Data Science Workshop (DSW) provides a cloud-based IDE for AI development. If you are familiar with tools like Jupyter Notebook or Visual Studio Code, you can quickly start developing models. This document shows you how to create a DSW instance and troubleshoot common issues.
Quickly create a basic DSW instance
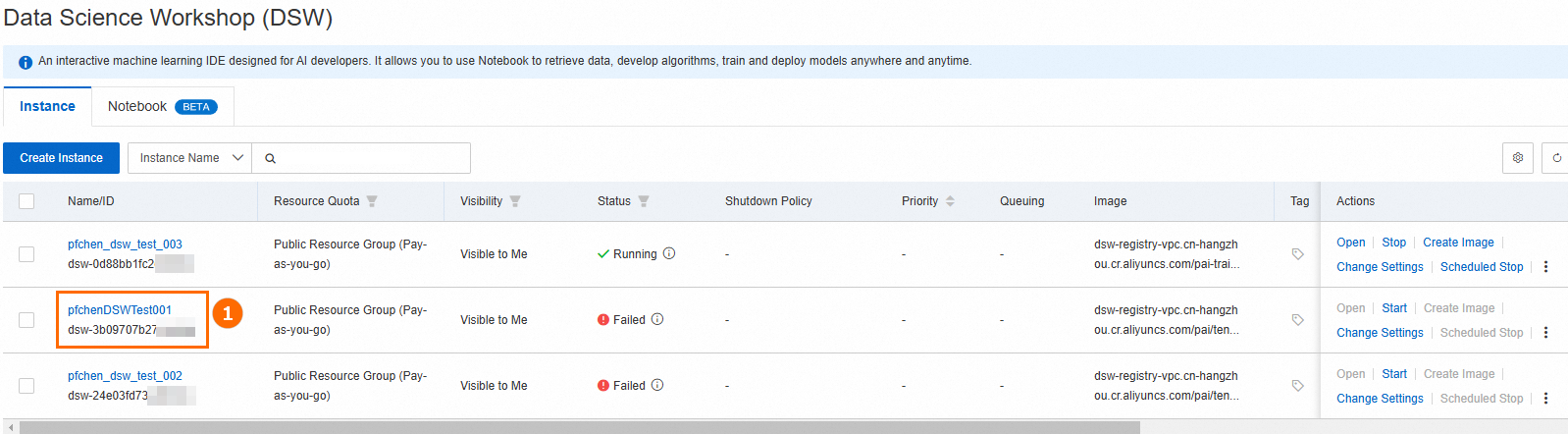
Log on to the PAI console, select a Region, and in the left-side navigation pane, click Workspaces. Select and enter the target workspace.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Interactive Modeling (DSW) > Create Instance. Configure the following key parameters and leave the others at their default settings. For a complete list of console parameters, see Full list of console parameters.
Parameter | Description |
Instance Name | Example: dsw_test. |
Resource Type | Select Public Resources. This resource type uses the pay-as-you-go billing method. |
Instance Type | Example: ecs.gn7i-c8g1.2xlarge (1 × A10 GPU, 8 vCPUs, 30 GiB memory). If this instance type is out of stock, try selecting another one from the list. |
Image config | Select Alibaba Cloud Image, then search for and select modelscope:1.31.0-pytorch2.8.0-gpu-py311-cu124-ubuntu22.04 (Python 3.11, CUDA 12.4). We recommend using ModelScope images for their broad compatibility and comprehensive set of third-party libraries. |
Click OK to create the instance. When the instance status changes to Running, it is ready.
If the instance fails to start, see Start a DSW instance.
On the DSW instance list page, find the instance and click Open in the Actions column to go to the DSW instance and start developing models.
For more information about the features of the DSW instance interface and how to stop, release, or change a DSW instance, see Access and manage DSW instances in the console.
Warning A DSW instance created with public resources starts incurring runtime charges as soon as it enters the running state, even if you do not open the WebIDE or run any code. To avoid unnecessary charges, stop or delete the DSW instance promptly when you no longer need it.
The system disk for the DSW instance created from public in this example is a free cloud disk. If the instance remains stopped for more than 15 consecutive days, the data on the cloud disk is permanently deleted and cannot be recovered. Back up important data in a timely manner, or mount a cloud storage service and transfer your data.
Configure for common use cases
A basic DSW instance might not meet all AI development needs. The following table summarizes configurations for common use cases.
