Join us at the Alibaba Cloud ACtivate Online Conference on March 5-6 to challenge assumptions, exchange ideas, and explore what is possible through digital transformation.
Traffic mirroring, also known as traffic shadowing, provides a powerful way to bring changes to production at the lowest possible risk. The mirror sends a copy of real-time traffic to the mirroring service. Mirrored traffic goes outside of the critical request path of the main services.
In non-production or test environments, trying to access all possible combinations of test cases for a service is unrealistic. In some cases, the work of writing these test cases may not match actual production needs. In the ideal case, you can use real-time production use and traffic to help improve the functional regions you miss in the test environment.
Once we are able to reliably mirror traffic, we can start other valuable tasks. For example, using Diffy, a request traffic comparison tool, we can compare the traffic of the introduced test cluster to the expected behavior of the production cluster. For example, we might want to compare the deviation between the request results and the expected results, or data corruption in the API Protocol, for better compatibility.
In addition, please note:
Here, by inserting a proxy, you can be responsible for the coordination of such traffic, and it makes an interesting comparison. Diffy is such a proxy tool. Diffy starts a proxy service (listening, for example, on port 8880 ), again, based on the primary and secondary old service addresses set by the user, (the primary and secondary codes are identical and the purpose is to reduce noise interference) and a new candidate service address.
It can also detect noise in the result, and ignore instances of two real-time services by first calling them (for example, timestamps, monotonically increasing counter and other prompts). In summary, it detects and then ignores these parts in the test service.
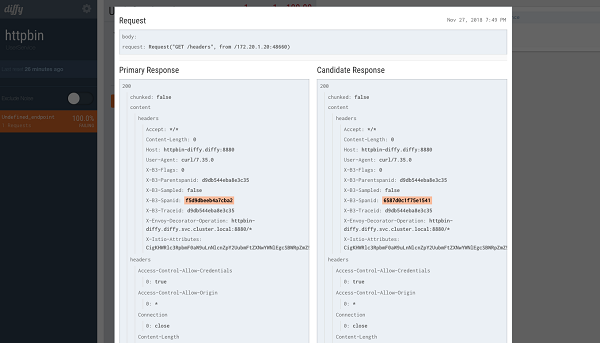
Diffy also provides a very good page to view the results of the call, and compare the conditions, which can be filtered by particular characteristics It also has a good management console where you can view the metrics and statistics of the comparing call results function.
In this task, you first force all traffic to the v1 version of the service. You will then use a rule to mirror a portion of the traffic to the v2 version.
Two versions of the sample service are first deployed.
Docker mirroring httpbin is used to provide common http access requests in the deployment of version 1:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mirrorservice-sample-v1
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mirrorservice-sample
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- image: docker.io/kennethreitz/httpbin
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: mirrorservice-sample
command: ["gunicorn", "--access-logfile", "-", "-b", "0.0.0.0:44134", "httpbin:app"]
ports:
- containerPort: 8114 A custom docker image is used in the deployment of version 2, and the corresponding Dockerfile is as follows:
FROM nginx:latest
COPY default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/
EXPOSE 80Required nginx configuration files:
server {
listen 44134;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://httpbin-diffy.diffy:8880/;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
}Version 2 is deployed to act as the traffic mirror target for Istio. After receiving the traffic, it is forwarded to the Diffy proxy. The Diffy proxy is not currently used as the Istio traffic mirror target. This is because of a conflict between the current versions of the Diffy proxy and the Envoy proxy, making normal traffic forwarding impossible. As a result, this deployment is needed to mediate the traffic.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mirrorservice-sample-v2
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mirrorservice-sample
version: v2
spec:
containers:
- name: mirrorservice-sample
image: registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/wangxining/mirrorservice:0.1
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8114Corresponding Kubernetes service:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mirrorservice-sample
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- name: http
port: 44134
selector:
