A map container is a container used to host the map itself and its sub-components in a basic flat map. You can add sub-components such as the regional thermal layer and point thermal layer, configure the location, color, and mouse interaction events of the map, and render real-time data of the geographic locations of cities across the country from multiple perspectives and in multiple forms. This topic describes the configuration items of the basic flat map container.
Settings Panel
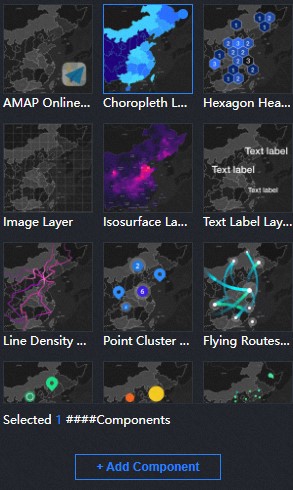
Manage sub-components
Add a component
In the left-side navigation pane, click Basic Flat Map. The Configure tab appears.
Click the
 icon on the left of Sub-components.
icon on the left of Sub-components. Select one or more child components and click Add Child Component. After the component is added, the component appears on the Manage Components page.
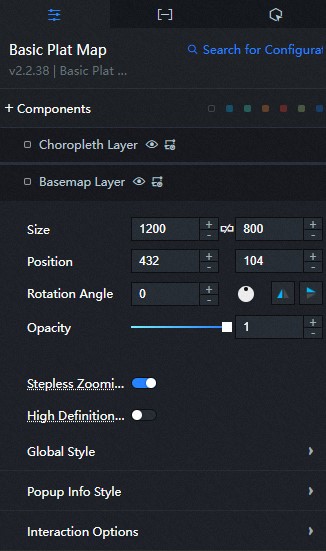
Click the added sub-component and configure the sub-component parameters, as shown in the following figure.
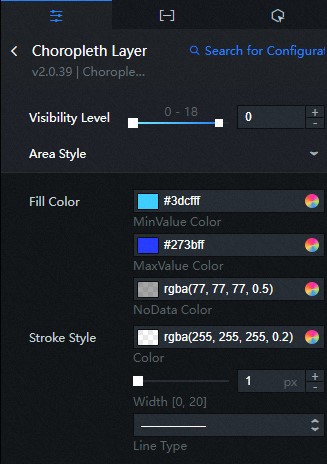
After the configuration is complete, click the
 icon to go back to the basic flat map configuration panel and configure other child components.
icon to go back to the basic flat map configuration panel and configure other child components.
To copy, rename, or delete a component, move the pointer over the component and click the
 icon to copy the component. Click
icon to copy the component. Click  to edit the name of the child widget. Click
to edit the name of the child widget. Click  to delete the child widget. Note
to delete the child widget. NoteFor more information about how to manage map components, see Manage map components.
- Search for Configurations: In the right-side panel of Canvas Editor, click the Settings tab, and click Search for Configurations in the upper-right corner. Enter the required configuration item in the search box, and click the search icon to quickly locate the configuration item. Fuzzy match is supported. For more information, see Search for asset configurations.
- Size: indicates the size of a widget, including its pixel width and height. You can click the
 icon to proportionally adjust the width and height of a widget. After you click this icon again, you can adjust the width and height as needed.
icon to proportionally adjust the width and height of a widget. After you click this icon again, you can adjust the width and height as needed. - Position: the position of a widget, which is indicated by pixel X and Y coordinates. X-coordinate indicates the pixel distance between the upper-left corner of the widget and the left border of the canvas. Y-coordinate indicates the pixel distance between the upper-left corner of the widget and the upper border of the canvas.
- Rotation Angle: the angle of a rotation that uses the center point of a widget as the rotation point. The unit is degrees (°). You can use one of the following methods to control the rotation angle of a widget:
- Directly enter the degrees in the Rotation Angle spin box or click the plus sign (+) or minus sign (-) to increase or decrease the value in the Rotation Angle spin box.
- Drag the black dot in the
 icon.
icon. - Click the
 icon to horizontally flip a widget.
icon to horizontally flip a widget. - Click the
 icon to vertically flip a widget.
icon to vertically flip a widget.