Use case | Need / Pain point | Key configuration | Related documentation |
Persistently store code and data | The system disk of a DSW instance provides temporary storage. Data is deleted when the instance is deleted or remains stopped for an extended period.
Save important files for long-term use or share data between multiple instances. | Use Dataset Mounting or Mount storage to mount cloud storage, such as Object Storage Service (OSS), to a specified folder on an instance. | Mount a dataset, OSS bucket, NAS file system, or CPFS file system |
Increase public network download speed | DSW instances use a shared gateway by default. Due to bandwidth limitations, download speeds for large files might be insufficient. | In the network information section, configure a VPC and use a Private Gateway. This also requires a NAT Gateway and an Elastic IP Address (EIP) for the VPC. | Use a dedicated gateway to increase the public network access speed |
Develop remotely using SSH | Use local tools like VSCode or PyCharm for development and debugging instead of being limited to a web-based IDE. | In the access configuration, select Enable SSH, enter the SSH Public Key, and select Access over Internet. Associate an existing NAT Gateway and Elastic IP Address (EIP). | Remote connection: Connect directly using SSH |
Access web services within the instance | Publish a web application running inside the instance to the public internet so it can be accessed or shared via a URL. | In the access configuration, add a Custom Services, configure the service port, and enable public network access. Add an inbound rule to the security group to allow traffic on that port. | Access services in an instance over the Internet |
Full list of console parameters
Basic information
Parameter | Description |
Instance Name | Enter a unique, descriptive name for the instance. |
Tag | Add tags to the instance based on business needs to facilitate multi-dimensional search, location, batch operations, and billing. |
Resource information
Parameter | Description |
Resource Type | |
Environment information
Parameter | Description |
Image Configuration | The following image types are supported: Alibaba Cloud Image: PAI provides images for popular open source frameworks and Python versions. For example, the pytorch:2.4.1-gpu-py312-cu124-ubuntu22.04 image is designed for PyTorch 2.4.1, runs on a GPU-accelerated instance, and includes Python 3.12 with CUDA 12.4. To find an image with a specific version dependency, you can search for a keyword in the search box. For example, searching for cu124 returns images that use CUDA 12.4. Custom Image: You can use a custom image that has been added to PAI. The image repository must be set to allow public pulls, or the image must be stored in Container Registry (ACR). For more information, see Custom images. Image Address: You can configure the URL of a custom or official image that is accessible on the public network. To increase the image pull speed, see Image acceleration. If it is a private image URL, click enter the username and password and configure the image repository username and password.
|
System Disk | Used to store files during development. When you set Resource Type to Public Resources, or when you set Resource Quota to subscription general computing resources (CPU cores ≥ 2 and memory ≥ 4 GB, or equipped with a GPU), each instance receives a 100 GiB free disk as a system disk. You can expand the disk. The expansion price is subject to the console interface.
Warning If you only use the free quota for the cloud disk, its contents are deleted if the instance is stopped for more than 15 consecutive days. After a scale-out, the entire disk, including its free and paid portions, is no longer released if the instance is stopped for 15 days. However, billing for the scaled-out portion continues until the instance is deleted. Downgrading the disk size after expansion is not supported. Expand the disk as needed. When an instance is deleted, the cloud disk is also deleted. Ensure you back up all necessary data before deletion.
To use permanent storage, configure Dataset Mounting or Mount storage. |
Dataset Mounting | Stores datasets for reading or persists files created during development. The following two dataset types are supported: Custom Dataset: Create a custom dataset to store your training data files. You can set it to read-only and select a specific version. Public Dataset: PAI provides pre-built public datasets, which can only be mounted in read-only mode.
Mount Path: The path where the dataset is mounted in the DSW instance, for example, /mnt/data. Access the dataset from your code using this path.
Note The mount paths for multiple datasets cannot be the same. If you configure a CPFS type dataset, you must configure the network settings and ensure the selected VPC is the same as the one used by CPFS. Otherwise, the DSW instance will fail to create. When the resource group is a dedicated resource group, the first dataset must be a NAS type, and it will be mounted to both your specified path and the default DSW working directory /mnt/workspace/.
