You can experience the best practices of GPU-accelerated instances by using the Function Compute console, SDKs, or Serverless Devs. This topic describes how to use Serverless Devs and function code to transcode a video from .mp4 to .flv. In this topic, Python is used as an example.
Scenarios and benefits
With the emergence of highly interactive application scenarios, such as social live streaming, online classrooms, and telemedicine, real-time and quasi-real-time Internet traffic is becoming the trend. In most cases, video platforms must transcode a source video content to output multiple distribution video formats in a 1:N manner based on factors such as bitrate, resolution, channel patch, and playback platform to provide viewers on different playback platforms with different network qualities. Video transcoding is a key step in video production and distribution. An ideal video transcoding solution must be cost-effective in terms of cost (RMB/stream) and power efficiency (watts/stream).
This section describes the benefits of GPU-accelerated instances compared with the instances with no GPU acceleration in Function Compute:
Real-time and quasi-real-time application scenarios
GPU-accelerated instances can transcode videos several times faster and push production content to users more efficiently.
Cost-prioritized GPU application scenarios
GPU-accelerated instances can be elastically provisioned based on your business requirements, and are more cost-effective than self-purchased virtual machines (VMs).
Efficiency-prioritized GPU application scenarios
Focus on code development and the business objectives without the need to perform O&M on GPU clusters, such as driver and CUDA version management, machine operation management, and faulty GPU management.
For more information about GPU-accelerated instances, see Instance types and instance modes.
Performance comparison
The GPU-accelerated instances of Function Compute are based on the Turing architecture and support the following encoding and decoding formats:
Encoding formats
H.264 (AVCHD) YUV 4:2:0
H.264 (AVCHD) YUV 4:4:4
H.264 (AVCHD) Lossless
H.265 (HEVC) 4K YUV 4:2:0
H.265 (HEVC) 4K YUV 4:4:4
H.265 (HEVC) 4K Lossless
H.265 (HEVC) 8k
HEVC10-bitsupport
HEVCB Framesupport
Decoding formats
MPEG-1
MPEG-2
VC-1
VP8
VP9
H.264 (AVCHD)
H.265 (HEVC) 4:2:0
*H.265 (HEVC) 4:4:4
8 bit
10 bit
12 bit
8 bit
10 bit
12 bit
8 bit
10 bit
12 bit
The following table describes the information about the source video.
Item | Value |
Duration | 2 minutes and 5 seconds |
Bitrate | 4085 Kb/s |
Video stream information | h264 (High), yuv420p (progressive), 1920x1080 [SAR 1:1 DAR 16:9], 25 fps, 25 tbr, 1k tbn, 50 tbc |
Audio and video information | aac (LC), 44100 Hz, stereo, fltp |
The following table describes information about the test machine that uses GPU acceleration and the machine without GPU acceleration.
Item | Machine without GPU acceleration | Machine with GPU acceleration |
CPU | CPU Xeon® Platinum 8163 4C | CPU Xeon® Platinum 8163 4C |
RAM | 16 GB | 16 GB |
GPU | N/A | T4 |
FFmpeg | git-2020-08-12-1201687 | git-2020-08-12-1201687 |
Video transcoding (1:1)
Performance test: 1 input steram and 1 output stream
Resolution | Transcoding duration without GPU acceleration | Transcoding duration with GPU acceleration |
H264∶1920x1080 (1080p) (Full HD) | 3 minutes and 19.331 seconds | 9.399 seconds |
H264∶1280x720 (720p) (Half HD) | 2 minutes and 3.708 seconds | 5.791 seconds |
H264∶640x480 (480p) | 1 minute and 1.018 seconds | 5.753 seconds |
H264∶480x360 (360p) | 44.376 seconds | 5.749 seconds |
Video transcoding (1: N)
Performance test: 1 input stream and 3 output streams
Resolution | Transcoding duration without GPU acceleration | Transcoding duration with GPU acceleration |
H264∶1920x1080 (1080p) (Full HD) | 5 minutes and 58.696 seconds | 45.268 seconds |
H264∶1280x720 (720p) (Half HD) | ||
H264∶640x480 (480p) |
Transcoding commands
Commands for transcoding without GPU acceleration
Single-stream transcoding (1:1)
docker run --rm -it --volume $PWD:/workspace --runtime=nvidia willprice/nvidia-ffmpeg -y -i input.mp4 -c:v h264 -vf scale=1920:1080 -b:v 5M output.mp4Multiple-stream transcoding (1:N)
docker run --rm -it --volume $PWD:/workspace --runtime=nvidia willprice/nvidia-ffmpeg \ -y -i input.mp4 \ -c:a copy -c:v h264 -vf scale=1920:1080 -b:v 5M output_1080.mp4 \ -c:a copy -c:v h264 -vf scale=1280:720 -b:v 5M output_720.mp4 \ -c:a copy -c:v h264 -vf scale=640:480 -b:v 5M output_480.mp4
Table 1. Parameter description Parameter
Description
-c:a copy
The audio stream can be copied without recoding.
