After you configure service level objectives (SLOs) for an application in Service Mesh (ASM), a Prometheus rule is automatically generated. This topic describes how to import the generated Prometheus rule to the Prometheus system for the SLOs to take effect.
Prerequisites
Prometheus monitoring is enabled for the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster. For more information, see Use open source Prometheus to monitor an ACK cluster and Monitor ASM instances by using a self-managed Prometheus instance.
Step 1: Import the generated Prometheus rule to the Prometheus system
In this example, Prometheus is deployed by using the Prometheus Operator. The Prometheus configurations are based on the custom resource definitions (CRDs). To define recording and alerting rules, you can create a Prometheus custom resource (CR) that includes a PrometheusRule object with app: ack-prometheus-operator and release: ack-prometheus-operator labels.
Whether to specify labels in the PrometheusRule CRD depends on the settings of the
ruleSelectorfield in the Prometheus CR. IfruleSelectoris left empty, labels are optional. Configure the Prometheus CR based on the actual situation.If you deploy Prometheus by using another method, use a different way to import the generated Prometheus rule. For more information about how to import a Prometheus rule, see Prometheus.
Obtain settings of the
ruleSelectorfield in the ACK console.Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster that you want to manage and choose in the left-side navigation pane.
On the CRDs tab, click the PrometheusRule.
On the Resource Objects tab, select monitoring from the Namespace drop-down list. Find ack-prometheus-operator-prometheus and click Edit YAML in the Actions column.
Obtain settings of the
ruleSelectorfield.The following code shows a sample
ruleSelectorfield. If you want the Prometheus Operator to select a Prometheus rule, thePrometheusRulemust have the same set of labels as that inmatchLabels.ruleSelector: matchLabels: app: ack-prometheus-operator release: ack-prometheus-operator
Deploy a PrometheusRule.
Create a prometheusrule.yaml file that contains the following content:
In the YAML file, the content in the
labelsfield is the same as that in the matchLabels field in the previous step. The content in thespecfield is the generated Prometheus rule.apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1 kind: PrometheusRule metadata: labels: app: ack-prometheus-operator release: ack-prometheus-operator name: asm-rules namespace: monitoring spec: # Replace with the generated Prometheus rule.Run the following command in the ACK cluster to deploy the PrometheusRule:
kubectl apply -f prometheusrule.yaml
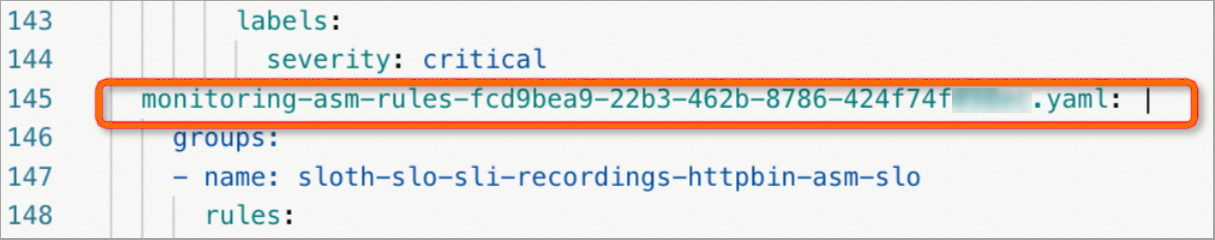
Check whether the PrometheusRule is deployed.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster that you want to manage and choose in the left-side navigation pane.
In the upper part of the ConfigMap page, select monitoring from the Namespace drop-down list, find the Prometheus ConfigMap, and click Edit YAML in the Actions column.
If the controller that corresponds to the PrometheusRule automatically writes the configurations to the ConfigMap for Prometheus to read, the PrometheusRule is deployed. The following figure shows a successful example.
Step 2: Verify the effect of SLOs
View Prometheus monitoring data and alerts
Use kubectl to connect to the ACK cluster. Run the following command on the CLI to forward all traffic from a local port to the ack-prometheus-operator-prometheus service:
kubectl --namespace monitoring port-forward svc/ack-prometheus-operator-prometheus 9090Click https://localhost:9090 to access the Prometheus console.