For more information about mounting, see Mount a dataset, OSS bucket, NAS file system, or CPFS file system. |
Mount storage | Use storage mounting to access datasets or persist files. For more information about mounting, see Mount a dataset, OSS bucket, NAS file system, or CPFS file system. |
Working Directory | The startup directory for JupyterLab and the Web IDE. The default is /mnt/workspace. |
Expand for more configurations
Parameter | Description |
Custom Startup Script | Customizes the environment or performs initialization tasks during instance startup. The custom script runs after the image and resources are ready but before development applications like JupyterLab and Web IDE start.
Note Timeout is 3 minutes: The custom script increases instance startup time and has a timeout of 3 minutes. Do not perform long-running tasks like image downloads in the script. View script run logs: After the instance starts, find the logs generated by the custom script in the /var/log/user-command/ directory.
|
Environment Variable | Used for the main container startup, system processes, and user processes. Add custom environment variables or override system defaults as needed. Note: Do not modify the following environment variables: # Modification will not take effect
USER_NAME # Will be overwritten by the logic in the service
# System variables that are not recommended for modification. Modification may affect normal use.
JUPYTER_NAME: Constructed from instance information by default. Can be used to modify the jupyterlab URL access path.
JUPYTER_COMMAND: Jupyter startup command. Default is set to lab to start jupyterlab.
JUPYTER_SERVER_ADDR: JupyterLab service listening address. Default is 0.0.0.0.
JUPYTER_SERVER_PORT: JupyterLab service listening port. Default is 8088.
JUPYTER_SERVER_AUTH: JupyterLab access password. Default is empty.
JUPYTER_SERVER_ROOT: Jupyter working directory. Priority is lower than WORKSPACE_DIR.
CODE_SERVER_ADDR: code-server service listening address. Default is 0.0.0.0.
CODE_SERVER_PORT: code-server service listening port. Default is 8082.
CODE_SERVER_AUTH: code-server access password. Default is empty.
WORKSPACE_DIR: The system sets this environment variable based on the working directory parameter set when the instance is created. It can change the startup directory of jupyter and code-server. An error may occur if the path does not exist.
|
Advanced Configurations | Adjusts certain secure kernel parameters required by your services. This is currently supported only for Lingjun resource group instances. For parameter details, see the table below. |
Advanced configuration parameter | Default value | Description | Notes |
VmMaxMapCount | 65530 | Sets the maximum number of memory map areas a process can have. For example, it can be set to 1024000. | Values below 65530 do not take effect. Excessively high values can lead to wasted memory resources. |
Network information
Parameter | Description |
VPC Settings | This parameter is available only when Resource Type is set to Public Resources. To use a DSW instance within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), create a VPC in the same region as the DSW instance and configure this parameter. You also need to configure a vSwitch and a Security Group. For details on configuration policies for different scenarios, see Network configuration. |
vSwitch | This parameter can be configured when a VPC is configured. A vSwitch is a subnet within a VPC. Your DSW instance and other cloud resources connect to the vSwitch. |
Security Group | This parameter is required when a VPC is configured. A security group is a virtual firewall for a DSW instance. It controls all inbound and outbound network traffic. |
Internet Access Gateway | The following configuration methods are supported: Public Gateway: The network bandwidth is limited. During periods of high user concurrency or when downloading large files, the network speed might be insufficient. Private Gateway: To solve the bandwidth limitations of the public gateway, create a public NAT Gateway in the DSW instance's VPC, bind an EIP, and configure SNAT entries. For more information, see Improve public network access speed with a dedicated gateway.
The following parameters are available only when a CPFS dataset is mounted:
Note If a CPFS dataset is mounted, you must configure a VPC, and the selected VPC must be the same as the one used by CPFS. |
Extended CIDR Block | This parameter can be configured after you configure a vSwitch. If the number of available IP addresses in the VPC is insufficient for your growing business, or if the initial network planning resulted in an address shortage, you can use an extended CIDR block to expand the VPC address space. For more information, see Use a secondary CIDR block. |
Access configuration
Parameter | Description |
Enable SSH | For remote connection to the instance. This option is available only after you select a VPC. When enabled, a Custom Services named SSH appears. If you use a custom image, ensure that sshd is installed. |
SSH Public Key | You can configure this parameter after turning on the SSH Configuration switch.
