FAQs about NAS file system mounting, protocols, unmounting, security, and configuration.
Question navigation
-
Mounting
-
Does NAS support mounting from the internet or a local IP address?
-
Does batch mounting support classic networks, cross-VPC mounting, and cross-region mounting?
-
Does the batch mounting feature support mounting from on-premises data centers (IDCs)?
-
How do I confirm the execution result of a batch mount or unmount command?
-
How do I create and mount a subdirectory of a NAS file system on a Linux instance?
-
Why can't I mount an SMB file system on a Windows Server version later than 2016?
-
Why does the mount fail with error 5 when I join an AD domain?
-
How do I mount the same SMB instance in multiple AD domains?
-
How do I check and resolve issues when I use IIS services on Alibaba Cloud NAS?
-
-
Protocols
-
Unmounting
Does NAS support mounting from the internet or a local IP address?
No. You must mount a NAS file system over an internal network. To mount from an external network, establish a connection to the VPC where the file system resides. For more information, see Access a file system from a data center.
Why can't I mount an SMB file system on a Linux instance?
The failure to mount an SMB file system on a Linux operating system can be caused by various reasons. For more information about how to troubleshoot this issue, see Troubleshoot the failure to mount an SMB file system on a Linux instance.
How do I mount and access an Alibaba Cloud NAS file system from an on-premises computer or a non-Alibaba Cloud host?
|
Operating environment |
Mounting instructions |
|
Linux operating system |
Mount and access the file system in one of the following ways:
|
|
Windows operating system |
|
|
macOS client |
You must first mount the SMB file system on the macOS client, and then access the SMB file system using the Kerberos protocol. For more information, see Access an SMB file system from a macOS client over a VPN connection. |
How do I mount a NAS file system on an Alibaba Cloud Workspace?
Cloud Workspace supports the use of File Storage NAS for shared storage. Create a NAS file system in each workspace to meet the file sharing needs among cloud desktops.
To share files among cloud desktops in the same workspace, mount a NAS file system in one of the following ways:
-
If a shared storage NAS file system is not created for the cloud desktop
Log on to the Cloud Desktop console to create a shared NAS file system. The system automatically mounts the NAS file system to the cloud desktops in the corresponding workspace. View the status of the file system on the File Storage NAS page. The file system is created when its status changes to Active. For more information, see Mount a NAS file system on a Windows cloud computer.
-
If a shared storage NAS file system is already created for the cloud desktop
When you create, start, restart, or rebuild a cloud desktop, the NAS file system is automatically mounted if it is available in the workspace to which the cloud desktop belongs. If the NAS file system on the cloud desktop is manually unmounted, or if you want to mount the NAS file system to another path, manually mount the NAS file system. For more information, see Mount a NAS file system on a Linux cloud computer.
Does Alibaba Cloud NAS support mounting a file system using the NFS and SMB protocols at the same time?
No. A file system can be mounted using only one protocol at a time.
Mount and access an NFS file system from a Linux operating system. Mount and access an SMB file system from a Windows operating system. Avoid mounting a NAS file system across platforms to prevent compatibility issues. For example, the supported character sets and the length of file names are inconsistent. Windows supports 255 wide characters, and Linux supports 255 UTF-8 bytes. For more information, see Scenarios for mounting a file system and File read and write issues.
What operating systems and file system protocols does the one-click mount feature support?
Currently, this feature supports only mounting an NFS file system on a Linux operating system. For other scenarios, such as mounting an SMB file system on a Windows operating system, mounting an NFS file system on a Windows operating system, or mounting an SMB file system on a Linux operating system, you must log on to the ECS instance and run a command to mount the file system. For more information, see Mount an SMB file system, Mount an NFS file system (General-purpose NAS), and Mount an SMB file system.
How do I mount a file system on an ECS instance that resides in a classic network or a connected VPC in the console?
This is not supported.
Use the one-click mount feature in the console only when the ECS instance and the NAS file system are in the same VPC. However, use the Cloud Assistant console to perform the mount operation. For more information, see Batch mount the same NFS file system on multiple ECS instances.
In a scenario where VPCs are connected, you can mount a file system only from a VPC in the same region. You cannot mount a file system from a VPC in a different region.
Does NAS support cross-zone mounting?
General-purpose NAS file systems support cross-zone mounting. Mount Extreme NAS file systems in the same zone. Otherwise, performance is affected.
After I mount a NAS file system on a Linux instance, is the data in the original directory overwritten?