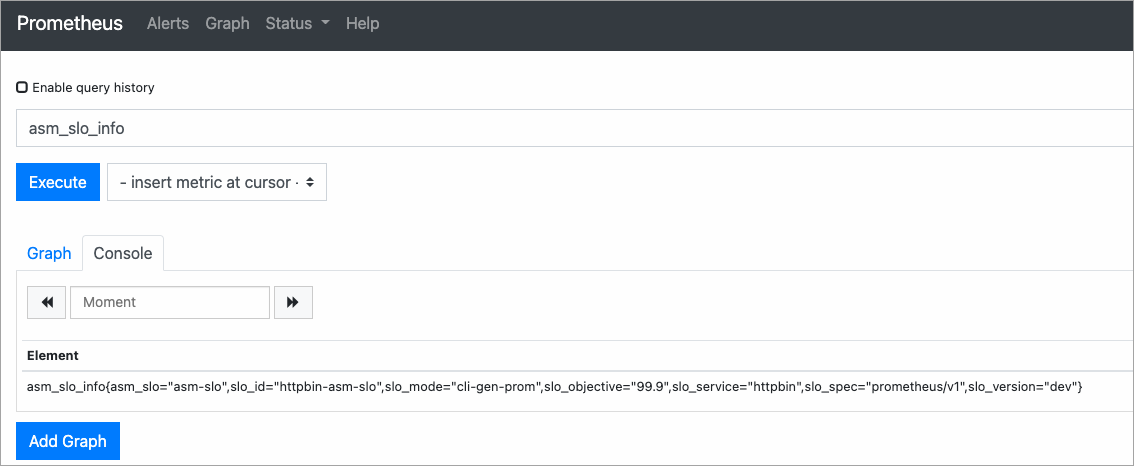
On the Prometheus page, enter asm_slo_info in the text box, and click Execute to view the SLO configurations.
The following figure shows that the Prometheus recording rule is configured.
In the top navigation bar, click Alerts to view the alerting rule.
If information similar to that in the following figure appears, the Prometheus alerting rule is configured.

Scenario 1: Simulate normal requests
Run the following script on the CLI to simulate the situation that 99.5% of requests are successfully responded to.
Replace
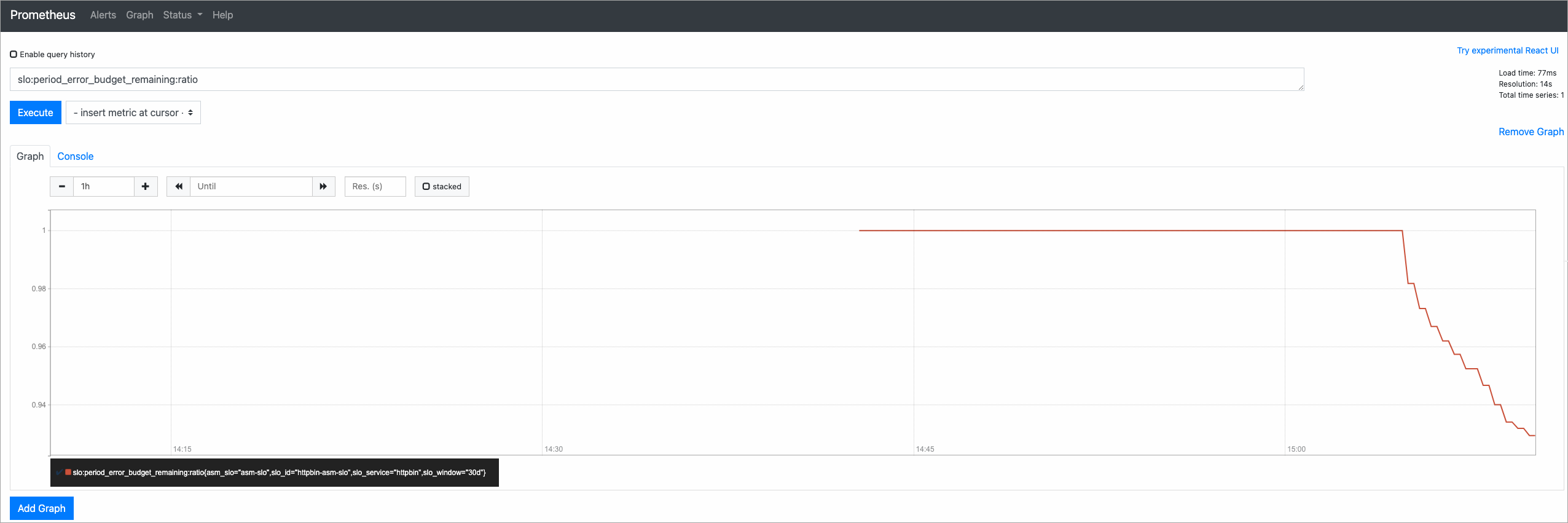
{IP address of the ingress gateway}in the script with the actual IP address of the ingress gateway. For more information about how to obtain the IP address of an ingress gateway, see Deploy an ingress gateway service.#!/bin/bash for i in `seq 200` do if (( $i == 100 )) then curl -I http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/status/500; else curl -I http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/; fi echo "OK" sleep 0.01; done;Return to the Prometheus page of the Prometheus console, enter slo:period_error_budget_remaining:ratio in the text box, and then click Execute. View the changes of the remaining error budget.
