Application Real-Time Monitoring Service (ARMS) allows you to turn on or turn off the switches of an ARMS agent to enable or disable specific features, or configure a sampling policy on the Custom Configuration tab of the Application Settings page.
For information about how to use the ARMS API to configure these settings, see SaveTraceAppConfig.
Prerequisites
The ARMS agent is installed for your application. For more information, see Application Monitoring overview.
Procedure
Log on to the ARMS console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Application List page, select a region in the top navigation bar and click the name of the application that you want to manage.
NoteIcons displayed in the Language column indicate languages in which applications are written.
 : Java application
: Java application : Go application
: Go application : Python application
: Python applicationHyphen (-): application monitored in Managed Service for OpenTelemetry.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Application Settings. On the page that appears, click the Custom Configuration tab.
Set the parameters as required and click Save in the lower part of the page.
Sampling rate settings
ARMS Pro Edition
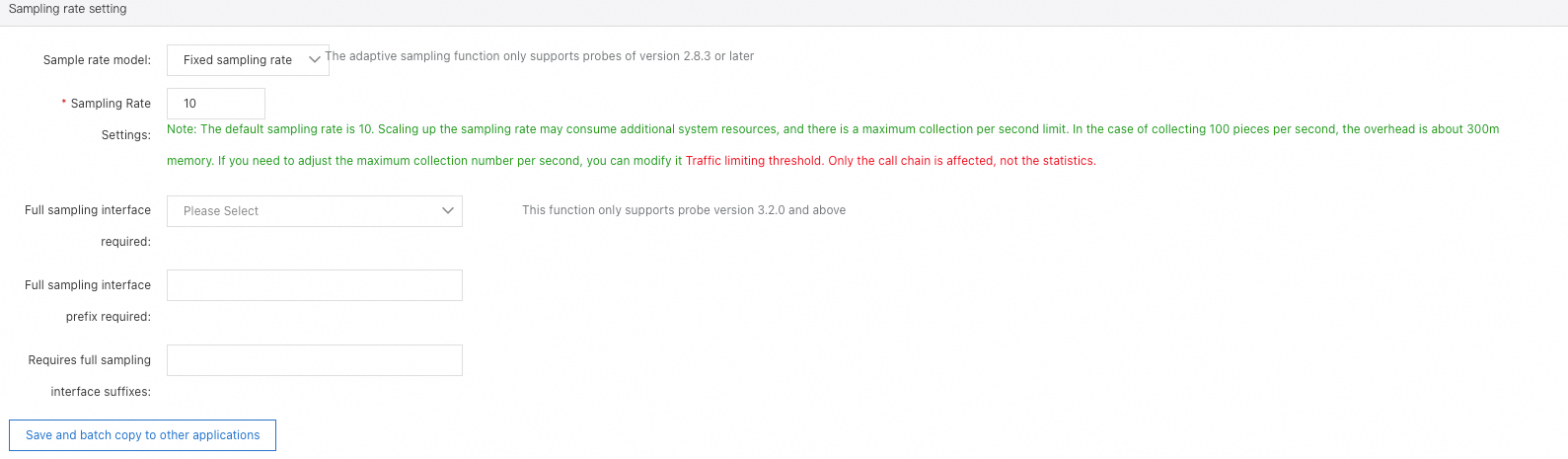
In the Sample rate setting section, you can specify the sampling policy and sampling interface for traces. For more information, see Select a trace sampling mode for the ARMS agent earlier than V3.2.8.
Trace sampling settings prevail over throttling settings.
ARMS Basic Edition
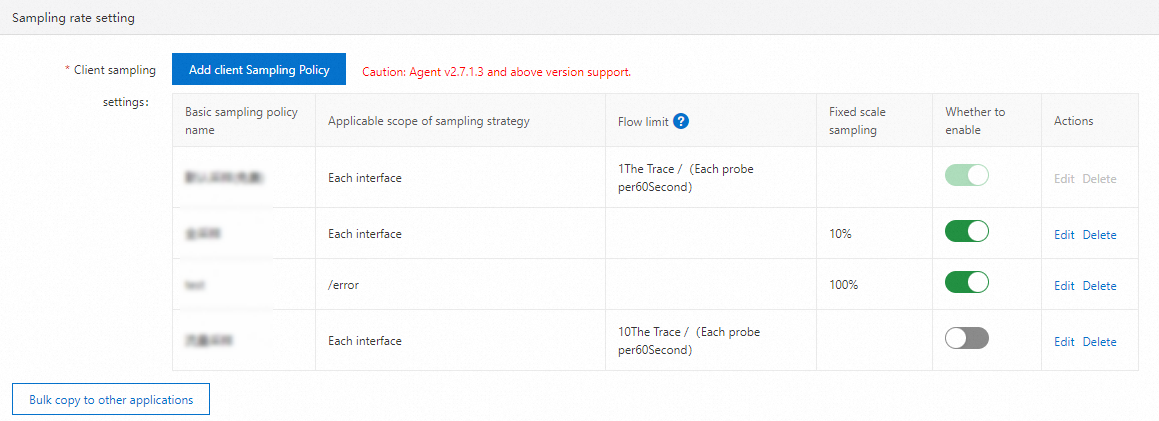
ARMS Basic Edition supports client sampling policies. You are charged based on the number of lines of data collected. By default, each ARMS agent collects one trace per minute for each interface in your account free of charge. You can also click Add Client Sampling Policy to add a custom sampling policy.
Parameter | Description |
Sampling Policy Name | The name of the sampling policy. |
Sampling type and Sampling value |
|
Applicable interface | The range of interfaces to which the sampling policy applies. Valid values: Each interface or Specify Interface. If you select Specify Interface, you must enter an interface name. Note If you select Specify Interface, you can enter only one interface name. If you want to specify multiple interfaces, you must set a sampling policy for each interface. |
After you set a sampling policy, you can specify whether to enable the policy in the console. If multiple sampling policies are enabled, the policies take effect in the following order: default sampling (free of charge) > traffic limit (a specified interface) > fixed ratio sampling (a specified interface) > traffic limit (all interfaces) > fixed ratio sampling (all interfaces). You can also modify the settings of a sampling policy or delete a sampling policy.
Agent switches and log level
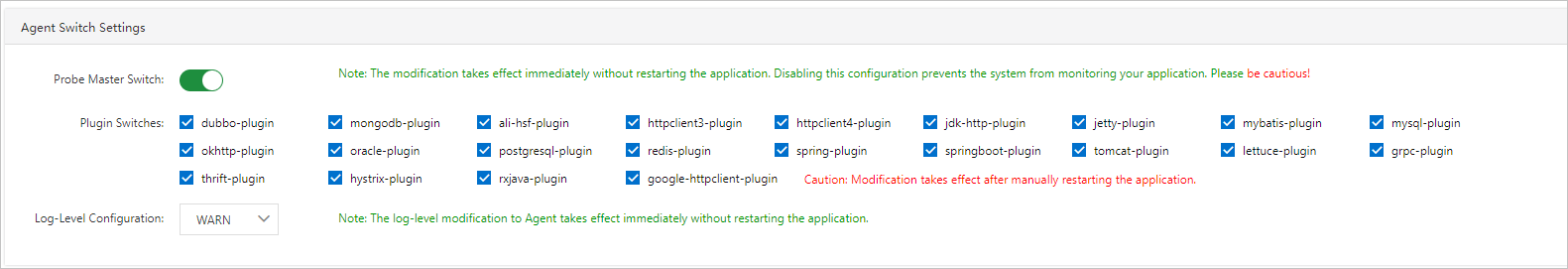
In the Agent Switch Settings section, you can turn on or off the switch of the ARMS agent and the switches of different plug-ins, and configure the log level.
The modifications to the ARMS agent and log level take effect immediately without the need to restart the application. If the switch of the ARMS agent is turned off, ARMS cannot monitor the application. Proceed with caution. To make the modification to each plug-in switch take effect, you must manually restart the application.
Threshold settings
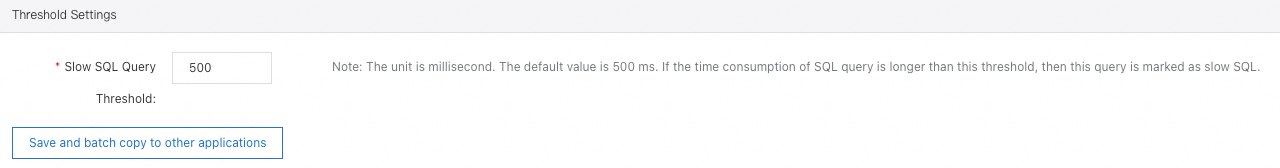
In the Threshold Settings section, you can configure the thresholds of slow SQL queries, interface response time, and throttling.
Message queue settings
In the Message Queue Configuration section, you can configure the monitoring settings about message queues.
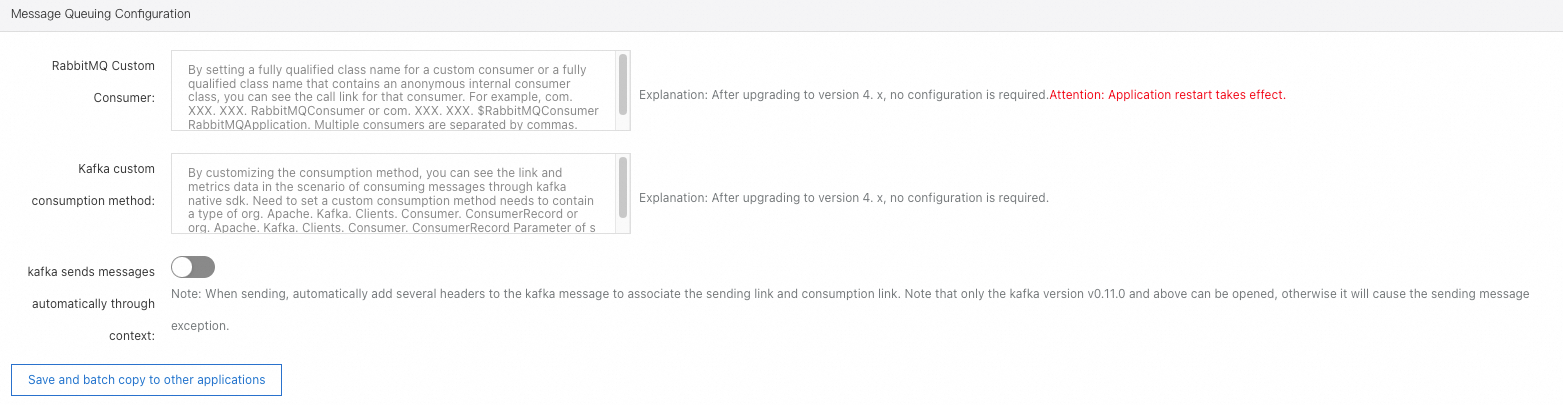
Custom RabbitMQ consumer: You can specify a class name for a custom consumer or a class name for an anonymous internal consumer to view the traces of the consumer. Separate multiple consumers with commas (,).
Custom Kafka consumption method: You can specify a custom consumption method to view the traces and metrics when you consume messages by using the native Kafka SDKs.
kafka sends automatic message pass-through context: Multiple headers are automatically added with Kafka messages to associate delivery traces with consumption traces.