Note To support both VPC and public network login, add public keys from multiple clients. Add each public key on a new line. You can add up to 10 public keys. |
Custom Services | Used to configure SSH remote access or access services in an instance over the Internet. |
Create Private Zone in VPC | Creates an internal authoritative domain (PrivateZone). Use this domain within the VPC to access the instance's SSH service or other custom services, which avoids the inconvenience of a changing instance IP address. Creating a PrivateZone domain incurs charges. For more information, see Alibaba Cloud DNS Product Billing. |
NAT Gateway | When accessing a service in the instance from the public network, this gateway maps public requests (EIP:Port) to the private DSW instance (Private IP:Port). |
EIP | Provides a public IP address for accessing services in the instance from the public network. |
Roles and permissions
Parameter | Description |
Visibility | Choose Visible to the Instance Owner or Visible to Current Workspace. |
Instance Owner | Only the workspace administrator can change the instance owner. |
Show More
Parameter | Description |
Instance RAM Role | Associate a RAM role with the instance to grant it access to other cloud resources. This method uses temporary credentials from STS to access other cloud resources, which avoids using long-term AccessKeys and reduces the risk of key exposure.
The following options are available: Default Roles of PAI: Has permissions to access internal PAI products, MaxCompute, and OSS. Temporary access credentials issued based on the default PAI role have permissions equivalent to the DSW instance owner when accessing internal PAI products and MaxCompute tables. When accessing OSS, it can only access the default storage path bucket configured for the current workspace. Custom Roles: Configure a custom role for customized or more fine-grained permission management. Does Not Associate Role: Select this if you want to access other cloud products directly using an AccessKey.