-c:v h264
Select the software H.264 encoder for the output stream.
-b:v 5M
Set the output bitrate to 5 Mb/s.
Commands for transcoding with GPU acceleration
Single-stream transcoding (1:1)
docker run --rm -it --volume $PWD:/workspace --runtime=nvidia willprice/nvidia-ffmpeg -y -hwaccel cuda -hwaccel_output_format cuda -i input.mp4 -c:v h264_nvenc -vf scale_cuda=1920:1080:1:4 -b:v 5M output.mp4Multiple-stream transcoding (1:N)
docker run --rm -it --volume $PWD:/workspace --runtime=nvidia willprice/nvidia-ffmpeg \ -y -hwaccel cuda -hwaccel_output_format cuda -i input.mp4 \ -c:a copy -c:v h264_nvenc -vf scale_npp=1920:1080 -b:v 5M output_1080.mp4 \ -c:a copy -c:v h264_nvenc -vf scale_npp=1280:720 -b:v 5M output_720.mp4 \ -c:a copy -c:v h264_nvenc -vf scale_npp=640:480 -b:v 5M output_480.mp4
Table 2. Parameter description Parameter
Description
-hwaccel cuda
Select a proper hardware accelerator.
-hwaccel_output_format cuda
Save the decoded frames in the GPU memory.
-c:v h264_nvenc
Use the NVIDIA hardware to accelerate the H.264 encoder.
Preparations
For optimal user experience, join the DingTalk group (ID 11721331) and provide the following information:
The organization name, such as the name of your company.
The ID of your Alibaba Cloud account.
The region where you want to use GPU-accelerated instances, such as China (Shenzhen).
The contact information, such as your mobile number, email address, or DingTalk account.
Perform the following operations in the region where the GPU-accelerated instances reside:
Create a Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance or Personal Edition instance. We recommend that you create an Enterprise Edition instance. For more information, see Step 1: Create a Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance.
Create a namespace and an image repository. For more information, see Step 2: Create a namespace and Step 3: Create an image repository.
Compile FFmpeg.
FFmpeg must be compiled before you can use GPU acceleration. The following items describe how to compile FFmpeg:
(Recommended) Use compiled FFmpeg through Docker. Download address: nvidia-ffmpeg or ffmpeg.
Manually compile FFmpeg. For more information, see the compilation guide.
Upload the audio and video resources that you want to process to an Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket in the region where the GPU-accelerated instances are located. Make sure that you have the read and write permissions on the objects in the bucket. For more information about how to upload audio and video resources, see Upload objects. For more information about permissions, see Modify the ACL of a bucket.
Deploy a GPU application by using Serverless Devs
Before you start
Procedure
Create a project.
s init devsapp/start-fc-custom-container-event-python3.9 -d fc-gpu-prjThe following sample code shows the directory of the created project:
fc-gpu-prj ├── code │ ├── app.py # Function code. │ └── Dockerfile # Dockerfile: The image Dockerfile that contains the code. ├── README.md └── s.yaml # Project configurations, which specify how the image is deployed in Function ComputeGo to the project directory.
cd fc-gpu-prjModify the parameter configurations in the following files based on your business requirements.