- Opacity: the opacity of a widget. Valid values: 0 and 1. If this parameter is set to 0, the widget is hidden. If this parameter is set to 1, the widget is completely displayed. Default value: 1.
Unlimited Zoom: If you enable this feature, the map zooms more smoothly. If you disable this feature, the map zooms more smoothly.
High-definition rendering: If you enable this feature for retina screens, ultra-high resolution adaptation is achieved. However, the performance of retina screens is degraded. You can enable this feature based on the machine configuration.
Global Settings: Set the background color, zoom level, latitude and longitude of the map center, and control scale ruler concealment.
Parameter
Description
Map background
The background color of the map. For more information, see color picker instructions.
Map Zoom
Controls the zoom range and default level of the map's parent container.
Zoom Range: The zoom range controls only the zoom range of the parent container. Valid values: 0 to 20.
Default Level: The default level of the parent container. The default level must be within the zoom range. Valid values: 0 to 20.
NoteThe map zoom supports fractional zoom. The zoom level controls that the parent container can only operate within the zoom range; the default level sets the default display level of the parent container, which needs to be set within the zoom range.
Map Center
The latitude and longitude of the center of the map.
Coordinate System
The coordinate system type of the map. You can select Universal Coordinate or Custom.
Common Coordinates: Common coordinates include EPSG3857, EPSG4326, and BD09. By default, the system sets the common coordinate system to EPSG3857. If you switch to another common coordinate system, the URL of the tile corresponding to the bottom layer needs to be reset.
Custom: You can customize the coordinate system, including the EPSG, proj parameters, longitude origin, latitude origin, and resolution. For more information about custom coordinate systems, see Custom coordinate system maps.
scale ruler
Click the icon to the right of the
 scale ruler to display the scale ruler on the map. When enabled, you can adjust the font color of the scale ruler, the color of the border, and the offset values of the scale ruler in the horizontal and vertical directions.
scale ruler to display the scale ruler on the map. When enabled, you can adjust the font color of the scale ruler, the color of the border, and the offset values of the scale ruler in the horizontal and vertical directions. You can also change the map center point and zoom level by configuring the data source.
Example:
[ { "zoom": 4, "lng": 112, "lat": 34 } ]Box Settings: You can configure parameters such as the text style, line height ratio, and corner radius.
Parameter
Description
Text Style
Set the font, weight, font size, and color of the text in the dialog box. For more information, see color picker instructions.
Row height ratio
The row height ratio in the dialog box. Valid values: 0.5 to 5.
Fillet Radius
Set the fillet radius of the dialog box. The larger the value, the larger the fillet radian. Valid values: 0 to 20.
Margins
Set the distance between the text in the dialog box and the four sides of the dialog box.
Background Color
Set the background color of the dialog box.
Close button
Set the color of the button to close the popup box, the size of the button, the distance between the button and the top of the widget box, and the distance between the button and the right side of the widget box. Valid values: 0 to 100.
Interactive Settings: Set the parameters for the interactive map feature.
Parameter
Description
Open Drag
Turn on the switch to enable the map dragging feature. On the Preview or Publish page, you can click and drag the map.
Enable scaling
Turn on the switch to enable the map zoom function. Under the preview or publish page, you can scroll the mouse wheel to zoom the map.
Map interaction
Turn on the switch to enable the map interaction feature. On the Preview or Publish page, you can click to focus on an area and view the data configuration information of the area.