Agent collection settings
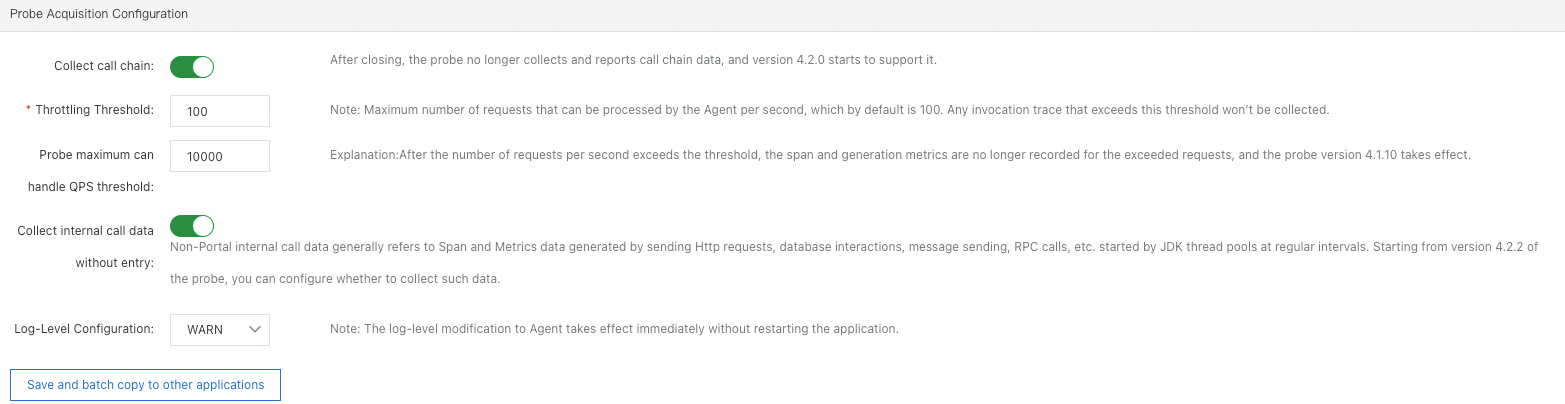
Collect call chain: Control whether trace data is reported. The switch is turned on by default. If it is turned off, trace data will no longer be reported.
Throttling Threshold: Specify the maximum number of requests the agent can process per second, with a default of 100. Trace data for requests exceeding this threshold will not be collected.
NoteTrace sampling settings prevail over throttling settings.
Probe maximum can handle QPS threshold: Specify the maximum number of requests the agent can process per second. Note that the system may adjust this threshold by up to 5% for performance optimization purposes. Requests exceeding this threshold will not be monitored. For these requests, no spans will be generated, no metrics will be recorded, and trace IDs will not be printed in the logs.
Collect internal call data without entry: Internal call data without entry points generally refers to span and metric data generated by activities such as scheduled HTTP requests, database interactions, message sending, or RPC calls initiated through JDK thread pools.
Log-Level Configuration: Adjust the logging level of the agent for troubleshooting purposes.
Interface call settings
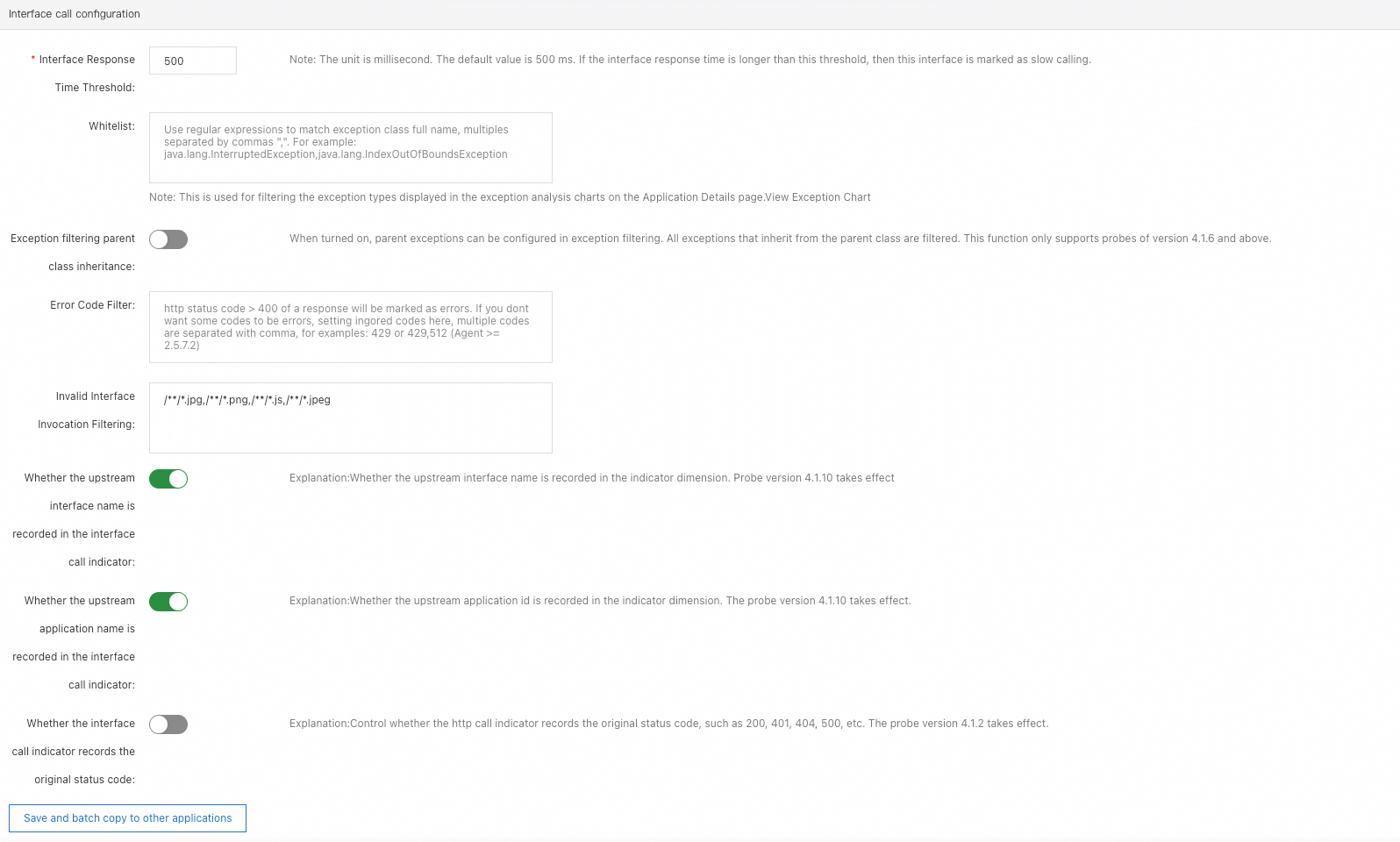
Interface Response Time Threshold: If the response time of a request exceeds the threshold, the request is marked as slow.