Edit the s.yaml file.
For more information about the parameters in the YAML file, see YAML specifications.
edition: 1.0.0 name: container-demo access: default vars: region: cn-shenzhen services: customContainer-demo: component: devsapp/fc props: region: ${vars.region} service: name: tgpu_ffmpeg_service internetAccess: true function: name: tgpu_ffmpeg_func description: test gpu for ffmpeg handler: not-used timeout: 600 caPort: 9000 instanceType: fc.gpu.tesla.1 gpuMemorySize: 8192 cpu: 4 memorySize: 16384 diskSize: 512 runtime: custom-container customContainerConfig: #1. Make sure that the namespace:demo namespace and the repo:gpu-transcoding_s repository are created in advance in Alibaba Cloud Container Registry. #2. Modify the tag from v0.1 to v0.2 when you update the function later and run s build && s deploy again. image: registry.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/demo/gpu-transcoding_s:v0.1 codeUri: ./codeEdit the app.py file.
Example:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # python2 and python3 from __future__ import print_function from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler import json import sys import logging import os import time import urllib.request import subprocess class Resquest(BaseHTTPRequestHandler): def download(self, url, path): print("enter download:", url) f = urllib.request.urlopen(url) with open(path, "wb") as local_file: local_file.write(f.read()) def upload(self, url, path): print("enter upload:", url) headers = { 'Content-Type': 'application/octet-stream', 'Content-Length': os.stat(path).st_size, } req = urllib.request.Request(url, open(path, 'rb'), headers=headers, method='PUT') urllib.request.urlopen(req) def trans(self, input_path, output_path, enable_gpu): print("enter trans input:", input_path, " output:", output_path, " enable_gpu:", enable_gpu) cmd = ['ffmpeg', '-y', '-i', input_path, "-c:a", "copy", "-c:v", "h264", "-b:v", "5M", output_path] if enable_gpu: cmd = ["ffmpeg", "-y", "-hwaccel", "cuda", "-hwaccel_output_format", "cuda", "-i", input_path, "-c:v", "h264_nvenc", "-b:v", "5M", output_path] try: subprocess.run(cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, check=True) except subprocess.CalledProcessError as exc: print('\nreturncode:{}'.format(exc.returncode)) print('\ncmd:{}'.format(exc.cmd)) print('\noutput:{}'.format(exc.output)) print('\nstderr:{}'.format(exc.stderr)) print('\nstdout:{}'.format(exc.stdout)) def trans_wrapper(self, enable_gpu): src_url = "https://your.domain/input.mp4" # Use the path of the OSS object under your Alibaba Cloud account. You must have the read and write permissions on the object. dst_url = "https://your.domain/output.flv" # Use the path of the OSS object under your Alibaba Cloud account. You must have the read and write permissions on the object. src_path = "/tmp/input_c.flv" dst_path = "/tmp/output_c.mp4" if enable_gpu: src_url = "https://your.domain/input.mp4" # Use the path of the OSS object under your Alibaba Cloud account. You must have the read and write permissions on the object. dst_url = "https://your.domain/output.flv" # Use the path of the OSS object under your Alibaba Cloud account. You must have the read and write permissions on the object. src_path = "/tmp/input_g.flv" dst_path = "/tmp/output_g.mp4" local_time = time.time() self.download(src_url, src_path) download_time = time.time() - local_time local_time = time.time() self.trans(src_path, dst_path, enable_gpu) trans_time = time.time() - local_time local_time = time.time() self.upload(dst_url, dst_path) upload_time = time.time() - local_time data = {'result':'ok', 'download_time':download_time, 'trans_time':trans_time, 'upload_time':upload_time} self.send_response(200) self.send_header('Content-type', 'application/json') self.end_headers() self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode()) def pong(self): data = {"function":"trans_gpu"} self.send_response(200) self.send_header('Content-type', 'application/json') self.end_headers() self.wfile.write(json.dumps(data).encode()) def dispatch(self): mode = self.headers.get('TRANS-MODE') if mode == "ping": self.pong() elif mode == "gpu": self.trans_wrapper(True) elif mode == "cpu": self.trans_wrapper(False) else: self.pong() def do_GET(self): self.dispatch() def do_POST(self): self.dispatch() if __name__ == '__main__': host = ('0.0.0.0', 9000) server = HTTPServer(host, Resquest) print("Starting server, listen at: %s:%s" % host) server.serve_forever()Edit the Dockerfile file.