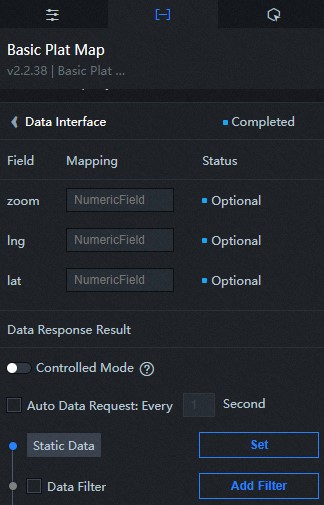
Data Panel
Parameter | Description |
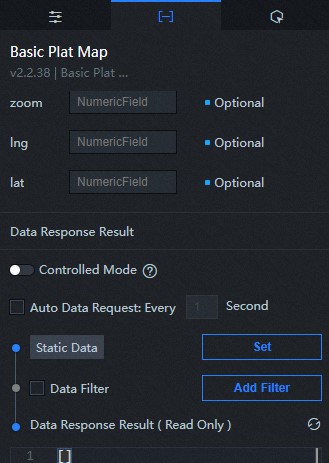
zoom | Optional. The zoom level of the map. This parameter corresponds to the Map Zoom parameter in the configuration panel. If both are configured, DataV preferentially uses the configuration in the data. |
lng | Optional. The longitude of the center of the map. This parameter is equivalent to the parameter in the configuration panel. If both are configured, DataV preferentially uses the configuration in the data. |
lat | Optional. The latitude of the map center, which corresponds to the parameter in the configuration panel. If both are configured, DataV preferentially uses the configuration in the data. |
| Parameter | Description |
| Controlled Mode | If you turn on the switch, data is not requested when a widget is initialized. Data requests are triggered only based on callback IDs or the method configured in Blueprint Editor. If you turn off the switch, data requests are automatically triggered. By default, the switch is turned off. |
| Auto Data Request | After you select the Auto Data Request check box, you can enable dynamic polling, and manually specify the polling interval. If you do not select this check box, data is not automatically requested. You must manually refresh the page to request data or use Blueprint Editor or callback ID events to trigger data requests. |
| Data Source | In the right-side panel of Canvas Editor, click the Data tab. Click Set next to Static Data. In the Configure Datasource panel, select a data source from the Data Source Type drop-down list. Enter code for data query in the code editor, click Preview Data Response to preview the response of the data source, and then view the response. For more information, see Configure asset data. |
| Data Filter | If you select the Data Filter check box, you can convert the data structure, filter data, and perform simple calculations. If you click the plus sign (+) next to Add Filter, you can configure the script for the data filter in the editor that appears. For more information, see Use the data filter. |
| Data Response Result | The response to a data request. If the data source changes, you can click the |
Interaction Panel
Select Enable to enable the widget interaction feature. The custom variable value is thrown when the map is moved and when the map is moved. For more information, see Configure callback IDs.
Some of its subcomponents support interactive configuration, that is, callback IDs, such as the regional thermal layer, line density map layer layer, and scatter layer. You can use callback IDs to interact with maps. For more information, see Configure widget interaction and Configure callback IDs.
Configure interactions in Blueprint Editor
- In Canvas Editor, right-click a widget in the Layer panel and select Add to Blueprint Editor.
- Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the page.
icon in the upper-left corner of the page. In Blueprint Editor, click the Basic Flat Map component in the Import Nodes pane. You can view the basic flat map configuration parameters on the canvas, as shown in the following figure.
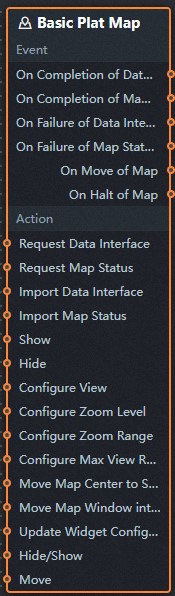
Event
Event
Description
When the data interface request is completed
The event is triggered with the processed JSON data after a data interface request is responded and processed by a filter. For more information about specific data examples, see the Data Response Result section of the Data tab in the right-side configuration panel of the canvas editor.
When a data interface request fails
The event that is returned when a data interface request fails (the request may be due to network problems or interface errors) and is processed by the filter. The event also throws the processed JSON data. For more information about specific data examples, see the Data Response Result section of the Data tab in the right-side configuration panel of the canvas editor.
When the map moves
The event that is thrown when the center point of the map is moved. The following example shows the reference data.
{ // The latitude. lat: 38.5714 // Longitude lng: 106.5306 // The zoom level. zoom: 4.3 // The type of the trigger. type: "move_mouse" }Map moving end
The event that is raised when the center point of the map is moved. The following example shows the reference data.