Whitelist: Specify the exceptions that you want to exclude from the Overview and Scenario-based Analysis > Exceptions tabs.
Exception filtering parent class inheritance: When enabled, if the currently collected exception is a subclass of an exception class configured in the exception filtering whitelist, it will also be filtered.
Configuration effect: Exceptions that meet the filtering criteria will not be displayed in the ARMS console.
Error Code Filter: By default, HTTP status codes greater than 400 are classified as error calls. If you do not want certain status codes greater than 400 to be classified as errors, you can set a whitelist to ignore these errors.
Invalid Interface Invocation Filtering: Enter the names of interfaces whose call details you do not need to view, thereby hiding them. The ARMS agent will not report their observability data.
Whether the upstream interface name is recorded in the interface call indicator and Whether the upstream application name is recorded in the interface call indicator: Specify whether to record the upstream applications and upstream interfaces that call this interface in the interface metrics. This primarily affects whether data exists on upstream and downstream traces in the services provided. When an application has many upstream applications, recording this information may lead to a significant increase in the amount of metric reports, thereby increasing costs.
Whether the interface call indicator records the original status code: Specify whether to record the original response code in the HTTP interface-related metrics.
Pooled monitoring settings
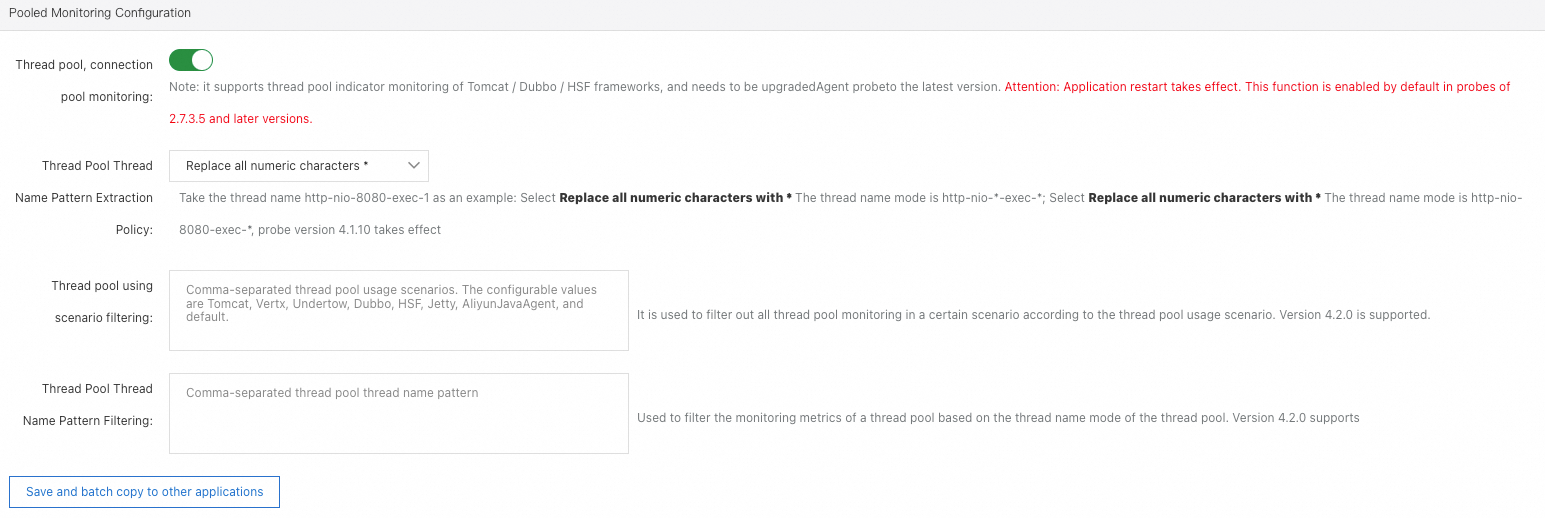
Thread pool and connection pool monitoring: Specify whether to monitor thread pool metrics in frameworks such as Apache Tomcat, Apache Dubbo, and High-speed Service Framework (HSF). To enable this feature, the ARMS agent must be updated to the latest version.