app: mirrorservice-sampleBy default, Kubernetes performs load balancing between the two versions of the service. Create the following traffic mirroring rule to send 100% of the traffic to v1, and specify that the traffic is mirrored to v2. When the traffic is mirrored, requests will be sent through its host/authorized header to the mirror service with the appended -shadow.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: mirrorservice-sample
spec:
host: mirrorservice-sample
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
Name: Maid service-Sample
spec:
hosts:
- mirrorservice-sample
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: mirrorservice-sample
subset: v1
weight: 100
#- destination:
# host: mirrorservice-sample
# subset: v2
# weight: 0
mirror:
host: mirrorservice-sample
subset: v2Diffy can be used as a proxy to intercept requests and send them to all instances of the running service. Problems that may exist in each iteration code are identified by comparing the response results. Among them, there are three code instances running on Diffy:
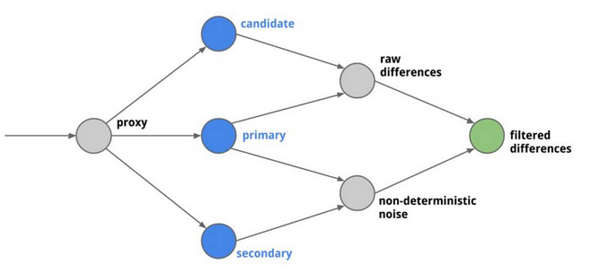
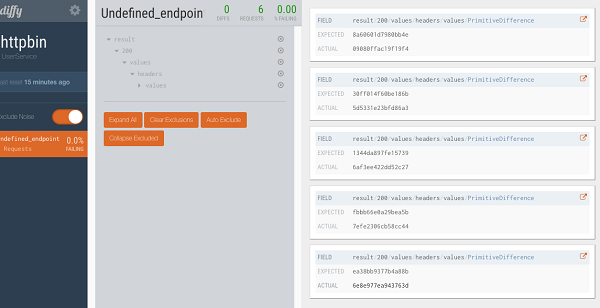
In the actual Diffy test, you will find there is some difference between the majority of interfaces. This is because of noise in the responses, including:
Diffy can eliminate such noise to ensure the results of the analysis are not affected.
Create the Diffy service with the following yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: httpbin-diffy
labels:
app: httpbin-diffy
spec:
ports:
- name: http-proxy
port: 8880
- name: http-admin
port: 8881
- name: http-console
port: 8888
selector:
app: httpbin-diffy
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: httpbin-diffy
version: v2
name: httpbin-diffy-v2
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: httpbin-diffy
version: v2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: httpbin-diffy
version: v2
spec:
containers:
- image: lordofthejars/diffy:1.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
exec:
command:
- curl
- localhost:8888
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 60
timeoutSeconds: 1
name: httpbin-diffy
args: ["-candidate=httpbin-candidate:8080", "-master.primary=httpbin-master:8080", "-master.secondary=httpbin-master:8080", "-service.protocol=http", "-serviceName=httpbin", "-proxy.port=:8880", "-admin.port=:8881", "-http.port=:8888", "-rootUrl='localhost:8888'"]
ports:
- containerPort: 8888
name: http-console
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 8888
name: http-proxy
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 8888
name: http-admin
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
exec:
command:
- curl
- localhost:8888
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 60
timeoutSeconds: 1
securityContext:
privileged: falseCreate the primary, secondary (same as the primary in the current sample) and candidate services used in the sample with the following YAML:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: httpbin-master
labels:
app: httpbin-master
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 8080
selector:
app: httpbin
version: v1
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: httpbin-candidate
labels:
app: httpbin-candidate
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 8080
selector:
app: httpbin
version: v2
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: httpbin-v1
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: httpbin
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- image: docker.io/kennethreitz/httpbin
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: httpbin
command: ["gunicorn", "--access-logfile", "-", "-b", "0.0.0.0:8080", "httpbin:app"]
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: httpbin-v2
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: httpbin
version: v2
spec:
containers:
- image: docker.io/kennethreitz/httpbin
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: httpbin
command: ["gunicorn", "--access-logfile", "-", "-b", "0.0.0.0:8080", "httpbin:app"]
ports:
- containerPort: 8080Start the sleep service so you can use curl to provide the load:
cat <<EOF | istioctl kube-inject -f - | kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sleep
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sleep
spec:
containers:
- name: sleep
image: tutum/curl
command: ["/bin/sleep","infinity"]
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
EOFEnter into SLEEP_POD. The specific pod name will vary according to the actual assignment.
