CronJob is a special type of workload that does not directly manage pods. Instead, it periodically creates multiple independent jobs based on a specified policy and monitors their status. CronJobs are suitable for periodic and repetitive operations, such as performing backup operations or sending emails. This topic describes how to create a CronJob by using the console or kubectl.
The sample images used in this topic are public images. Your cluster or nodes must have public network access to pull them:
Enable an existing ACK cluster to access the Internet (recommended): Create a public NAT gateway for the virtual private cloud (VPC) hosting the cluster. All cluster resources will gain public access.
Assign static public IP addresses to nodes: Nodes with public IPs can pull public images, but every node running workloads must be assigned a public IP.
Create a Cronjob
Use the console
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the CronJobs page, click Create from Image.
On the Basic Information wizard page, configure the basic parameters of the application. Then, click Next to go to the Container wizard page.
In the General section, enter
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginx:latestas the Image Name. In the Lifecycle section, enter/bin/shin the Command box of the Start parameter, and enter["-c", "echo 'starting...'; COUNTER=0; while [ $COUNTER -lt 5 ]; do sleep 2; COUNTER=$((COUNTER+1)); echo $COUNTER; done; echo 'finished'; exit 0"]in the Parameter box. Click Next to go to the Advanced wizard page.ImportantBefore you pull the
registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginx:latestimage, you must enable Internet access for the cluster. If you select Configure SNAT for VPC when you create the cluster, the cluster has Internet access. If you do not select this option, see Enable an existing ACK cluster to access the Internet.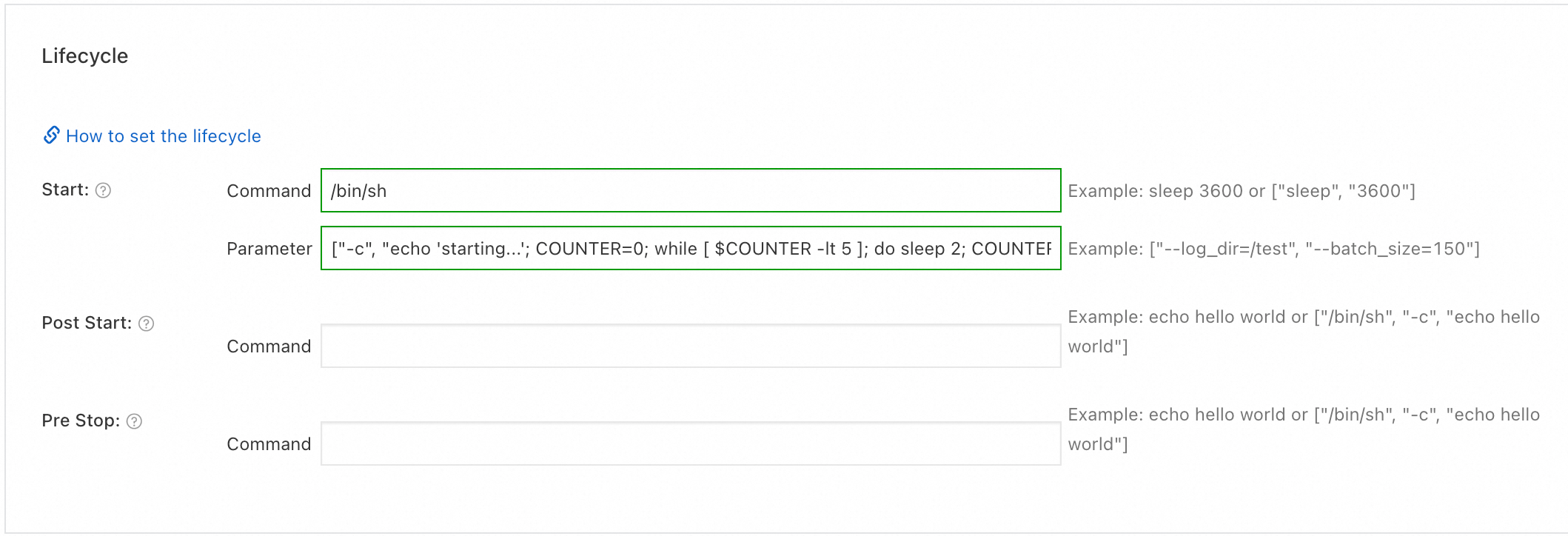
On the Advanced wizard page, you can configure the scheduling and job settings for the CronJob. In this example, set the scheduling rule to run every 2 minutes and keep other options as default. Then, click Create at the bottom of the page.

