This topic describes how to use Alibaba Cloud SDKs for Go in an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) on Windows. In this example, Visual Studio (VS) Code is used.
Prerequisites
Go is installed. For more information, see Install Go on Windows.
VS Code is installed. For more information about how to install VS Code, see Build a Go development environment on Windows.
Use SDKs
Use a sample project provided by in OpenAPI Explorer
You may be unable to download sample projects for specific API operations. In this case, use SDKs in your existing projects.
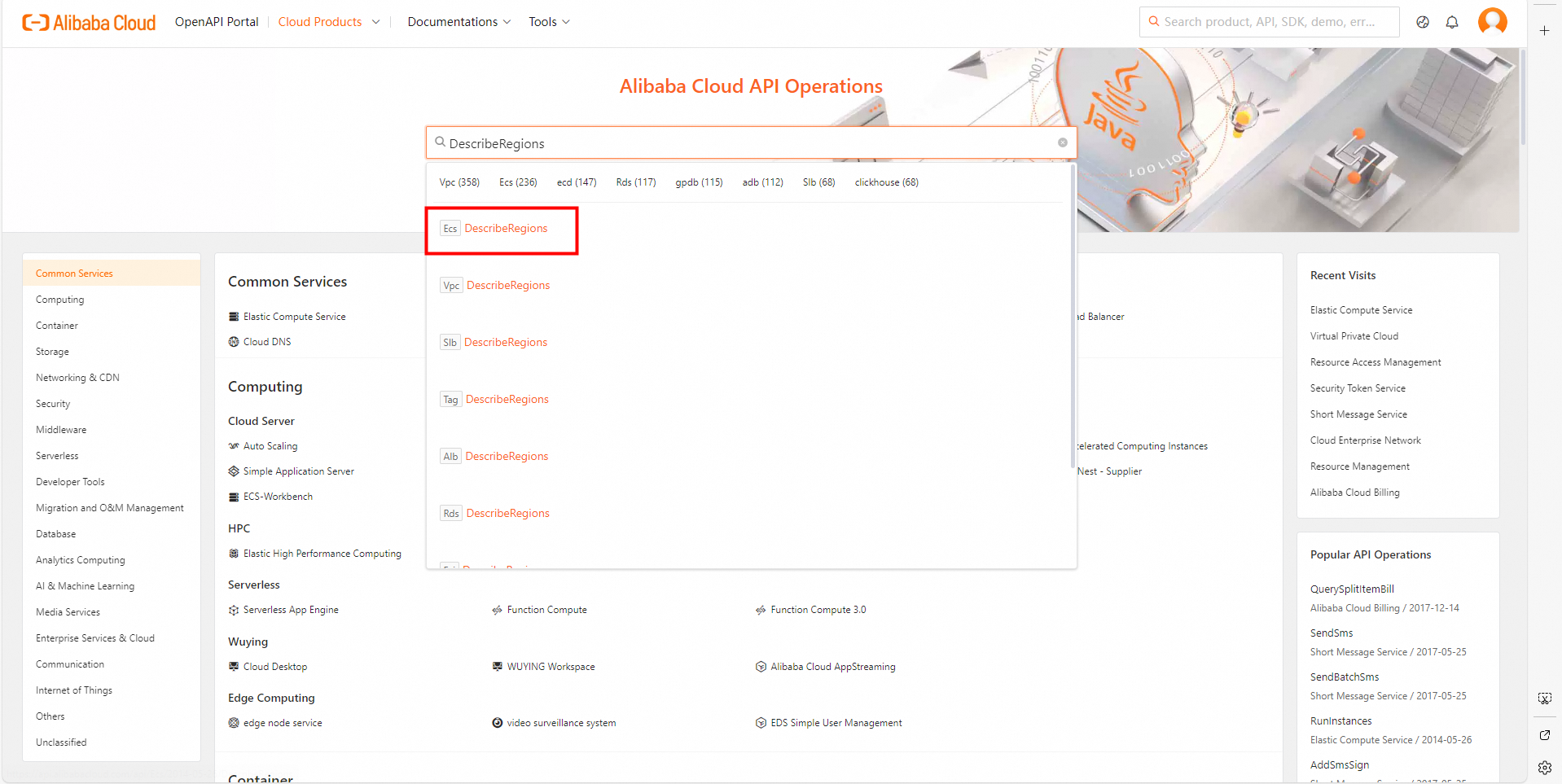
Go to OpenAPI Explorer. Search for the API operation that you want to use. In this example, the DescribeRegions operation of Elastic Compute Service (ECS) is used. Enter DescribeRegions in the search box and click the operation name in the search results to go to the API debugging page.
