Application performance optimization is a hierarchical project or method that necessitates a high level of technological expertise from engineers. A basic framework includes not just the application code, but also the operating system, storage, network, and file system, as well as the container, or virtual machine. Therefore, when an online application has performance problems, we need to consider many different factors and complications.
At the same time, besides some performance problems caused by low-level code issues, many performance problems also lurk deep in the application and are difficult to troubleshoot. To address them, we need to have a working knowledge of the sub-modules, frameworks, and components used by the application as well as some common performance optimization tools.

In this article, I will summarize some of the tools and techniques often used for performance optimization, and through doing so, I will also try to show how performance optimization works. This article will be divided into four parts. The first part will provide an overview about the idea behind performance optimization. The second part will introduce the general process involved with performance optimization and some common misconceptions. Next, the third part will discuss some worthwhile performance troubleshooting tools and common performance bottlenecks you should be aware of. Last, the fourth part will bring together the tools introduced previously to describe some common optimization methods that are focused on improving CPU, memory, network, and service performance.
Note that, unless specified otherwise, thread, heap, garbage collection, and other terms mentioned in this article refer to their related concepts in Java applications.
So far, there is no strictly defined process in the field of performance optimization. However, for most optimization scenarios, the process can be abstracted into the following four steps:
These steps are illustrated in the following diagram:
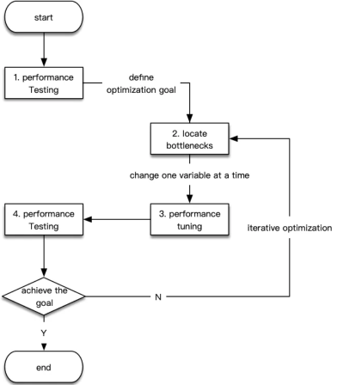
General Process Details
Among the four steps in this process, we will focus on steps 2 and 3 in the next two sections. First, let's take a look at what we need to do during the preparation and testing phases.
Preparation Phase
The preparation phase is a critical step and cannot be omitted.
First, for this phase, you need to have a detailed understanding of the optimization objects. As the saying goes, the sure way to victory is to know your own strength and that of your enemy.
Second, you need to obtain the benchmark data. You can only tell if you have achieved your final performance optimization goals based on benchmark data and current business indicators.
Testing Phase
When we enter this stage, we have already provisionally determined the performance bottlenecks of the application and have completed the initial tuning processes. To check whether the tuning is effective, we must perform stress testing on the application under simulated conditions.
Note that Java involves the just-in-time (JIT) compilation process, and therefore warm-up may be required during stress testing.
If the stress test results meet the expected optimization goals or represent a significant improvement compared with the benchmark data, we can continue to use tools to locate more bottlenecks. Otherwise, we need to provisionally eliminate the current bottleneck and continue to look for the next variable.
Precautions
During performance optimization, taking note of the following precautions can reduce the number of undesired wrong turns.
This article introduces three ways to improve your Java code based on the actual coding work of an Alibaba Cloud engineer, with bad code samples provided.
Iterate entrySet() When the Primary Key and Value of Map Are Used
You should iterate entrySet() when the primary key and value are used. This is more efficient than iterating keySet() and then getting the value.
Bad code:
Map<String, String> map = ...;
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
String value = map.get(key);
...
}Good code:
Map<String, String> map = ...;
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
...
} Use Collection.isEmpty() to Detect Null Values
Compared with Collection.size(),Collection.isEmpty() is much more readable and provides better performance when it comes to detecting null values. The time complexity of Collection.isEmpty()
is always O(1), but that of Collection.size() may be O(n).
Bad code:
if (collection.size() == 0) {
...
}Good code:
if (collection.isEmpty()) {
...
}To detect null values, you can useCollectionUtils.isEmpty(collection) and CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(collection).
Do Not Pass Collection Objects to the Collection Itself
Passing a collection as a parameter to the collection itself is an error or meaningless code.
For methods that require unchanged parameters during execution, an error may occur when you pass a collection to itself.
Bad code:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Hello");
list.add("World");
if (list.containsAll(list)) { // 无意义,总是返回true
...
}
list.removeAll(list); // 性能差, 直接使用clear()Specify the Collection Size During Collection Initialization
The collection class of Java is easy to use, but the collection size is limited in source code. The time complexity of each scaling operation may be O(n). You can specify the predictable collection size whenever possible to reduce the occurrences of collection scaling.
Bad code:
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i : arr) {
list.add(i);
}Good code:
int[] arr = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(arr.length);
for (int i : arr) {
list.add(i);
}Concatenate Strings by UsingStringBuilder
In Java, concatenated strings are tuned during compilation. However, strings that are concatenated in a cycle are not concatenated during compilation. In this case, concatenate strings by using StringBuilder.
Bad code:
String s = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
s += i;
}Good code:
String a = "a";
String b = "b";
String c = "c";
String s = a + b + c; // 没问题,java编译器会进行优化
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sb.append(i); // 循环中,java编译器无法进行优化,所以要手动使用StringBuilder
}Access List Randomly
Random access to arrays is more efficient than that to linked lists. When a called method needs to randomly access data in the acquired List, without knowing whether an array or a linked list is internally implemented, you can check whether the RandomAccess operation is used.
Good code:
// 调用别人的服务获取到list
List<Integer> list = otherService.getList();
if (list instanceof RandomAccess) {
// 内部数组实现,可以随机访问
System.out.println(list.get(list.size() - 1));
} else {
// 内部可能是链表实现,随机访问效率低
}Use Set to Frequently Call the Collection.contains Method
In the collection class library of Java, the time complexity of the contains method for List is O(n). If you need to frequently call the contains method in the code to search for data, you can convert List into HashSet to reduce the time complexity to O(1).
Bad code:
ArrayList<Integer> list = otherService.getList();
for (int i = 0; i <= Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
// 时间复杂度O(n)
list.contains(i);
}Good code:
ArrayList<Integer> list = otherService.getList();
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet(list);
for (int i = 0; i <= Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
// 时间复杂度O(1)
set.contains(i);
}Are you eager to know the latest tech trends in Alibaba Cloud? Hear it from our top experts in our newly launched series, Tech Show!

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Container Service - April 28, 2020
OpenAnolis - January 26, 2026
OpenAnolis - April 20, 2022
OpenAnolis - April 11, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - May 9, 2023
Alibaba Clouder - April 8, 2019

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow YiDA Low-code Development Platform
YiDA Low-code Development Platform
A low-code development platform to make work easier
Learn More Application Real-Time Monitoring Service
Application Real-Time Monitoring Service
Build business monitoring capabilities with real time response based on frontend monitoring, application monitoring, and custom business monitoring capabilities
Learn More Global Network Solution
Global Network Solution
Alibaba Cloud's global infrastructure and cloud-native SD-WAN technology-based solution can help you build a dedicated global network
Learn More Phone Number Verification Service
Phone Number Verification Service
A one-stop, multi-channel verification solution
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder