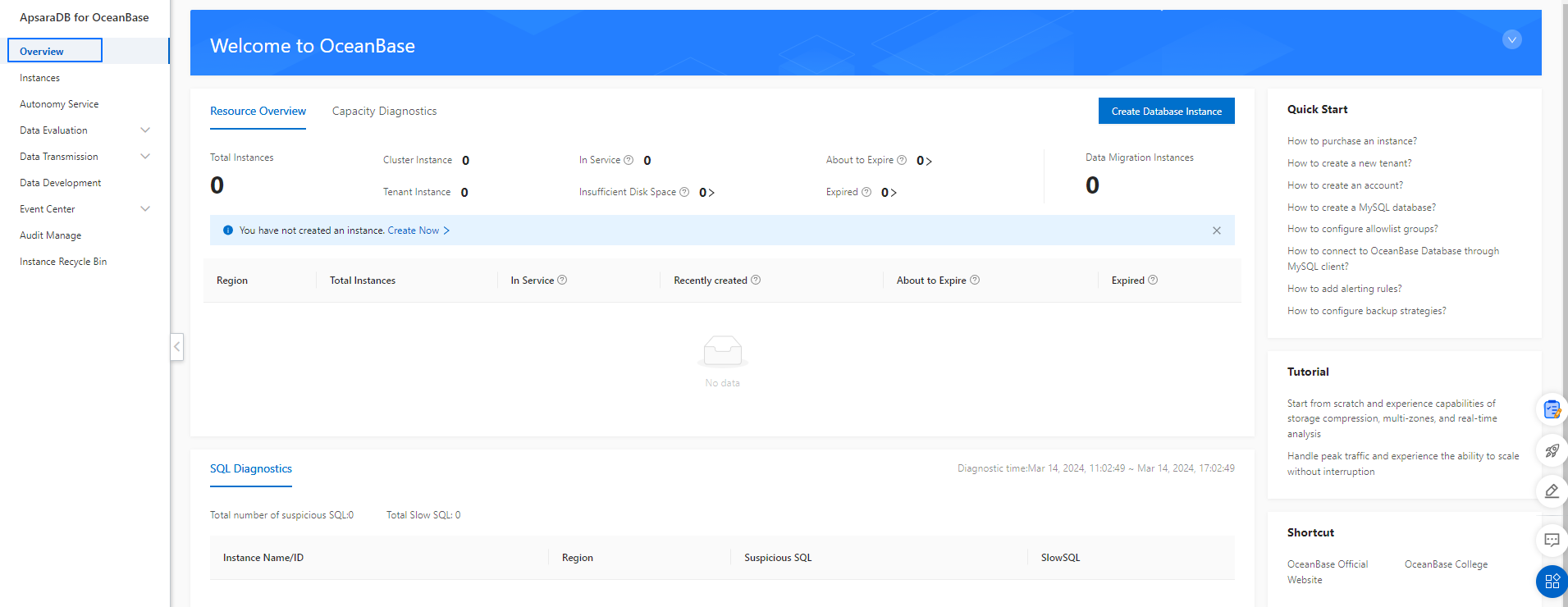
The Overview page provides guidance on the operation process of the ApsaraDB for OceanBase console and provides information such as resource overview, capacity diagnostics, and SQL diagnostics.
Concepts
ApsaraDB for OceanBase provides two types of database instances: cluster instances and tenant instances.
Cluster instance: In ApsaraDB for OceanBase, a cluster instance is a set of resources required for running OceanBase Database. The cluster instance is associated with several server nodes and cloud resources such as a virtual private cloud (VPC).
Tenant instance: A tenant instance is a separate computing resource that you can obtain after a tenant is virtually isolated in a large cluster based on the unique tenant isolation technology of ApsaraDB for OceanBase. You can create a database in a tenant instance and create tables in the database to independently provide services for upper-layer apps.
For the differences between a cluster instance and a tenant instance, see Instance types.
View the Overview page
Log on to the ApsaraDB for OceanBase console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Overview.
Guidance on the operation process
You can see the operation process guidance when you log on to the ApsaraDB for OceanBase console for the first time.
This guidance introduces the operation process in the console, including operations you can perform to create an instance, a tenant, and a database, and use a database.
When you log on to the ApsaraDB for OceanBase console again, you can go to the Overview page and click the  icon to view the operation process guidance.
icon to view the operation process guidance.
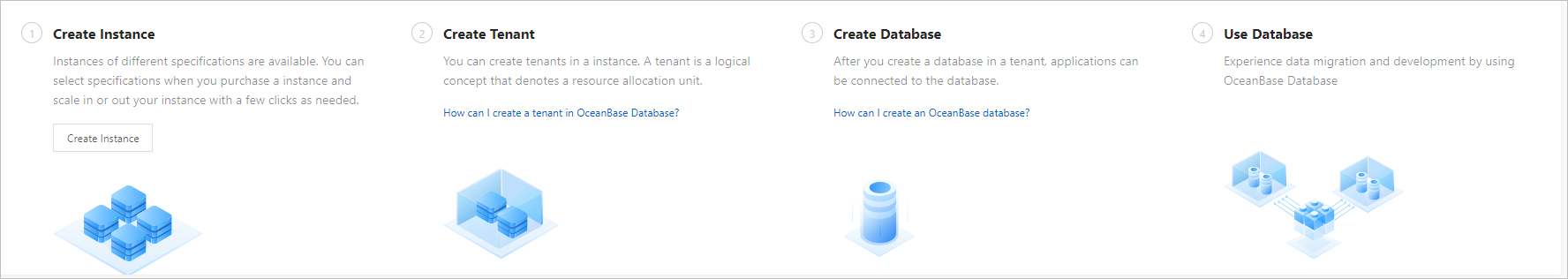
No. | Operation | Description |
1 | Create Instance | Cluster instances of various specifications are available and quick scale-out and scale-in are supported. You can purchase instances with desired specifications. For more information, see Purchase an instance. |
2 | Create Tenant | You can create a tenant in a cluster. A tenant is a logical unit for resource allocation. For more information, see Create a tenant. |
3 | Create Database | You can create a database in a tenant and then connect the database to an application. For more information, see Create a database (MySQL mode). You do not need to create a database for an Oracle tenant. |
4 | Use Database | Data migration and development tools are provided to help you manage your data in ApsaraDB for OceanBase. |
Resource information
You can view global resource information on the Overview page, including resource overview, capacity diagnosis, and geographical distribution of instances.
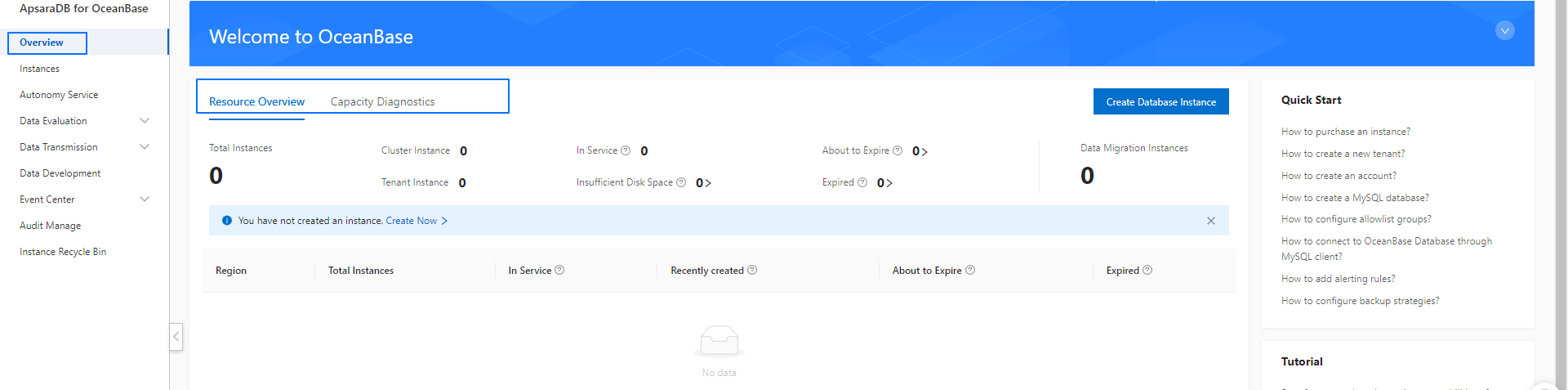
Tab | Description |
Resource Overview | On the Resource Overview tab, you can view the following resource information:
|
Capacity Diagnostics | You can click the Capacity Diagnostics tab to view the following capacity diagnostic information:
|
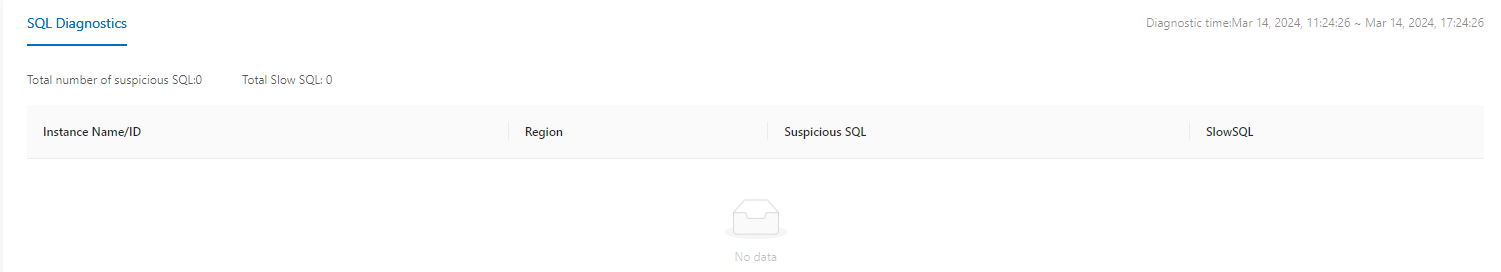
Data Monitoring
On the Overview page, you can view the global SQL diagnostics in the last six hours, such as the total numbers of suspicious SQL statements and slow SQL statements and the list of clusters with suspicious SQL statements or slow SQL statements. Click the instance name to go to the autonomy center page of the instance and view details on the One-click Diagnostics tab.