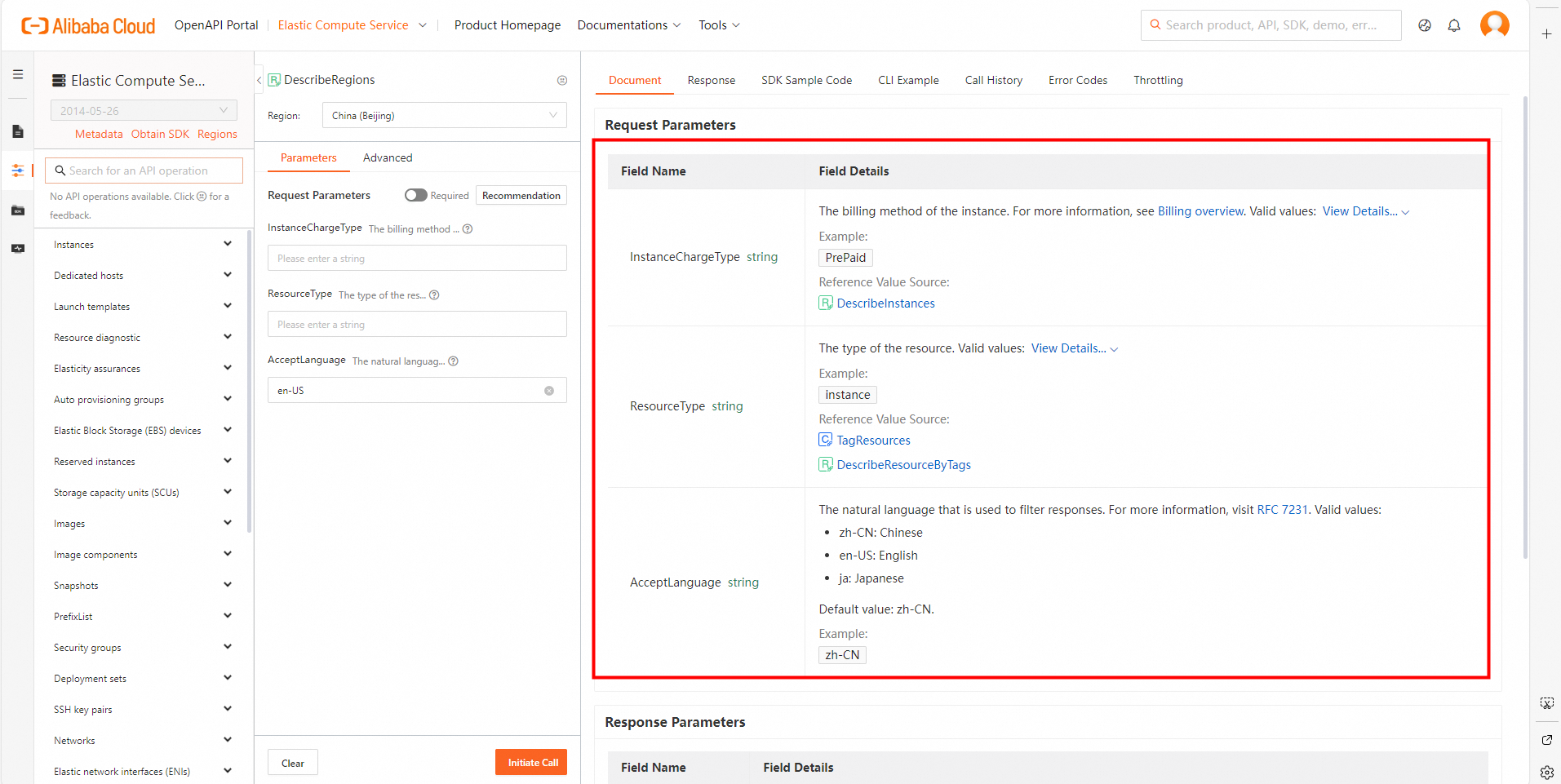
On the Parameters tab in the middle column, specify the parameters based on your requirements. When you specify the parameters, read the information on the Document tab in the rightmost column. Make sure that you understand the usage notes of the operation and the description of each parameter. Pay attention to billing-related information.
In this example, the DescribeRegions operation supports three request parameters.
Parameter
Required
Description
InstanceChargeType
No
The billing method of instances. The supported regions vary based on the billing method. Default value: PrePaid, which indicates the subscription billing method.
ResourceType
No
The resource type. The supported regions vary based on the resource type. Default value: instance.
AcceptLanguage
No
The language in which the response is to be returned. Default value: zh-CN.