Example:
FROM registry.cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com/serverless_devs/nvidia-ffmpeg:latest WORKDIR /usr/src/app RUN apt-get update --fix-missing RUN apt-get install -y python3 RUN apt-get install -y python3-pip COPY . . ENTRYPOINT [ "python3", "-u", "/usr/src/app/app.py" ] EXPOSE 9000
Build an image.
s build --dockerfile ./code/DockerfileDeploy the code to Function Compute.
s deployNoteIf you run the preceding command repeatedly and service name and function name remain unchanged, run the
use localcommand to use local configurations.Configure provisioned instances.
s provision put --target 1 --qualifier LATESTCheck whether the provisioned instances are ready.
s provision get --qualifier LATESTIf the value of
currentis 1, the provisioned mode of GPU-accelerated instances is ready. Example:[2021-12-14 08:45:24] [INFO] [S-CLI] - Start ... [2021-12-14 08:45:24] [INFO] [FC] - Getting provision: tgpu_ffmpeg_service.LATEST/tgpu_ffmpeg_func customContainer-demo: serviceName: tgpu_ffmpeg_service functionName: tgpu_ffmpeg_func qualifier: LATEST resource: 188077086902****#tgpu_ffmpeg_service#LATEST#tgpu_ffmpeg_func target: 1 current: 1 scheduledActions: (empty array) targetTrackingPolicies: (empty array) currentError:Invoke the function.
View the version of the online function
s invokeUse CPUs for transcoding
s invoke -e '{"method":"GET","headers":{"TRANS-MODE":"cpu"}}'Use GPU for transcoding
s invoke -e '{"method":"GET","headers":{"TRANS-MODE":"gpu"}}'
Release the GPU-accelerated instances.
s provision put --target 0 --qualifier LATEST
Use the Function Compute console to deploy a GPU application
Deploy an image.
Create a Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance or Container Registry Personal Edition instance.
We recommend that you create an Enterprise Edition instance. For more information, see Create a Container Registry Enterprise Edition instance.
Create a namespace and an image repository.
For more information, see the Step 2: Create a namespace and Step 3: Create an image repository sections of the "Use Container Registry Enterprise Edition instances to build images" topic.
Perform operations on Docker as prompted in the Container Registry console. Then, push the preceding sample app.py and Dockerfile to the instance image repository. For more information about the files, see app.py and Dockerfile in the /code directory when you deploy a GPU application by using Serverless Devs.