{ // The latitude. lat: 38.5714 // Longitude lng: 106.5306 // The zoom level. zoom: 4.3 // The type of the trigger. type: "moveend_mouse" }Action
Policy Action
Description
Request Data Interface
This action is performed to request the server data again. The data sent by an upstream data processing node or layer node is used as a parameter. For example, if the basic flat map is configured with the API data source as
http://api.testand the data passed to the request data interface as{ id: '1'}, the final request interface ishttp://api.test?id=1.Import data
After data of a widget is processed in accordance with its drawing format, the widget is imported for redrawing. You do not need to request server data again. For more information about specific data examples, see the Data Response Result section of the Data tab in the right-side configuration panel of the canvas editor.
Display
A widget is shown without the need to specify parameters.
Hide
A widget is hidden without the need to specify parameters.
Set View
Sets the map center point and zoom level for the map view. Examples of reference data are as follows.
{ // The zoom level, which must be within the set zoom level range. "zoom":4.5, // Longitude range:[-180,180] "lng":108, // Latitude range:[-180,180] "lat":38 }Set Zoom Level
Sets the zoom level of the map. Examples of reference data are as follows.
{ // The zoom level, which must be within the set zoom level range. "zoom":4.5 }Set Zoom Range
Sets the level zoom range of the map. Examples of reference data are as follows.
{ // Zoom level range: [minimum level, maximum level]. "range":[ 3, 18 ] }Set the maximum view range
Sets the coordinate range for the largest view of the map. Examples of reference data are as follows.
{ // Coordinate range:[[minimum latitude, minimum longitude],[maximum latitude, maximum longitude]] "bounds": [ [ 0, 72 ], [ 53, 138 ] ] }Fly to the designated position
Set the latitude and longitude and zoom level of the flight to the specified location point and the time interval of the flight. Examples of reference data are as follows.
{ // The zoom level, which must be within the set zoom level range. "zoom": 4.5, // Longitude range:[-180,180] "lng": 108, // Latitude range:[-90,90] "lat": 38, // gap. Unit: seconds. "duration": 0.25 }Fly to Specified Range
Set the coordinate range and flight gap for flying to the specified range. Examples of reference data are as follows.
{ // Coordinate range:[[minimum latitude, minimum longitude],[maximum latitude, maximum longitude]] "bounds": [ [ 0, 72 ], [ 53, 138 ] ], // The time interval. Unit: seconds. "duration": 0.25 }Update component configurations
Style configurations of widgets are dynamically updated. In the Configuration panel, click Copy Configuration to Clipboard to obtain the configuration data of the component. After that, change the style field for the data processing node in Blueprint Editor.
Switch to the hidden state
A widget is hidden or shown. Examples of reference data are as follows.
{ //true indicates that a widget is shown, whereas false indicates that a widget is hidden. "status": true, // Animation is displayed. "animationIn": { // The animation type, which can be set to fade. If it is not specified, no animation is displayed. "animationType": "fade", // The duration in which animation is displayed. It is in the unit of milliseconds. "animationDuration": 1000, // The function that is used to display animation. You can set this parameter to linear|easeInOutQuad|easeInOutExpo. "animationEasing": "linear" }, // Animation is hidden. "animationOut": { // The animation type, which can be set to fade. If it is not specified, no animation is displayed. "animationType": "fade", // The duration in which animation is hidden. It is in the unit of milliseconds. "animationDuration": 1000, // The function that is used to hide animation. You can set this parameter to linear|easeInOutQuad|easeInOutExpo. "animationEasing": "linear" } }Move
A widget is moved to a specified location. Examples of reference data are as follows.
{ // The positioning type. to indicates absolute positioning, whereas by indicates relative positioning. The default value is to. "positionType": "to", // The location, which is indicated by the x and y coordinates. "attr": { "x": 0, "y": 0 }, // The animation type. "animation": { "enable": false, // The duration in which animation is displayed. "animationDuration": 1000, // The animation curve, which can be set to linear|easeInOutQuad|easeInOutExpo. "animationEasing": "linear" } }