For more information on configuring instance RAM roles, see Configure an instance RAM role for a DSW instance. |
FAQ
Start a DSW instance
Click to expand
Q: How can I diagnose and fix DSW instance startup failures?
First, check the Events tab on the instance details page for specific error messages. Common errors and their solutions are listed below.

The following are common errors and their solutions:
Your requested resource type [ecs.******] is not enough currently, please try other regions or other resource types
Cause: The selected instance type is unavailable in the current region.
Solution: Try creating the instance again later, or switch to a different instance type or region.
Your resource usage has exceeded the default limitation. Please contact us via ticket system to raise the limitation.
Cause: Your account has a default quota that limits instance specifications (e.g., a maximum of two GPUs per region per creation). This error occurs if your selection exceeds this limit.
Solution: To request a quota increase, submit a ticket.
Sales of this resource are temporarily suspended in the specified zone. We recommend that you use the multi-zone creation function to avoid the risk of insufficient resource.
CommodityInstanceNotAvailableError: Commodity instance has been released due to prolonged arrears at past. Please create a new instance for use
The charge of current ECI instance has been stopped, but the related resources are still being cleaned. or The cluster resources are fully utilized. Please try later or other regions. or Create ECI failed because the specified instance is out of stock.
back-off 10s restarting failed container=dsw-notebook pod
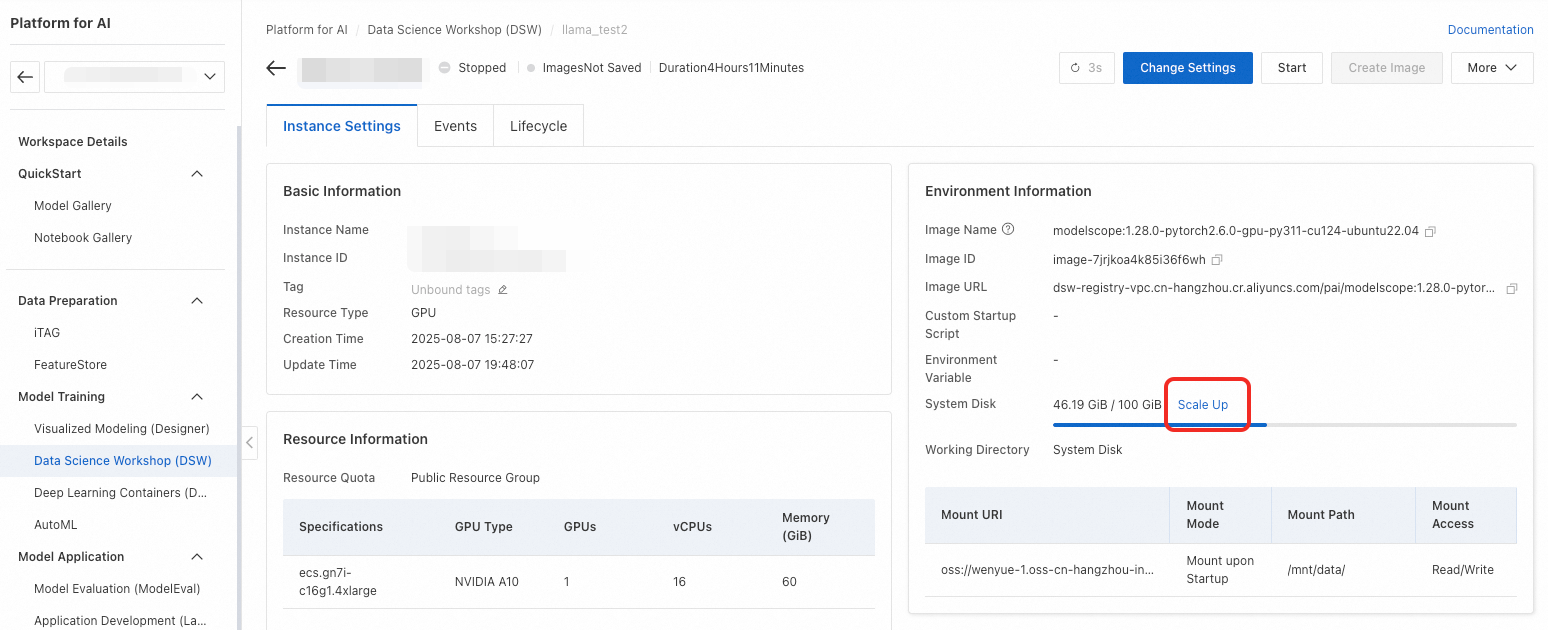
Cause: This error indicates your system disk is full. You can check disk usage in the DSW terminal:
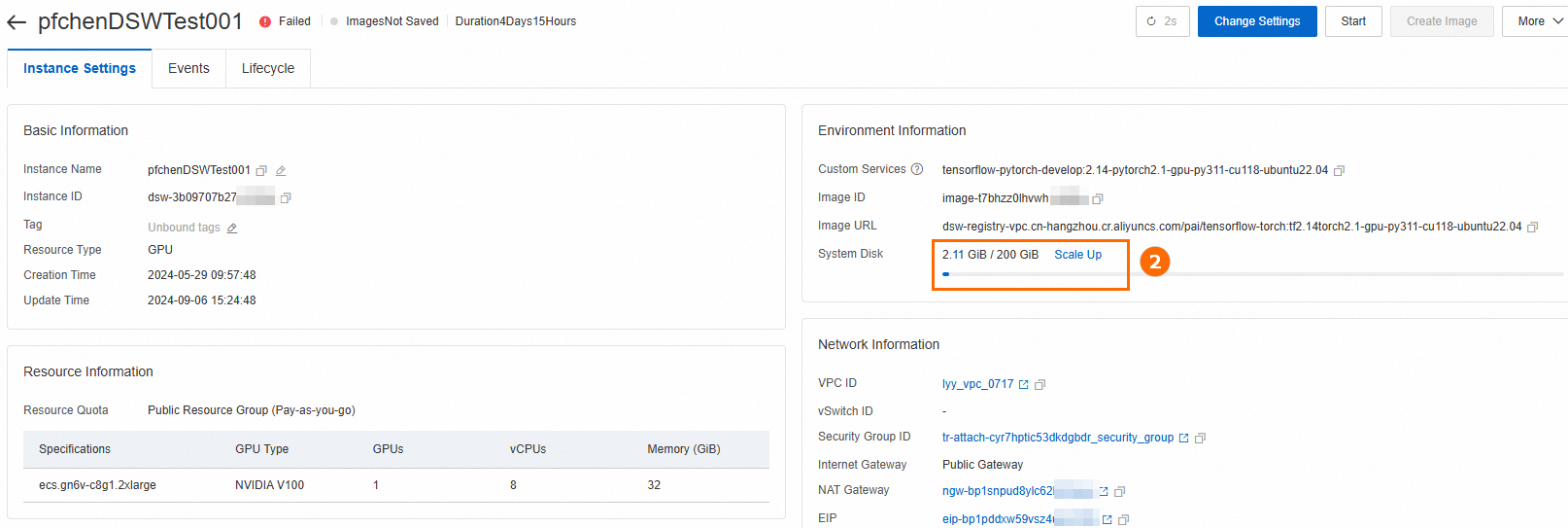
Solution: Expand the system disk. Go to the instance details page and use the Change Configuration feature.
