This topic describes how to create an external store to associate Simple Log Service (SLS) with a MySQL database.
Prerequisites
Data is collected in SLS. For more information, see Data collection.
The SLS command-line interface (CLI) is installed and configured with an endpoint and an AccessKey pair. For more information, see Install SLS CLI and Configure an endpoint and an AccessKey pair.
Data is stored in an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database, an AnalyticDB for MySQL database, or a self-managed MySQL database on an ECS instance.
The MySQL database is in an Alibaba Cloud virtual private cloud (VPC). The RDS instance, AnalyticDB for MySQL instance, or ECS instance must be in the same region as the SLS project.
ImportantYou cannot directly connect to a MySQL database using a public IP address.
Background information
The external store feature of SLS lets you associate SLS with an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database, an AnalyticDB for MySQL database, or a self-managed MySQL database on an ECS instance. You can also write query and analysis results to the MySQL database for further processing.
Procedure
1. Configure a whitelist
RDS for MySQL database
Add the CIDR blocks 100.104.0.0/16, 11.194.0.0/16, and 11.201.0.0/16 to the whitelist. For more information, see Configure an IP address whitelist.
Self-managed MySQL database on an ECS instance
Add security group rules to allow access from the 100.104.0.0/16, 11.194.0.0/16, and 11.201.0.0/16 CIDR blocks. For more information, see Add a security group rule.
AnalyticDB for MySQL database
Add the CIDR blocks 100.104.0.0/16, 11.194.0.0/16, and 11.201.0.0/16 to the whitelist. For more information, see Configure a whitelist.
2. Create an ExternalStore
Log on to the server where the CLI is installed. Run the
touchcommand to create the /home/shell/config.json configuration file. Add the following script to the config.json file. Replace the values of theregion,vpc-id,host,port,username,password,db, andtableparameters as needed.Parameter description
Example
{ "externalStoreName":"sls_join_meta_store", "storeType":"rds-vpc", "parameter":{ "region":"cn-qingdao", "vpc-id":"vpc-m5eq4irc1pucp*******", "host":"rm-bp1******rm76.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.com", "port":"3306", "username":"user", "password":"****", "db":"scmc", "table":"join_meta" } }externalStoreNameThe name of the ExternalStore. The name must be in lowercase.
storeTypeThe type of the data source. Set this parameter to
rds-vpc.regionThe region where the database instance resides. The details are as follows:
If you use an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database, set the region parameter to the region of the RDS instance.
If you use an AnalyticDB for MySQL database, set the region parameter to the region of the AnalyticDB for MySQL instance.
If you use a self-managed MySQL database on an ECS instance, set the region parameter to the region of the ECS instance.
ImportantThe RDS instance, AnalyticDB for MySQL instance, or ECS instance must be in the same region as the SLS project.
vpc-idThe ID of the VPC where the database instance resides. The details are as follows:
If your RDS PostgreSQL instance is in a virtual private cloud (VPC), set vpc-id to the ID of the VPC.
For an ADB PostgreSQL database in a virtual private cloud (VPC), set vpc-id to the ID of that VPC.
If the Alibaba Cloud Hologres database is in a virtual private cloud (VPC), set vpc-id to the ID of the VPC.
hostThe address of the database. The details are as follows:
In a VPC, if the IP address of a database instance changes after you create an external table, access to the external table is affected. For example, this can happen if the database instance is migrated. This issue occurs even if you use an internal endpoint in the configuration. When the external table is created, the backend resolves the domain name to an IP address and saves the IP address to the backend configuration. The IP address that corresponds to the domain name is not automatically refreshed. In this case, you must update or re-create the external table.
If you use an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database, set the host parameter to the internal address of the RDS instance. The internal address can be an internal endpoint or a private IP address.
If you use an AnalyticDB for MySQL database, set the host parameter to the internal address of the AnalyticDB for MySQL instance. The internal address can be an internal endpoint or a private IP address.
If you use a self-managed MySQL database on an ECS instance, set the host parameter to the private IP address of the ECS instance.
If the database is accessible over the Internet, set this parameter to the public domain name or public IP address.
portThe port number. The details are as follows:
If you use an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database, set the port parameter to the port number of the RDS instance.
If you use an AnalyticDB for MySQL database, set the port parameter to the port number of the AnalyticDB for MySQL instance.
If you use a self-managed MySQL database on an ECS instance, set the port parameter to the service port of MySQL on the ECS instance.
usernameThe username of the database account.
passwordThe password of the database account.
dbThe name of the database.
tableThe name of the database table. The following formats are supported:
`table_name`, such as `test`.
`schema_name.table_name`, such as `public.test`.
