By Raghunathan Ramesh, Alibaba Cloud Community Blog author.
Know Your Customer (KYC) is an important concept to know nowadays. Generally speaking, it can be understood as the process of verifying the customer's integrity and identity through a trusted identity proof that is authorized by some government body or a similar trusted organization or institution.
The manual process involved with KYC, or more specifically the process of verifying each and every employee, or analogously each and every customer that comes by your store, is, naturally, a difficult task for any organization, big or small. And, adding to this fact, the vulnerabilities involved in this process has lead to many financial and integrity issues.
Of course, the answer to all of these problems is to streamline this process and make it a more robust and reliable process. In my opinion, Blockchain is the answer because it is a more suitable technology for this particular use case. This technology can actually provide several different framework based on your particular use case. For this tutorial in particular, we're going to use Hyperledger Fabric, which is a private blockchain framework. Also, we will be looking at how hypeledger fabric can be leveraged to achieve our particular use case
There are many blockchain platforms currently available in market. Fortunately, for financial use cases, Hyperledger Fabric in many ways is the best fit among all the other choices. In this tutorial, I'll show you how you can leverage the Hyperledger Fabric platform to streamline the KYC process.
The technical architecture using Hyperledger Fabric proposed that we will go through in this article involve the following processes:
Next, it also assumes the following technical architecture:
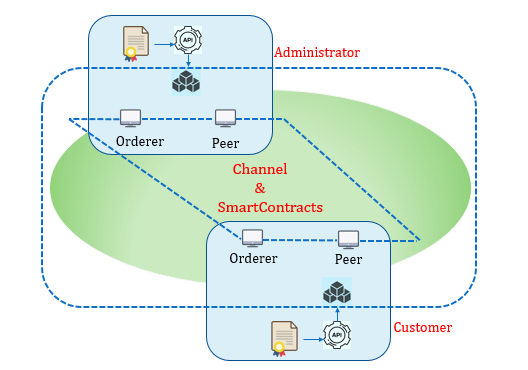
In the above diagram, you can see the components involved in blockchain environment. Let's discuss the component and the process involved in the diagram above in a bit more detail:
Smart contract deployed in the channel developed using Go language is explained below
The following code gets the file from the user, encrypts the file sha256 algorithm and gives the encrypted value to the respective user for validation.
package main
import (
"crypto/aes"
"crypto/cipher"
"crypto/rand"
"errors"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/core/chaincode/shim"
sc "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/peer"
//packages used for smart contract
)
func main() {
//Reading the file
data, err := ioutil.ReadFile("test1.pdf")
ciphertext, err := encrypt(data)
if err != nil
// TODO: Properly handle error
log.Fatal(err)
//encrypting the file and uploading in blockchain
fmt.Printf("Sha256: %x\n\n", sha256.Sum256(data))
}This part of the code converts the encrypted value into string and stores the encrypted value into blockchain. Once it is stored the encrypted value for that particular id will be replicated to all the respective peers, Hence it cannot be tampered or altered without the permission of majority of peers connected to the blockchain network.
package shim
import (
"bytes"
"os"
"strconv"
"strings"
"testing"
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/common/flogging"
mockpeer "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/common/mocks/peer"
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/common/util"
lproto "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/ledger/queryresult"
pb "github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/peer"
"github.com/hyperledger/fabric/protos/utils"
)
err = stub.PutState(A, []byte(strconv.Itoa(data)))
if err != nil {
return Error(err.Error())
}This part of the code will return the history of the particular user i.e., all the identities attached to that particular user. Id will be used to refer each individual.
func (t *shimTestCC) historyq(stub ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
if len(args) < 1 {
return Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting 1")
}
id := args[0]
resultsIterator, err := stub.GetHistoryForKey(id)
if err != nil {
return Error(err.Error())
}
defer resultsIterator.Close()
var buffer bytes.Buffer
buffer.WriteString("[")
bArrayMemberAlreadyWritten := false
for resultsIterator.HasNext() {
response, err := resultsIterator.Next()
if err != nil {
return Error(err.Error())
}
// Add a comma before array members, suppress it for the first array member
if bArrayMemberAlreadyWritten == true {
buffer.WriteString(",")
}
buffer.WriteString("{\"TxId\":")
buffer.WriteString("\"")
buffer.WriteString(response.TxId)
buffer.WriteString("\"")
buffer.WriteString(", \"Value\":")
if response.IsDelete {
buffer.WriteString("null")
} else {
buffer.WriteString(string(response.Value))
}
buffer.WriteString(", \"IsDelete\":")
buffer.WriteString("\"")
buffer.WriteString(strconv.FormatBool(response.IsDelete))
buffer.WriteString("\"")
buffer.WriteString("}")
bArrayMemberAlreadyWritten = true
}
buffer.WriteString("]")
return Success(buffer.Bytes())
}This part of the code returns the query for the particular id. The above smart contract will take care of all the events that needs to be happen in blockchain network.
Note: The front end part can be developed using any appropriate language such as Nodejs, HTML.
func (t *shimTestCC) richq(stub ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
if len(args) != 1 {
return Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting keys for range query")
}
id := args[0]
resultsIterator, err := stub.GetQueryResult(query)
if err != nil {
return Error(err.Error())
}
defer resultsIterator.Close()
var buffer bytes.Buffer
buffer.WriteString("[")
bArrayMemberAlreadyWritten := false
for resultsIterator.HasNext() {
queryResponse, err := resultsIterator.Next()
if err != nil {
return Error(err.Error())
}
if bArrayMemberAlreadyWritten == true {
buffer.WriteString(",")
}
buffer.WriteString("{\"Key\":")
buffer.WriteString("\"")
buffer.WriteString(queryResponse.Key)
buffer.WriteString("\"")
buffer.WriteString(", \"Record\":")
buffer.WriteString(string(queryResponse.Value))
buffer.WriteString("}")
bArrayMemberAlreadyWritten = true
}
buffer.WriteString("]")
return Success(buffer.Bytes())
}
func (t *shimTestCC) historyq(stub ChaincodeStubInterface, args []string) pb.Response {
if len(args) < 1 {
return Error("Incorrect number of arguments. Expecting 1")
} 
2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - September 27, 2018
Alibaba Cloud Blockchain Service Team - August 29, 2018
Alibaba Cloud Blockchain Service Team - September 6, 2018
Alibaba Clouder - June 26, 2019
Alibaba Cloud Blockchain Service Team - September 6, 2018
Alibaba Clouder - November 6, 2019

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow LedgerDB
LedgerDB
A ledger database that provides powerful data audit capabilities.
Learn More Blockchain as a Service
Blockchain as a Service
BaaS provides an enterprise-level platform service based on leading blockchain technologies, which helps you build a trusted cloud infrastructure.
Learn More YiDA Low-code Development Platform
YiDA Low-code Development Platform
A low-code development platform to make work easier
Learn More mPaaS
mPaaS
Help enterprises build high-quality, stable mobile apps
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder