Application Load Balancer (ALB) can forward IPv6 requests. This topic describes how to configure a dual-stack server group that contains IPv4 and IPv6 Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances for a dual-stack ALB instance. This way, IPv6 clients can access the backend IPv4 and IPv6 services by using the ALB instance.
Sample scenario
The following figure shows an example. A company wants to use ALB to forward requests from IPv6 clients to the IPv4 and IPv6 services in a virtual private cloud (VPC) over the Internet. To meet this requirement, the company needs to create ECS instances that support IPv4 and IPv6, create a dual-stack ALB instance in the VPC, and create a server group that supports IPv6. After the preceding steps are complete, requests from IPv6 clients can be forwarded to the IPv4 and IPv6 services on the backend ECS instances by using the ALB instance.

Limits
For more information about the regions that support dual-stack ALB instances, see ALB instance overview.
To use the dual-stack feature, you must enable the IPv6 feature for the vSwitches in the zones of the VPC.
Dual-stack ALB instances can forward requests from IPv4 and IPv6 clients to IPv4 and IPv6 backend services. For details, see Protocol version.
A server group with IPv6 enabled can be associated with listeners and forwarding rules of only dual-stack ALB instances.
Prerequisites
A VPC that supports IPv6 is created. In this example, a VPC named VPC1 is created in the China (Shanghai) region. After IPv6 is enabled for the VPC, an IPv6 gateway is automatically created.
In the VPC, a vSwitch is created in each of two zones and IPv6 is enabled for the vSwitches. In this example, vSwitch 1 is created in Shanghai Zone E and vSwitch 2 is created in Shanghai Zone G.
To deploy ALB within vSwitch 1 and vSwitch 2, pay attention to this: Each upgraded ALB instance is allocated with three IP addresses from vSwitch 1 and vSwitch 2, respectively: One acts as a VIP to provide load balancing services, and the other two as local IP addresses to communicate with backend servers and perform health checks. If vSwitch 1 or vSwitch 2 does not have enough available IP addresses, an error is reported and ALB instances cannot be created. This does not apply to non-upgraded ALB instances.
NoteTo ensure upgraded ALB instances auto-scale resources as expected, we recommend that each vSwitch you specify for them has at least eight available IP addresses.
To ensure upgraded ALB instances properly communicate with backend servers, if any security policies such as iptables rules and third-party security policy software, are configured on your backend servers, we recommend that you configure your backend servers to allow the CIDR block of the vSwitch to which the upgraded ALB instance is connected.
You have registered a domain name, and obtained an Internet content provider (ICP) number for the domain name.
Step 1: Create and configure ECS instances
Log on to the VPC console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click vSwitch.
Select the region of the vSwitch. In this example, China (Shanghai) is selected.
On the vSwitch page, find the vSwitch that you want to manage and choose in the Actions column.
On the Custom Launch tab of the Elastic Compute Service page, create an IPv4 ECS instance named ECS01 and an IPv6 ECS instance named ECS02. The security groups to which the ECS instances are added must allow traffic on port 80. For more information, see Create an instance on the Custom Launch tab.
Remotely log on to ECS01 and ECS02. For more information, see Choose an ECS remote connection method.
Run the following commands on ECS01 to deploy an NGINX service:
yum install -y nginx systemctl start nginx.service cd /usr/share/nginx/html/ echo "Hello World ! this is ipv4 rs." > index.htmlRun the following commands on ECS02 to deploy an NGINX service:
yum install -y nginx systemctl start nginx.service cd /usr/share/nginx/html/ echo "Hello World ! this is ipv6 rs." > index.htmlConfigure an IPv6 address for ECS02. For more information, see IPv6 communication.
NoteSkip this step if Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.2104 LTS 64-bit is selected in the Image section and Assign IPv6 Address Free of Charge is selected in the IPv6 section.
Log on to ECS02.
Configure an IPv6 address for ECS02.