Important An expanded system disk is billed continuously, even when the instance is stopped. To stop all billing, you must delete the instance. Before you delete the instance, make sure that you have backed up all necessary data.
the available zone with vSwitch is out of stock
Cause: If you configured a VPC at creation, the associated vSwitch locks the resource search to a single availability zone, which may have a resource shortage.
Solution: Change the configuration of the DSW instance and set the VPC to empty. This allows the system to search for resources across all AZs in the region.
Note To use a VPC, we recommend that you switch to another zone and create a new vSwitch and DSW instance. This expands the range of available resources and prevents shortages caused by a limited resource scope.
Startup failed with the message "Workspace member not found"
failed to create containerd container: failed to prepare layer from archive: failed to validate archive quota ...
Cause: The Image used for the instance is too large for the current system disk size.
Solution: Expand the System Disk via the Change Settings feature on the instance details page. Note that this incurs additional storage charges.
Other Cause: Overdue Payments
Q: Can I run a Python file when a DSW instance starts?
Use the Custom Startup Script option. You can set this when creating a new instance or by modifying an existing one via the Change Settings panel.

The script runs after the instance's underlying resources are ready but before development tools like JupyterLab or WebIDE are started. This is useful for environment customization or initialization tasks.
Note 3-Minute Timeout: The script has a 3-minute timeout. Avoid long-running tasks like downloading large files.
Log Location: After startup, you can find the script's execution logs in the /var/log/user-command/ directory inside the instance.
Q: How do I find my DSW instance if it's not visible in the console?
Your instance may be in a different region or workspace. Use the dropdown menus on the PAI-DSW console page to switch between available regions and workspaces.

Q: Why is my DSW page blank, or why is the Notebook/Terminal unresponsive?
These issues are typically caused by your local browser or network environment. Try the following steps in order:
Clear your browser's cache and cookies, then reload the page.
Open the DSW page in your browser's incognito or private mode.
Switch your network. For example, if you are on a corporate network, try a mobile hotspot to rule out firewall issues.
Try a different browser, such as Chrome or Firefox.
Q: What happens to my data on a DSW instance's Cloud Disk when I stop, restart, or modify the instance?
Data persistence depends on the action taken and whether the instance uses a Cloud Disk or Temporary Storage for its System Disk. This answer applies to instances with a Cloud Disk System Disk.
Stopping the instance: Data may be lost.
If the Cloud Disk was expanded or the instance is stopped for fewer than 15 days, your data is preserved.
If the Cloud Disk was not expanded and the instance remains stopped for more than 15 days, the system permanently erases all data.
Restarting the instance: Data is not lost. All files and installed packages on the System Disk are retained.
Changing the instance specification (CPU/GPU/Memory): Data is not lost.
Changing the instance image: Data on the System Disk may be lost. The system may reset the disk contents. Data on mounted storage (like OSS or NAS) is unaffected. Always back up your System Disk data before changing the image.
For instances using Temporary Storage, all data on the System Disk is permanently deleted upon stopping, restarting, or any configuration change.
Q: How can I recover a DSW instance from a public resource group that was auto-released after 15 days of being stopped?
You can't. An instance created from public resources with an un-expanded Cloud Disk is automatically and permanently deleted if it remains stopped for more than 15 consecutive days. The data cannot be recovered.
Stop or release a DSW instance
Click to expand
Q: What is the correct way to release a DSW instance and its resources?
On the DSW console, you can either Stop or Delete an instance.
