To mount a File Storage NAS (NAS) file system on a macOS client, you must connect the macOS client to the file system's virtual private cloud (VPC). This topic describes how to mount a Server Message Block (SMB) file system over a virtual private network (VPN) and then access the it securely using the Kerberos protocol with Active Directory (AD).
Prerequisites
An SMB file system is created. For more information, see Create a file system.
A mount target is created in a VPC. For more information, see Create a mount target.
Mount the SMB file system
Connect your Mac to the VPC through VPN. For more information, see Connect a macOS client to a VPC.
In Step 2: Create an SSL server, Client Subnet and Local Network must be unique. The value of Local Network is the CIDR block of the VPC. Log on to the VPC console and view the CIDR block of the VPC on the VPC details page.
Verify the connectivity.
Check the network connectivity
After the VPN gateway is connected, run the ping command to ping the mount target of the SMB file system in the VPC.
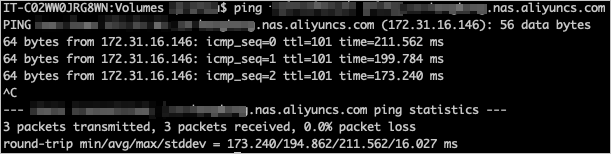 Note
NoteIf the ping command fails (which can happen due to network configurations), find the mount target's IP address by pinging it from an ECS instance within the same VPC. Then, use this IP address directly for mounting.
Check the port connectivity
telnet [Mount target of the SMB file system] 445
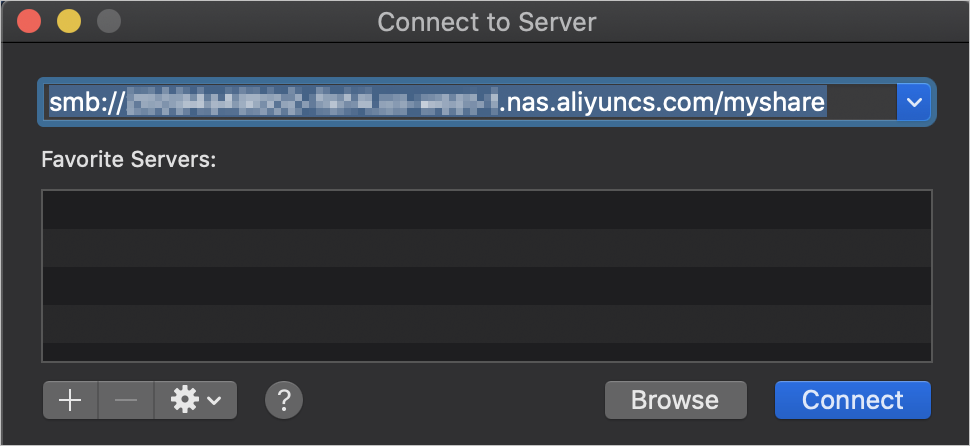
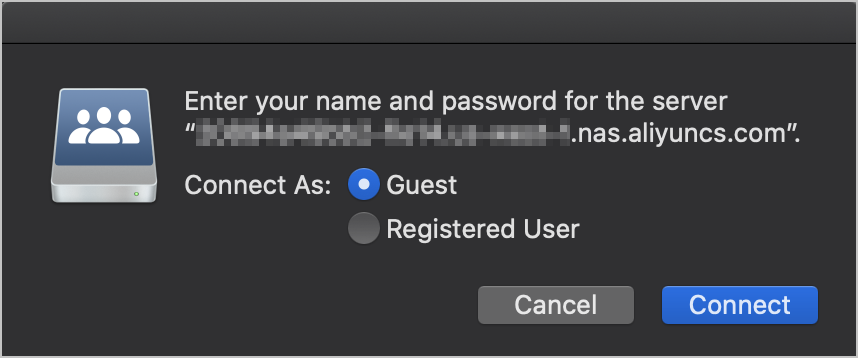
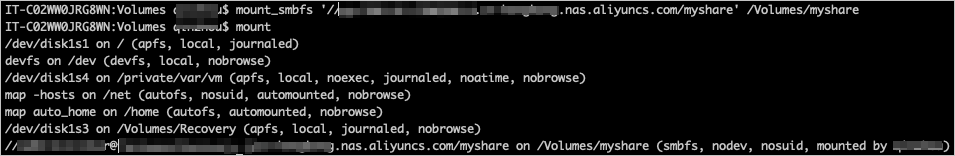
Mount the SMB file system.
Access with Kerberos Authentication (Active Directory)
By default, mounting through NTLM grants broad permissions. For fine-grained access control, NAS supports AD-based user authentication. This allows you to manage permissions for different users and groups. Perform the following steps to control access to the SMB file system.
Build an AD domain.
Establish a connection between the mount target of the SMB file system and the AD domain. For more information, see Join the mount target of an SMB file system to an AD domain.
Add the CIDR block of the SSL VPN network to a security group of the ECS instance. For more information, see Add a security group rule.
Add rules for the following ports to a security group of the ECS instance. This ensures that the SMB file system can be mounted on the macOS client based on the AD domain.
