Network bandwidth is the maximum amount of data that can be transferred over a network in a specific period of time. Higher network bandwidth allows the transfer of a larger amount of data in the same period of time. Network bandwidth is classified into public bandwidth and internal bandwidth.
Public bandwidth
Public bandwidth is used to transfer data between Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances and the Internet. Public bandwidth is classified into outbound public bandwidth and inbound public bandwidth. The public bandwidth that you purchase is outbound public bandwidth. The following figure shows the directions of data flows.
The data flow is presented from the perspective of the Elastic Computing Service.

Bandwidth type | Inbound public bandwidth | Outbound public bandwidth |
Definition | Inbound (downstream) traffic is data that flows from an external network to your ECS instance and consumes public bandwidth. For example:
| Outbound (upstream) traffic is data that flows from an ECS instance to an external network over the public bandwidth. For example:
|
Billing | Free of charge. Alibaba Cloud places a limit on inbound public bandwidth. However, the maximum inbound public bandwidth varies based on the outbound public bandwidth.
| Chargeable. You are charged for outbound public bandwidth. Purchase an appropriate amount of outbound public bandwidth based on your business requirements. The prices and limits of outbound public bandwidth vary based on the metering method (also known as the billing method for network usage). Public bandwidth supports the pay-by-bandwidth and pay-by-traffic metering methods. In most cases, the maximum outbound public bandwidth of a static public IP address is 200 Mbit/s. The value on the ECS buy page prevails. If the maximum outbound public bandwidth does not meet your business requirements, consider using elastic IP addresses (EIPs) or Internet Shared Bandwidth instances. For more information, see What is an Elastic IP Address? and What is an Internet Shared Bandwidth? Important If the pay-by-traffic metering method is used, the maximum inbound and outbound bandwidths are used as upper limits of bandwidths instead of guaranteed performance specifications. In scenarios in which demand exceeds available resources, the maximum bandwidths may not be reached. If you want guaranteed bandwidths for your instances, use the pay-by-bandwidth metering method. |
The measurement unit used for bandwidth on the ECS console is Mbps. You can manually convert the bandwidth value displayed to your desired units. For example, if the ECS console shows that your ECS instance has 5 Mbps bandwidth, you can calculate the outbound bandwidth (upstream bandwidth) of your instance in KB/s using the following conversion: 5 Mbps = 5 Mbit/s = 0.625 MB/s = 640 KB/s.
Enable public bandwidth
To allow an ECS instance to communicate with the Internet, you can enable public bandwidth for the instance by automatically assigning a public IP address to the instance. The automatically assigned public IP address is called a static public IP address. To automatically assign a public IP address to an ECS instance, you can select Assign Public IPv4 Address when you create the instance or increase public bandwidth to a value greater than 0 Mbit/s after the instance is created. For more information, see the Static public IP addresses section of the "Static public IP address" topic, and Modify the bandwidth of a subscription instance.
You can also enable public bandwidth for an ECS instance by using other methods, such as associating an EIP with the instance and creating an Internet NAT gateway for the instance. For more information, see Associate one or more EIPs with an instance of the "EIP" topic and Internet NAT gateway. You can assign an IPv6 address to an ECS instance and enable IPv6 public bandwidth for the instance. For more information, see Step 4: Enable IPv6 Internet bandwidth.
Bandwidth billing
The public bandwidths of static public IP addresses support the pay-by-bandwidth and pay-by-traffic metering methods. For information about these metering methods, see Public bandwidth billing.
If you use EIPs for ECS instances, see Billing overview for the billing rules. If you use Internet NAT gateways for ECS instances, see Billing of Internet NAT gateway for the billing rules.
To share and reuse network bandwidth in a region, create an Internet Shared Bandwidth instance in the region. For information about Internet Shared Bandwidth, see What is an Internet Shared Bandwidth? You can associate EIPs with an Internet Shared Bandwidth instance that resides in the same region as the EIPs. This way, you can reuse network bandwidth on the Internet Shared Bandwidth instance to reduce costs. You can apply data transfer plans to the IPv4 data transfer of eligible resources to reduce the costs of your public bandwidth usage. Eligible resources include static public IP addresses, EIPs, Classic Load Balancer (CLB) instances, and Internet Shared Bandwidth instances that use the pay-by-traffic (also known as pay-by-data-transfer) metering method. You cannot apply data transfer plans to BGP (Multi-ISP) Pro EIPs. For more information about data transfer plans, see What is a data transfer plan?