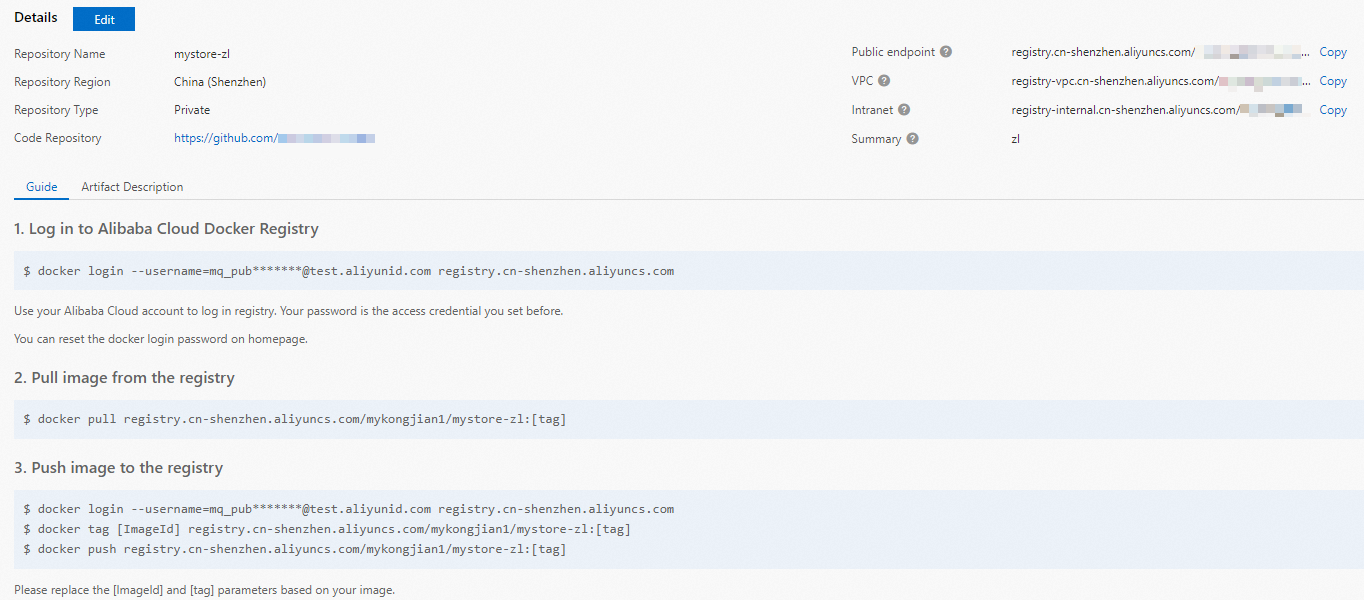
Create a service. For more information, see the "Create a service“ section of the Manage services section.
Create a function. For more information, see Create a custom container function.
NoteSelect GPU Instance for Instance Type and Process HTTP Requests for Request Handler Type.
Change the execution timeout period of the function.
Find the function that you want to manage and click Configure in the Actions column.
In the Environment Information section, change the value of Execution Timeout Period and click Save.
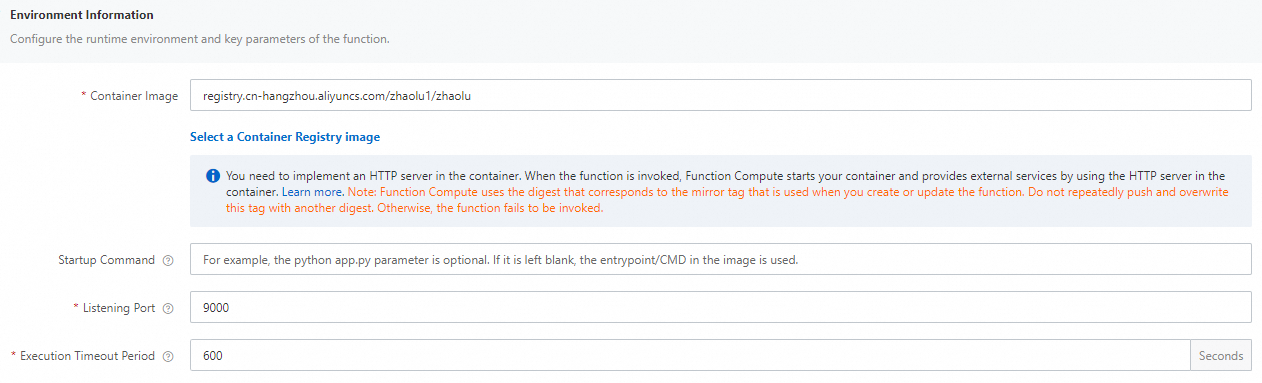
NoteTranscoding duration by using CPU exceeds the default value of 60 seconds. Therefore, we recommend that you set the value of Execution Timeout Period to a larger value.