Category
Parameter
Description
CronJob
Schedule
You can specify a schedule on an hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly basis. You can also specify a cron expression.
For more information about Cron expressions, see Cron Expressions.
Concurrency Policy
Specifies whether a new job can be created when the current job is not completed.
Forbid: Skips the creation of a new job. This option is suitable for scenarios where jobs must run in a specific order or depend on each other.Allow: Allows concurrent execution and directly creates a new job. This option is suitable for scenarios where jobs do not affect each other.Replace: Terminates the current Job and creates a new job. This option is suitable for scenarios where the latest execution results are required.
Job History
The number of successful and failed jobs that the CronJob retains to avoid excessive historical records from occupying resources.
Successful Jobs History Limit: The number of the latest successful jobs to retain.
Failed Jobs History Limit: The number of the latest failed jobs to retain.
Job Settings
Completions
jobTemplate.spec.completions, which specifies the number of pods that enter the completed state.Parallelism
jobTemplate.spec.parallelism, which specifies the number of pods that can run concurrently.Timeout
jobTemplate.spec.activeDeadlineSeconds, which specifies the maximum runtime of a single job. The Job is stopped immediately after the runtime exceeds this value, regardless of whether the job is completed. This option is suitable for jobs that have strict time requirements or may enter an infinite loop. The default value is600seconds (s).BackoffLimit
jobTemplate.spec.backoffLimit: The maximum number of retries after a pod fails, which is the total number of failures for all pods. The default value is6.Restart
jobTemplate.spec.template.spec.restartPolicy, which specifies the restart policy after a pod fails.Never: After a container in the pod exits abnormally, the system attempts to restart the pod in place (without creating a new pod). The restart is not counted in
spec.backoffLimit.On Failure: After a pod fails, the system creates a new pod to replace it.
Labels, Annotations
Pod Labels
Add a label to each pod to which the workload belongs. All resources in the cluster, including workloads and services, are matched with pods by using labels. ACK adds a label in the format of
app:(application name)to pods by default.Pod Annotations
Add an annotation to each pod to which the workload belongs. Some features in ACK use annotations. You can configure the annotations when you use these features.
After the CronJob is created, you can see jobs created at 2-minute intervals in the console.

Use kubectl
Before you create a workload, make sure that you have connected to the cluster by using kubectl. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
Copy the following YAML file and save it as cronjob.yaml. The
jobTemplate.specsection of the CronJob has the same format as thespecsection of a job. The following example uses the job example in Create a Job.
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: example-cronjob
labels:
app: cronjob
spec:
schedule: "*/2 * * * *" # Run every 2 minutes
concurrencyPolicy: Forbid # Forbid concurrent execution
successfulJobsHistoryLimit: 3 # Retain the latest 3 successful jobs
failedJobsHistoryLimit: 2 # Retain the latest 2 failed jobs
jobTemplate:
spec:
completions: 1 # Stop the job after two pods are completed
parallelism: 1 # Run only one pod at a time
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: counter
image: anolis-registry.cn-zhangjiakou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/nginx:1.14.1-8.6
command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- |
echo "starting...";
COUNTER=0;
while [ $COUNTER -lt 5 ]; do
sleep 2;
COUNTER=$((COUNTER+1));
echo "${COUNTER}";
done;
echo "finished";
exit 0
restartPolicy: Never # Do not restart the podRun the following command to create a CronJob:
kubectl apply -f cronjob.yamlExpected output:
cronjob.batch/example-cronjob createdWait for about 10 minutes and run the following command to check the job execution status:
kubectl get jobExpected output:
NAME STATUS COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE example-cronjob-2901**22 Complete 2/2 31s 5m13s example-cronjob-2901**23 Complete 2/2 31s 3m13s example-cronjob-2901**24 Complete 2/2 26s 73s
References
For more information about the issues you may encounter when you create a workload, see FAQ about workloads.
For more information about pod exceptions, see Pod troubleshooting.