You can initiate a restore for a tenant, database, or table.
Background information
You can restore data based on the existing backup sets, including physical backup sets and logical backup sets.
If you want to enable logical backup and restore, contact OceanBase Technical Support.
Assume that you want to restore the data at a specific point in time from Tenant A to Tenant B. In this case, Tenant A is the source tenant and Tenant B is the destination tenant.
OceanBase Database supports both local and remote backup and restore. If remote backup and restore is enabled, you can restore data from remote backup files.
The limitations on backup and restore are as follows:
The destination cluster must be running or undergoing allowlist modification.
A standby cluster cannot serve as the restore destination. A primary cluster can serve as the restore destination only in OceanBase Database V4.x.
If the product series of the source and destination instances do not match, data can be restored only between relational databases or between non-relational databases.
Data cannot be restored from an instance of a later version to an instance of an earlier version.
Generally, data in an instance of an earlier version can be restored to an instance of the same version or a later version. However, this feature is not supported in some special scenarios.
You cannot restore data backups from OceanBase Database V2.x or V3.x to a cluster instance of OceanBase Database V4.x.
You cannot restore data backups from OceanBase Database V4.0 to a cluster instance of OceanBase Database V4.1.
Restore a cluster instance
Log on to the ApsaraDB for OceanBase console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Instances and select the target cluster instance.
On the workspace page of the cluster instance, click Backup and Restore in the left-side navigation pane.
Click Initiate Restore, select the level of restore objects and configure relevant parameters. At present, you can restore data at the tenant, database, or table level. The following tables describe the parameters.
Click OK. In the pop-up window, confirm the available storage space at the restore destination.
If the restore destination has sufficient storage space, a pop-up window similar to the following is displayed.
If the restore destination does not have sufficient storage space, a pop-up window similar to the following is displayed.
In the pop-up window, click OK. Then, you can view the restore status on the Data Restore tab of the destination cluster. For more information, see Data restore.
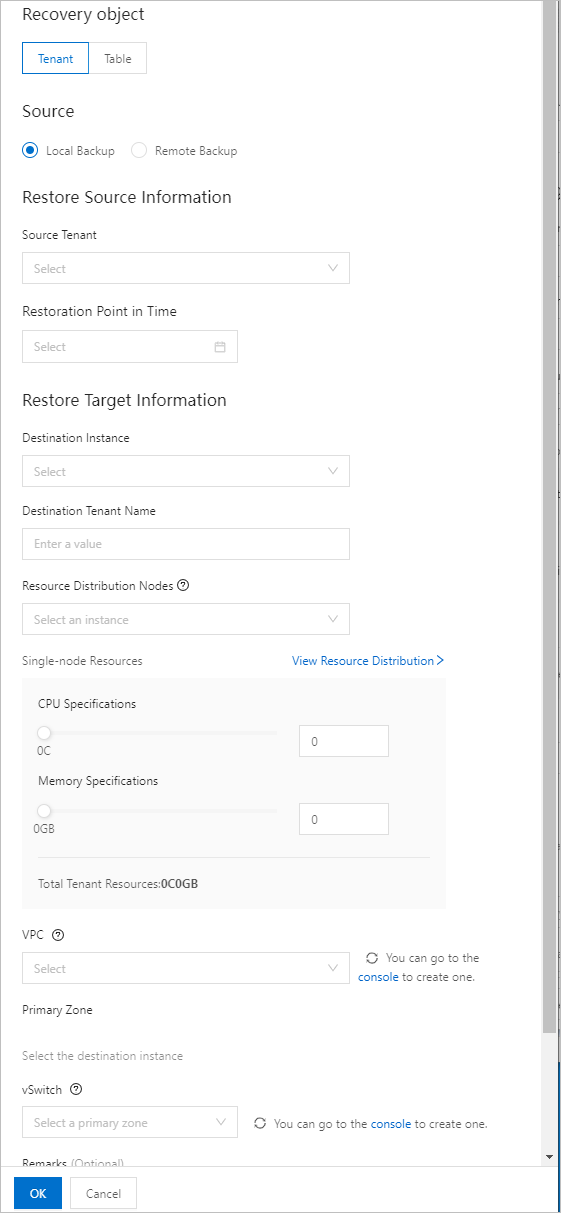
Restore a tenant
Parameter | Description |
Source | The source of the data to be restored. Note When you select Remote Backup, the current cluster serves as a destination cluster for restore. If another cluster is remotely backed up to the region where the current cluster is deployed, you can use the remote backup files of another cluster to restore tenants of another cluster to the current cluster. For example, if Cluster B is deployed in Shanghai and Cluster A that is deployed in Hangzhou is remotely backed up to Shanghai, you can use the remote backup files of Cluster A that are stored in Shanghai to restore tenants of Cluster A to Cluster B. |
Recovery Method | Specifies whether to restore data by point in time or backup set.