Bandwidth security
By default, Alibaba Cloud Security Center provides a certain DDoS mitigation capacity for each ECS instance free of charge. The mitigation capacity varies based on the instance type and can be up to 5 Gbit/s. For more information, see View the thresholds that trigger blackhole filtering in Anti-DDoS Basic.
After you activate Anti-DDoS Basic, Alibaba Cloud Security Center monitors inbound traffic to ECS instances in real time. When an ultra-large amount of traffic or suspicious traffic such as DDoS attack traffic is detected, Security Center redirects the traffic from the intended paths to a scrubbing device. The scrubbing device identifies and removes malicious traffic, and then returns legitimate traffic. Then, the legitimate traffic is forwarded to ECS instances by using the intended paths. For more information, see What is Anti-DDoS Origin?
When an ECS instance is under a DDoS attack, you receive pushed event notifications that allow you to take defensive measures at the earliest opportunity. For more information, see Instance security events.
Limits
Starting November 27, 2020, the maximum bandwidth values available for new or updated ECS instances differ based on the throttling policies of your account. To apply for an increase in bandwidth quotas, submit a ticket.
The following throttling policies apply:
In each region, the total maximum bandwidth of all ECS instances that use the pay-by-traffic metering method cannot exceed 5 Gbit/s.
In each region, the total maximum bandwidth of all ECS instances that use the pay-by-bandwidth metering method cannot exceed 50 Gbit/s.
The maximum public bandwidth that an ECS instance can have varies based on the instance type. For information about the maximum public bandwidth that is supported by each ECS instance type, see the "Network baseline bandwidth (Gbit/s)" or "Network baseline/burst bandwidth (Gbit/s)" columns in Overview of instance families. The total public bandwidths used by an ECS instance cannot exceed the maximum public bandwidth of the ECS instance.
For more details, see Public bandwidth.
Internal bandwidth
Internal bandwidth is used to transfer data between ECS instances over the internal network in the same virtual private cloud (VPC) and region. You can connect ECS instances to ApsaraDB RDS instances, Server Load Balancer (SLB) instances, and Object Storage Service (OSS) buckets over the internal network. You are not charged for in-region data transfer over the internal network. Internal bandwidth values vary based on the ECS instance type. For information about the internal bandwidth value that is supported by each ECS instance type, see the "Network baseline bandwidth (Gbit/s)" or "Network baseline/burst bandwidth (Gbit/s)" columns in Overview of instance families. Internal bandwidth is allocated to each ECS instance. If multiple network interfaces are bound to an ECS instance, the total internal bandwidth that is used by the network interfaces cannot exceed the internal bandwidth of the instance.
Cross-zone internal bandwidth varies based on the bandwidth specifications of instance types. Network latency increases with the distance between zones.
Internal bandwidth in a deployment set or across deployment sets also varies based on the bandwidth specifications of instance types.
In most cases, the network bandwidth performance of an ECS instance type is defined based on the transmission of data packets that are 1,514 bytes in size. If the size of data packets transmitted on an ECS instance is less than 1,514 bytes, the achievable network bandwidth performance decreases.
When you use internal bandwidth, take note of the following items:
Physical network bandwidth is shared across ECS instances. The internal bandwidth of an ECS instance may be affected by the internal bandwidth usage of other ECS instances. In most cases, an ECS instance can achieve the internal bandwidth provided by the instance type. For information about how to test internal bandwidth performance, see Test the network performance of an instance.
If your business occasionally requires a network bandwidth that exceeds the baseline bandwidth of your ECS instances, you can select an instance type that supports burst bandwidth.
In scenarios such as high-performance computing, big data processing, and AI training, you can select an Elastic Remote Direct Memory Access (eRDMA)-capable instance type to provide low-latency, high-throughput network services. RDMA transfers data from user-mode programs to Host Channel Adapters (HCAs) for network transmission, without involving the kernel stack. RDMA helps greatly reduce CPU load and latency.