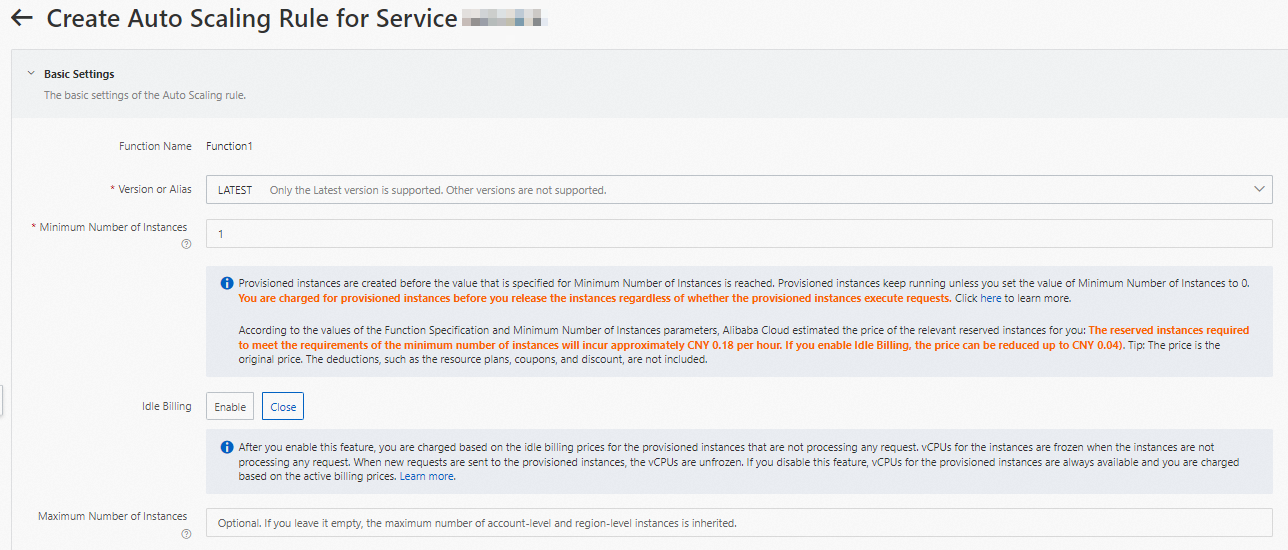
Configure provisioned GPU-accelerated instances.
On the Function Details page, click the Auto Scaling tab and click Create Rule.
On the page that appears, configure the following parameters to provision GPU-accelerated instances and click Create.
For more information about how to configure provisioned instances, see Configure auto scaling rules.
After the configuration is complete, you can check whether the provisioned GPU-accelerated instances are ready in the rule list. Specifically, check whether the value of Current Reserved Instances is the specified number of provisioned instances.
Use cURL to test the function
On the function details page, click the Triggers tab to view the configurations of the trigger and obtain the endpoint of the trigger.
Run the following command in the command line interface (CLI) to invoke the GPU function:
View the version of the online function
curl -v "https://tgpu-ff-console-tgpu-ff-console-ajezot****.cn-shenzhen.fcapp.run" {"function": "trans_gpu"}Use CPUs for transcoding
curl "https://tgpu-ff-console-tgpu-ff-console-ajezot****.cn-shenzhen.fcapp.run" -H 'TRANS-MODE: cpu' {"result": "ok", "upload_time": 8.75510573387146, "download_time": 4.910430669784546, "trans_time": 105.37688875198364}Use GPU for transcoding
curl "https://tgpu-ff-console-tgpu-ff-console-ajezotchpx.cn-shenzhen.fcapp.run" -H 'TRANS-MODE: gpu' {"result": "ok", "upload_time": 8.313958644866943, "download_time": 5.096682548522949, "trans_time": 8.72346019744873}
Result
You can view the video after transcoding by accessing the following domain name in your browser:
https://cri-zbtsehbrr8******-registry.oss-cn-shenzhen.aliyuncs.com/output.flvThis domain name is used as an example. The actual domain name prevails.