On the backup and restore page, you can initiate a restore or manual backup, or modify the backup strategies for a cluster instance. You can also view the information about data backup, backup strategies, and restore tasks. At present, the backup and restore feature is supported only for cluster instances and serverless instances, and not supported for tenant instances.
Backup principle
OceanBase Database uses the read/write splitting architecture, where internal data is divided into baseline data that is stored in SSTables and incremental data that is stored in MemTables.
The baseline data is the total data compacted and stored on disks. It is split into multiple partitions, copied into multiple replicas, and evenly distributed in data files on OBServer nodes. The backup of baseline data is called data backup.
The incremental data consists of all the new data generated since the last major compaction. It is usually stored in the MemTable and also instantiated into a commit log file. The backup of incremental data is called log backup.
OceanBase Database provides two flexible and efficient backup mechanisms: physical backup and logical backup. You can select a backup mechanism based on the actual scenario and resource requirements.
Physical backup: OceanBase Database captures the baseline data after a major compaction and replicates the captured baseline data together with subsequent commit logs to a storage facility in the same region or another region, so as to restore the physical status of the entire database.
Logical backup: Logical backup is more abstract and performed based on logical data structures, such as tables, indexes, triggers, and stored procedures. Logical backup allows you to back up specific data. For example, you can back up specific tables in a database or specific databases in a tenant. Logical backup backs up not only the data but also the logical definitions and content of database objects.
Backup content
The backup and restore feature of OceanBase Database allows you to restore the logical data such as user privileges, table definitions, system variables, user information, and view information, as well as other data of a database.
Page overview
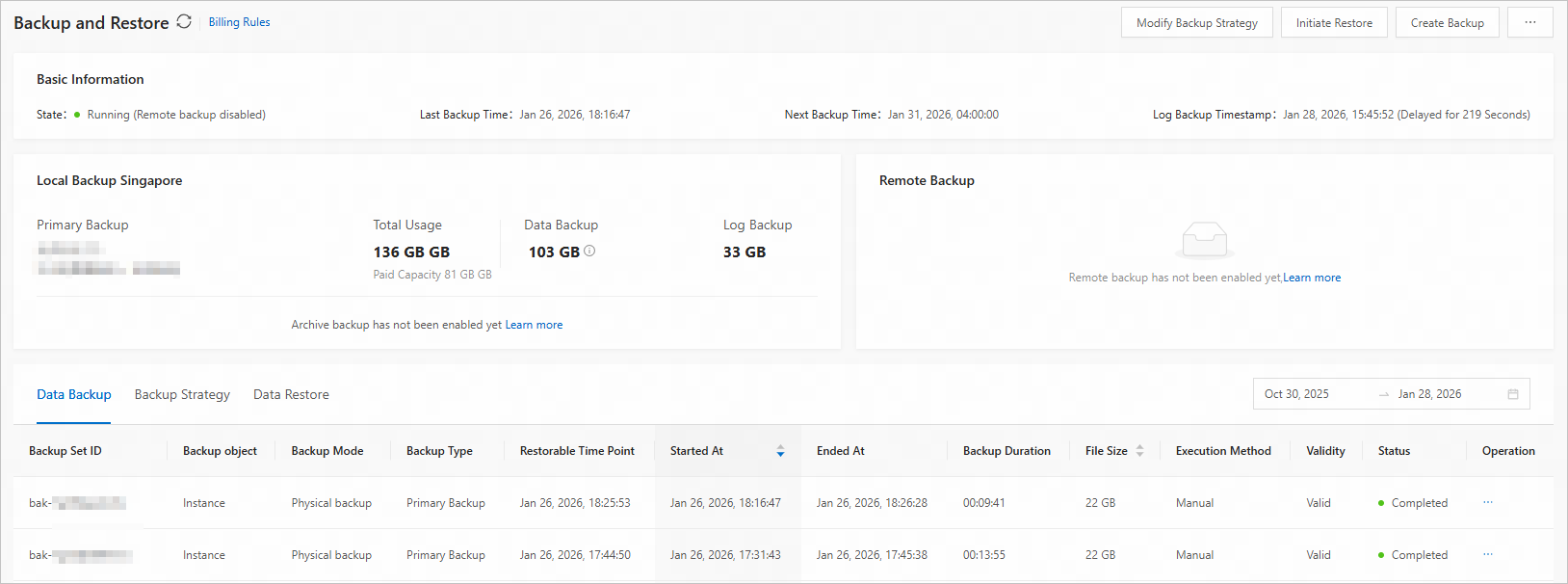
Go to the workspace page of a cluster instance. In the left-side navigation pane, click Backup and Restore. On the page that appears, you can view the backup status and latest data backup information of the current cluster, as well as the data backup and log backup information about the local primary backup, local archive backup, and remote backup features.
By default, the local archive backup and remote backup features are disabled. You can enable the features as needed. For more information, see Backup strategies.
For information about routine O&M on backup and restore, see Initiate a backup, Data backup, Backup strategies, Initiate a restore, and Data restore.
On the Backup and Restore page, you can view and download the backup usage information of the tenant. Specifically, click
 in the upper-right corner of the page, select Tenant Backup Usage Statistics, and then view and download the backup usage information of the tenant in the pop-up window.
in the upper-right corner of the page, select Tenant Backup Usage Statistics, and then view and download the backup usage information of the tenant in the pop-up window.You can enable backup sampling check in the upper-right corner. After you enable backup sampling check and specify the check time, OceanBase Database will automatically sample backup sets in your instance for restorability check, thereby verifying the integrity and validity of data in backup sets. During the check, OceanBase Database only accesses backup sets and does not read or modify any data in the backup sets. OceanBase Database does not occupy resources of your database instance during the execution of a check task. Therefore, normal business operations are not affected. After the check, all replica data generated will be automatically destroyed and cleared.
NoteBackup sampling check is available only to allowlisted users. To use this feature, contact OceanBase Technical Support.
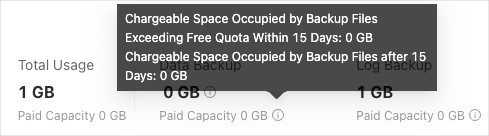
In the local backup and remote backup sections, you can view the overall storage capacity usage information.
In the local backup section, you can hover over
 next to the storage capacity usage to view the storage capacity used by physical backup and that used by logical backup.
next to the storage capacity usage to view the storage capacity used by physical backup and that used by logical backup. 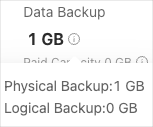
You can hover over
 next to the paid storage capacity to view the details.
next to the paid storage capacity to view the details.