Domain Name System (DNS) port: UDP 53
Kerberos port: TCP 88
LDAP port: TCP 389
LDAP Global Catalog port: TCP 3268
Set the DNS server of the macOS client to the internal IP address of the AD domain controller.
Run the ipconfig command on the ECS instance to query the internal IP address of the AD domain controller.
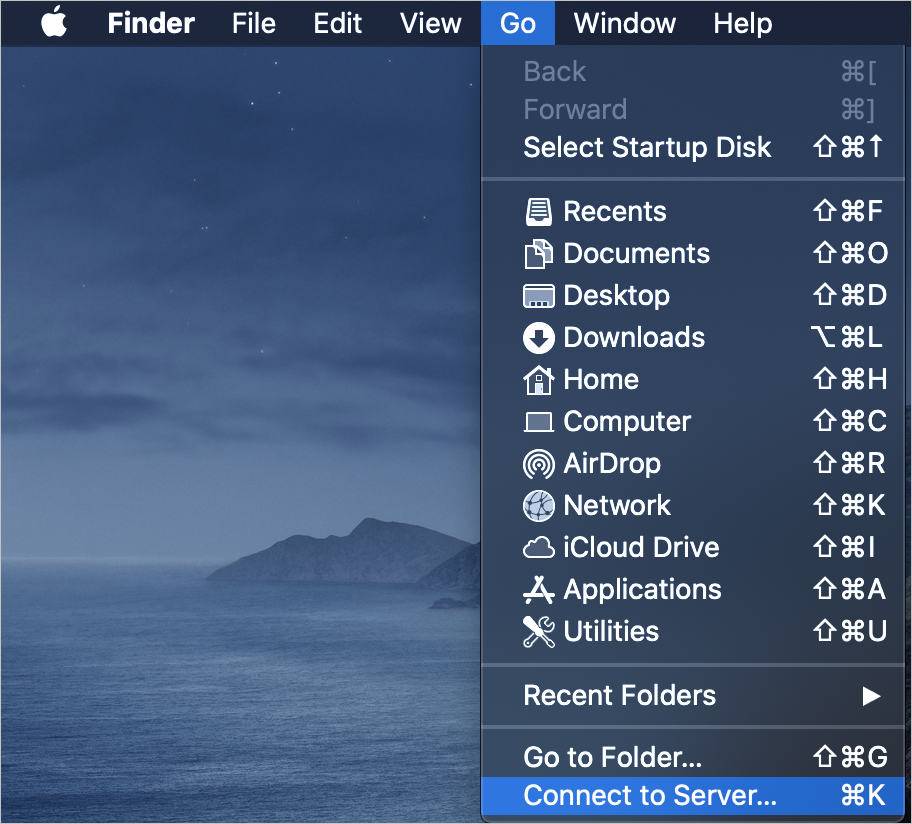
In the Finder bar of the macOS client desktop, choose .
In the Network dialog box, set the DNS server of the macOS client to the internal IP address of the AD domain controller.
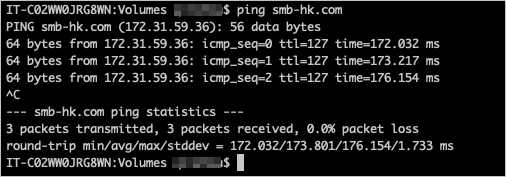
Verify the connection between the macOS client and the AD domain.
On the macOS client, run the ping command to connect to the AD domain controller. The following figure shows a successful connection.
Use an AD domain identity to mount the SMB file system on the macOS client by using the Kerberos protocol.