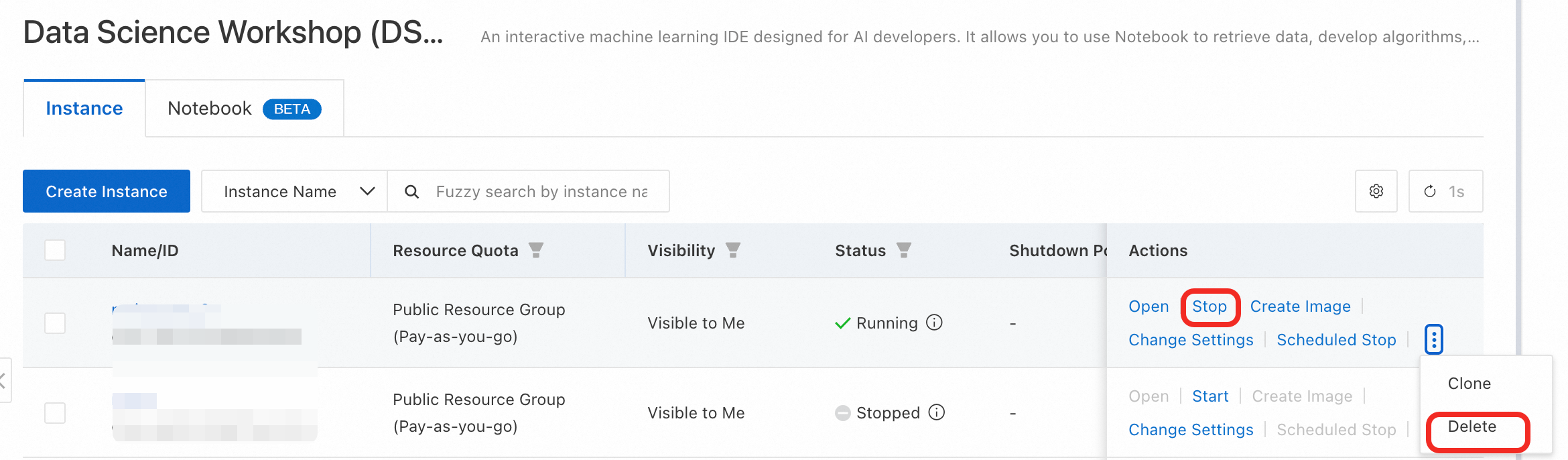
Stop: Halts compute billing but preserves the instance for later use.
Delete: Permanently removes the instance and all its resources, stopping all billing.
Important: If you expanded the System Disk, it continues to incur storage charges even when the instance is stopped. To stop all charges, you must delete the instance.
Q: How do I find my DSW instance if it's not visible in the console?
Your instance may be in a different region or workspace. Use the dropdown menus on the PAI-DSW console page to switch between available regions and workspaces.
Q: Do I need to manually release a free trial resource package?
No. Free trial resource packages expire automatically and do not need to be manually stopped or released.
Q: What is the difference between stopping and deleting a DSW instance, and how do I stop all billing?
To completely stop all billing associated with a DSW instance, you must delete it.
Stop: This action releases the compute resources (CPU/GPU) and pauses billing for them. However, if you have expanded the System Disk, storage charges for the disk will continue.
Delete: This action permanently removes the instance and all its resources, including the system disk. All associated billing stops completely.
How to choose:
Use Stop if you plan to use the instance again and want to preserve its environment and data.
Use Delete if you no longer need the instance and want to avoid all future charges. Always back up your data before deleting.
Q: What should I do if my DSW instance is stuck in the 'Stopping' or 'Deleting' state?
This can happen if processes inside the instance are not terminating correctly or if high memory usage prevents the instance from responding.
Solution: Wait a few minutes and refresh the page. The system is designed to eventually terminate the instance safely. The status should update to "Stopped" or the instance will be removed from the list if deleted.
Q: Is my data preserved when I stop or delete a DSW instance?
It depends on the action and the type of system disk your instance uses.
Recommendation: To ensure data persistence, save your important files to a mounted storage solution like OSS or NAS. Always back up your data before deleting an instance.
Q: Why did my DSW instance shut down automatically while it was running?
Your instance was likely stopped by the Idle Auto-shutdown policy. This feature automatically stops an instance if its CPU and GPU utilization remains below a set threshold for a specified period (e.g., 3 hours). It is enabled by default on free trial instances to conserve resources.
How to disable or modify the policy:
Manual stop: To ensure resource savings, you can manually stop the instance when it is not in use. The auto-shutdown policy is not guaranteed to be triggered every time.
Modify policy: To run long-term tasks, you can modify or disable this policy. The steps are as follows:
Modify the DSW auto-shutdown policy
Navigate to your workspace details page and go to Configure Workspace > Auto-stop Settings.