If the local path that you mount is not empty, the directory displays the data from the NAS file system, and the local data becomes temporarily invisible. However, the local data is not deleted or overwritten. After you unmount the NAS file system, the directory displays the original local data again.
What are the risks of forcibly unmounting a NAS file system?
Forcibly unmounting a file system may cause data that is not written to disks to be lost and related applications to exit unexpectedly. Log on to the ECS instance and run the fuser -mv <mount path> command to view application processes other than the mount process. After you confirm that the processes are closed, try to unmount the file system again.
If you are sure that no applications are using the NAS file system but you still cannot unmount it, try to forcibly unmount it. After a forced unmount, kernel states may remain. You must restart the ECS instance to clear them. Otherwise, you may not be able to remount the same mount target.
When I use the one-click mount feature in the console, why can't I find the newly created ECS instance in the ECS instance list?
Manually refresh the browser page and then try to mount the file system again to view the ECS instance.
When I use the one-click mount feature, why don't the new protocol type or mount parameters take effect?
If the specified mount path is already mounted to the current mount target, the new protocol type and mount parameters are ignored. Unmount the destination mount path and then run the mount command again with the new protocol type and mount parameters.
What operating systems and file system protocols does the batch mounting feature support?
Currently, this feature supports only mounting an NFS file system on a Linux operating system. For other scenarios, such as mounting an SMB file system on a Windows operating system, mounting an NFS file system on a Windows operating system, or mounting an SMB file system on a Linux operating system, you must log on to the ECS instance and run a command to mount the file system. For more information, see Mount an SMB file system, Mount an NFS file system (General-purpose NAS), and Mount an SMB file system.
Does batch mounting support classic networks, cross-VPC mounting, and cross-region mounting?
It supports classic networks and cross-VPC mounting within the same region. It does not support cross-region mounting, even if the VPCs are connected.
Does the batch mounting feature support mounting from on-premises IDCs?
No. Mount a file system from an on-premises data center (IDC) by configuring a VPN Gateway or a NAT Gateway. For more information, see Access an Alibaba Cloud NAS file system from a data center using a NAT gateway or Access an Alibaba Cloud NAS file system from a data center using a VPN gateway.
How do I confirm the execution result of a batch mount or unmount command?
Log on to the ECS console and choose . On the Cloud Assistant page, view the task status in the operation records, which can be Successful, Failed, or Partially Failed. Click View in the Actions column for a task to check the execution status of each ECS instance.
After I batch mount a file system in the Cloud Assistant console, how do I interpret the ECS mount information?
Log on to the NAS console, go to the details page of the target file system, and click the Mount Targets tab to view the mount status of the ECS instance using the query feature. For more information, see Query the status of an ECS instance.
When I use the batch mounting feature, why don't the new protocol type or mount parameters take effect?
If the specified mount path is already mounted to the current mount target, the new protocol type and mount parameters are ignored. Unmount the destination mount path and then run the mount command again with the new protocol type and mount parameters.
How do I modify the number of concurrent NFS requests?
The NFS client controls the number of concurrent NFS requests. The default value of this parameter in the compiled kernel is 2, which severely affects performance. Change this parameter to 128.
-
Install an NFS client. For more information, see Install an NFS client.
-
Run the following command to change the number of concurrent NFS requests to 128.
echo "options sunrpc tcp_slot_table_entries=128" >> /etc/modprobe.d/sunrpc.conf echo "options sunrpc tcp_max_slot_table_entries=128" >> /etc/modprobe.d/sunrpc.conf sysctl -w sunrpc.tcp_slot_table_entries=128NoteYou need to perform this operation only once as the root user after you install the NFS client for the first time. You do not need to repeat this operation.
-
Optional: Restart the ECS instance.
rebootImportantRestarting the ECS instance interrupts your services. Restart the ECS instance during off-peak hours.
-
Mount the file system. For more information, see Mount an NFS file system.
-
Run the following command to check whether the modification is successful.
If 128 is returned, the modification is successful.
cat /proc/sys/sunrpc/tcp_slot_table_entries
How do I create and mount a subdirectory of a NAS file system on a Linux instance?
Make sure that you have mounted the file system. For more information, see Mount an NFS file system.
Assume that you mount the root directory of the NAS file system to the /mnt directory on a Linux-based ECS instance. After the file system is mounted, the /mnt directory is equivalent to the root directory of the NAS file system. Create a subdirectory of the NAS file system in the /mnt directory.