To achieve an internal bandwidth of 100 Gbit/s or higher per ECS instance, select an instance type that supports network card mappings and specify network card indexes to bind elastic network interfaces (ENIs) to different network cards at the underlying layer. This helps maximize bandwidth utilization. For information about network card mappings, see the Overview section of the "Overview" topic.
If your business requires concurrent data transmission and reception over the internal network, we recommend that you use seventh-generation or later ECS instance types to achieve full-duplex transmit and receive bandwidth. In this case, the transmission and reception rates are separately calculated. Data can be transmitted and received at the full rate at the same time. The data transmission and data reception do not interfere with each other. This way, communication efficiency is improved. For example, if an ECS instance has 1 Gbit/s of internal bandwidth, the instance can simultaneously receive data over the internal network at a speed of 1 Gbit/s and transmit data over the internal network at a speed of 1 Gbit/s.
Burst bandwidth
Specific instance types in sixth-generation or later ECS instance families support network burst bandwidth. When an ECS instance of these instance types has sufficient network bandwidth resources and available network burst credits, the instance can consume network burst credits to burst beyond its network baseline and achieve a higher transmission speed in response to traffic spikes. Network burst bandwidth is a way to utilize idle resources. No service level agreement (SLA) commitments are made for network burst bandwidth. If you want your ECS instance to have a specific bandwidth to use, choose an appropriate instance type based on the baseline bandwidth capabilities and set the desired bandwidth value when creating the instance.
For information about the burstable bandwidth capabilities and maximum burst bandwidth of an ECS instance type, see Overview of instance families.
The burstable bandwidth is used only for internel networks, not for the Internet.
Network burst credits
An ECS instance can accrue credits when the instance uses network bandwidth that is lower than its baseline bandwidth in the internal network. The maximum number of network burst credits that an instance can accrue varies based on the instance type. When an ECS instance requires network bandwidth that is higher than its baseline bandwidth, the instance consumes credits to temporarily burst the network bandwidth beyond the baseline bandwidth. When the network burst credits of the ECS instance are exhausted, the instance returns to its baseline bandwidth. Apart from available network burst credits, there are other prerequisites for triggering network burst bandwidth. No SLA commitments are made for the credits, and no credit query function is provided.