Thread Pool Thread Name Pattern Extraction Policy: This feature, by default, replaces all numeric characters in the thread names of any running threads within a thread pool with
*. You can also adjust this to only replace the ending characters of the thread names with*. In applications where multiple Dubbo Providers are initiated and these providers have different listening ports, if the default strategy is applied, two thread pools from two Dubbo Providers could be aggregated into one due to identical extracted thread name templates. At this point, adjusting this strategy can help distinguish between the two thread pools.Thread pool using scenario filtering and Thread Pool Thread Name Pattern Filtering: Metrics of certain thread pools can be excluded based on their usage scenarios and thread name patterns.
NoteThese settings only take effect for the ARMS agent for Java v4.2.0 and later.
Thread pool usage scenario refers to the context in which the thread is used, currently supporting several types including Tomcat, Vert.x, Undertow, Dubbo, Jetty, AliyunJavaAgent, and default. Among these, AliyunJavaAgent represents the thread pool used by the agent, while "default" stands for other unclassified thread pools.
The thread pool thread name pattern indicates the pattern obtained after processing the thread names in the thread pool, such as transforming parts of the thread names that contain numbers into * to get a pattern like http-nio-*-exec-*.
Span Attributes settings

Document the OTel Spec convention attributes: The OpenTelemetry Specification stipulates the attributes that should be included in the spans generated by each plugin type. However, considering the amount of data reported, the ARMS agent does not record these attributes in spans by default. You can enable this based on your needs. For information about the additional attributes added by various frameworks after enabling, see OpenTelemetry Specification documentation.
Document the OTel Spec convention attributes: The OpenTelemetry Specification stipulates the attributes that should be included in the spans generated by each plugin type. However, considering the amount of data reported, the ARMS agent does not record these attributes in spans by default. You can enable this based on your needs. For information about the additional attributes added by various frameworks after enabling, see OpenTelemetry Specification documentation.
Advanced settings
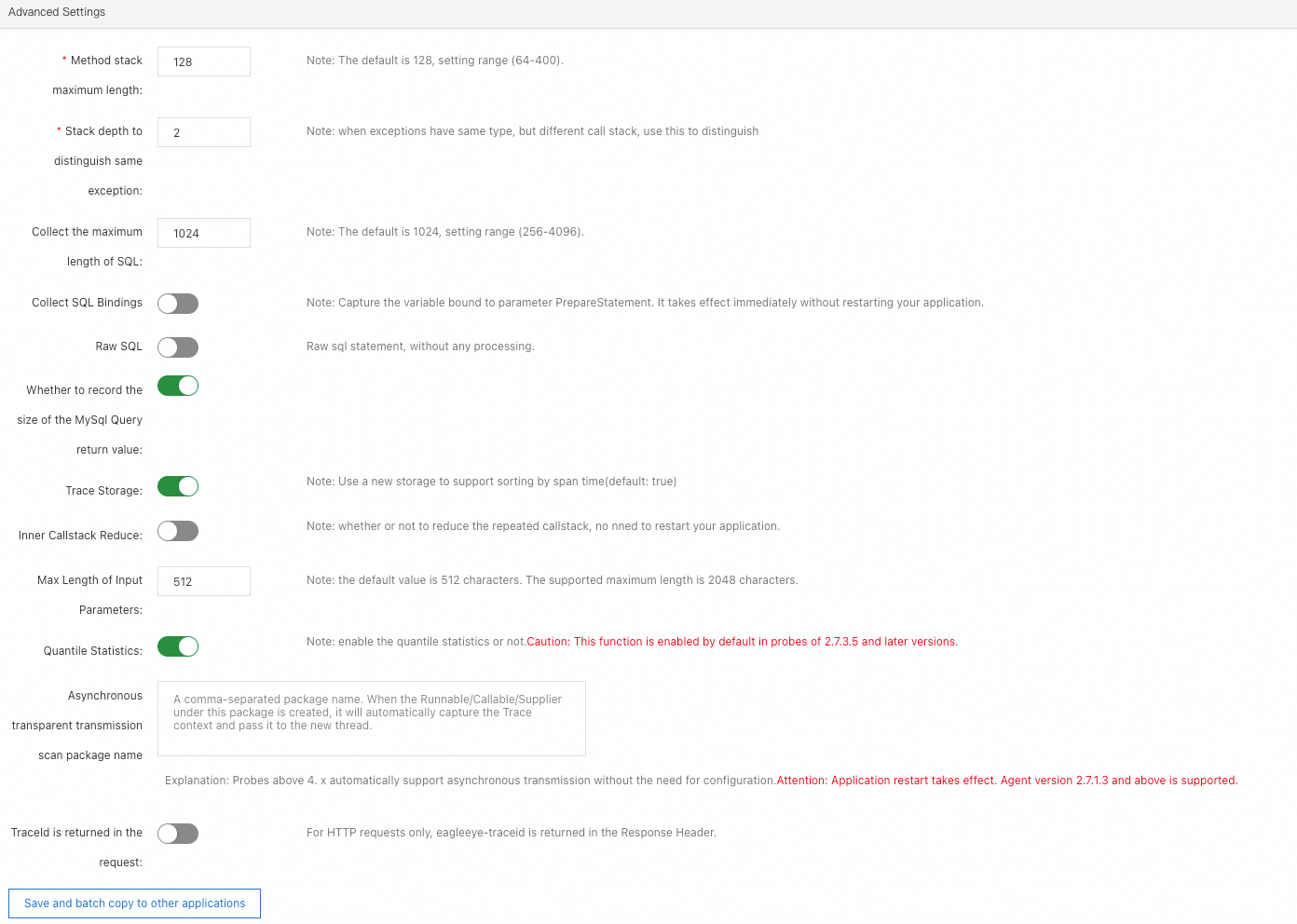
Method stack maximum length: Specify the maximum length of a method stack. Default value: 128. Maximum value: 400. The value indicates the number of entries.
Stack depth to distinguish same exception: Specify the stack depth that is used to distinguish exceptions of the same type. Generally, this parameter is set to the call depth of the first difference.
Collect the maximum length of SQL: Specify the maximum length of a SQL statement. Default value: 1024. Valid values: 256 to 4096. The value indicates the number of characters.
Collect SQL Bindings: Specify whether to capture the variable value bound to the PrepareStatement parameter. The modification takes effect immediately without the need to restart the application. Currently, this parameter can be set only when the variable value is set for the PrepareStatement parameter.
Raw SQL: Specify whether to perform operations other than truncation on SQL statements.
Whether to record the size of the MySql Query return value: Specify whether to allow ARMS to record the size of MySQL query return values.
Trace Storage: Specify whether to use the new storage format that sorts traces by time. By default, this switch is turned on.
Inner Callstack Reduce: Specify whether to simplify duplicated calls such as for loops. The modification takes effect immediately without the need to restart the application.
Max Length of Input Parameters: Specify the maximum length of an input parameter value. Default value: 512. Maximum value: 2048. The value indicates the number of characters.
Quantile Statistics: Specify whether to enable quantile statistics.
NoteA quantile is a value that splits the probability distribution of a random variable into multiple equal parts. Common quantiles include medians, quartiles, and percentiles.
Automatic pass-through asynchronous: When an asynchronous task is submitted by using the thread pool, the asynchronous context is automatically passed through.
Asynchronous transparent transmission scan package name: You can add a scan package for asynchronous pass-through to the configurations of your application to monitor asynchronous tasks. After a Runnable object, a Callable object, or a Supplier object is created, the corresponding method in the scan package for asynchronous pass-through automatically captures the trace context of the current thread. Then, when threads are used in asynchronous mode, the method passes the captured trace context to the threads. The version of the ARMS agent must be v2.7.1.3 or later.
TraceId is returned in the request: Specify whether to return the
eagleeye-traceidfield in the response headers for HTTP requests.
Thread settings
In the Thread settings section, you can turn on or turn off the Thread analysis master switch.
Only Application Monitoring Pro Edition supports this feature.
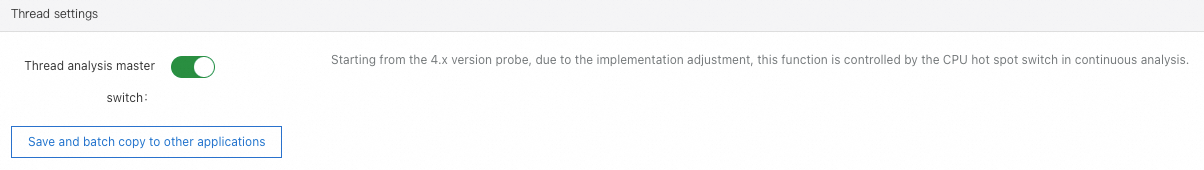
Application logs association
In the Log Collect Configuration section, configure the log sources that you want to associate with the application. For more information, see Log analysis.
Only Application Monitoring Pro Edition supports this feature.
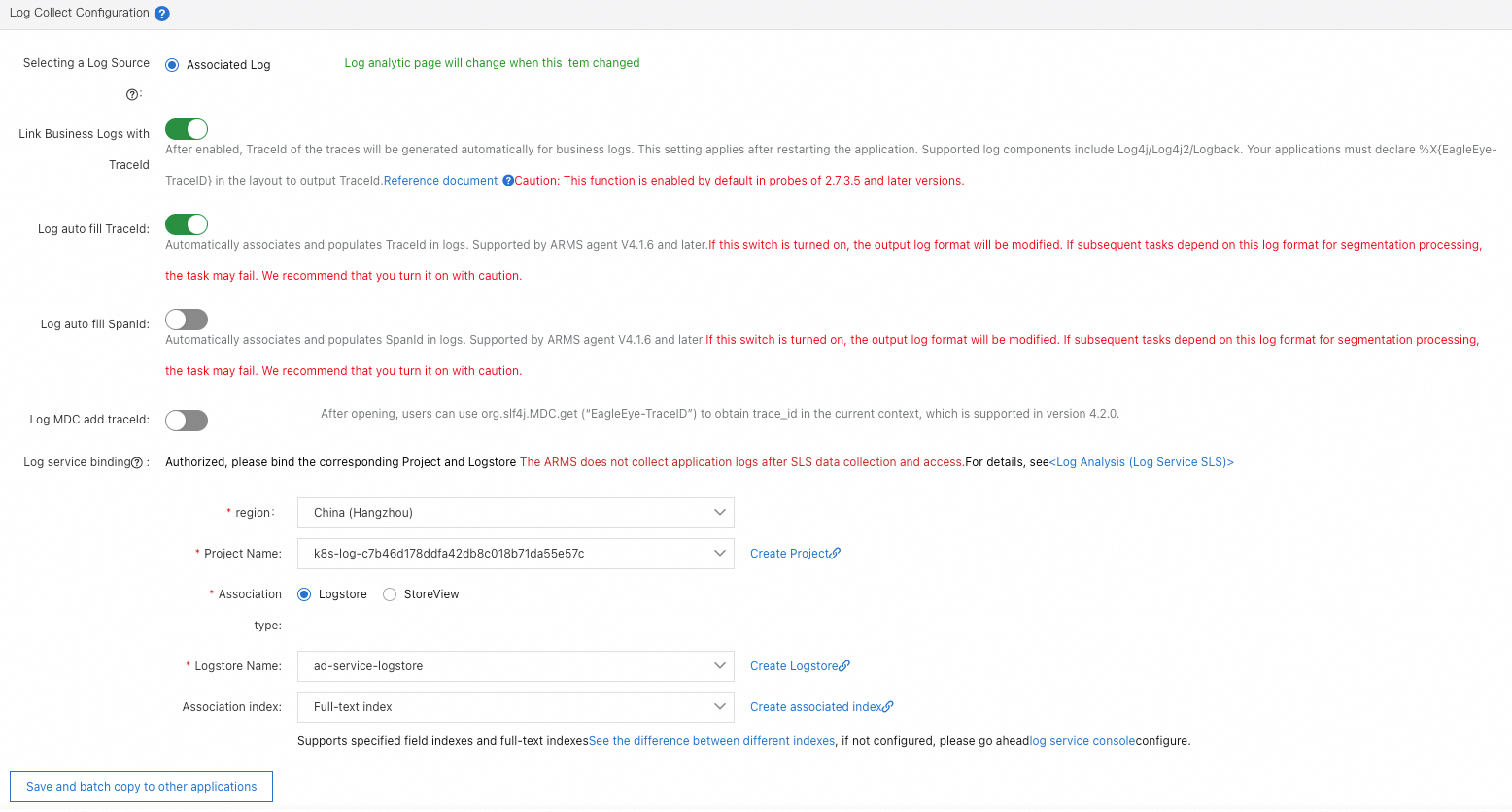
URL convergence rules
In the URL Aggregation section, you can enable or disable the convergence feature. You can also set the convergence threshold and convergence rules. URL convergence means that similar URLs are displayed together as a single object. For example, URLs prefixed with /service/demo/ are displayed as an object. The convergence threshold is the minimum number of URLs required to trigger URL convergence. For example, if the threshold is set to 100, URLs are converged only when 100 URLs meet the regular expression of the rules.
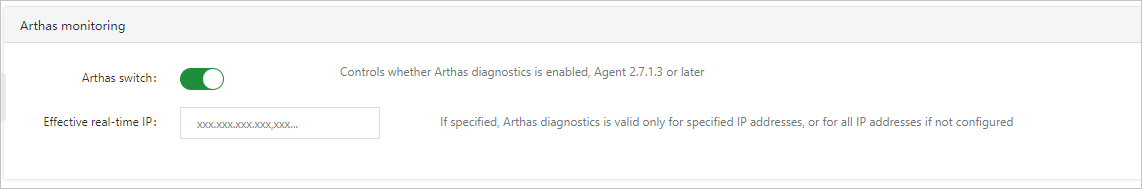
Configure Arthas monitoring
In the Arthas monitoring section, you can enable or disable the Arthas diagnostics feature. You can also specify the IP addresses on which you want to perform Arthas diagnostics. For more information, see Use Arthas diagnostics.
Only Application Monitoring Pro Edition supports this feature.
Continuous profiling
In the Continuous profiling section, you can turn on or turn off the main switch and the switches for CPU hotspot, memory hotspot, and code hotspot. You can also specify IP addresses or CIDR blocks for continuous profiling to take effect. For more information, see Use the continuous profiling feature. 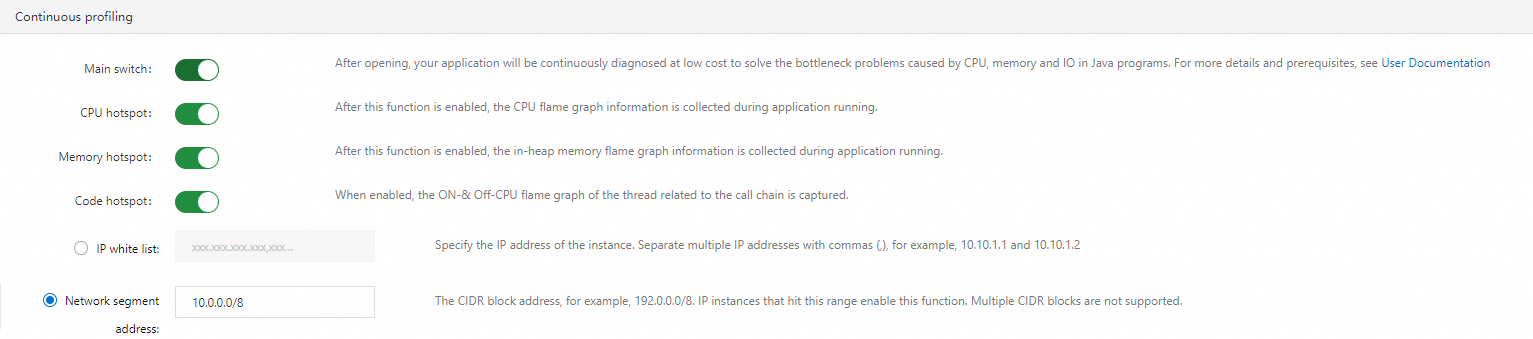
Tracing protocol settings
In the Tracing Protocol Settings section, you can select a tracing protocol based on your business requirement. For more information about the tracing protocols supported by ARMS, see Supported trace propagation protocols.
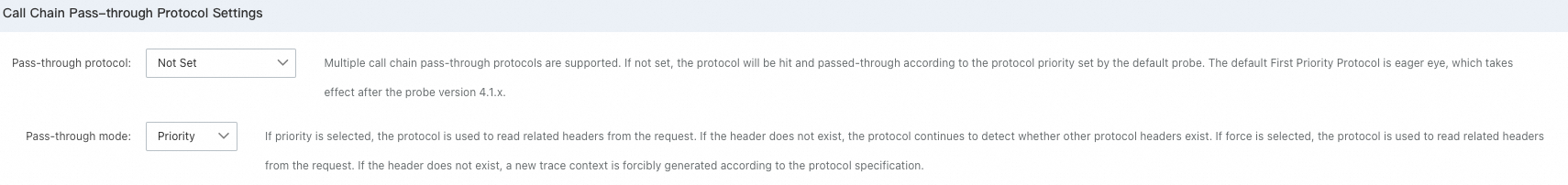
By default, when a call arrives, the ARMS agent checks for the header of a specific protocol in the order of EagleEye, OpenTelemetry, SkyWalking, Jaeger, and Zipkin. If a protocol header is detected, the agent restores the trace context based on the protocol and subsequent downstream calls will include the detected protocol header. If no protocol header is detected, the EagleEye protocol is used by default.
