You can grant operation permissions on resources in Microservices Engine (MSE) to a RAM user by using an Alibaba Cloud account. This method helps prevent security risks that may occur if the AccessKey pair of your Alibaba Cloud account is exposed. This topic describes how to create a RAM user and grant the RAM user permissions on Microservices Registry resources. After you grant the required permissions to a RAM user, you can perform the related operations as the RAM user.
Scenarios
The MSE service is activated for an enterprise. The resource permissions that are required for employees vary based on their roles. The enterprise has the following requirements:
The AccessKey pair of the Alibaba Cloud account of the enterprise must be kept confidential to ensure security. The enterprise wants to grant different permissions to users.
Only users who are granted permissions can manage resources. Resource usage and costs are not calculated separately for each user. Bills are generated on the Alibaba Cloud account of the enterprise.
The enterprise can revoke the permissions that are granted to RAM users and delete RAM users.
MSE is a managed service that provides two roles: developer and O&M. Developers are responsible for configuration and service management. O&M personnel are responsible for instance, namespace, and permission management.
Usage notes
In this topic, permissions on the engine access control link shown in the following figure are configured and used. After you grant the required permissions on this link to a RAM user by using your Alibaba Cloud account, you can access MSE in Console Access mode or OpenAPI Access mode as the RAM user.
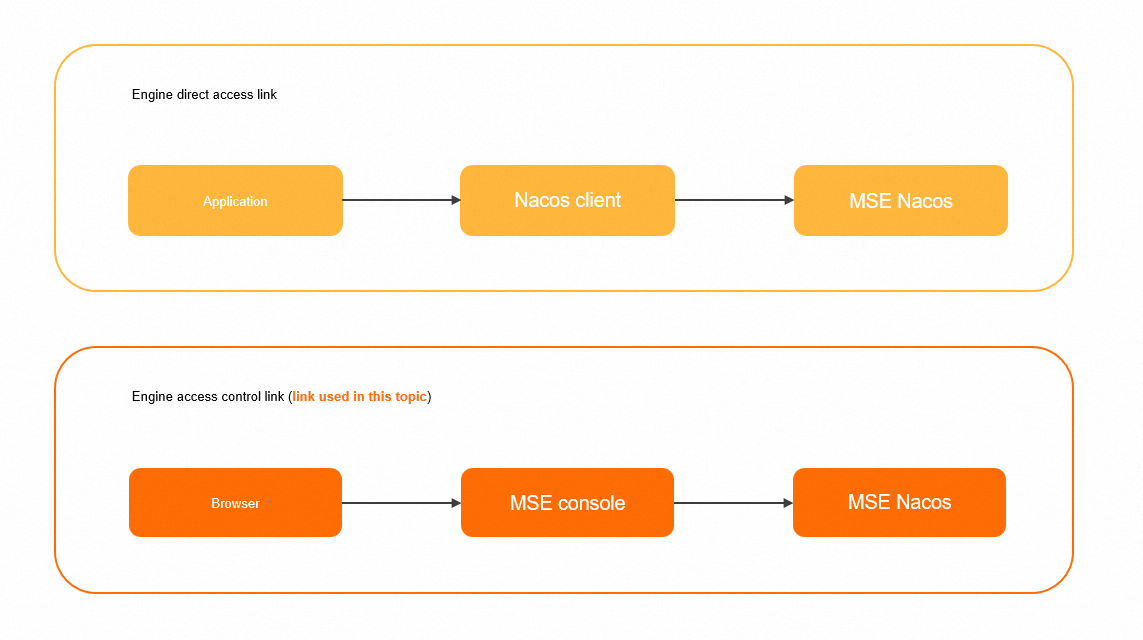
You can also use the engine direct access link shown in the preceding figure to access an MSE Nacos instance by using the Nacos client as a RAM user. For more information about the access authentication and usage of this link, see Access authentication by the Nacos client.
Step 1: Create a RAM user
Log on to the Resource Access Management (RAM) console and create a RAM user by using your Alibaba Cloud account.
Log on to the RAM console by using an Alibaba Cloud account or a RAM user who has administrative rights.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Users page, click Create User.
In the User Account Information section of the Create User page, configure the following parameters:
Logon Name: The logon name can be up to 64 characters in length, and can contain letters, digits, periods (.), hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
Display Name: The display name can be up to 128 characters in length.
Tag: Click the
 icon and enter a tag key and a tag value. You can add one or more tags to the RAM user. This way, you can manage the RAM user based on the tags.
icon and enter a tag key and a tag value. You can add one or more tags to the RAM user. This way, you can manage the RAM user based on the tags.
NoteYou can click Add User to create multiple RAM users at a time.