Run the kinit command to verify the security of the AD domain identity. The following sample code provides an example:
kinit user@MYDOMAIN.COMRun the
klistcommand to view the AD domain identity. The following sample code provides an example:klistRun the
kinitcommand to use the AD domain identity to log on to the macOS client. The following sample code provides an example:kinitRun the following command to mount the SMB file system. The following sample code provides an example:
mount_smbfs //administrator@nas-mount-point.nas.aliyuncs.com/myshare /Volumes/myshareNoteIf the error message
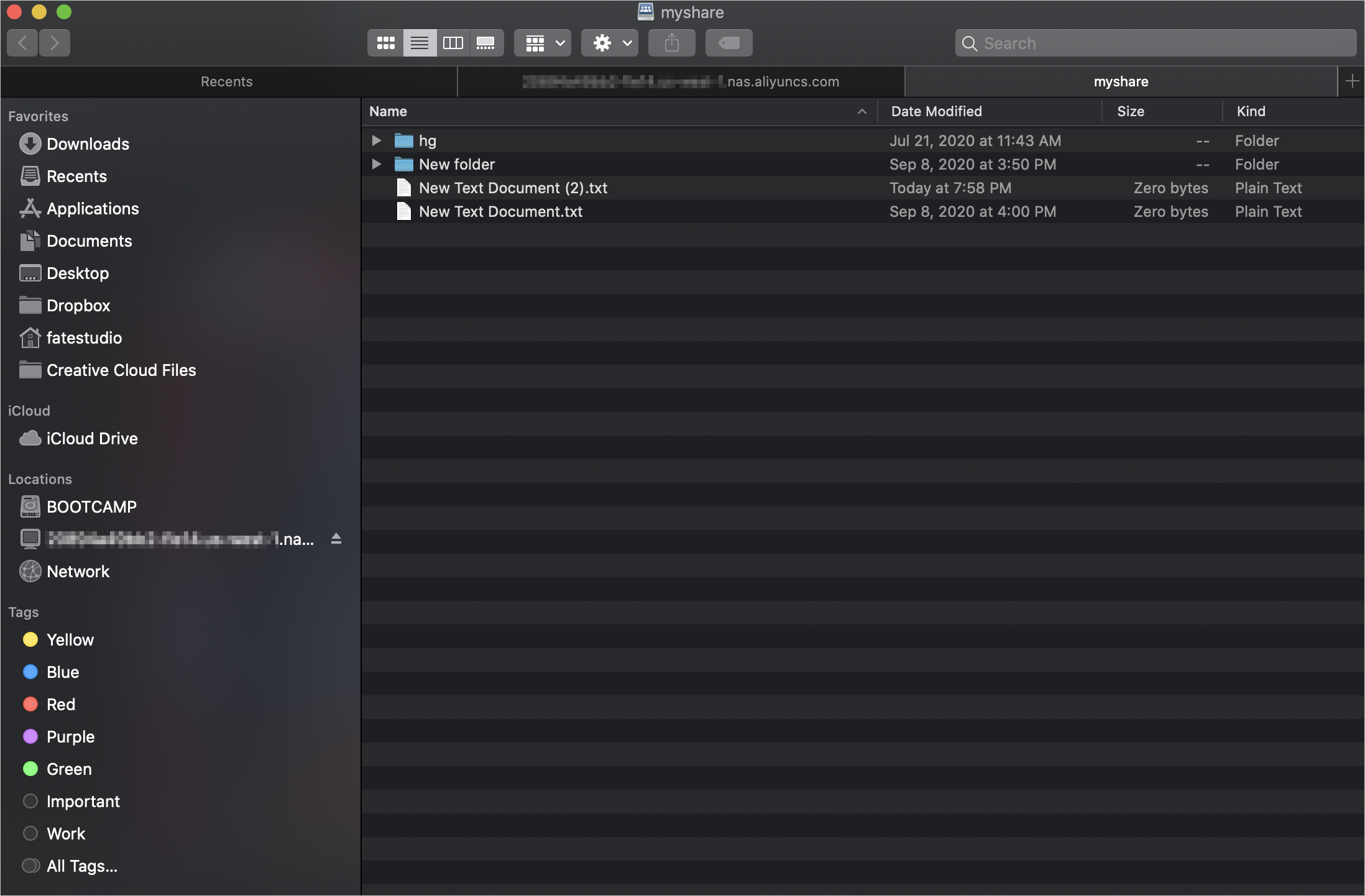
mount_smbfs: server rejected the connection: Authentication errorappears, run the kinit command to verify the AD domain identity and mount the SMB file system again.The following figure shows a successful mount:
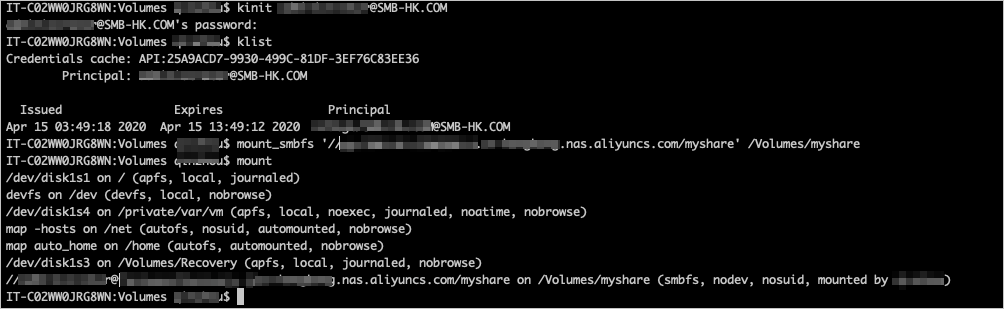 After the SMB file system is mounted, run the klist command. Two service principals are returned, as shown in the following figure.
After the SMB file system is mounted, run the klist command. Two service principals are returned, as shown in the following figure.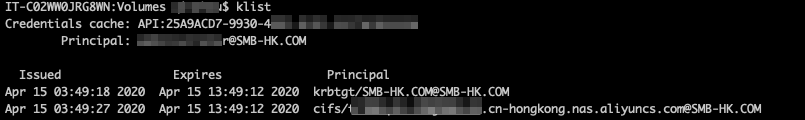 Note
NoteWhile macOS Finder does not display Windows ACLs, the NAS server still enforces them. Any operation (read, write, delete) will be allowed or denied based on the permissions configured for your user in Active Directory. Configure the ACLs of the SMB file system when you mount the SMB file system on the AD domain controller.