Detailed rules for network burst credits
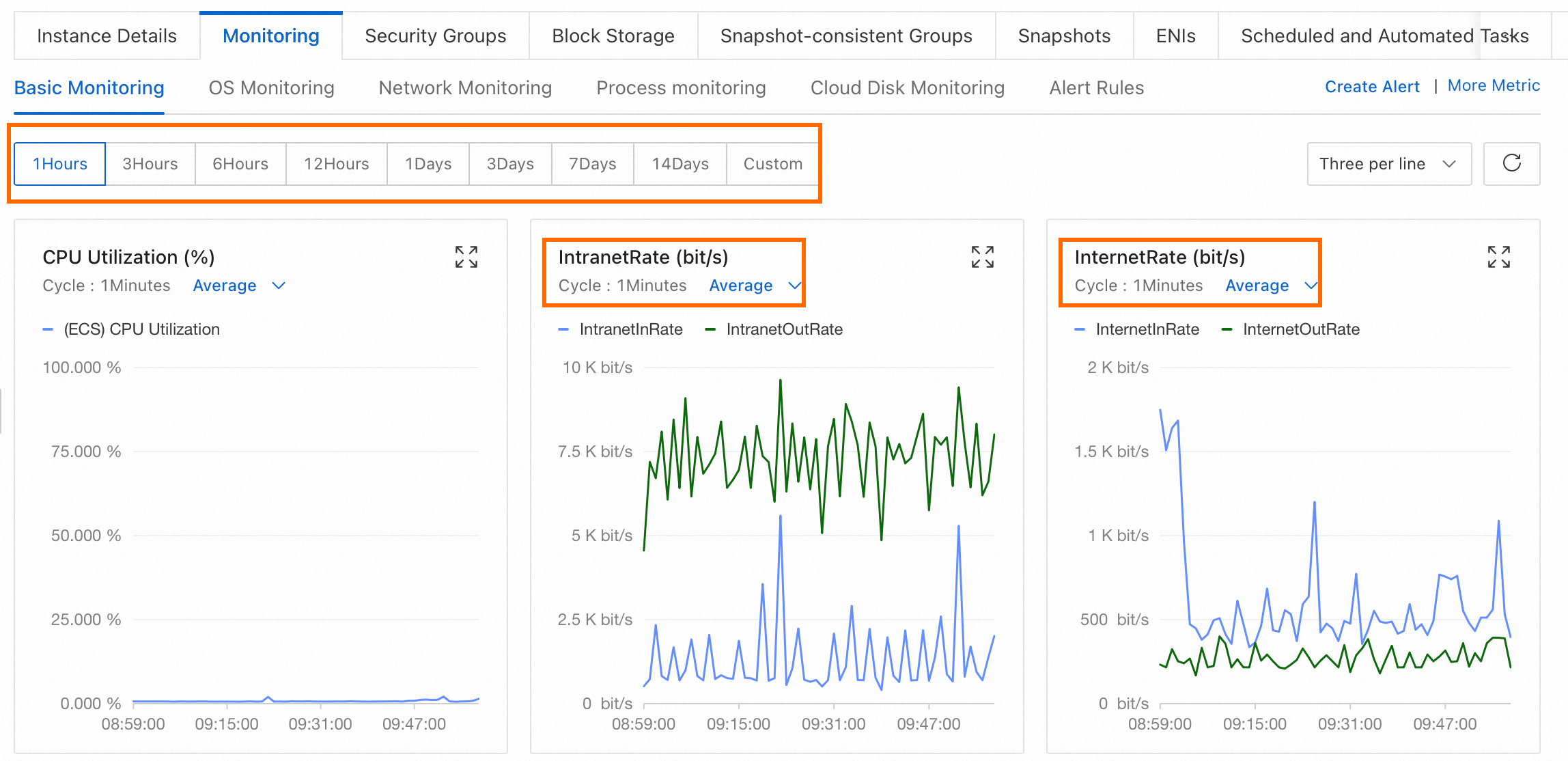
Monitor network bandwidth
To monitor the internal and public bandwidth usage of ECS instances in the ECS console, perform the following steps:
Go to ECS console - Instances.
In the top navigation bar, select the region and resource group of the resource that you want to manage.

Find the ECS instance whose bandwidth usage you want to view and click the instance ID to go to the instance details page.
Click the Monitoring tab.
Specify a time range for which to view internal and public bandwidth information.
The granularity of the displayed data varies based on the length of the specified time range. When you select a shorter time range, the data granularity is smaller. For example, the aggregation interval is different for a 1-hour period and a 6-hour period, which results in different average values. Specify a time range based on your business requirements.
For example, if you purchased 1 Mbit/s of public bandwidth for an ECS instance, the public bandwidth of the instance is fully utilized when the outbound public bandwidth reaches 1,024 Kbit/s. If the bandwidth usage of an ECS instance routinely exceeds or falls below its baseline configuration, you can modify the bandwidth configurations of the instance. For more information, see Modify bandwidth configurations.
 Note
NoteIf no data is displayed on the Monitoring page, it may be because either the CloudMonitor agent is not installed in the ECS instance or its status is abnormal. Try to re-install the agent. For more information, see Manage a Cloud Monitor agent.
You can also use CloudMonitor to monitor network bandwidth.
References
For information about how to change the metering method of an ECS instance, see Change the billing method for network usage of an ECS instance that uses a static public IP address.
If the public bandwidth of an ECS instance does not meet your business requirements or exceeds your business requirements, you can modify the public bandwidth configurations of the ECS instance. For more information, see Modify the public bandwidth configurations of an instance associated with a static public IP address.
For information about how to change the bandwidth and billing method of an EIP, see Modify the bandwidth of an EIP.
BGP (Multi-ISP) is suitable for Internet access in the China (Hong Kong) region and between the China (Hong Kong) region and other regions outside the Chinese mainland. If you use BGP (Multi-ISP) lines to connect instances located in the China (Hong Kong) region with instances located in regions in the Chinese mainland, international ISP services are used. To reduce network latency in this scenario, select BGP (Multi-ISP) Pro.
You can use Anycast EIPs to improve Internet access based on the stable BGP lines and the global transmission network of Alibaba Cloud. For information about Anycast EIPs, see What is Anycast EIP?