In the Access Mode section, select Console Access or Using permanent AccessKey to access.
Console Access: If you select Console Access, you must configure the basic settings for logon security. These settings specify whether to use a system-generated logon password or a custom logon password, whether to reset the password at the next logon, and whether to enable multi-factor authentication (MFA).
NoteIf you select Custom Logon Password in the Console Password section, you must specify a password. The password must meet the complexity requirements that you specified on the page. For more information about the password complexity requirements, see Configure a password policy for RAM users.
Using permanent AccessKey to access: If you select Using permanent AccessKey to access, an AccessKey pair is automatically created for the RAM user that you create. The RAM user can call API operations or use other development tools to access Alibaba Cloud resources.
NoteTo ensure the security of your resources, we recommend that you select Console Access for the RAM user. This way, the RAM user can no longer use an AccessKey pair to access Alibaba Cloud resources after the RAM user leaves the organization.
Click OK.
Step 2: Grant permissions to the RAM user
Before you use a RAM user, grant the required permissions to the RAM user.
Log on to the RAM console as a RAM administrator.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Users page, find the required RAM user, and click Add Permissions in the Actions column.
You can also select multiple RAM users and click Add Permissions in the lower part of the page to grant permissions to the RAM users at a time.
In the Grant Permission panel, select a policy in the Policy section. Enter the policy that you want to add in the search box in the Policy section, click the displayed policy, and then click Grant permissions.
System policies for coarse-grained authorization
MSE supports two system policies for coarse-grained authorization. The following table describes the policies.
Policy
Description
AliyunMSEFullAccess
The permissions to manage MSE. You can use a RAM user to whom this policy is attached to manage all features in the MSE console in the same way as you use an Alibaba Cloud account to manage MSE.
AliyunMSEReadOnlyAccess
The read-only permissions of MSE. A RAM user to whom this policy is attached can read all resources of the Alibaba Cloud account.
NoteWe recommend that you attach the AliyunMSEFullAccess policy to O&M personnel. This way, O&M personnel can create and delete resources. We recommend that you attach the AliyunMSEReadOnlyAccess policy to developers. This way, developers can view resources but cannot delete or create resources. If you want to manage the permissions of developers in a fine-grained manner, you can use one of the following custom policies:
Custom policies for fine-grained authorization
NoteIf you want to perform fine-grained authorization, you can create a custom policy for access control.
For more information about fine-grained authorization and configurations in Nacos registries, see Fine-grained authentication in registries. For more information about fine-grained authorization and configurations in Nacos configuration centers, see Fine-grained authentication in configuration centers.
The following table describes the MSE permissions to help you configure custom policies.
Action
Description
Read-only
CreateCluster
Creates an instance
No
DeleteCluster
Deletes an instance
No
QueryClusterDetail
Queries the details of an instance
Yes
RestartCluster
Restarts an instance
No
RetryCluster
Retries an instance
No
UpdateCluster
Updates an instance
No
CreateNacosConfig
Creates a Nacos configuration
No
DeleteNacosConfig
Deletes a Nacos configuration
No
DeleteNacosConfigs
Deletes Nacos configurations at a time
No
GetNacosConfig
Views a Nacos configuration
Yes
GetNacosHistoryConfig
Views historical details of a Nacos configuration
Yes
UpdateNacosConfig
Updates a Nacos configuration
No
UpdateNacosInstance
Updates a Nacos instance
No
DeleteNacosService
Deletes a Nacos service
No
CreateNacosService
Creates a Nacos service
No
UpdateNacosService
Updates a Nacos service
No
CreateNacosInstance
Creates a Nacos instance
No
UpdateNacosCluster
Updates a Nacos cluster
No
The permission that is described in the following table can be granted only at the account level. The permission cannot be displayed by instance.
Action
Description
Read-only
ListClusters
Queries the list of instances.
Yes
ListServiceQuotas
Queries and displays the quotas. We recommend that you grant this permission.
Yes
The permissions that are described in the following table can be granted only at the instance level. Fine-grained permission display is not supported.
Action
Description
Read-only
ListNacosConfigs
Queries the list of Nacos configurations.
Yes
ListNacosHistoryConfigs
Queries the list of Nacos historical configurations.
Yes
ListAnsServices
Queries the list of all services.
Yes
ListAnsServiceClusters
Queries the list of clusters of a service.
Yes
ListAnsInstances
Queries the list of instances of a service.
