A subquery is a query in which a SELECT statement is nested inside another SELECT statement. You can use subqueries to meet complex analysis requirements.
Syntax
Specify the FROM clause in a SELECT statement.
* | SELECT key FROM (sub_query)Important
- You must enclose the subquery statement in the FROM clause in parentheses
(). - If you want to analyze log data in the current Logstore, you must specify the keyword
FROM log.
Examples
Example 1
Calculate the number of page views (PVs) by request method and obtain the minimum number of PVs.
- Query statement
* | SELECT min(PV) FROM ( SELECT count(1) as PV FROM log GROUP BY request_method ) - Query and analysis results

Example 2
Calculate the ratio of the PVs in the current hour to the PVs in the same time period on the previous day. The time range for the query is 1 hour (on the hour). 86400 indicates the result of the current time minus 86400 seconds, which is equivalent to 1 day. log indicates the name of the Logstore.
- Query statement
* | SELECT diff [1] AS today, diff [2] AS yesterday, diff [3] AS ratio FROM ( SELECT compare(PV, 86400) AS diff FROM ( SELECT count(*) AS PV FROM log ) ) - Query and analysis results

- 3337.0 indicates the PVs in the current hour. Example: the PVs from 14:00:00 to 15:00:00 on December 25, 2020.
- 3522.0 indicates the PVs in the same time period on the previous day. Example: the PVs from 14:00:00 to 15:00:00 on December 24, 2020.
- 0.947473026689381 indicates the ratio of the PVs in the current hour to the PVs in the same time period on the previous day.
Example 3
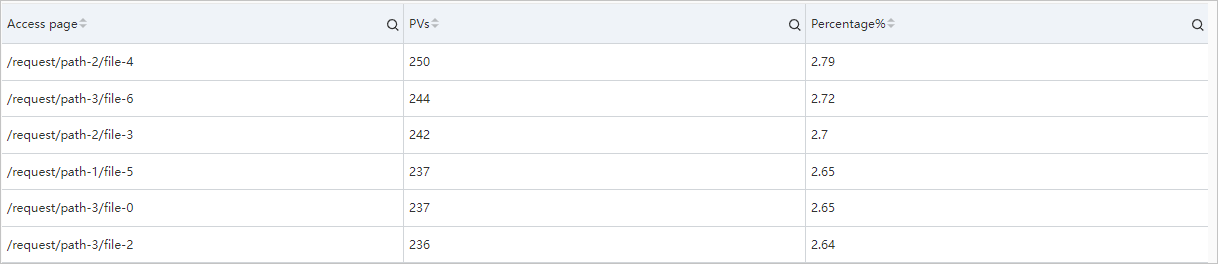
Calculate the number of PVs on each page and the percentage of the PVs on each page to the total PVs.
- Query statement
* | SELECT request_uri AS "Access page", c as "PVs", round(c * 100.0 /(sum(c) over()), 2) AS "Percentage%" FROM ( SELECT request_uri AS request_uri, count(*) AS c FROM log GROUP BY request_uri ORDER BY c DESC ) - Query and analysis results