kubectl exec -it $SLEEP_POD -c sleep shSend traffic:
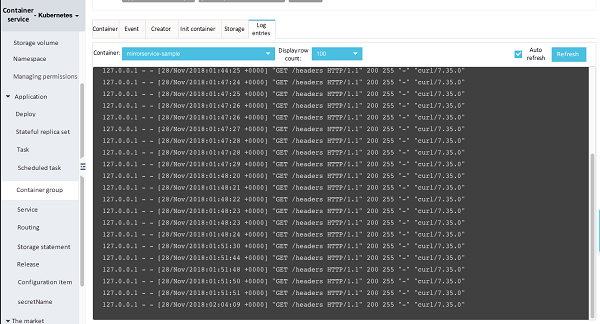
curl -v http://mirrorservice-sample:44134/headersCheck the access log for v1. As shown below, 100% of the requests created were for v1.
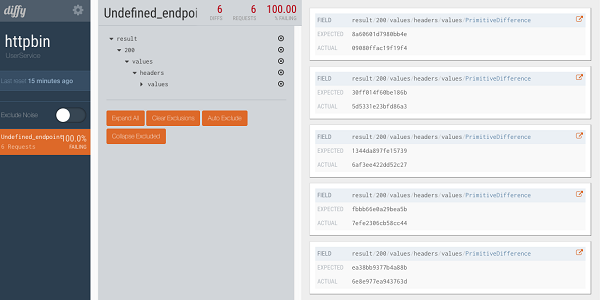
Also, if you check the Diffy web interface, you can see that the created requests were also mirrored to the Diffy proxy.
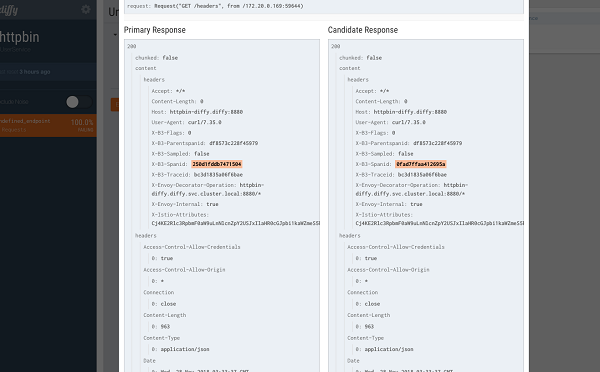
Diffy can eliminate such noise to ensure the results of the analysis are not affected.
Traffic mirroring offers powerful features that bring changes to production with as little risk as possible. Mirroring sends a copy of live traffic to a mirrored service. The mirrored traffic occurs outside the critical request path of the primary service. Once we are able to reliably mirror traffic, we can start doing other valuable tasks. For example, using Diffy - a request volume comparison tool - we can compare the traffic of the introduced test cluster to the expected behavior of the production cluster.
Supporting traffic mirroring is just one of Istio's numerous features which will simplify the production deployment and management of large microservice-based applications. We invite you to use Alibaba Cloud Container Service to quickly set up Istio, an open management platform for microservices that can be more easily integrated into any microservice projects you are working on.
Traffic Management with Istio (2): Grayscale Release of Applications by Istio Management
Traffic Management with Istio (4): DNS Resolution with CoreDNS
56 posts | 8 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native Community - November 22, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Storage - June 4, 2019
Alibaba Container Service - September 18, 2025
feuyeux - May 8, 2021
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - November 15, 2023
Alibaba Developer - September 22, 2020

56 posts | 8 followers
Follow Container Service for Kubernetes
Container Service for Kubernetes
Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes is a fully managed cloud container management service that supports native Kubernetes and integrates with other Alibaba Cloud products.
Learn More Container Compute Service (ACS)
Container Compute Service (ACS)
A cloud computing service that provides container compute resources that comply with the container specifications of Kubernetes
Learn More ACK One
ACK One
Provides a control plane to allow users to manage Kubernetes clusters that run based on different infrastructure resources
Learn More Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Accelerate and secure the development, deployment, and management of containerized applications cost-effectively.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Xi Ning Wang(王夕宁)