Yes
Example 1: Grant a RAM user the read and write permissions on instance
mse-cn-0pp1j8om80a.NoteIn this example,
mse-cn-0pp1j8om80aindicates the ID specified by InstanceId but not the ID specified by ClusterId.{ "Statement": [ { "Action": "mse:ListClusters", "Resource": "acs:mse:*:*:*", "Effect": "Allow" }, { "Action": "mse:*", "Resource": "acs:mse:*:*:instance/mse-cn-0pp1j8om80a", "Effect": "Allow" } ], "Version": "1" }Example 2: Grant a RAM user the read permissions on all instances.
{ "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "mse:List*", "mse:Query*", "mse:Get*" ], "Resource": "acs:mse:*:*:*", "Effect": "Allow" } ], "Version": "1" }Example 3: Grant a RAM user the read and write permissions on the configurations of the namespace
3fd98c48-a709-4061-bba1-e341d79d681bin the instancemse-cn-0pp1j8om80a.This example shows a complex authorization scenario. The following levels of permissions are required to achieve fine-grained authorization:
The permission to query instances. The permission allows the RAM user to view the instance information.
The read permission on all resources in the instance. The permissions allow the RAM user to access the instance and view all resources of the instance.
The permissions to create and modify the configurations in the namespace.
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [{ "Action": [ "mse:ListClusters" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:*" ], "Effect": "Allow" }, { "Action": [ "mse:List*", "mse:Query*", "mse:Get*" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:instance/mse-cn-0pp1j8om8" ], "Effect": "Allow" }, { "Action": [ "mse:CreateNacosConfig", "mse:UpdateNacosConfig" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:instance/mse-cn-0pp1j8om8/3fd98c48-a709-4061-bba1-e341d79d681b" ], "Effect": "Allow" } ] }Example 4: Grant a RAM user the read and write permissions on the configurations specified by DataId in the instance
mse-cn-0pp1j8om80a.This example shows a complex authorization scenario. The following levels of permissions are required to achieve fine-grained authorization:
The permission to query instances. The permission allows the RAM user to view the instance information.
The read permission on all resources in the instance. The permission allows the RAM user to access the instance and view all resources of the instance.
The permissions to create and modify the configurations in the namespace.
The permissions to create and modify the configurations in the group.
Resource source:
acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instanceId}/${namespaceId}/${groupId}/${dataId}.
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [{ "Action": [ "mse:ListClusters" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:*" ], "Effect": "Allow" }, { "Action": [ "mse:List*", "mse:Query*", "mse:Get*" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:instance/mse-cn-0pp1j8om8" ], "Effect": "Allow" }, { "Action": [ "mse:CreateNacosConfig", "mse:UpdateNacosConfig" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:instance/mse-cn-0pp1j8om8/3fd98c48-a709-4061-bba1-e341d79d681b/DEFAULT_GROUP/prod.yaml" ], "Effect": "Allow" } ] }Example 5: Grant a RAM user the read and write permissions on the configurations of the specified service in the instance
mse-cn-0pp1j8om80a.This example shows a complex authorization scenario. The following levels of permissions are required to achieve fine-grained authorization:
The permission to query instances. The permission allows the RAM user to view the instance information.
The read permission on all resources in the instance. The permission allows the RAM user to access the instance and view all resources of the instance.
The permissions to create and modify the configurations in the namespace.
The permissions to create and modify the configurations in the group.
Resource source:
acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instanceId}/${namespaceId}/${groupId}/${serviceName}.{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [{ "Action": [ "mse:ListClusters" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:*" ], "Effect": "Allow" }, { "Action": [ "mse:List*", "mse:Query*", "mse:Get*" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:instance/mse-cn-0pp1j8om8" ], "Effect": "Allow" }, { "Action": [ "mse:CreateNacosConfig", "mse:UpdateNacosConfig" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:instance/mse-cn-0pp1j8om8/3fd98c48-a709-4061-bba1-e341d79d681b/DEFAULT_GROUP/test-service" ], "Effect": "Allow" } ] }
In the Grant Permission panel, confirm that the authorization is successful and click Close.
What to do next
After you create a RAM user by using an Alibaba Cloud account, you can share the logon name and password or the AccessKey pair of the RAM user to other employees. The employees can perform the following steps to log on to the RAM console or call an API operation by using the RAM user.
Log on to the MSE console
Go to the RAM User Logon page.
On the RAM User Logon page, enter the name of the RAM user, and click Next. Then, enter the password and click Log On.
NoteThe logon name of the RAM user is in the
<$username>@<$AccountAlias>or<$username>@<$AccountAlias>.onaliyun.comformat. <$AccountAlias> specifies the alias of the RAM user. If you do not specify an alias, the ID of the Alibaba Cloud account is used by default.On the RAM user center page, click a service on which the RAM user has the permissions to access the console of the service.
Call an API operation.
Use the AccessKey pair of the RAM user to call an API operation. Specify the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the RAM user in the code.