Run the
ip addr | grep inet6orifconfig | grep inet6command.If an IPv6 address has been configured for ECS02, as shown in the following figure, skip this step.

If the command output does not contain the information about inet6, IPv6 is disabled for ECS02. Enable IPv6 for ECS02 first.
If the command output contains the information about inet6, IPv6 is enabled for ECS02 and the IPv6 address assigned to ECS02 can be identified. Configure the IPv6 address for ECS02.
Step 2: Configure a security group rule for ECS02
Configure a security group rule for ECS02 to allow inbound IPv6 traffic.
Log on to the ECS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region of the security group. In this example, China (Shanghai) is selected.
On the Security Groups page, find the security group that you want to manage and click Manage Rules in the Actions column.
On the Security Group Details tab, in the Rules section, click tbe Inbound tab.
Click Add Rule. Configure a security group rule for IPv6 requests based on the following information. Click Submit.
Parameter | Description |
Action | Select an action for the rule. In this example, Allow is selected. |
Priority | Select a priority for the rule. A smaller value indicates a higher priority. Valid values: 1 to 100. In this example, the default value 1 is used. |
Protocol | Select the type of allowed inbound requests. In this example, All ICMPv6 is selected. |
Source | Enter the IPv6 CIDR block to which the rule applies. In this example, ::/0 is used, which indicates that the rule applies to all IPv6 addresses. Note You can specify IPv6 addresses based on your business requirements. |
Destination (Current Instance) | Specify a range of ports to accept requests from IPv6 clients. If you set the Protocol parameter to All ICMPv6, All (-1/-1) is automatically selected from the Destination drop-down list and cannot be modified. |
Description | Enter a description for the rule. |
Step 3: Create an ALB instance
Log on to the ALB console.
On the Instances page, click Create ALB.
On the buy page, configure the parameters, click Buy Now, and then complete the payment as prompted.
The following table describes only some of the parameters. Use the default values for other parameters. For more information about the parameters, see Create an ECS instance.
Parameter
Description
Region
The region in which you want to create the ALB instance. In this example, China (Shanghai) is selected.
Network Type
Select a network type for the ALB instance. The system assigns public or private IP addresses to the ALB instance based on the selected network type. In this example, Internet is selected.
NoteThe Internet network type is supported only by IPv4 ALB instances. By default, IPv6 ALB instances are internal-facing. In this example, an Internet-facing IPv6 ALB instance is created. In Step 4, the IPv6 address is changed to a public IPv6 address.
VPC
Select the VPC in which you want to deploy the ALB instance.
NoteMake sure that the IPv6 feature is enabled for the VPC.
Zone
Select at least two zones. In this example, Shanghai Zone E and Shanghai Zone G are selected.
Select a vSwitch in each of the zones. In this example, vSwitch 1 in Zone E and vSwitch 2 in Zone G are selected.
IP Version
Select an IP version for the ALB instance. In this example, Dual-stack is selected.
Edition
Select an edition for the ALB instance. In this example, Standard is selected.
Instance Name
Enter a name for the ALB instance.
Service-linked Role
The first time you create an ALB instance, click Create Service-linked Role to create the AliyunServiceRoleForAlb role. The policy AliyunServiceRolePolicyForAlb is attached to the service-linked role to allow the ALB instance to access other cloud services. For more information, see System policies for ALB.
After you create the dual-stack ALB instance, you must perform the following step to change the IPv6 address of the ALB instance to a public IPv6 address. For more information, see IP versions.
Return to the Instances page and click the ID of the ALB instance.
On the Instance Details tab, navigate to the Basic Information section and find the Network parameter. Then, click Change Network Type next to IPv6:Private.
In the Change Network Type message, click OK.
After the change takes effect, you can verify that the IPv6 network type changes to Public.
Step 4: Create a server group
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Server Groups page, click Create Server Group.
In the Create Server Group dialog box, configure the parameters and click Create.
The following table describes only some of the parameters. Use the default values for other parameters. For more information, see Create and manage a server group.
Parameter
Description
Server Group Type
Specify a type of server group. In this example, Server Type is selected.
Server Group Name
Enter a name for the server group.
VPC
Select a VPC from the VPC drop-down list. Only servers in the VPC can be added to the server group.
NoteSelect the VPC in which the ALB instance is created. Make sure that IPv6 is enabled for the selected VPC.
Backend Server Protocol
Select a backend protocol. In this example, HTTP is selected.
Scheduling Algorithm
Select a scheduling algorithm. In this example, Weighted Round-robin is selected.
IPv6
Specifies whether to enable IPv6. In this example, IPv6 is turned on.
Session Persistence
Specifies whether to enable session persistence. In this example, the default value is used. Session persistence is disabled.
Health Check
Specifies whether to enable the health check feature. In this example, the health check feature is enabled.
Health Check Settings
After you enable the health check feature, click Modify to configure the health check settings.
On the Server Group page, click the ID of the server group that you want to manage.
Click the Backend Servers tab and then click Add Backend Server.
In the Add Backend Server panel, select ECS01 and ECS02. In the IP column, select the IPv4 address of ECS01 and the IPv6 address of ECS02 and click Next.
In the Ports/Weights step, specify the ports and weights of ECS01 and ECS02 and click OK.
In this example, both ECS instances use the port number 80 and the default weight 100.
Step 5: Configure a listener
On the Instances page, click the ID of the ALB instance that you want to manage.
Click the Listener tab and then click Create Listener.
In the Configure Listener step, configure the parameters and click Next.
The following table describes only some of the parameters. Use the default values for other parameters. For more information, see Add an HTTP listener.
Parameter
Description
Select Listener Protocol
Select a listener protocol. In this example, HTTP is selected.
Listener Port
Specify a listener port to receive requests and forward them to backend servers. In this example, port 80 is specified.
Listener Name
Enter a name for the listener.
Advanced Settings
In this example, the default settings are used. You can click Modify to modify the settings.
In the Server Group step, configure the Server Type parameter, select a server group based on the specified Server Type, confirm the backend servers, and then click Next.
In the Confirm step, confirm the configurations and click Submit.
Click OK to return to the Listener tab. If the listener status in the Health Check Status column is Healthy, ECS01 and ECS02 can process requests forwarded by the ALB instance.
Step 6: Create a DNS record
In actual business scenarios, we recommend that you use CNAME records to map custom domain names to the domain name of your ALB instance.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Instances page, copy the domain name of the ALB instance.
Perform the following steps to create a CNAME record:
NoteIf your domain name is not registered by using Alibaba Cloud Domains, you must add your domain name to Alibaba Cloud DNS before you can configure a DNS record. For more information, see Manage domain names.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.
On the Public Zone page, find your domain name and click Settings in the Actions column.
On the Settings tab of the domain name details page, click Add Record.
In the Add Record panel, configure the parameters and click OK. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Record Type
Select CNAME from the drop-down list.
Hostname
Enter the prefix of the domain name. In this example, @ is entered.
NoteIf you use a root domain name, enter
@.Query Source
Select Default.
Record Value
Enter the CNAME, which is the domain name of the ALB instance.
TTL
Select a time-to-live (TTL) value for the CNAME record to be cached on the DNS server. In this example, the default value is used.
Step 7: Test network connectivity
Before you perform the test, make sure that your client supports IPv6. To check whether your client supports IPv6, visit http://test-ipv6.com/ to run a test.
Use a client that supports IPv6 to access the servers ECS01 and ECS02.
Open the CLI of the client.
Run the following command multiple times to test whether requests from the IPv6 client are forwarded to the IPv4 and IPv6 ECS instances based on round-robin.
curl -6 http://<Domain name> -vThe following echo reply packet indicates that the IPv6 client can access the IPv4 ECS instance.
