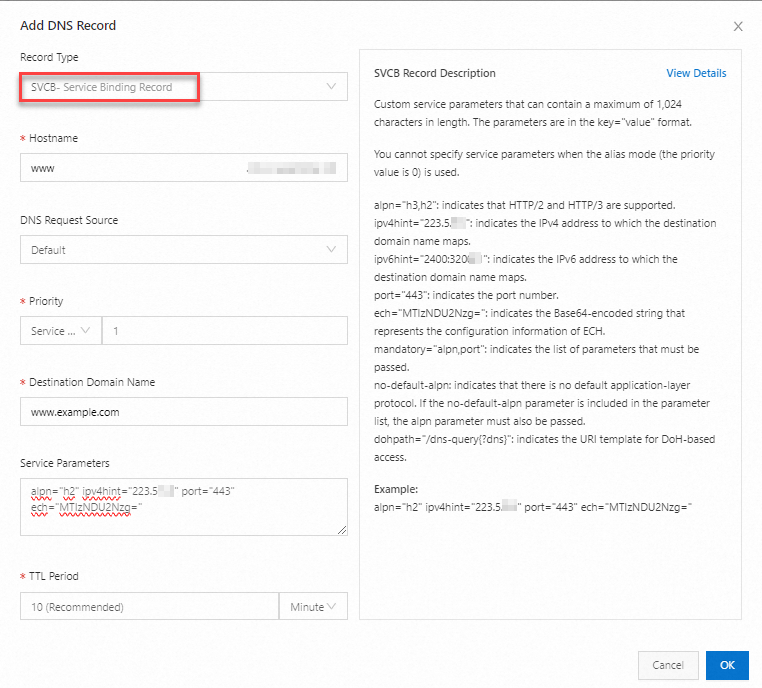
| Record Type: Select SVCB; Hostname: Enter the prefix of a subdomain name. For example: If you want to create an SVCB record for the subdomain name www.aliyundoc.com, enter www If you want to create an SVCB record for the domain name aliyundoc.com, enter @.
DNS Request Source: specifies the source from which DNS queries are sent. In most cases, Default is selected. If you want to return different IP addresses for DNS requests from different sources, you can add other DNS request sources, such as ISP lines and lines for regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Intelligent DNS resolution.
Important Be sure to set a DNS record with the request source configured as Default for fallback resolution. This prevents resolution failures when some DNS requests do not match the DNS records with the satisfied request sources. Priority: Enter an integer ranging from 0 to 65535. The service instance corresponding to the SVCB record with the highest priority is selected by clients first. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. If a service has more than one SVCB record, clients sort the SVCB records by priority and attempt to access the service instance corresponding to the SVCB record with the highest priority (the lowest value). The Priority parameter for SVCB records is similar to the Priority parameter for MX records in email services.
Note If the Priority parameter is set to 0 for an SVCB record, the SVCB record is in alias mode and you cannot specify service parameters. In this case, the SVCB record is similar to a CNAME record, which can point to the name of the service instance that clients attempt to access. If the Priority parameter is not set to 0 for an SVCB record, the SVCB record is in service mode and you can specify service parameters.
Destination Domain Name: Enter the domain name of a server to which clients need to connect. In an SVCB record in alias mode, the Destination Domain Name parameter specifies the name of the service instance that clients need to access. In an SVCB record in service mode, the Destination Domain Name parameter specifies the hostname of a service. In this case, clients initiate DNS requests to the specified domain name to obtain the IP address of the service instance. Example: www.example.com.
Service Parameters: Enter a set of key-value pairs that define service configurations and required features. These parameters can provide various information. For example, the information includes the desired protocol version, application-layer protocols such as Application-Layer Protocol Negotiation (ALPN), transport-layer security requirements such as the desired TLS version, transport parameters, and IP address prompts. Service parameters allow service providers to provide clients with detailed guidelines for accessing their services, and provide clients with pre-connection information. This optimizes the performance and security of connections. Example: alpn="h2" ipv4hint="223.5.5.5" port="443" ech="MTIzNDU2Nzg=".
Note Common service parameters: alpn="h3,h2": indicates that HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 are supported. ipv4hint="223.5.XX.XX": indicates the IPv4 address to which the destination domain name maps. ipv6hint="2400:3200::XX": indicates the IPv6 address to which the destination domain name maps. port="443": indicates the port number. ech="MTIzNDU2Nzg=": indicates the Base64-encoded string that represents the configuration information of ECH. mandatory="alpn,port": indicates the list of parameters that must be passed. no-default-alpn: indicates that there is no default application-layer protocol. If the no-default-alpn parameter is included in the parameter list, the alpn parameter must also be passed. dohpath="/dns-query{?dns}": indicates the URL template for DoH-based access.
Multiple key-value pairs must be separated with spaces and can be up to 1,024 characters in length. TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
HTTPS record
Scenarios
The HTTPS record is a special version of the SVCB records. HTTPS records are used to describe HTTPS services. HTTPS records contain key-value pair parameters of the same type as key-value pair parameters in SVCB records. The key-value pair parameters in HTTPS records are interpreted and processed by assuming that the service protocol is HTTPS.
HTTPS records allow website operators to provide more detailed information about their HTTPS services, including which IP addresses are available and which protocols or service parameters are supported. This ensures that the most appropriate configurations can be selected when clients access services for the first time. In this way, handshake latency and the probability of connection failures are reduced, and the protection of user privacy is enhanced.