-
On the Linux-based ECS instance, create a subdirectory for the NAS file system.
mkdir /mnt/subdir -
Create a local directory to mount the NAS file system.
mkdir /tmp/mntNoteA local directory on a server can be mounted with only one file system. Create multiple local directories to mount file systems.
-
Remount the file system.
sudo mount -t nfs -o vers=3,nolock,proto=tcp,rsize=1048576,wsize=1048576,hard,timeo=600,retrans=2,noresvport file-system-id.region.nas.aliyuncs.com:/subdir /tmp/mntThe following table describes the important fields. Replace the placeholders with your actual values.
-
file-system-id.region.nas.aliyuncs.com: the mount target address. Log on to the NAS console, click the ID of the target file system on the File System List page, and then click Mount Targets on the file system details page.
-
/subdir: The subdirectory of the NAS file system.
-
/tmp/mnt: The local directory on the server.
-
How do I handle Linux server exceptions caused by the accidental deletion of a mount target?
Symptom
Assume that you mount a file system using mount target A on a Linux operating system. If you delete mount target A in the NAS console without unmounting it, the Linux system may experience exceptions such as command stuttering or no response.
Solution
-
On the server, such as a Linux-based ECS instance, press
Ctrl+Cto interrupt the command execution. -
Run the
mountcommand to view the mount information.Obtain the mount path from the mount information. In the following figure, /mnt/data is the current mount path.
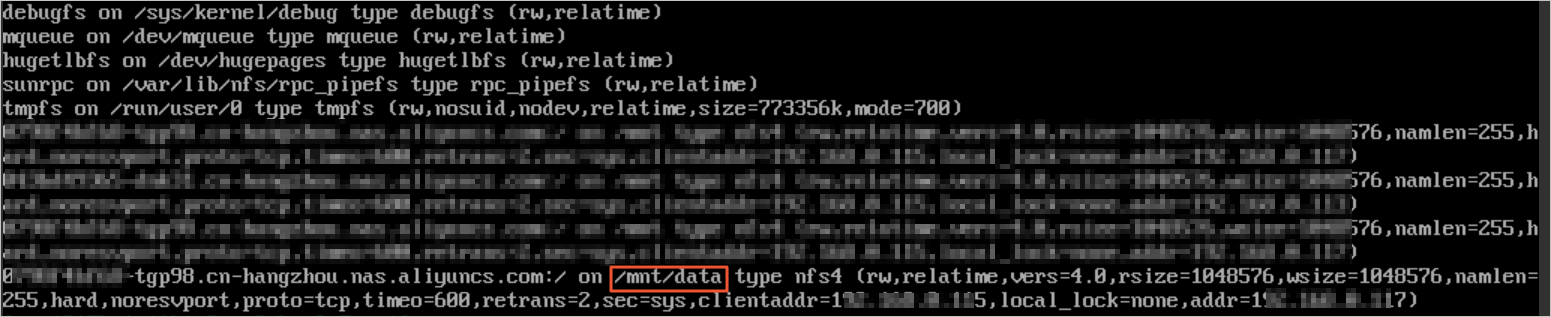
-
Run the
umount -f /mnt/datacommand to forcibly unmount the file system.Command format:
umount -f <mount path>NoteIf the issue persists after you run the
umount -f <mount path>command, run theumount -l <mount path>command.After the file system is unmounted, create a mount target again and then mount the file system.
How do I prevent the NFS 4.0 listener port from being mistaken for a Trojan?
Symptom
After you mount a NAS file system using the NFSv4.0 protocol, a random port listens on 0.0.0.0, and netstat cannot locate the listener process.
Because the listened port is not fixed and the listener process cannot be located, it is easy to misjudge this activity as a Trojan attack.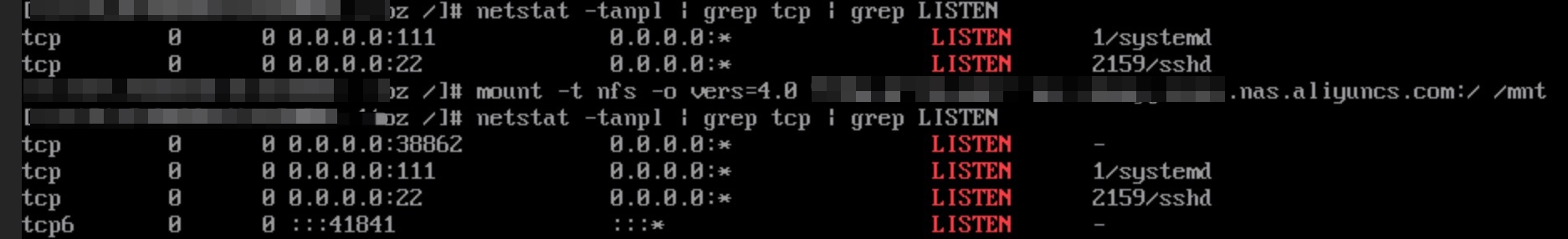
Cause
The NFSv4.0 client listens on this random port to support Callback. Because the default value of the kernel parameter fs.nfs.nfs_callback_tcpport is 0, the client randomly selects a port. This random port does not pose a security risk.