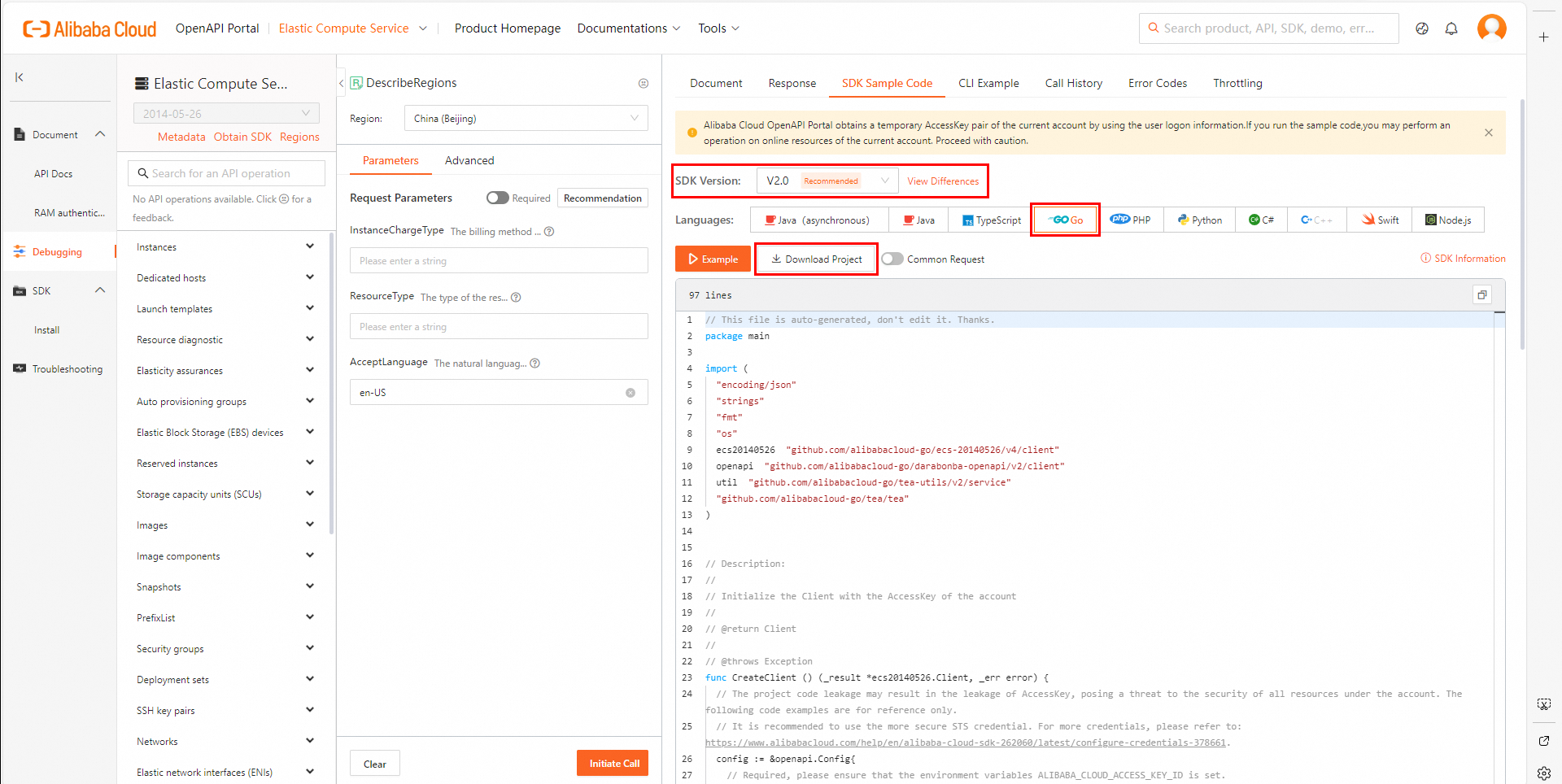
On the SDK Sample Code tab in the rightmost column, select a programming language and click Download Project to download the complete SDK project to your computer. Then, decompress the package.
Open VS Code, choose File > Open Folder in the top navigation bar, and then select the decompressed folder.
In the top navigation bar of the VS Code console, choose Terminal > New Terminal. The TERMINAL window appears in the lower part of the console.