Limits
If the hostname is not @, HTTP records and NS or CNAME records that have the same hostname and resolution line conflict with each other, and HTTP records in alias mode and in service mode conflict with each other. If Alibaba Cloud DNS prompts a record conflict when you add an HTTP record, you can delete the involved DNS records or change the hostname to resolve record conflicts. For more information, see DNS record conflict rules.
Procedure
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. On the Authoritative Domain Names tab of the Authoritative DNS Resolution page, find the domain name that you want to configure and click DNS Settings in the Actions column.
On the DNS Settings page, click Add DNS Record. In the panel that appears, specify the following parameters:
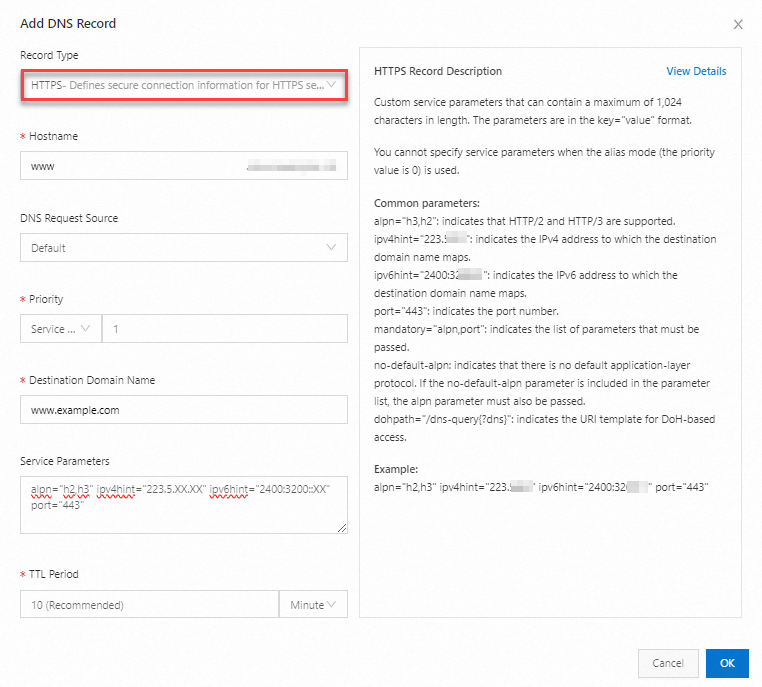
| Record Type: Select HTTPS; Hostname: Enter the prefix of a subdomain name. For example: If you want to create an HTTPS record for the subdomain name www.aliyundoc.com, enter www. If you want to create an HTTPS record for the domain name aliyundoc.com, enter @.
DNS Request Source: specifies the source from which DNS queries are sent. In most cases, Default is selected. If you want to return different IP addresses for DNS requests from different sources, you can add other DNS request sources, such as ISP lines and lines for regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Intelligent DNS resolution.
Important Be sure to set a DNS record with the request source configured as Default for fallback resolution. This prevents resolution failures when some DNS requests do not match the DNS records with the satisfied request sources. Priority: Enter an integer ranging from 0 to 65535. The service instance corresponding to the HTTPS record with the highest priority is selected by clients first. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. If a service has more than one HTTPS records, clients sort the HTTPS records by priority and attempt to access the service instance corresponding to the HTTPS record with the highest priority (the lowest value). The Priority parameter for HTTPS records is similar to the Priority parameter for MX records in email services.
Note If the Priority parameter is set to 0 for an HTTPS record, the HTTPS record is in alias mode and you cannot specify service parameters. In this case, the HTTPS record is similar to a CNAME record, which can point to the name of the service instance that clients attempt to access. If the Priority parameter is not set to 0 for an HTTPS record, the HTTPS record is in service mode and you can specify service parameters.
Destination Domain Name: Enter the domain name of a server to which a client needs to connect. In an HTTPS record in alias mode, the Destination Domain Name parameter specifies the name of the service instance that clients need to access. In an HTTPS record in service mode, the Destination Domain Name parameter specifies the hostname of a service. In this case, clients initiate DNS requests to the specified domain name to obtain the IP address of the service instance. Example: www.example.com. Service parameters: Enter a set of key-value pairs that define service configurations and required features. These parameters can provide various information. For example, the information includes the desired protocol version, application-layer protocols such as ALPN, transport-layer security requirements such as the desired TLS version, transport parameters, and IP address prompts. Service parameters allow service providers to provide clients with detailed guidelines for accessing services and provide clients with pre-connection information, thereby optimizing the performance and security of the connection. Example: alpn="h2,h3" ipv4hint="223.5.XX.XX" ipv6hint="2400:3200::XX" port="443"
Note Common service parameters: alpn="h3,h2": indicates that HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 are supported; ipv4hint="223.5.XX.XX": indicates the IPv4 address of the destination domain name; ipv6hint="2400:3200::XX": indicates the IPv6 address of the destination domain name; port="443": indicates the port number; mandatory="alpn,port": indicates the list of parameters that must be passed; no-default-alpn: indicates that there is no default application-layer protocol. If the no-default-alpn parameter is included in the parameter list, the alpn parameter must also be passed; dohpath="/dns-query{?dns}": indicates the URL template for DoH-based access;
Multiple key-value pairs must be separated with spaces and can be up to 1,024 characters in length. TTL: Time to Live (TTL) refers to the time that the local DNS servers of global ISPs cache the resolution results. We recommend that you set this parameter to 10 minutes. In most cases, a smaller TTL value indicates shorter time required for DNS changes to take effect for end users. For more information, see Set the TTL period.
|
FAQ and references
The following topics are provided to help you troubleshoot issues that you may encounter when you add DNS records: