This topic describes how to view and manage the backup size of an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. You can delete backups or reduce their size as needed. For more information, see Backup billing.
View backup size
Total backup size = Data backup size + Log backup size
You can view the value of the Backup Usage parameter in the Instance Resource section on the Basic Information page of the instance.
After you perform a minor version update on an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance or a Serverless ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance of the Basic Edition, the Backup Usage on the Basic Information page of the instance may show a value of 0. The value is automatically restored after the next scheduled backup is complete.
For example, in the following figure, the total backup size is 33.2 GB for data backups plus 20.19 MB for log backups. In the figure, Archived Backup refers to data backups retained for more than two years (730 days), and Data refers to non-archived data backups.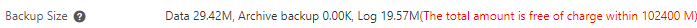
Backup size details
Delete or reduce data backups
Manually delete data backups
You can manually delete only the MySQL backup data that is generated by a manual backup. You cannot manually delete automatic backup data. You can hover over the
 icon in the Backup Policy column of the target backup set to determine whether the backup set was automatically generated or manually created.
icon in the Backup Policy column of the target backup set to determine whether the backup set was automatically generated or manually created.You cannot manually delete manual backup sets that are database and table backups. Check the Backup Policy column for the target backup set to determine whether it is a Database/Table Backup.
The deletion of a manual backup set is permanent and cannot be recovered.
Go to the RDS instance list, select a region in the top navigation bar, and then click the target instance ID.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Backup and Restoration.
On the Backup and Restoration page, choose Base Backups > Data Backup.
In the Actions column of the target backup set, click
 > Delete.
> Delete.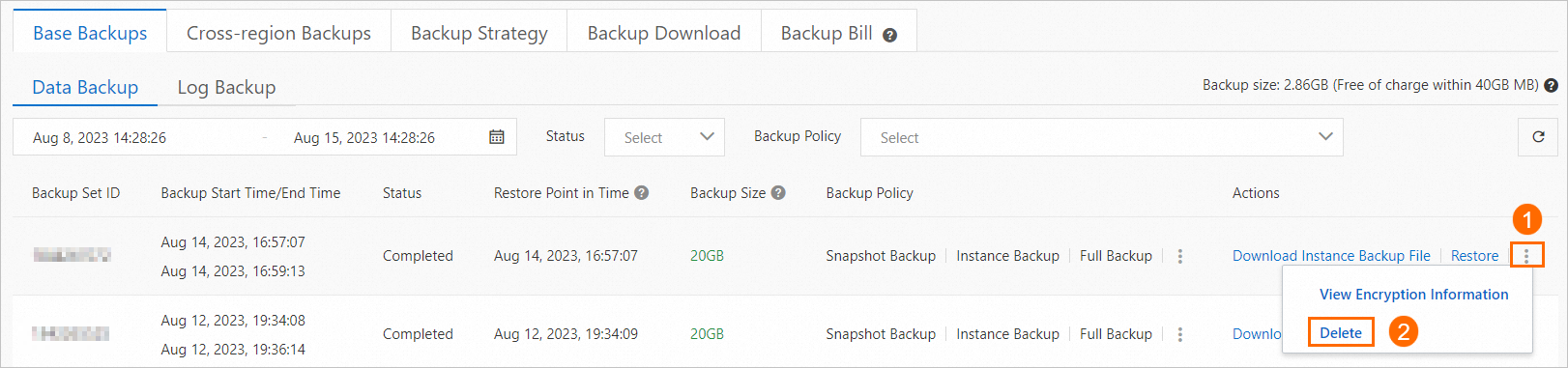
Automatically delete data backups
This method applies to deleting MySQL backup data from both manual backups and automatic backups.
Go to the RDS instance list, select a region in the top navigation bar, and then click the target instance ID.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Backup and Restoration.
On the Backup and Restoration page, click the Backup Strategy tab.
In the Basic Backup section, click Edit and shorten the data backup retention period.
ImportantFor example, if the data backup retention period is set to 30 days:
For instances that are not upgraded to support point-in-time recovery, the system automatically deletes data backup sets that are older than 30 days. These backups cannot be recovered. Proceed with caution.
For instances that are upgraded to support point-in-time recovery, the retention period of data backup sets may exceed 30 days. For more information, see Point-in-time recovery policies, and the differences between point-in-time recovery and log backup.
Reduce data backups
Method 1: Reduce the number of data backups
Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console and go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the instance ID.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Backup and Restoration.
On the Backup and Restoration page, click the Backup Strategy tab.
In the Basic Backup section, click Edit and reduce the backup cycle.
Method 2: Use sparse backup to retain a minimum number of backup sets
Instances in some regions support upgrading the Backup Policy page to the Premium Edition. After the upgrade, you can use sparse backup to configure backup policies with more flexibility and retain a minimum number of backup sets. For more information, see Sparse backup.
Method 3: Delete or migrate data that does not require backups
Reduce or disable log backups
When you enable the log backup feature, local logs (binary logs) are uploaded to your backup storage space in real time. You can delete or reduce these log backups as needed.
Local logs for MySQL are log files that record all operations that change data in a MySQL database. You can use these logs for purposes such as building a custom master-slave architecture or subscribing to data. For more information about how to query or delete local logs, see Manage local logs (binary logs).
Reduce log backups
Method 1: Shorten the log backup retention period
You can set the log backup retention period only if Log Backup or Point-in-time Restore is enabled. To check the enabling status, see View the log backup policy.
Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console and go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the instance ID.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Backup and Restoration.
On the Backup and Restoration page, click the Backup Strategy tab.
In the Basic Backup section, click Edit. Then, shorten the Log Backup Retention Period (days). For more information, see Differences between the PITR and log backup features.
ImportantFor example, if Log Backup Retention Period (days) is set to 30:
For instances that have not been upgraded to support point-in-time recovery, log backup sets older than 30 days are automatically deleted and cannot be recovered. Proceed with caution.
For instances that have been upgraded to support point-in-time recovery, the system retains the log backups required to perform point-in-time recovery to any point within the 30-day period. As a result, the total retention period for some log backups may exceed 30 days. For more information, see Point-in-time recovery policy.
Method 2: Use sparse backup to retain the minimum number of backup sets
Instances in some regions now support upgrading the backup policy page to the Premium Edition. After you upgrade, you can use sparse backup to configure backup policies more flexibly and retain the minimum number of backup sets. For more information, see Sparse backup.
Method 3: Reduce unnecessary insert, delete, and update operations, and minimize updates to large objects
Insert, delete, and update operations on a database increase the size of its log backups.
You can use the SQL Explorer feature to view the insert, delete, update, and query records in your database.
Disable log backup
Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console and go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the instance ID.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Backup and Restoration.
On the Backup and Restoration page, click the Backup Strategy tab.
In the Basic Backup section, click Edit. Then, turn off the Log Backup or Point-in-time Restore switch.
ImportantAfter you disable the log backup feature, the system automatically deletes existing log backup files within 1 to 3 minutes. Deleted log backup files cannot be restored. Proceed with caution.
Related operations
To delete a data backup file for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance, see DeleteBackup - Delete a data backup file of an instance.
To change the data backup or log backup policy for an instance, see ModifyBackupPolicy - Modify the backup policy of an instance.