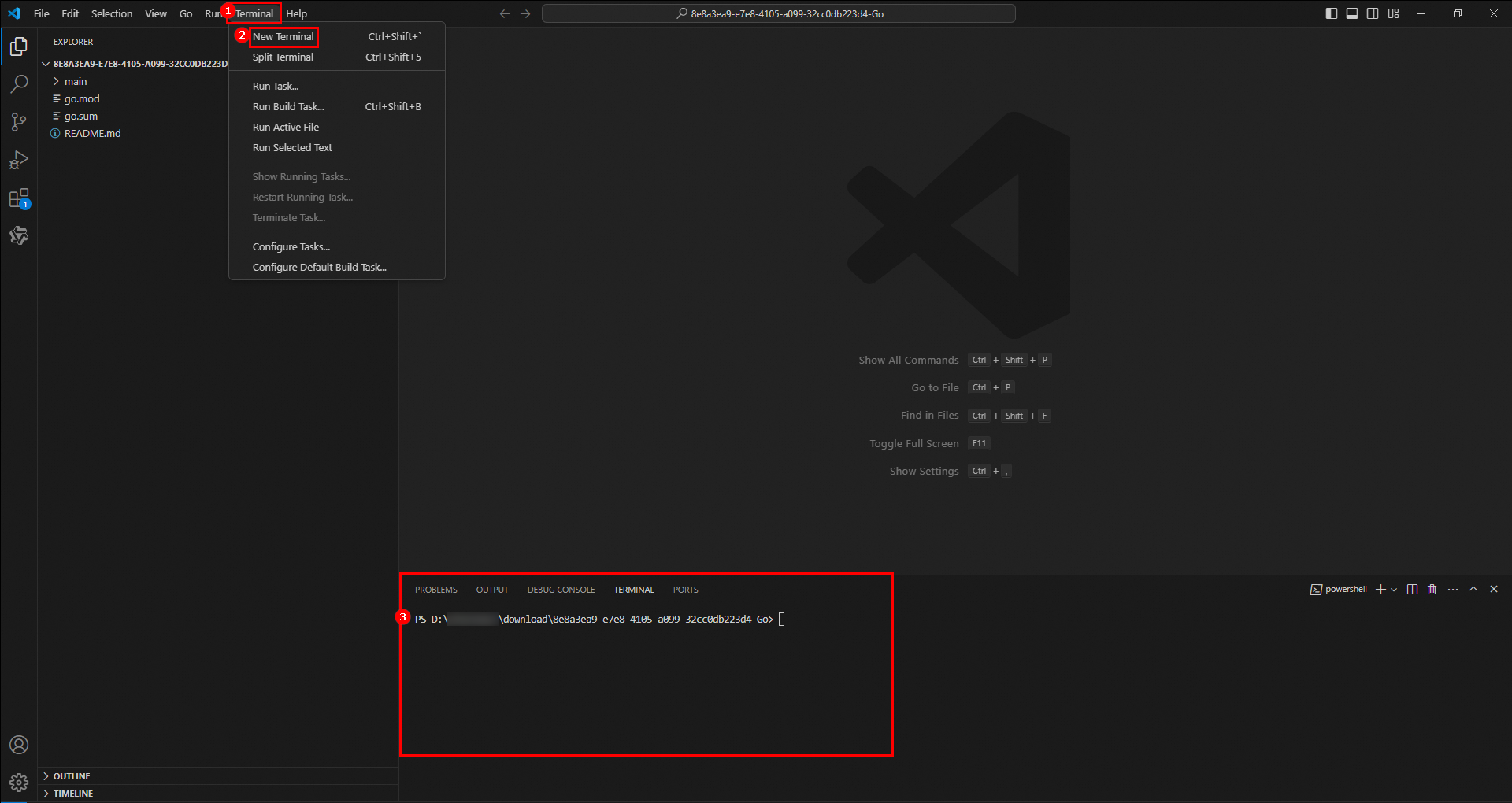
Run the following command in the terminal to tidy and update the dependencies of the current module:
go mod tidyRun the SDK demo code. Run the following command in the terminal to run the sample code in the main file:
go run ./mainView the result. Click anywhere in the terminal and press
Ctrl+Fto search forstatusCode. If"statusCode":200is displayed, the call was successful.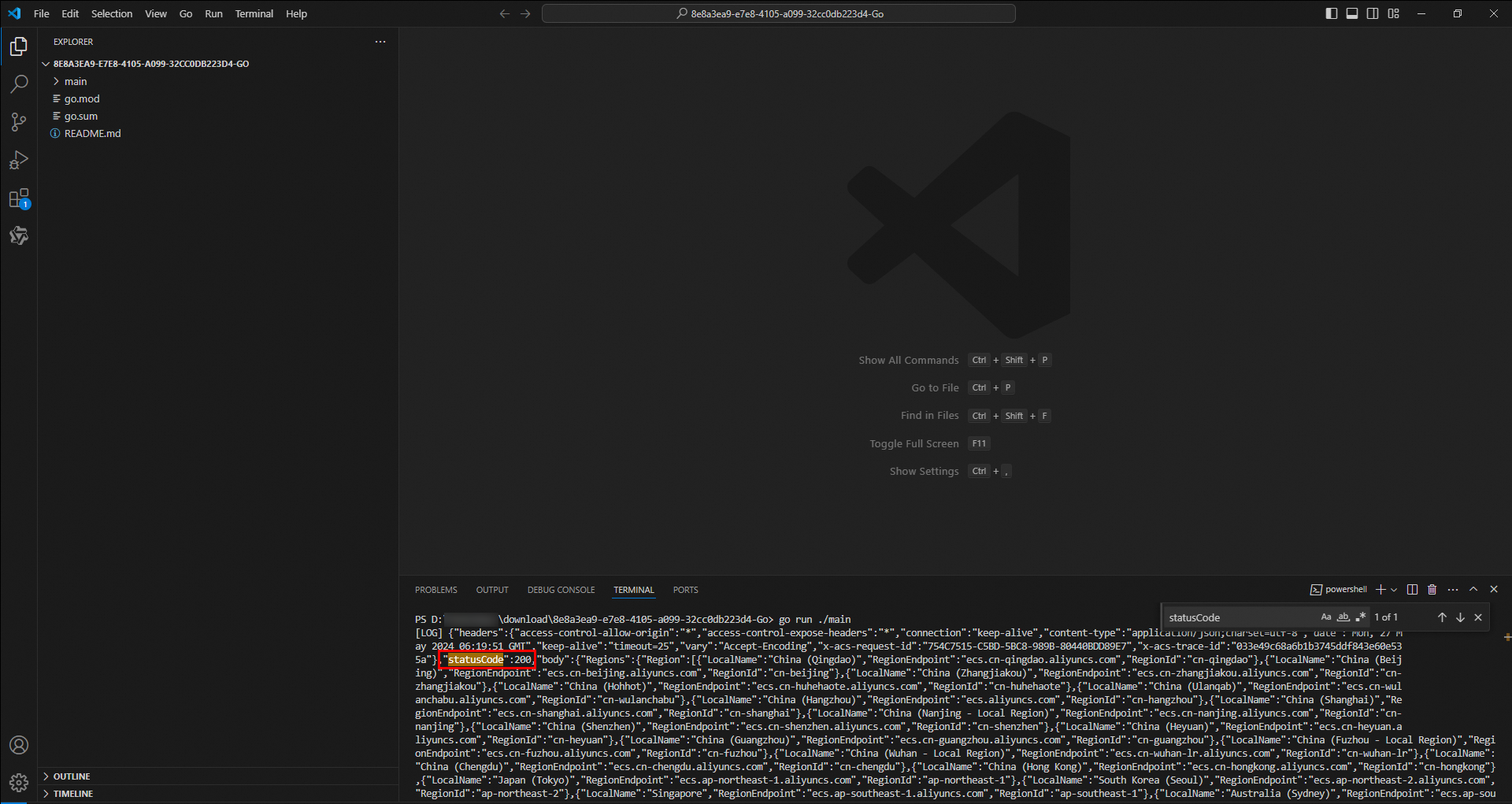
Use an SDK in an existing project
Open VS Code and choose File > Open Folder in the top navigation bar. Create and select a project folder or select an existing project folder. In this example, a folder named gosdkproject is created and selected.
In the top navigation bar, choose Terminal > New Terminal. The TERMINAL window appears in the lower part of the console. Run the
go mod init gosdkprojectscommand in the terminal to initialize the Go project.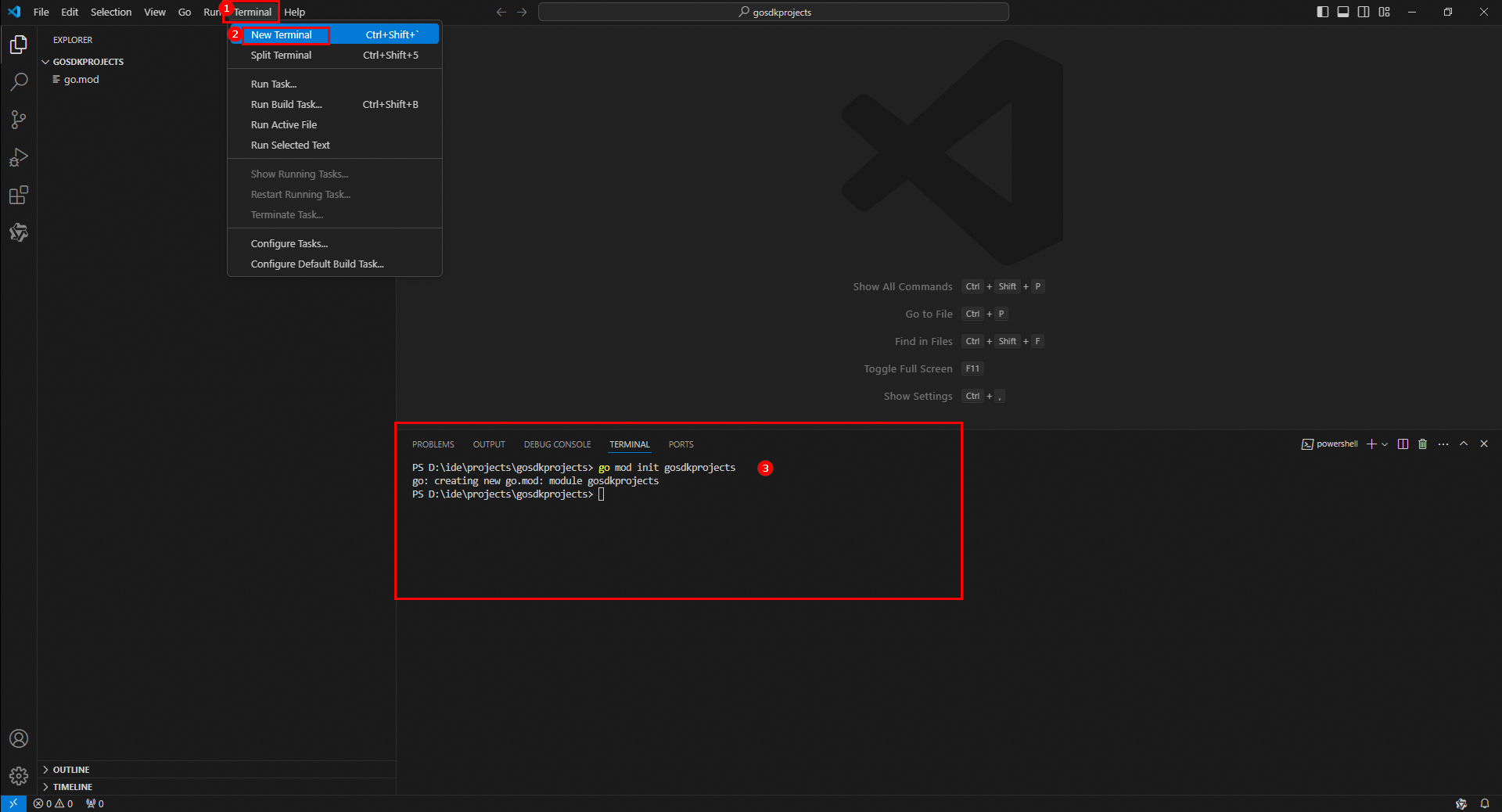
Obtain the SDK.
Visit SDK Center and select the cloud service whose SDK you want to use. In this example, ECS is used. Select V2.0 as the SDK version and Go as the programming language.
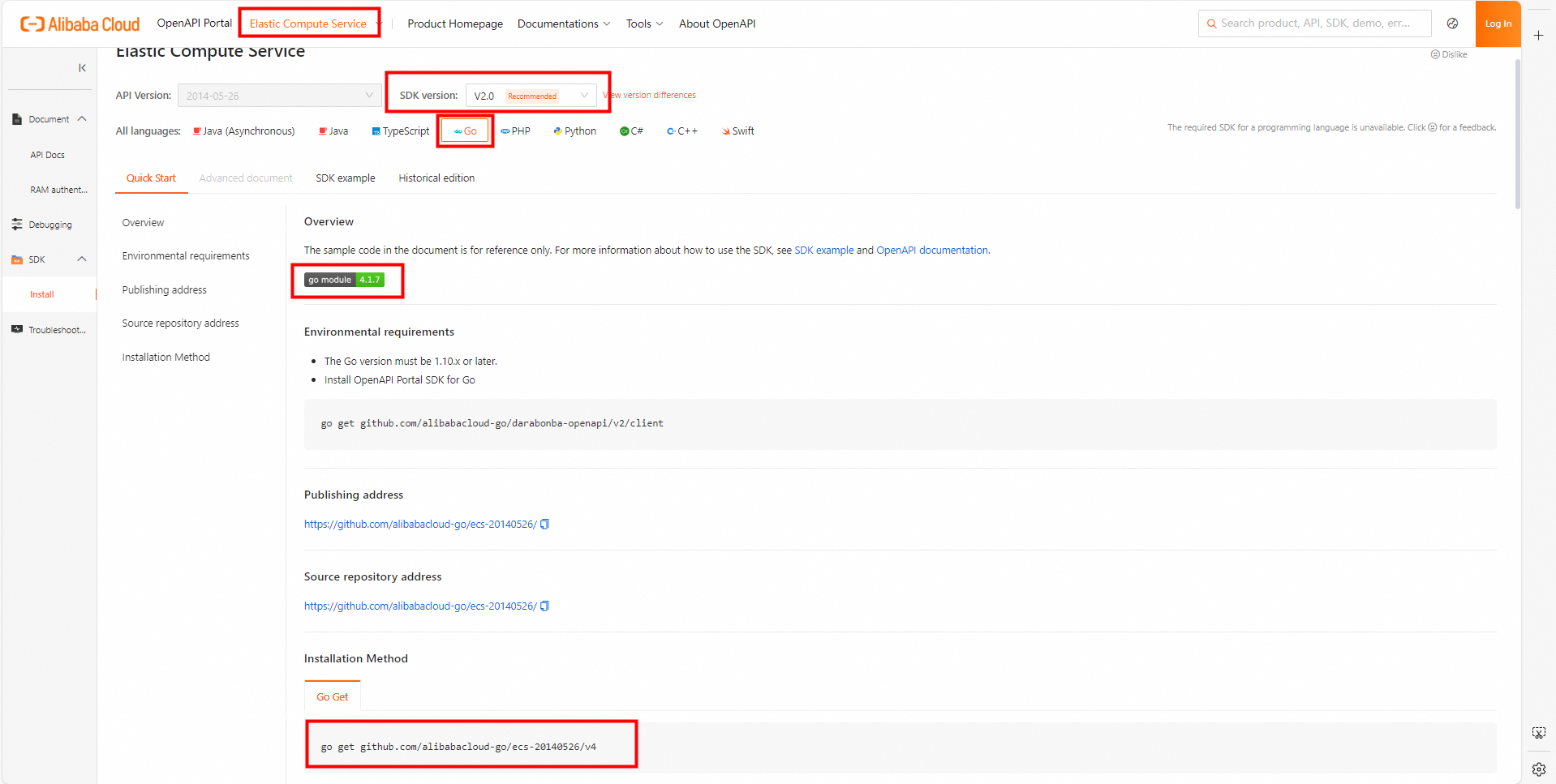
Install the SDK.
Copy the installation command to the terminal and press the Enter key.
Create a .go file. Click the New File... icon to the right of the project name and enter a file name such as ecsDescribeRegions.go.
