The point-in-time restoration (PITR) feature is supported for ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instances. To use the PITR feature, you must turn on Restoration to Specific Point in Time and configure the Time Range of Specific Points in Time for Restoration parameter on the Backup Strategy tab. The system retains backup sets based on the correlation between the full and log backup files and implements PITR based on the value of the Time Range of Specific Points in Time for Restoration parameter that you specify.
Feature description
If you use conventional backup methods, backup sets of your RDS instance are retained based on the backup retention period that you specify. Even if no exceptions occur during the backup process and the retention of backup sets, the restorable time range of your RDS instance is shorter than the log retention period. The restorable time range varies based on the number of days between consecutive full backups and the retention period of backup sets. If issues such as backup latency or backup failures occur, the restorable time range of your RDS instance is not guaranteed.
The PITR feature organizes and manages the backup sets of your RDS instance based on PITR requirements. When a backup set is retained, the feature ensures that a valid full backup and a continuous log backup chain exist outside of the specified restorable time range. This ensures that you can restore the data of your RDS instance to any point in time.

Differences between the PITR and log backup features
The PITR and log backup features use the same log generation and backup mechanisms. However, the PITR feature uses the optimized expiration and retention policies for backup sets. The following table compares the features when full backups are performed three times a week on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday, and the Time Range of Specific Points in Time for Restoration or Log Backup Retention Period (Days) parameter is set to 7.
Item | Log backup (Log Backup Retention Period (Days) is set to 7) | PITR (Time Range of Specific Points in Time for Restoration is set to 7) |
Restorable time range in expected cases | Up to seven days. Note In expected cases, the restorable time range is shorter than seven days. The restorable time range can reach seven days only when the backup sets expire and are scheduled for deletion. | Fixed as seven days. |
Restorable time range in most cases | Four to five days. Note The restorable time range depends on the number of days between consecutive full backups. The restorable time range is shortened at regular intervals, which can be calculated by using the following calculation: | Fixed as seven days. |
Restorable time range in extreme cases | Shorter than three days. Note If continuous full backup failures or occasional data exceptions occur due to database deadlocks, the restorable time range may be shortened to three days or less. In extreme cases, you may even fail to restore data. | Fixed as seven days. |
Restoration cost | If the system retains backup sets for seven days, you are charged for the storage of the backup sets for seven days. | If the system retains backup sets for seven to nine days, you are charged for the storage of the backup sets for seven to nine days. Important The system retains an additional full backup for more than seven days and all consecutive log backups generated from the seventh day to the day in which the last full backup is generated. You are charged for the storage of one full backup and additional log backups that are generated within one week at most. |
Prerequisites
Your RDS instance meets the following requirements:
The RDS instance uses local SSDs, standard SSDs, general Enterprise SSDs (ESSDs), or ESSDs. Serverless RDS instances are supported.
The PITR feature is rolled out for RDS instances in regions in phases. The information in the ApsaraDB RDS console shall prevail. For more information about supported regions, see [Product changes/Feature changes] PITR is rolled out in phases for ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instances from January 11, 2024.
You can go to the Basic Information page of your RDS instance to obtain the preceding information.
Usage notes
After you enable the PITR feature, all backup sets that have not expired and are newly generated are retained based on the value of the Time Range of Specific Points in Time for Restoration parameter.
Limits
You can configure PITR settings only on the regular backup policy page. The advanced backup policy or sparse backup policy page does not support the settings. You can continue to use the log backup feature. For more information, see Procedure.
You cannot use the PITR feature for a serverless RDS instance within the periods of time between the stop and startup of the serverless RDS instance and between the startup and the completion of the first full backup of the serverless RDS instance.
Billing rules
The billing rules remain unchanged. To implement PITR, the system retains additional backup sets based on the value of the Time Range of Specific Points in Time for Restoration parameter. You are also charged for the storage of the additional backup sets. For more information, see View and manage the size of backup files. A free quota on storage is provided to store backup files. If the total size of the backup files of your RDS instance does not exceed the free quota, you are not charged. If the total size exceeds the free quota, you are charged for the excess storage. For more information, see Backup storage fees.
Procedure
If your RDS instance is created on or after January 11, 2024, you can perform the following operations to configure a PITR policy. After you enable the PITR feature for your RDS instance, subsequent backup sets and the backup sets that have not expired are retained based on the value of the Time Range of Specific Points in Time for Restoration parameter.
If your RDS instance was created before January 11, 2024, you can use the settings in the dialog box on the Backup Strategy tab to upgrade the log backup feature to the PITR feature. The upgrade cannot be rolled back. For more information, see Upgrade to the PITR feature.
Go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the ID of the instance.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Backup and Restoration.
On the Backup and Restoration page, click the Backup Strategy tab. In the Basic Backup section, click Edit.
Configure the following parameters and click OK.
 Important
ImportantIf you do not find Restoration to Specific Point in Time, you can join the DingTalk group (ID: 35585947) for Data Disaster Recovery to consult or apply for using the feature.
Parameter
Description
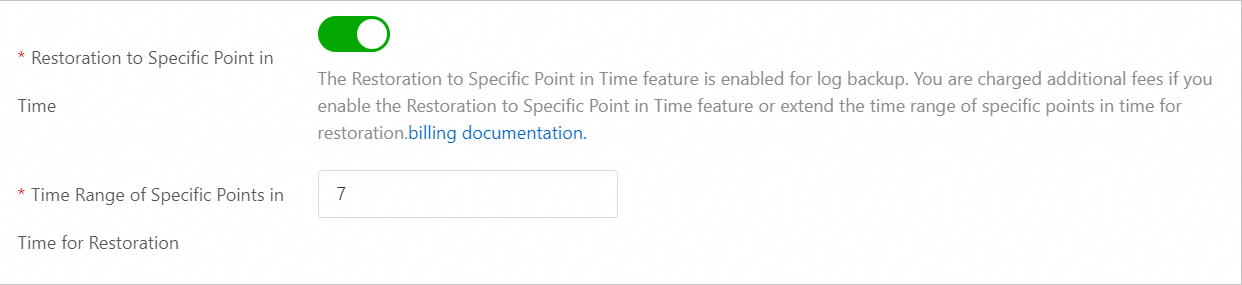
Restoration to Specific Point in Time
Specifies whether to enable the PITR feature. After the feature is enabled, you can restore the data of your RDS instance to any point in time. The feature is an enhancement of the log backup feature. By default, Time Range of Specific Points in Time for Restoration is turned on for new RDS instances.
Time Range of Specific Points in Time for Restoration
The number of days during which you can restore data of your RDS instance to any point in time. If the value of this parameter is modified, the retention period of log backups is also modified.
Valid values: 7 to 730. Default value: 7.
The value must be less than or equal to the retention period of full backups.
NoteIf your RDS instance runs MySQL 5.7 on RDS Basic Edition, the value is fixed as 7.
Turn off Restoration to Specific Point in Time
On the Backup Strategy tab, click Edit to the right of Basic Backup. In the dialog box that appears, turn off Restoration to Specific Point in Time.
If you turn off Restoration to Specific Point in Time, the log backup feature is disabled, and the PITR feature is unavailable. Exercise caution when you perform this operation.

What to do next
Use data backups and log backups to restore data to an existing RDS instance, a new RDS instance, or a self-managed MySQL instance. For more information, see Overview of data restoration methods.
Download existing data backups or log backups to your on-premises device for archiving, or download backup files and upload the backup files to Object Storage Service (OSS) buckets. For more information, see Download backup files.