Unlike Deployments, StatefulSets maintain information about the status of pods. Therefore, StatefulSets are ideal for scenarios where databases, message queues, or distributed storage systems are used. This topic introduces StatefulSets and describes how to create a StatefulSet in the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) console or using kubectl.
StatefulSet introduction
Similar to a Deployment, a StatefulSet maintains a specific number of pods that run normally. However, StatefulSets provide the following features to preserve the identity information of pods:
Ordered and fixed pod names: The pods created by a StatefulSet are sequentially named in the
<StatefulSet name>-<Serial number>format. For example, if two pods are provisioned by a StatefulSet named db-app, the pods are named db-app-0 and db-app-1. When a pod is recreated, it uses the original name.Stable network identifier: In most cases, you need to associate a headless Service with a StatefulSet. You can specify the name of a headless Service in the
spec.serviceNameparameter of the StatefulSet. The headless Service does not load balance the pods of the StatefulSet. Instead, it only provides a fixed domain name for the pod. The IP addresses of all backend pods of the headless Service are returned for DNS queries for the headless Service. After you associate a headless Service with the StatefulSet, the domain names of the pods use the<Pod name>.<Headless Service name>.<namespace>.svc.<ClusterDomain>format. Example:db-app-01.db-app.default.svc.cluster.local. If a pod is recreated, the domain name of the pod is automatically resolved to the IP address of the new pod.Stable persistent storage: You can specify a persistent volume claim (PVC) template in the
spec.volumeClaimTemplatesparameter of the StatefulSet. The StatefulSet automatically creates a separate PVC for each pod based on the specified template. The PVCs are named in the<PVC template name>-<Pod name>format. When a pod is deleted, the related PVC is retained. When the pod is recreated, the PVC is automatically associated with the new pod, which has the original serial number.
When a pod of a StatefulSet is recreated, these features ensure that the new pod inherits the network and storage status of the original pod. This allows the new pod to recover with the data in persistent storage. For more information about StatefulSets, see StatefulSets.
The sample images used in this topic are public images. Your cluster or nodes must have public network access to pull them:
Enable an existing ACK cluster to access the Internet (recommended): Create a public NAT gateway for the virtual private cloud (VPC) hosting the cluster. All cluster resources will gain public access.
Assign static public IP addresses to nodes: Nodes with public IPs can pull public images, but every node running workloads must be assigned a public IP.
Create a StatefulSet
Create from the console
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
In the upper-left corner of the StatefulSets page, click Create from Image.
In the Basic Information step, configure the basic settings of the application. Click Next to go to the Container step.
In the Container step, configure the Image Name and Port parameters. Other parameters are optional and you can keep the default settings. Click Next to go to the Advanced step. The following section describes the details of the container images.
ImportantBefore pulling this image, you need to enable Internet access for the cluster. If you keep the default value for the Configure SNAT for VPC parameter when you create a cluster, the cluster can access the Internet. For more information about how to enable Internet access for an existing cluster, see Enable an existing ACK cluster to access the Internet.
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginx:latest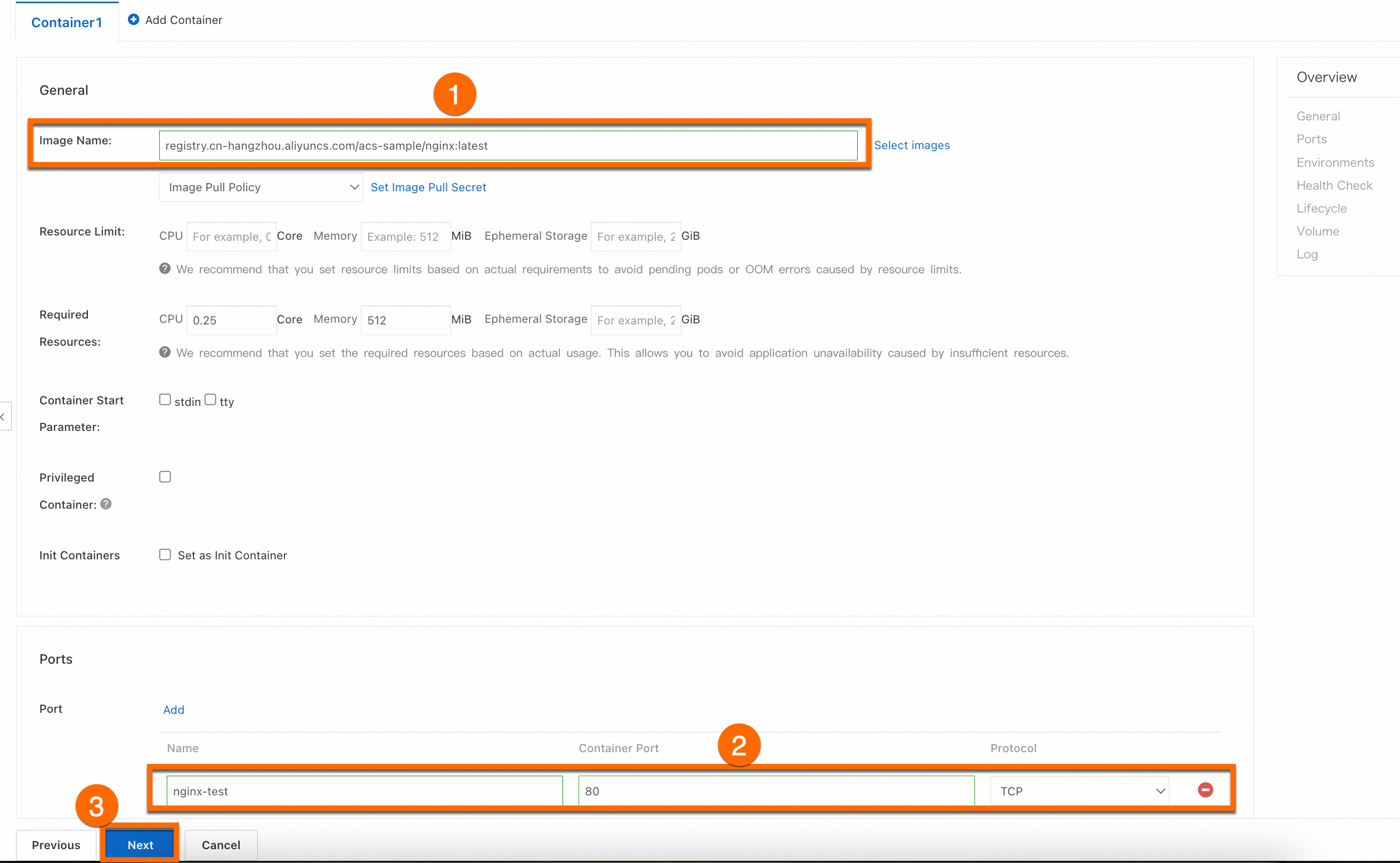
In the Advanced step, configure the following settings: access control, scaling, scheduling, labels, and annotations. In the Access Control section, create a Cluster IP Service. When you configure the Service, select Headless Service and click OK. Then, click Create in the lower part of the page.
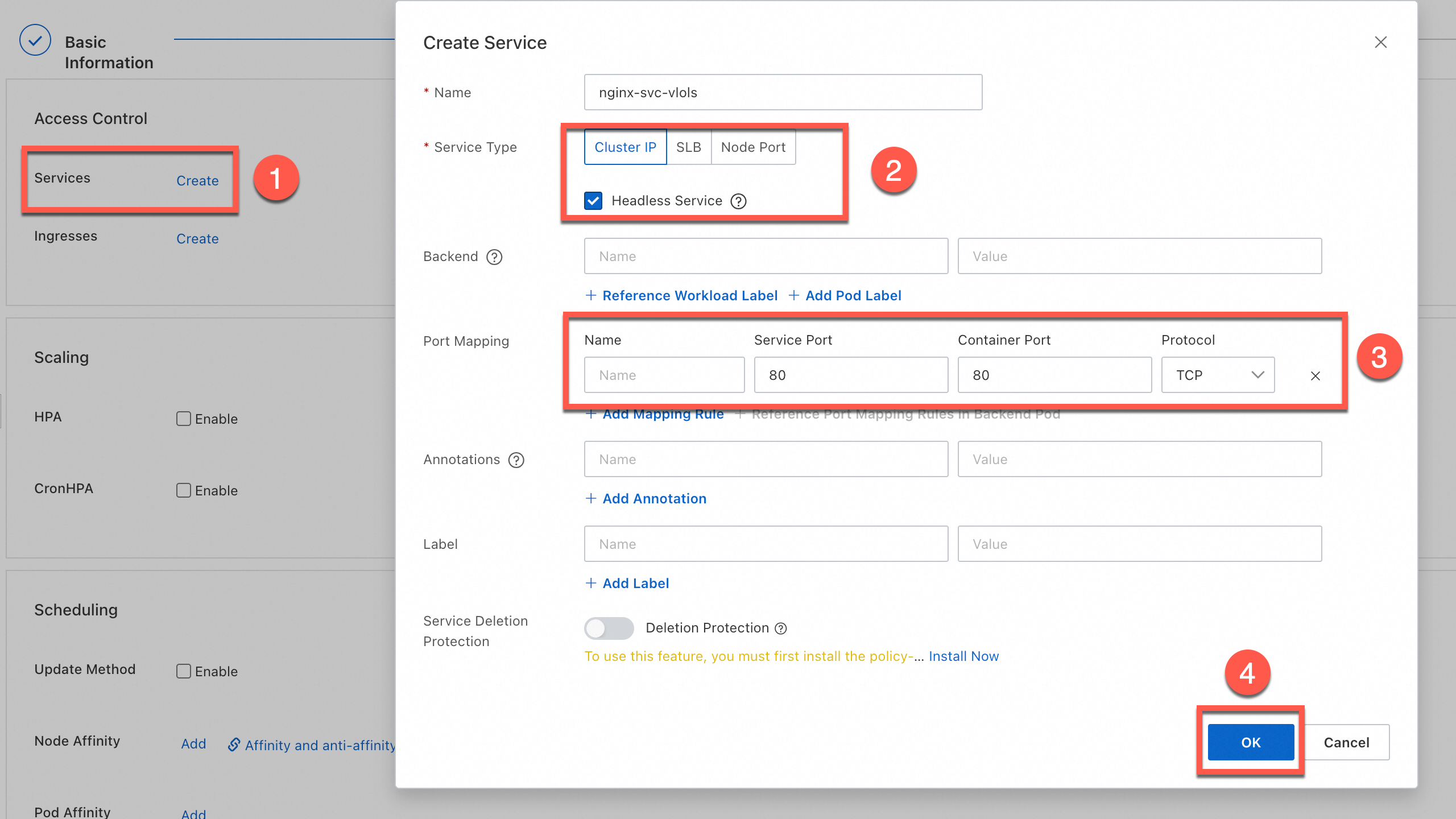
The parameters in the Basic Information, Container, and Advanced steps are the same as those when you create a Deployment. For more information about other parameters, see Parameters.
Use kubectl
Before you create a workload, make sure that you have connected to the cluster using kubectl. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
Create a file named statefulset.yaml and copy the following YAML template to the file. The YAML template includes the following resources:
A headless Service named
nginx. The headless Service is used to provide a stable domain name.A StatefulSet that has a
hostPathvolume mounted.A LoadBalancer Service that is used to expose the
StatefulSet. In this example, the Service helps you verify the features of the StatefulSet.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx labels: app: nginx spec: clusterIP: None # Headless Service selector: app: nginx ports: - port: 80 name: http --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: StatefulSet # The workload type. metadata: name: nginx-test namespace: default # Change the namespace as needed. labels: app: nginx spec: serviceName: "nginx" # Specify the name of the headless Service you created. replicas: 2 # Specify the number of pods. selector: matchLabels: app: nginx template: # The pod configurations. metadata: labels: # The pod labels. app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx # The name of the container. image: anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6 # The version of the NGINX image. ports: - containerPort: 80 # The port exposed by the container. protocol: TCP # Set the protocol to TCP or UDP. volumeMounts: - name: node-dir-volume # The volume name. The value must be the same as the volume name specified in the following volumes section. mountPath: /tmp # The mount path of the volume in the container. volumes: - name: node-dir-volume hostPath: path: /local_storage # The directory on the host that you want to mount as a volume. type: DirectoryOrCreate # If the specified directory does not exist, the system automatically creates the directory. --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx-test-svc namespace: default # Change the namespace as needed. labels: app: nginx spec: selector: app: nginx # The label used to match backend pods. ports: - port: 80 # The port provided by the Service in the cluster. targetPort: 80 # The port on which the application in the container listens (containerPort). protocol: TCP # The protocol. Default value: TCP. type: LoadBalancer # The Service type. Default value: ClusterIP. ClusterIP Services are accessible from within the cluster.Run the following command to create a StatefulSet and a Service:
kubectl apply -f statefulset.yamlExpected output:
service/nginx created statefulset.apps/nginx-test created service/nginx-test-svc createdRun the following command to query the public IP address of the Service:
kubectl get svcExpected output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 172.16.**.*** <none> 443/TCP 4h47m nginx ClusterIP None <none> 80/TCP 1h10m nginx-test-svc LoadBalancer 172.16.**.*** 106.14.**.*** 80:31130/TCP 1h10mEnter the public IP address (
106.14.**.***) of NGINX in the address bar of your browser to access the NGINX container to which the workload belongs.
Verify the features of the StatefulSet
Run the following command to query the status of the pod:
kubectl get pod nginx-test-0Expected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-test-0 1/1 Running 0 7m41sRun the following command to delete the pod:
kubectl delete pod nginx-test-0Expected output:
pod "nginx-test-0" deletedRun the following command to query the status of the pod:
kubectl get pod nginx-test-0Runningis displayed in theSTATUScolumn of the output. This indicates that a new pod is created with the original name and runs normally.NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-test-0 1/1 Running 0 20s
References
For more information about how to resolve issues that occur when you create a workload, see FAQ about workloads.
For more information about how to troubleshoot pod exceptions, see Pod troubleshooting.