Sample result:
The following table describes the main metrics of the SLO. For more information, see SLO overview.
Metric
Description
slo:period_error_budget_remaining:ratio
The remaining error budget during the 30-day compliance period of the SLO.
slo:sli_error:ratio_rate30d
The average error rate during the 30-day compliance period of the SLO.
slo:period_burn_rate:ratio
The burn rate for the 30-day compliance period of the SLO.
slo:current_burn_rate:ratio
The current burn rate.
Scenario 2: Simulate error requests
Manually simulate faults to trigger alerts.
Run the following script on the CLI to simulate the situation that 50% of requests fail and the burn rate is 50%.
Replace
{IP address of the ingress gateway}in the script with the actual IP address of the ingress gateway.#!/bin/bash for i in `seq 200` do curl -I http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/ curl -I http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/status/500; echo "OK" sleep 0.01; done;Return to the Alerts page of the Prometheus console to view alerts.
Sample result:
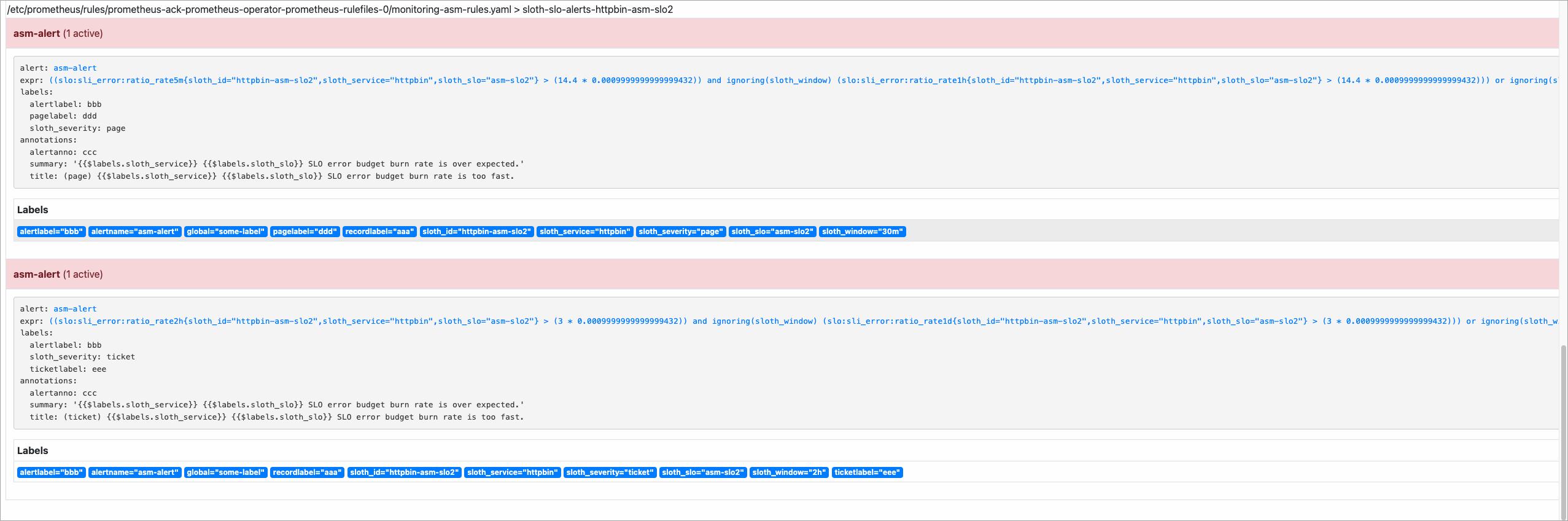
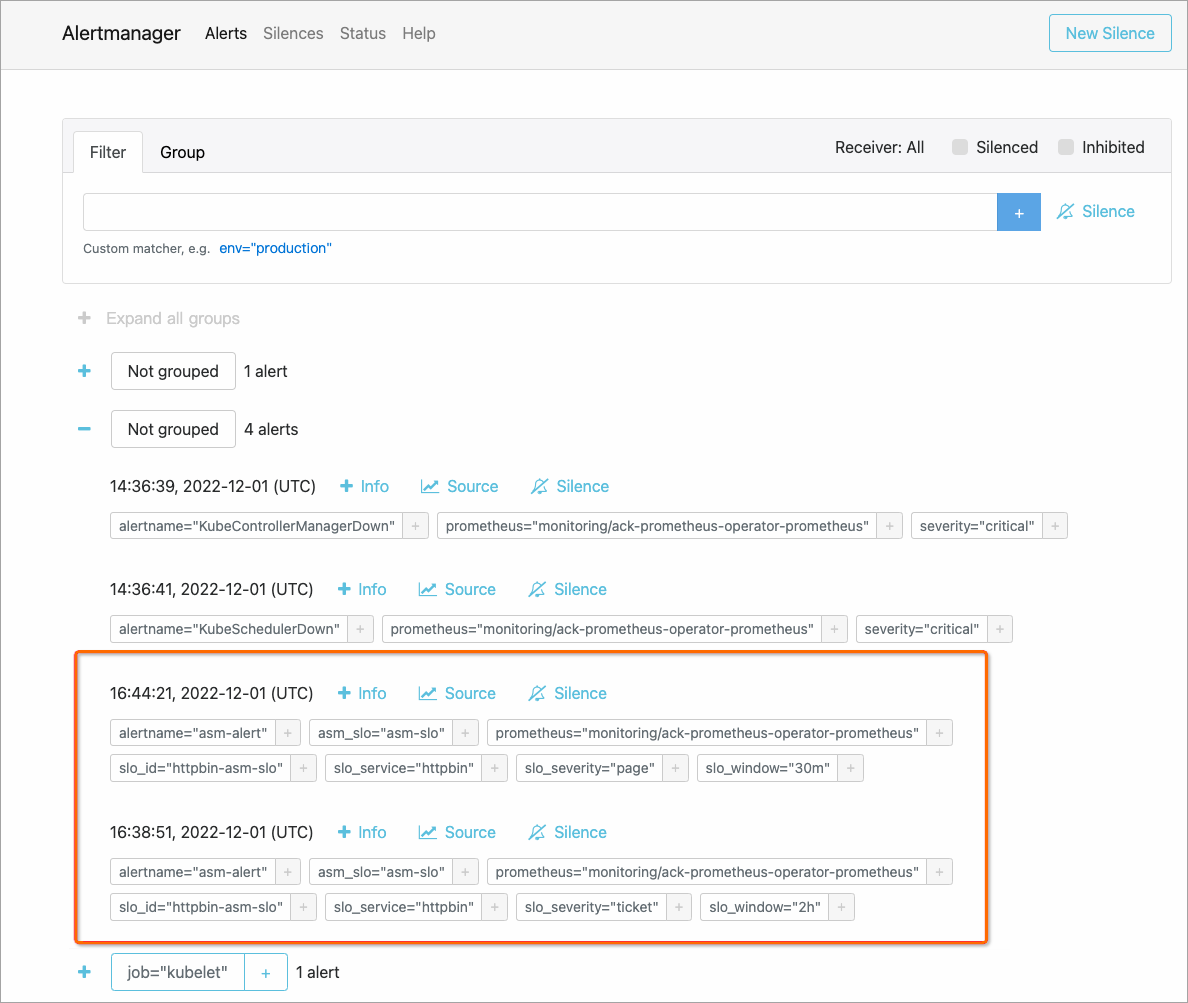
View alerts in the Alertmanager console
The Alertmanager component collects alerts generated by the Prometheus server and sends the alerts to the specified contacts.
Run the following command to forward all traffic from the local port to the ack-prometheus-operator-alertmanager service:
kubectl --namespace monitoring port-forward svc/ack-prometheus-operator-alertmanager 9093Click https://localhost:9093 to access to the Alertmanager console.
On the Alertmanager page, click the
 icon to view alerts.
icon to view alerts. The following figure shows that custom alert information is collected.