In this section, you can specify a protocol to be prioritized. After you save the settings, ARMS preferentially checks for the header of the specified protocol. For example, with the following configuration, the ARMS agent checks for the protocol header in the order of Jaeger, EagleEye, OpenTelemetry, SkyWalking, and Zipkin.

You can also choose to use one protocol exclusively. For example, with the following configuration, when a call arrives, the ARMS agent only checks for the Jaeger header. If no Jaeger header is found, the agent does not check for other protocol headers but generates a new trace context.

Information desensitization
In the Information desensitization section, configure a rule to desensitize JVM system parameters, Kubernetes YAML configurations, method input parameters, Arthas environment variables, and system variables during data collection. Each element in the rule represents a case-insensitive regular expression. For example, password indicates the regular expression .*password.*. Separate the elements with commas (,).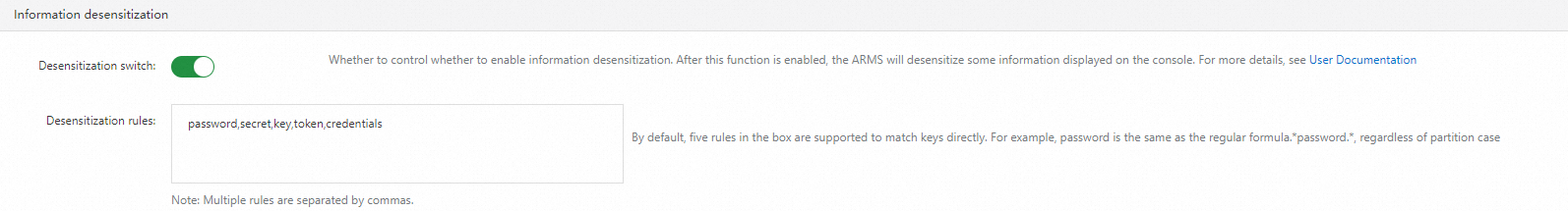
When the ARMS agent collects data, the agent desensitizes the data based on the key. If a key matches a regular expression, the corresponding value is desensitized. As shown in the following figure, if you specify licenseKey in the rule, the value of -Darms.licenseKey key is desensitized.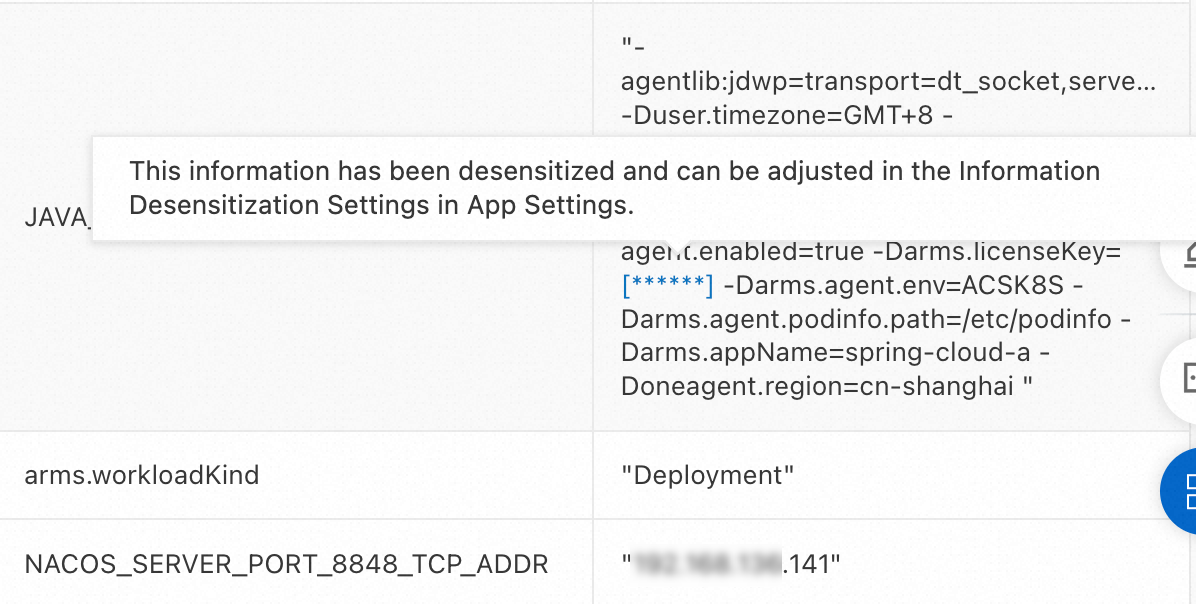
Synchronize application settings to other applications
You can synchronize the settings of an application to other applications.
Synchronize a single configuration item to other applications
In the section of the configuration item, click Save and batch copy to other applications.
In the dialog box that appears, select a specific application or all other applications and click Ok.
Synchronize all configuration items to other applications
In the lower part of the page, click Save and batch copy to other applications.
In the dialog box that appears, select a specific application or all other applications and click Ok.

Globally apply application settings
You can globally apply the specified application settings. If you create a new application, these settings are used by default.
In the lower part of the page, click Save the current application Settings to the global default Settings.
In the message that appears, click Ok.