Initialize the client.
If you want to call the ECS API, you must initialize the ECS client first.
ImportantYou must use an AccessKey pair to complete identity verification when you initialize the client. In this case, you must obtain an AccessKey pair in advance. For more information about how to obtain an AccessKey pair, see Create an AccessKey.
After you obtain the AccessKey pair of a RAM user, you must configure the AccessKey pair in environment variables. For more information, see Configure environment variables in Linux, macOS, and Windows.
For more information about how to configure the endpoint, see Endpoints.
package main import ( "os" openapi "github.com/alibabacloud-go/darabonba-openapi/v2/client" ecs20140526 "github.com/alibabacloud-go/ecs-20140526/v4/client" "github.com/alibabacloud-go/tea/tea" ) // The CreateClient function initializes and returns an ECS client. // This function takes no arguments, but you must make sure that the environment variables ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET are configured. // return *ecs20140526.Client // return error: If an error occurs during client creation, a non-nil error object is returned. func CreateClient() (_result *ecs20140526.Client, _err error) { // Initialize the openapi. Config object to configure the ECS client. config := &openapi.Config{ AccessKeyId: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID")), AccessKeySecret: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")), Endpoint: tea.String("ecs.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com"), } // Use the configurations to create and return an ECS client instance. return ecs20140526.NewClient(config) }Call the API operation. Before you call an API operation, you must read the corresponding API documentation. In this example, the DescribeRegions operation of ECS is used.
NoteEach API operation has a request object, named in the ${API name}${Request} format. Example: DescribeRegionsRequest.
package main import ( "os" openapi "github.com/alibabacloud-go/darabonba-openapi/v2/client" ecs20140526 "github.com/alibabacloud-go/ecs-20140526/v4/client" "github.com/alibabacloud-go/tea/tea" ) // The CreateClient function initializes and returns an ECS client. // This function takes no arguments, but you must make sure that the environment variables ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET are configured. // return *ecs20140526.Client // return error: If an error occurs during client creation, a non-nil error object is returned. func CreateClient() (_result *ecs20140526.Client, _err error) { // Initialize the openapi. Config object to configure the ECS client. config := &openapi.Config{ AccessKeyId: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID")), AccessKeySecret: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")), Endpoint: tea.String("ecs.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com"), } // Use the configurations to create and return an ECS client instance. return ecs20140526.NewClient(config) } // The InvokeApi function is used to call the DescribeRegions operation of ECS to query the available regions. // // Response: // _result: returns a pointer of the *ecs20140526.DescribeRegionsResponse type, which contains the queried regions. // _err: returns an error message of the error type. If an error occurs during the call, the value is not empty. func InvokeApi()(_result *ecs20140526.DescribeRegionsResponse, _err error) { // Create an ECS client. client, _err := CreateClient() if _err != nil { // If an error occurs during client creation, an error message is returned. return _result, _err } // Create a DescribeRegions request. describeRegionsRequest := &ecs20140526.DescribeRegionsRequest{} // Initiate a DescribeRegions request and return the result. return client.DescribeRegions(describeRegionsRequest) }Handle exceptions.