Solution
Before you mount the file system, configure the fs.nfs.nfs_callback_tcpport parameter to a non-zero specific value to use a fixed port.
sudo sysctl fs.nfs.nfs_callback_tcpport=<port> In the following example, fs.nfs.nfs_callback_tcpport is manually configured to port 45450. After the file system is mounted using the NFSv4.0 protocol, the port listened on by netstat is the manually configured port 45450.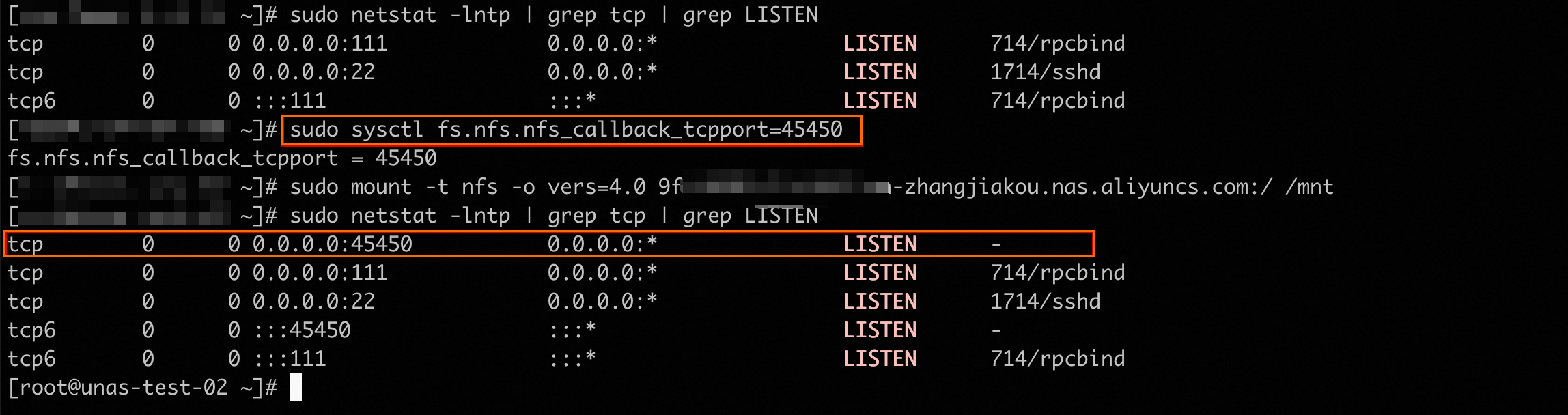
Why can't I mount an SMB file system on a Windows Server version later than 2016?
Symptom
Command and error message:
C:\Users\Administrator>net use z: \\xxxxx-xxxx.xxxxx.nas.aliyuncs.com\myshare
System error 1272 has occurred.
You can't access this shared folder because your organization's security policies block unauthenticated guest access. These policies help protect your PC from unsafe or malicious devices on the network.Cause
This issue occurs because the security feature of this version of Windows Server does not allow guest users to access remote shared directories by default.
Solution
-
Modify the registry.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation\Parameters] "AllowInsecureGuestAuth"=dword:0Change it to the following:
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanWorkstation\Parameters] "AllowInsecureGuestAuth"=dword:1 -
Switch to PowerShell and run the following command:
New-ItemProperty -Path $registryPath -Name $name -Value $value -PropertyType DWORD -Force
For more information, see Guest access in SMB2 disabled by default in Windows 10, Windows Server 2016 version 1709, and Windows Server 2019.
How do I check and resolve issues when I use IIS services on Alibaba Cloud NAS?
If you encounter issues such as the failure to mount an SMB file system on a Windows Server 2016 instance, HTTP error 500.19, or error code 0x8007003a, see Best practices for using IIS services on Alibaba Cloud NAS.
When a process on an SMB file system cannot be terminated, how do I clear the leaked handles on the client?
Use the following tools to disconnect all connections to the SMB file system to release all handles.
