Nacos registries of Microservices Engine (MSE) allow you to configure access permissions based on instances, namespaces, groups, or service names. This prevents malicious users from obtaining or modifying information about an instance. This topic describes how to configure fine-grained authentication for Nacos registries of MSE.
Prerequisites
MSE is activated. For more information, see Activate MSE.
An MSE Nacos instance is created. For more information, see Create a Nacos engine.
Authentication is enabled. For more information, see Enable authentication.
A RAM user or a RAM role is created. For more information, see Create a RAM user or Create a RAM role.
Procedure
This topic describes how to grant and configure access permissions on the direct connection of the engine shown in the following figure. After the permissions are granted, you can use the Nacos client to access the MSE Nacos instance as a RAM user.
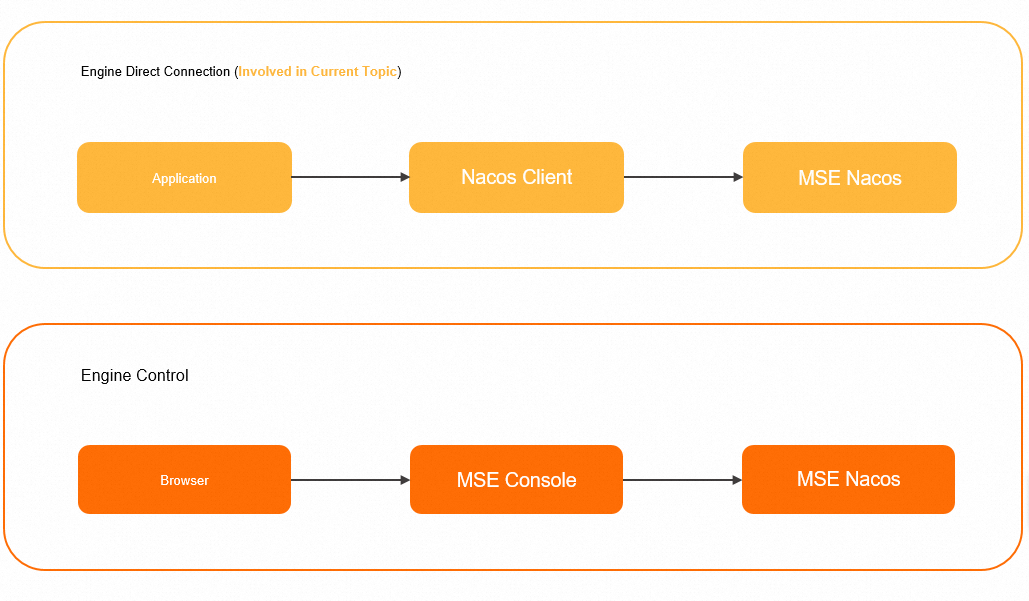
To configure and use access authentication for engine control, you need to grant the RAM user the permissions to use the MSE console. For more information, see Grant permissions on Microservices Registry resources.
Step 1: Create a fine-grained policy
Log on to the RAM console as a RAM administrator.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Policies page, click Create Policy.
On the Create Policy page, click the JSON tab.

Configure the policy.
The following table describes the actions that are involved in fine-grained authentication in registries.
Action
Description
mse:QueryNacosNaming
The read permissions on services of an MSE Nacos registry. These permissions allow you to obtain and monitor services by using SDKs.
mse:UpdateNacosNaming
The update permission on services of an MSE Nacos registry. This permission allows you to release and modify services by using SDKs.
The resources that are involved in fine-grained authentication in a registry must be specified in the following format:
acs:mse:*:*:instance/{instance_id}/{namespaceId}/{group}/naming/{serviceName}You can also modify the policy document based on the description provided in Examples.
For more information about the syntax and structure of RAM policies, see Policy structure and syntax.
Click Optional advanced optimize in the upper part of the page, and click Perform. The system performs the following operations during the advanced optimization.
The advanced policy optimization feature allows you to perform the following operations:
Split resources or conditions that are incompatible with actions.
Narrow down resources.
Deduplicate or merge policy statements.
On the Create Policy page, click OK.
In the Create Policy dialog box, specify Name and Description for the policy, and click OK.
Step 2: Grant permissions to a RAM user or a RAM role
Grant permissions to a RAM user
Log on to the RAM console as a RAM administrator.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Users page, find the required RAM user, and click Add Permissions in the Actions column.
You can also select multiple RAM users and click Add Permissions in the lower part of the page to grant permissions to the RAM users at a time.
In the Grant Permission panel, select Custom Policy from the drop-down list in the Policy section. Enter the name of the policy that you created in Step 1 in the field, click the name of the policy that is displayed, and then click Grant permissions.
In the Grant Permission panel, confirm that authorization is successful and click Close.
Grant permissions to a RAM role
Log on to the RAM console as a RAM administrator.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Roles page, find the RAM role that you want to manage and click Grant Permission in the Actions column.
You can also select multiple RAM roles and click Grant Permission in the lower part of the RAM role list to grant permissions to multiple RAM roles at a time.
In the Grant Permission panel, select Custom Policy from the drop-down list in the Policy section. Enter the name of the policy that you created in Step 1 in the field, click the name of the policy that is displayed, and then click Grant permissions.
In the Grant Permission panel, confirm that authorization is successful and click Close.
Examples
Grant a user the read-only permissions on services of specific instances.
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "mse:QueryNacosNaming" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instanceId1}", "acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instanceId2}" ], "Effect": "Allow" } ] }Grant a user the permissions to read and modify services of specific instances.
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Action": [ "mse:QueryNacosNaming", "mse:UpdateNacosNaming" ], "Resource": [ "acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instanceId1}", "acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instanceId2}" ], "Effect": "Allow" } ] }Note${instanceId1} and ${instanceId2} indicate the instance IDs.
Grant a user the read-only permissions on services in a specific namespace of an instance.
{ "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "mse:QueryNacosNaming", "Resource": "acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instance_id}/${namespaceId}" } ], "Version": "1" }Grant a user the permissions to read and modify services of the ${group} group in a specific namespace of an instance.
{ "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "mse:QueryNacosNaming", "mse:UpdateNacosNaming" ], "Resource": "acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instance_id}/${namespaceId}/${group}" } ], "Version": "1" }Grant a user the read-only permissions on the ${serviceName} service of the ${group} group.
{ "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "mse:QueryNacosNaming", "Resource": "acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instance_id}/${namespaceId}/${group}/naming/${serviceName}" } ], "Version": "1" }Grant a user the permissions to read and modify the ${serviceName} service of the ${group} group.
{ "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "mse:QueryNacosNaming", "mse:UpdateNacosNaming" ], "Resource": "acs:mse:*:*:instance/${instance_id}/${namespaceId}/${group}/naming/${serviceName}" } ], "Version": "1" }
References
For more information about how to enable authentication for MSE instances, see Access authentication by the Nacos client.