|
Source Cluster | The cluster that has remote backup files in the current region. This parameter is required if you set Source to Remote Backup. |
Source Tenant | The tenant whose data is to be restored. |
Restoration Point in Time | The point in time to which data is to be restored. |
From a Backup Set | The backup set to be used for restore. |
Destination Instance | The instance to which data is to be restored. If you set Source to Remote Backup, the current cluster serves as a destination instance for restore. Note An instance in gray cannot be restored. You can hover over the cluster name to view the cause. |
Whitelist Restoration | Specifies whether to restore the allowlists of the source tenant. Note If you choose to restore the allowlists of the source tenant to another cluster, you must select the allowlists to restore. |
Destination Tenant Name | The name of the tenant to which data is to be restored. |
Number of Units | The number of resource units for the tenant. Each resource unit contains three nodes. Three nodes are added each time you add a resource unit. |
Allocated Resources | The number of CPU cores and size of memory for the tenant on a single node. Note
|
VPC | The ID of the virtual private cloud (VPC) to which the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance belongs. If no suitable VPC is available, create a VPC as prompted. For more information, see What is a VPC?. |
Primary Zone | The primary zone of the destination tenant. |
vSwitch | The ID of the vSwitch to which the ECS instance belongs. You can view the number of available IP addresses of the vSwitch. If no suitable vSwitch is available, create a vSwitch as prompted. For more information, see Create and manage vSwitches. |
Remarks (Optional) | The remarks on the restore, which cannot exceed 30 characters in length. |
Restore a database
You can restore a database based on logical backup. The following table describes the parameters.
If you want to enable logical backup and restore, contact OceanBase Technical Support.
Parameter | Description |
Recovery Method | You can restore a database only from a backup set. |
From a Backup Set | The backup set to be used for restore. |
Destination Instance | The instance to which data is to be restored. If you set Source to Remote Backup, the current cluster serves as a destination instance for restore. Note An instance in gray cannot be restored. You can hover over the cluster name to view the cause. |
Destination Tenant Name | The name of the tenant to which data is to be restored. |
Remarks (Optional) | The remarks on the restore, which cannot exceed 30 characters in length. |
Restore a table
You can restore both logical tables and physical tables.
Restore a logical table.
You can restore a logical table to an existing tenant.
NoteIf you want to enable logical backup and restore, contact OceanBase Technical Support.
Parameter
Description
Recovery Method
If you choose to restore by backup set, you can restore a logical table.
Select Backup Set
The backup set for restoring the table.
Select Table Objects
Select a database and a table to be restored, or enter the name of a tenant, database, or table in the search box to search for the desired object.
NoteYou can restore at most 200 tables at a time.
Destination Instance
The instance to which data is to be restored.
Destination Tenant Name
The name of the tenant to which data is to be restored.
Destination Database Name
The name of the database to which data is to be restored.
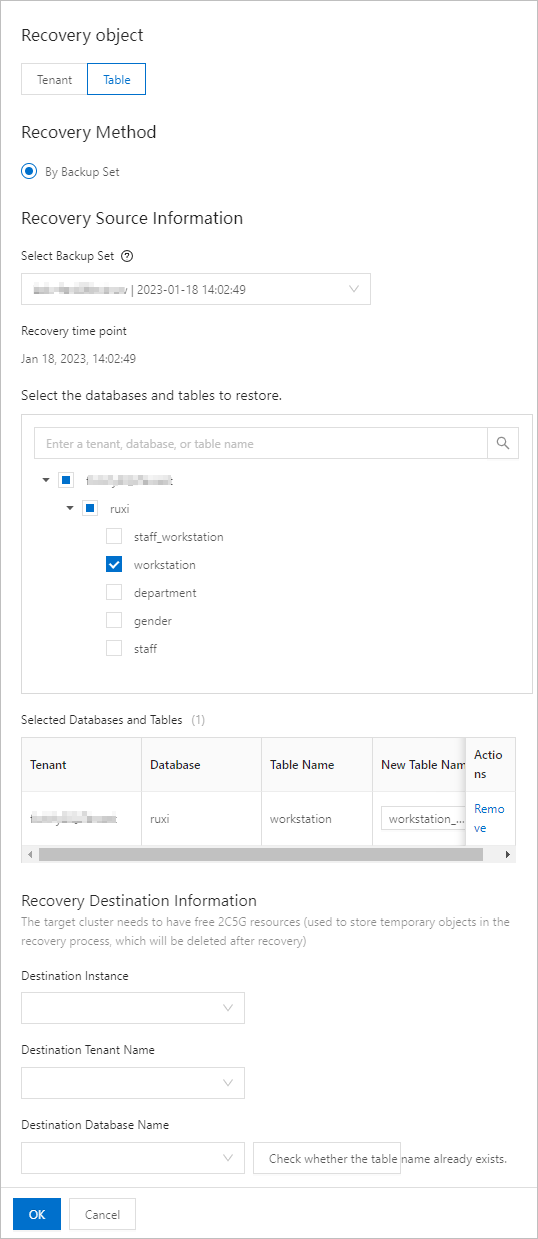
Restore a physical table. You can restore a physical table to a new tenant in the cluster.
NoteOnly OceanBase Database V3.x supports the restore of physical tables.
Parameter
Description
Recovery Method
You can choose to restore by backup set or point in time.
If you choose to restore by backup set, select a backup set for the source.
If you choose to restore by point in time, select a source tenant and a restore point in time for the source.
Select Backup Set
The backup set for restoring the table.
Source Tenant
The tenant whose data is to be restored.
Restoration Point in Time
The point in time to which data is to be restored.
Select Table Objects
Select a database and a table to be restored, or enter the name of a tenant, database, or table in the search box to search for the desired object.
NoteYou can restore at most 200 tables at a time.
Destination Instance
The instance to which data is to be restored.
Whitelist Restoration
Specifies whether to restore the allowlists of the source tenant.
NoteIf you choose to restore the allowlists of the source tenant to another cluster, you must select the allowlists to restore.
Destination Tenant Name
The name of the tenant to which data is to be restored.
Number of Units
The number of resource units for the tenant. Each resource unit contains three nodes. Three nodes are added each time you add a resource unit.
Allocated Resources
The number of CPU cores and size of memory on each node that are available for the tenant, as well as the size of the log disk for the tenant.
NoteYou can specify the log disk size for a tenant only in OceanBase Database V4.x.
You can create a tenant with specifications of 1C4G (1 CPU core and 4 GB of memory) in a cluster instance of OceanBase Database V3.x and V4.x.
The total CPU and memory capacities of all tenants cannot exceed the specifications of the cluster to which they belong.
Total resources available for a tenant = Single-node resources × Number of resource distribution nodes × Number of replicas
VPC
The ID of the virtual private cloud (VPC) to which the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance belongs.
If no suitable VPC is available, create a VPC as prompted. For more information, see What is a VPC?.
Primary Zone
The primary zone of the destination tenant.
vSwitch
The ID of the vSwitch to which the ECS instance belongs. You can view the number of available IP addresses of the vSwitch.
If no suitable vSwitch is available, create a vSwitch as prompted. For more information, see Create and manage vSwitches.
Remarks (Optional)
The remarks on the restore, which cannot exceed 30 characters in length.