Does the file lock feature work when I use an NFS file system on a Windows instance?
No, it does not. To use the file lock feature on a Windows instance, use a NAS SMB file system.
How do I troubleshoot the configurations of an ECS security group?
When you mount and access a NAS file system from an ECS instance, port 2049 and port 111 are required for a NAS NFS file system, and port 445 is required for a NAS SMB file system. If the outbound rules of the security group are configured to deny access to these ports, you cannot mount or access the NAS file system.
Follow these steps to troubleshoot and modify the security group rules.
Log on to the ECS console.
-
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
-
In the top navigation bar, select a resource group and a region.
-
Click the ID of the target security group rule to go to the security group rule details page.
-
On the Security Group Details tab, click the Outbound tab to check whether access to the IP address or CIDR block of the file system mount target and the relevant ports (NFS: 2049 and 111, SMB: 445) is allowed over the TCP protocol in the outbound direction.
Note-
By default, a basic security group allows all outbound access. In this case, you do not need to modify the security group.
-
By default, an advanced security group denies all outbound access. In this case, you must add a rule to the outbound rules to allow access to the relevant ports over the TCP protocol for the IP address of the file system mount target.
If a security group rule denies outbound access to the required ports or the IP address or CIDR block of the file system mount target, click Edit in the Actions column of the rule to modify the Action or Destination. For more information, see Security group rules.
If a parsing issue occurs, add the following rule to the security group to support default DNS parsing.
Action
Priority
Protocol
Destination
IPv4
Port
Allow
1
Custom UDP
0.0.0.0/0
53/53
For example, to allow outbound access to port 2049 for the IP address of the file system mount target (192.168.12.151), configure the following rule.
-
Basic security group
Action
Priority
Protocol
Destination
IPv4
Port
Allow
1
Custom TCP
The following addresses all cover the mount target IP address (192.168.12.151). Configure any one of them.
-
0.0.0.0/0
-
192.0.0.0/8
-
192.168.0.0/16
-
192.168.12.0/24
-
192.168.12.151/32
2049/2049
-
-
Advanced security group
Action
Priority
Protocol
Destination
IPv4
Port
Allow
1
Custom TCP
The following addresses all cover the mount target IP address (192.168.12.151). Configure any one of them.
-
0.0.0.0/0
-
192.0.0.0/8
-
192.168.0.0/16
-
192.168.12.0/24
-
192.168.12.151/32
2049/2049
-
-
How do I troubleshoot the rules of a NAS permission group?
In File Storage NAS, a permission group is a whitelist mechanism. The private IP address of an ECS instance must be in the whitelist of the permission group that is configured for the mount target to access the mount target. If the IP address or CIDR block of the ECS instance that needs to access the file system is not in the rule of the permission group used by the mount target, you cannot mount or access the NAS file system.
Add all private IP addresses of the ECS instance, including secondary private IP addresses, to the permission group attached to the mount target to prevent mount failures caused by network interface card switching.
Follow these steps to troubleshoot and modify the permission group rules.
-
Log on to the NAS console.
-
In the navigation pane on the left, choose File System > File System List.
-
In the top menu bar, select the resource group and region where the file system resides.
-
Click Manage in the Actions column of the target file system.
-
On the file system details page, click the Mount Targets tab in the navigation pane on the left. Then, on the Mount Target tab, view the permission group configured for the mount target.
-
If the permission group is Default VPC permission group (all allowed), you do not need to modify it.
The default permission group allows any IP address to access the file system with the highest permissions. These permissions include read and write permissions and no restrictions on the access of Linux system users to the file system. You cannot delete or modify the default permission group.
-
If it is a custom permission group, click the permission group name in the Permission Group column of the mount target. On the rule list page of the permission group, view the custom permission group rules.
If the rule list does not contain the IP address or CIDR block of the ECS instance that needs to access the file system, click Edit in the Actions column of the target rule to include the ECS IP address in the authorized address.
For example, in a custom permission group rule, if the authorized address does not include the IP address of the ECS instance that needs to access the file system (192.168.12.150), add any of the following CIDR blocks to the authorized address.
-
192.168.12.150/32
-
192.168.12.0/24
-
192.168.0.0/16
-
192.0.0.0/8
-
0.0.0.0/0
-
-
Can I modify the security group policy that is automatically generated for an Extreme NAS file system?
No. If the security group policy description is Createdbynas.Shouldnotdeleteit, it is an automatically generated security group policy for the Extreme NAS file system. This security group applies only to the ENI of the Extreme NAS file system on the server side. If you receive a high-risk alert from a cloud security product for the security group of the Extreme NAS file system, add it to the whitelist.