Alibaba Cloud SDKs for Go handle exceptions by returning error messages. For more information, see Exception handling. However, in unpredictable situations, you may need to use
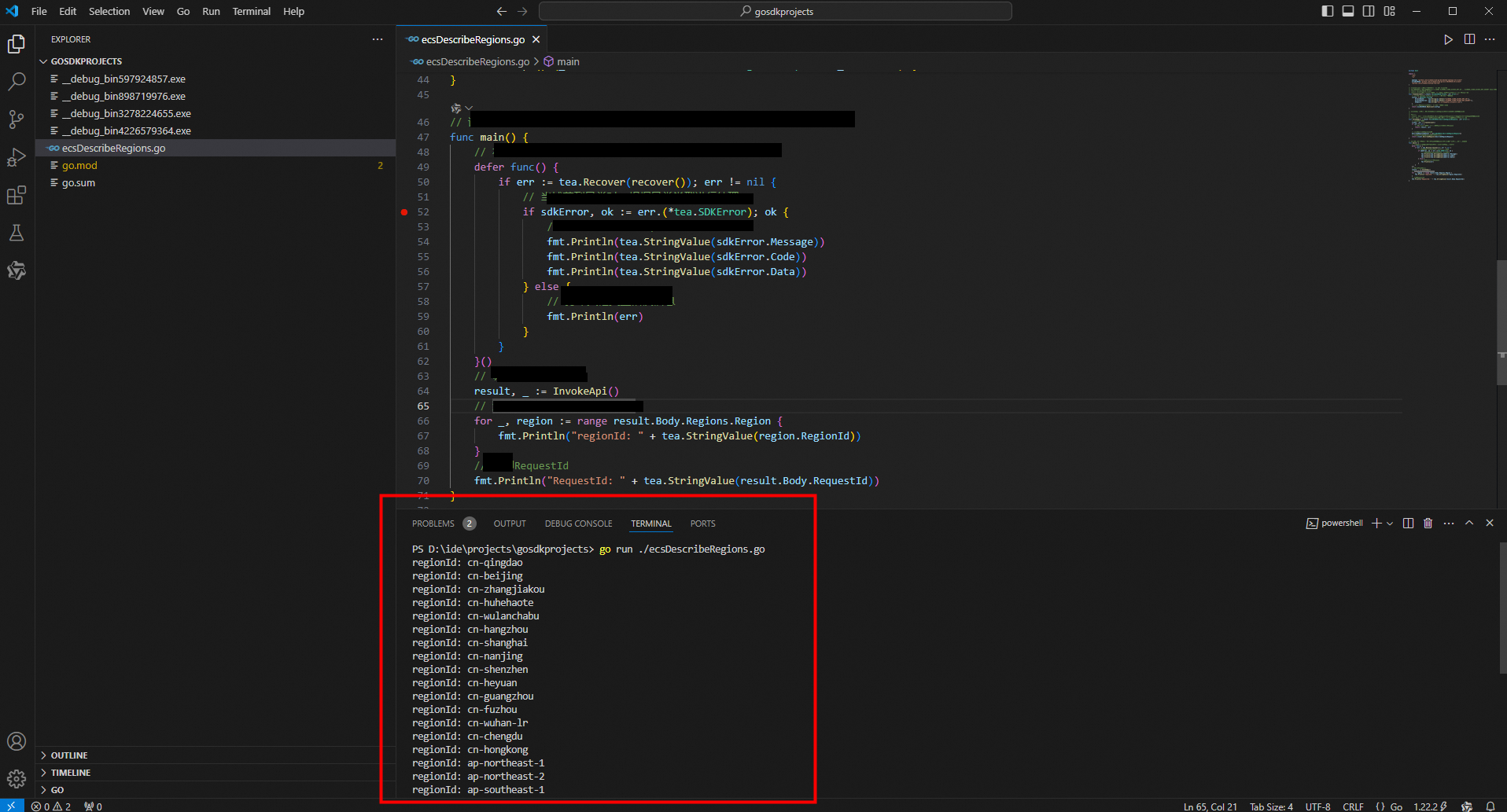
panicandrecoverto handle exceptions. Whenpanicis used to handle exceptions in Go, it immediately stops the execution of the current function. In this case, panic is generally used together with defer to capture the currentpanicby usingrecoverindeferto restore the normal execution process. Therefore, proper use ofpanic,defer, andrecovercan help build more robust error-handling logic, especially when dealing with critical errors that can cause a program to crash.package main import ( "fmt" "os" openapi "github.com/alibabacloud-go/darabonba-openapi/v2/client" ecs20140526 "github.com/alibabacloud-go/ecs-20140526/v4/client" "github.com/alibabacloud-go/tea/tea" ) // The CreateClient function initializes and returns an ECS client. // This function takes no arguments, but you must make sure that the environment variables ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID and ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET are configured. // return *ecs20140526.Client // return error: If an error occurs during client creation, a non-nil error object is returned. func CreateClient() (_result *ecs20140526.Client, _err error) { // Initialize the openapi. Config object to configure the ECS client. config := &openapi.Config{ AccessKeyId: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID")), AccessKeySecret: tea.String(os.Getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")), Endpoint: tea.String("ecs.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com"), } // Use the configurations to create and return an ECS client instance. return ecs20140526.NewClient(config) } // The InvokeApi function is used to call the DescribeRegions operation of ECS to query the available regions. // // Response: // _result: returns a pointer of the *ecs20140526.DescribeRegionsResponse type, which contains the queried regions. // _err: returns an error message of the error type. If an error occurs during the call, the value is not empty. func InvokeApi() (_result *ecs20140526.DescribeRegionsResponse, _err error) { // Create an ECS client. client, _err := CreateClient() if _err != nil { // If an error occurs during client creation, an error message is returned. return _result, _err } // Create a DescribeRegions request. describeRegionsRequest := &ecs20140526.DescribeRegionsRequest{} // Initiate a DescribeRegions request and return the result. return client.DescribeRegions(describeRegionsRequest) } // This function can obtain region information by calling API operation and handle and recover from exceptions. func main() { // We recommend that you use defer only for deep recursion scenarios or unexpected errors. defer func() { if err := tea.Recover(recover()); err != nil { // When an exception is caught, handle it based on the exception type. if sdkError, ok := err.(*tea.SDKError); ok { // Display the error message, error code, and related data. fmt.Println(tea.StringValue(sdkError.Message)) fmt.Println(tea.StringValue(sdkError.Code)) fmt.Println(tea.StringValue(sdkError.Data)) } else { // Display other types of error messages. fmt.Println(err) } } }() // Call the API operation to obtain the result. result, _ := InvokeApi() // Traverse and display the regions that are returned. for _, region := range result.Body.Regions.Region { fmt.Println("regionId: " + tea.StringValue(region.RegionId)) } // Display the request ID. fmt.Println("RequestId: " + tea.StringValue(result.Body.RequestId)) }Run the code by using the
go runcommand in the terminal.