Run the following command on the command line to create the ExternalStore. project_name is the name of the SLS project. Replace it as needed. In this topic,
log-rds-demois used as an example.aliyunlog log create_external_store --project_name="log-rds-demo" --config="file:///home/shell/config.json"Query the ExternalStore information. If the command is successful, no response is returned. Run the
aliyunlog log get_external_store --project_name="log-rds-demo" --store_name="sls_join_meta_store" --format-output=jsoncommand to query the details of the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL external data source. The following information is returned:{ "externalStoreName":"sls_join_meta_store", "storeType":"rds-vpc", "parameter":{ "db": "scmc", "host": "rm-bp1******rm76.mysql.rds.aliyuncs.com", "port": "3306", "region": "cn-wulanchabu", "table": "test", "username": "user", "vpc-id": "vpc-m5eq4irc1pucp*******" } }
3. Use the external store
Run a query analysis
Use the external store
After you associate the external data source, go to the SLS console. In the project named
log-rds-demo, click any logstore. Then, run the query statement* | select * from sls_join_meta_storeto query data from the associated MySQL table.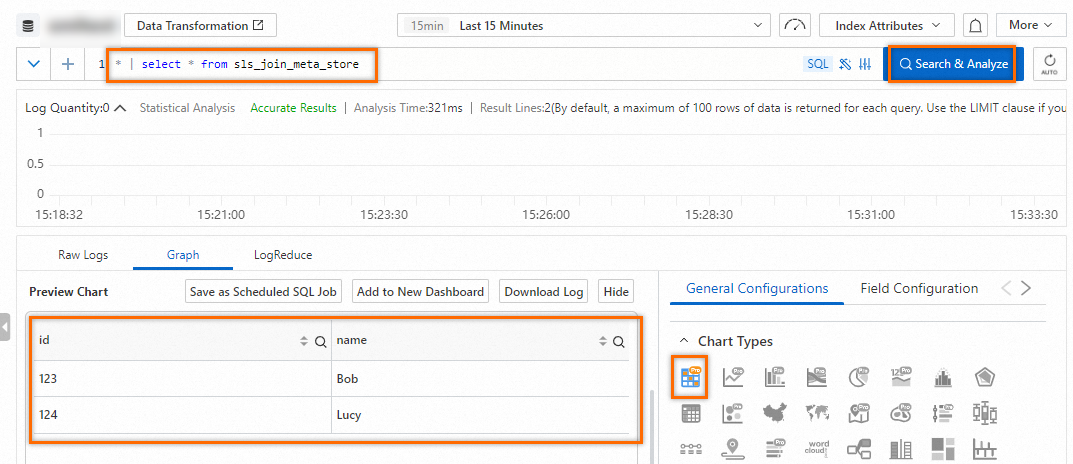
Use JOIN to associate SLS with a MySQL table
You can join a logstore only with a MySQL database table that is less than 20 MB in size.
In the query statement, the logstore must be placed before the join keyword, and the ExternalStore must be placed after the join keyword.
In the query statement, you must specify the ExternalStore name. The system automatically replaces the name with the MySQL database name and table name. Do not directly specify the MySQL table name.
Supported JOIN syntax includes INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, and FULL JOIN.
[ INNER ] JOIN LEFT [ OUTER ] JOIN RIGHT [ OUTER ] JOIN FULL [ OUTER ] JOINThe following example shows the JOIN syntax.
method:postlogstorelogs | select count(1) , histogram(logstore) from log l join sls_join_meta_store m on l.projectid = cast( m.ikey as varchar)
Save query and analysis results to a MySQL database
The fields in the MySQL database table are of the varchar type. You must convert the fields from the logstore to match the fields in the MySQL table. For example, if thedetailfield in the MySQL table isvarchar(60), use the cast function to convert thecontentindex in the logstore:cast(content as varchar(60)). For more information about the cast function, see Type conversion functions.
SLS lets you use the INSERT syntax to insert query results into a MySQL database. The following example shows the INSERT syntax:
method:postlogstorelogs | insert into join_meta select cast(method as varchar(65535)),count(1) from log group by methodSDK operations
Python sample program
# encoding: utf-8
from __future__ import print_function
from aliyun.log import *
from aliyun.log.util import base64_encodestring
from random import randint
import time
import os
from datetime import datetime
endpoint = os.environ.get('ALIYUN_LOG_SAMPLE_ENDPOINT', 'cn-chengdu.log.aliyuncs.com')
accessKeyId = os.environ.get('ALIYUN_LOG_SAMPLE_ACCESSID', '')
accessKey = os.environ.get('ALIYUN_LOG_SAMPLE_ACCESSKEY', '')
logstore = os.environ.get('ALIYUN_LOG_SAMPLE_LOGSTORE', '')
project = "ali-yunlei-chengdu"
client = LogClient(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKey, '')
# Create an ExternalStore.
res = client.create_external_store(project,
ExternalStoreConfig(externalStoreName="rds_store", region="cn-chengdu",
storeType="rds-vpc",
vpcId="vpc-2vctx8reuqswmk********",
host='rm-2vc6x67972iv********.mysql.cn-chengdu.rds.aliyuncs.com',
port="3306", username="root", password="123456",
database="test_database", table="test"))
res.log_print()
# Get the details of the ExternalStore.
res = client.get_external_store(project,"rds_store")
res.log_print()
res = client.list_external_store(project,"")
res.log_print()
# Perform a JOIN query.
req = GetLogsRequest(project,logstore,From,To,"","* | select count(1) from "+ logstore +" s join meta m on s.projectid = cast(m.ikey as varchar)")
res = client.get_logs(req)
res.log_print()
# Write the query and analysis results to the MySQL database.
req = GetLogsRequest(project,logstore,From,To,"","* | insert into rds_store select count(1) from "+ logstore )
res = client.get_logs(req)
res.log_print()Related operations
Update the MySQL external store.
aliyunlog log update_external_store --project_name="log-rds-demo" --config="file:///home/shell/config.json"Delete the MySQL external store.
aliyunlog log delete_external_store --project_name="log-rds-demo" --store_name=sls_join_meta_store
References
For more information about the best practices for creating an external MySQL store, see Associate a logstore with a MySQL database for query analysis.
For more information about how to create a self-managed MySQL database on an Alibaba Cloud ECS instance, see Manually deploy a MySQL database (Linux).
For more information about how to quickly create an AnalyticDB for MySQL database, see Quick start overview.
For more information about how to quickly create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database, see Quickly create an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and configure a database.