Why does a cloud security product report a high-risk alert for the security group of an Extreme NAS file system?
Security Center checks ECS security group policies based on modules. The security group on the ECS instance is the default security group. When unnecessary ports are detected, an alert is generated, prompting you to configure access policies with the minimum granularity for the security group. If the security group policy description is Createdbynas.Shouldnotdeleteit, it is an automatically generated security group policy for the Extreme NAS file system. This security group policy applies only to the ENI of the Extreme NAS file system on the server side. If this alert affects your use, add it to the whitelist.
Can I use a NAS file system as the storage directory for Docker services?
No. Docker storage requires the overlay feature, which is not supported by NAS.
How do I view the directory where a NAS file system is mounted on a server?
-
Linux system: Log on to the target server and run the
df -hcommand to view the mount directory.The following example shows a sample output. The
/mntin the Mounted on column is the ECS directory where the NAS file system is mounted.Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on devtmpfs 3.7G 0 3.7G 0% /devtmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 3.8G 452K 3.8G 1% /run tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/vda1 40G 3.0G 35G 8% / tmpfs 3.8G 0 3.8G 0% /tmp tmpfs 761M 0 761M 0% /run/user/0 19f04a4****-i****.cn-chengdu.nas.aliyuncs.com:/ 10P 0 10P 0% /mnt -
Windows system: Directly view the mount directory in File Explorer.
NFS client retry mechanism and error codes
NAS is a distributed file system. Due to factors such as network jitter, concurrent access, and backend exceptions, client requests may not be executed in a timely manner, which causes applications to receive error codes. When an application receives one of the following error codes when accessing NAS, it may be due to a brief backend exception. Retry the operation when receiving these error codes. These errors can usually be resolved by retrying.
|
Error code |
Description |
|
EAGAIN |
The resource is temporarily unavailable. |
|
EBUSY |
The device or resource is busy. |
|
EIO |
Input/output error. |
|
ENOMEM |
Out of memory. |
|
ETIMEDOUT |
The connection timed out. |
|
EREMOTEIO |
Remote I/O error. |
|
ESTALE |
The file handle is stale. If there are concurrent access and delete operations between different nodes, you do not need to retry this error code. If the file is exclusively accessed by a single node, retry this error code. |
When you mount a NAS NFS instance, use the hard option instead of the soft option. The soft option may cause data consistency risks. If you want to use the soft option, you must bear the risks yourself.
After I mount a NAS file system on a Linux instance, how do I use a graphical method to upload and download files?
Select one of the following graphical methods to upload and download files based on your scenario:
-
If you mount a NAS file system on an ECS instance, use Workbench to upload or download files.
-
If you mount a NAS file system on an on-premises Linux server, use an SFTP client to upload or download files. For more information, see Migrate data using an SFTP client.
After I mount an NFS file system on a Windows instance, how do I resolve the issue of garbled Chinese file names?
Cause
The NFS protocol on Windows does not support UTF-8 encoding by default.
Solution
Enable global UTF-8 support in Windows to resolve this issue.
-
In the search box on the taskbar, enter
intl.cpland click Open. -
Switch to the Administrative tab and click the Change system locale button.
-
Select the "Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support" option.
-
Click OK and restart the ECS instance for the settings to take effect.
Why does the mount fail with error 5 when I join an AD domain?
Symptom
The attempt to join the host to the AD domain fails and error code 5 is returned.

Solution
-
Press Win+R to open the Run dialog box, enter
gpedit.msc, and click OK to open the Local Group Policy Editor. -
Expand the following nodes in sequence: Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options.
-
Check the Kerberos-related configurations as shown in the figure and select the first three encryption methods.
-
Click Apply > OK.
How do I mount the same SMB instance in multiple AD domains?
-
Generate a corresponding keytab file for each domain. For more information about how to generate a keytab file, see Join the mount target of an SMB file system to an AD domain.
-
Merge multiple keytab files.
-
Log on to a Linux host and upload all keytab files to the host.
-
Install the ktutil tool.
yum install -y krb5-workstation -
Enter the interactive mode.
ktutil -
Read the keytab files one by one.
read_kt domain-a.keytab read_kt domain-b.keytab -
View the loaded keytab entries.
list -
Write the merged information to a new file. merged.keytab is the new file name.
write_kt merged.keytab
-
-
Upload the merged keytab file to the console to allow multiple domains to access the SMB instance at the same time.