A node pool is a collection of nodes with the same attributes, enabling streamlined management and operation, such as node upgrades and auto scaling. Node pools also support automated operations, including OS CVE vulnerability repairs, automatic node recovery, and kubelet and containerd version upgrades, to minimize operational costs.
Introduction to node pools
Consider a node pool as a configuration template; nodes added to the pool inherit its configuration. Within a cluster, you can establish multiple node pools with diverse configurations and types. The configuration of a node pool configuration includes properties such as instance specifications, billing type, zone (vSwitch), operating system image, CPU architecture, tags, and taints. These properties are set during node pool creation or can be modified later. For more information about how to create a node pool, see Create and manage a node pool.
Clusters created before the introduction of node pools contain free nodes. To continue using these nodes, we recommend managing them by incorporating them into a node pool. For instructions, see Add free nodes to a node pool.
A single node pool simplifies management and configuration, while multiple node pools enable refined resource isolation and mixed deployment of different node types.
Single node pool | Multiple node pools |
Manage computing resources for multiple teams or various workloads through a single node pool, simplifying operations and maintenance. A single node pool can support the following features.
Currently, mixing instances of different operating system types and CPU architectures (Arm and x86) is not supported. | Create multiple node pools to provide independent computing resources for different workloads or teams, thereby avoiding resource contention and potential security risks. Suitable for the following scenarios.
|
By utilizing multiple node pools, you can prioritize different node pools through scheduling policies to enhance resource and cost management. Consider the following scenarios:
Manage the priority order of computing resources with varying costs, such as preemptible instances and subscription instances, to minimize expenses.
Allocate various instance types based on workload requirements, including the proportion of x86 and Arm architectures utilized.
Node pool features
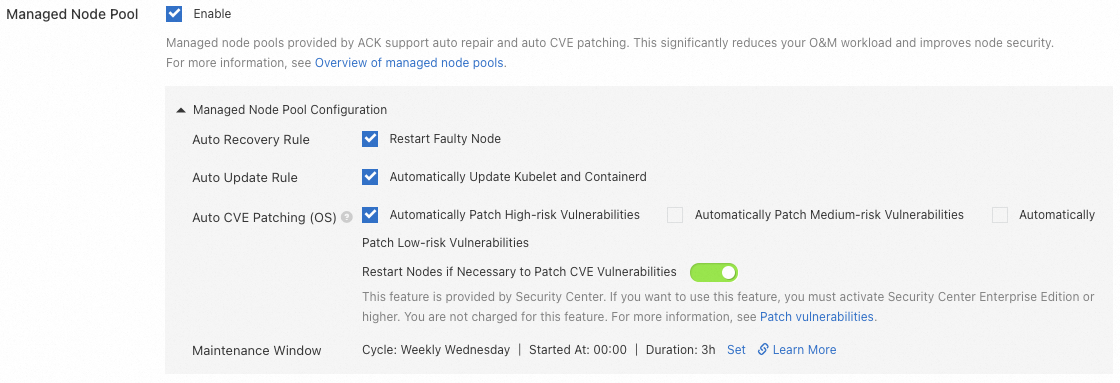
Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) offers a range of features at the node pool level to simplify node management. For those who prefer to concentrate on developing higher-level applications without the burden of extensive worker node maintenance, the managed node pool feature can be enabled to utilize various automated operations and maintenance capabilities.
Basic features
Feature item | Description | Related documents |
Create, edit, delete, and view |
| |
Manual or automatic scaling |
| |
Add existing nodes | If you need to add purchased ECS instances to an ACK cluster as worker nodes or re-add worker nodes to a node pool after removal, you can use the add existing nodes feature. This feature has some usage restrictions and notes. See the document for details. | |
Remove nodes | If certain nodes are no longer needed, you can remove them from the cluster or node pool. Perform standardized operations to remove them to avoid unexpected behavior. | |
Upgrade kubelet version | Enable automated O&M capabilities Upgrade the kubelet version and containerd version of nodes in the node pool. | |
Replace operating system | Support upgrading the operating system version and replacing the operating system type (such as switching an EOL operating system to ContainerOS or Alibaba Cloud Linux). | |
CVE vulnerability repair | Enable automated O&M capabilities Manually scan and repair security vulnerabilities in the node operating system. Some CVE vulnerabilities require node restart to be repaired. See the document for feature description and notes. | |
Customize node pool kubelet parameters | Log on to the console to customize the kubelet parameter configuration of nodes at the node pool level, adjusting node behavior, such as reserving resources for the entire cluster to allocate resource usage. We recommend that you do not use the CLI to customize kubelet parameters that are unavailable in the ACK console. | |
Customize node pool OS parameters | Log on to the console to customize the OS parameter configuration of nodes at the node pool level to optimize system performance. We recommend that you do not use the CLI to customize OS parameters that are unavailable in the ACK console. |
Automated O&M capabilities
Activating automated O&M features for a node pool reduces the maintenance burden, allowing ACK to handle tasks such as OS CVE vulnerability repairs, kubelet upgrades, and node self-recovery. However, if your applications are sensitive to underlying node changes and cannot tolerate restarts or pod migrations, enabling these features is not recommended.
Preparations
Ensure your operating system is one of the following: Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 Container-optimized, ContainerOS, Alibaba Cloud Linux, Red Hat, or Ubuntu.
For supported operating system images and their usage restrictions in ACK clusters, see OS images.
Before using automated O&M features in a node pool, complete the following on the ACK console Node Pools page (settings can be adjusted afterward).
For instructions on creating and editing node pools, see Create and manage a node pool.
Feature introduction
Feature Item | Description |
Automatic upgrade of the kubelet and runtime versions | Automatically maintain kubelet version and containerd runtime upgrades.
For an introduction to related features and important notes, see Update a node pool. |
OS CVE vulnerability auto repair | ACK scans for security vulnerabilities on nodes and schedules CVE vulnerability repairs according to the cluster maintenance window, enhancing cluster stability, security, and compliance. For related notes, see Patch OS CVE vulnerabilities for node pools. |
Automatic responses to ECS system events | Support automatic responses to ECS system events. The supported system event types include the following:
|
Node auto repair | ACK continuously monitors node health, such as |
Node pool lifecycle
The lifecycle of a node pool in an ACK cluster encompasses several stages, from creation and deployment to ongoing maintenance activities like scaling, upgrading, and node removal, and ultimately, deletion. The various states and their transitions are outlined below.

Node pool status | Description |
Initializing (initial) | The node pool is being created. |
Activated (active) | The node pool is successfully created and running. |
Failed (failed) | The node pool creation failed. |
Scaling Out (scaling) | The node pool is scaling out or adding nodes. |
Updating (updating) | The node pool configuration is being updated. |
Removing (removing_nodes) | Nodes are being removed from the node pool. |
Upgrading (upgrading) | The node pool is being upgraded. |
Repairing (repairing) | Repairing in the node pool, such as repairing node pool nodes, node pool CVE vulnerabilities, etc. |
Deleting (deleting) | The node pool is being deleted. |
Deleted (deleted, this status is invisible to you) | The node pool is successfully deleted. |
Node pool billing
While using node pools and their automated O&M capabilities is free, the cloud resources within the node pool, such as ECS instances, incur charges from the respective cloud products.
For more information about the billing rules of ECS instances, see Billing overview.
To change the billing type of existing nodes in the node pool, see Change the billing method of an instance from pay-as-you-go to subscription. Note that changing the billing type of the node pool only affects newly added nodes and does not alter the billing type of existing nodes.
For details on scaling group billing, see Billing overview.
Related terms
Familiarize yourself with the following concepts and terms related to node pools before using them for the first time:
Scaling group: ACK leverages the Auto Scaling service for node pool expansion (scale-out) and reduction (scale-in) activities. Each node pool is directly associated with a single scaling group instance. A scaling group consists of one or more ECS instances, which serve as worker nodes.
Scaling configuration: Node pools use scaling configurations to manage node properties at the foundational level. Auto Scaling configurations serve as templates for ECS instances during auto scaling, automatically creating instances based on these templates when scaling activities are triggered.
Scaling activity: Each node addition or removal in a node pool initiates a scaling activity. The system automatically completes all scaling actions and logs the activity, allowing you to review historical scaling records through the scaling activities of node pool.
Replace system disk: Some node pool operations, such as adding existing nodes or updating the container runtime, involve reinitializing nodes by replacing the system disk. This process does not alter node-specific properties like name, instance ID, or IP, but it does erase data on the system disk. Attached data disks remain unaffected.
When ACK conducts disk replacement, it initiates node drainage to relocate pods from the affected node to other available nodes, adhering to the PDB. To maintain high service availability, we recommend that you implement a multi-replica deployment strategy, spreading workloads over several nodes, and to set up PDB for critical services to manage the simultaneous disruption of pods.
In-place upgrade: An alternative to disk replacement, this method updates and replaces necessary components directly on the original node without reinitializing it or affecting the data present on the node.
References
For more information about the best practices for node pools, see Best practices for nodes and node pools.
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.24 will no longer support Docker as the built-in container runtime. For more information about how to migrate to containerd, see Upgrade the container runtime from Docker to containerd.
As cluster load increases, consider enabling the auto scaling solution to dynamically adjust node resources. For more information, see Auto scaling.
For more information about how to specify the node pool for application pods, see Schedule application pods to a specific node pool.
An ACK Basic cluster supports up to 10 nodes. If you need to increase the limit, we recommend that you perform a hot migration to an ACK Pro cluster. For more information, see Hot migration from ACK basic clusters to ACK Pro clusters.
For more information about how to troubleshoot issue related to nodes or node pools, see FAQ about nodes and node pools.
ACK offers a cluster cost management solution. For more information, see Cost suite.