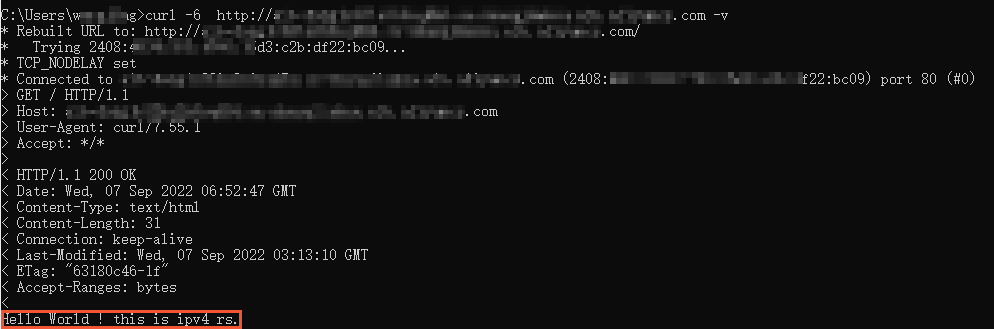
The following echo reply packet indicates that the IPv6 client can access the IPv6 ECS instance.
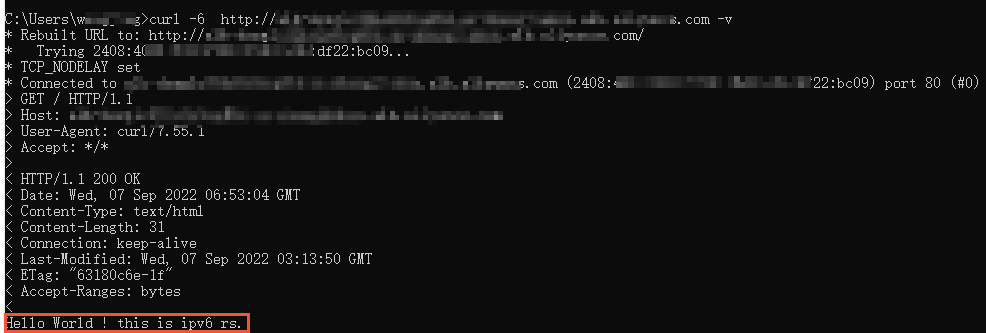
The preceding results show that requests from the IPv6 client are forwarded to the IPv4 and IPv6 services in the VPC based on round-robin.
Release resources
Release the ECS instances and the security groups.
Delete ECS01 and its security group:
Log on to the ECS console. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which ECS01 instance resides, and click the
 icon on the right side of ECS01. In the dialog box that appears, select Release to immediately release the instance.
icon on the right side of ECS01. In the dialog box that appears, select Release to immediately release the instance. Log on to the ECS console. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which ECS01 resides, select the security group of ECS01, and then click Delete to delete the security group.
Repeat the preceding steps to delete ECS02 and its security group.
Delete the DNS records:
For more information, see Delete a DNS Record.
Release ALB resources:
Log on to the ALB console. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the ALB instance resides. Find the ALB instance, click the
 icon in the Actions column, and click Release. In the message that appears, click Confirm.
icon in the Actions column, and click Release. In the message that appears, click Confirm.For more information about how to remove backend servers, see Remove a backend server.
For more information about how to delete a server group, see Delete a server group.
Release VPC resources:
Log on to the VPC console. In the top navigation bar, select the region where the VPC resides.
Click Delete on the right side of the VPC. The system checks if any cloud service or network resources are still associated with the VPC and have not been deleted. The VPC can only be deleted once no resources are associated with it.
References
For ALB use scenarios and components, see What is ALB?
For ALB features, see Features.
For ALB quotas and how to request a quota increase, see Limits.
For ALB-available regions and zones, see Regions and zones.
For ALB billing rules, billable items, and pricing, see ALB billing overview.