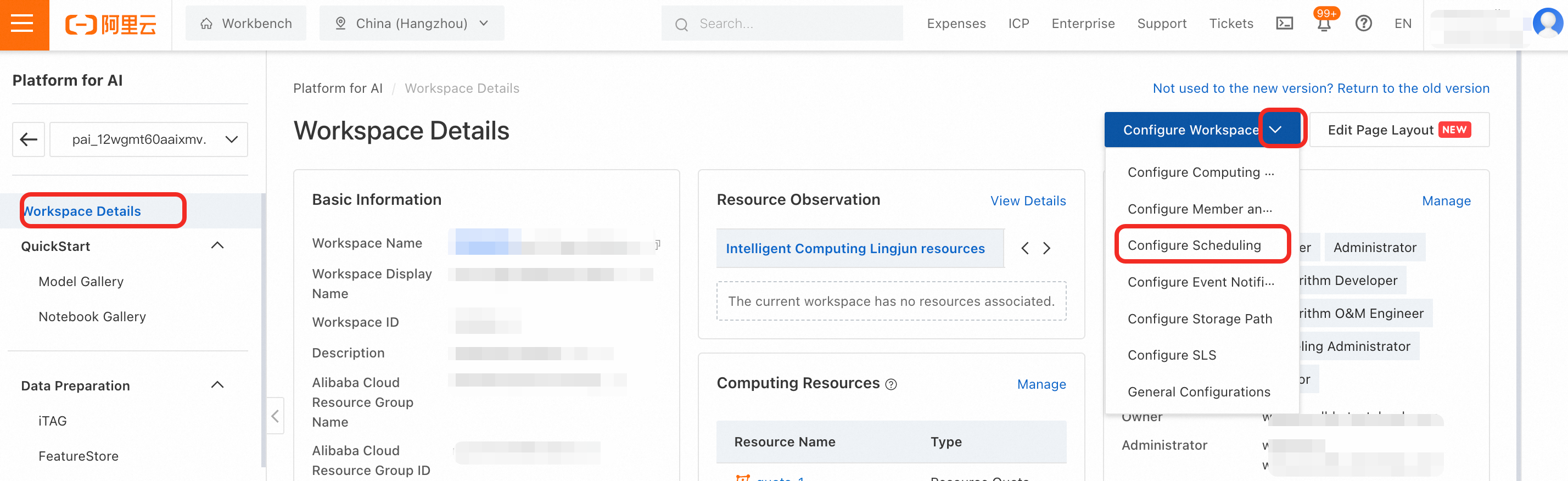
In the DSW configuration section, you can modify the shutdown policy or add your instance's name to the exclusion list to prevent it from being automatically stopped.
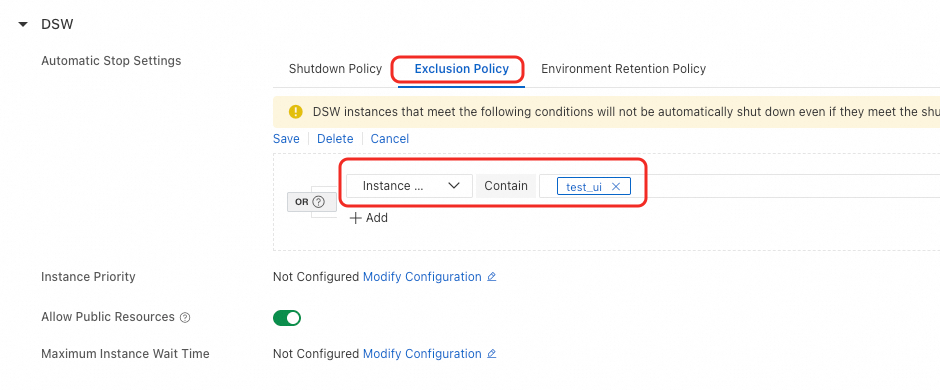
Q: Why am I still being billed or seeing a 'Running' status after stopping/deleting all my DSW instances?
This usually happens for one of three reasons:
"Running" status refers to a resource package: The "Running" status you see on a billing or free trial page may refer to an active resource package (e.g., "250 compute hours/month"), not an actual DSW instance. The package remains active until it expires.
An expanded system disk is still being billed: Stopping an instance only pauses compute charges. If you expanded the System Disk, you are still being charged for storage. To stop these charges, you must delete the instance.
Billing data has a delay: There is a delay between resource usage and when the bill is generated. The charges you see may be for usage that occurred before you stopped or deleted the instance.











