On December 12, 2016, Oracle released exciting news to the MySQL circle. It officially launched version 5.7.17 of MySQL, which includes the long-awaited MySQL Group Replication (MGR). This article provides insights on the basics of MGR and Galera and ponders the question of whether or not MongoDB will become the next Galera.
MGR is a highly available solution officially launched by MySQL. It is based on the native replication technology and is available in the plug-in form. For those of you not in the know, below are some of the main features of MGR:
●Backup and Change Master for replication is no longer viable. With MGR, the replication management operations are more automated.
●MGR uses the Paxos protocol and displays high data consistency among the database cluster node.
●All nodes among clusters can be replicated, which is the dream function of many developers. The inconvenience of data-writing performance of a single group is solved as MGR allows all nodes to be replicated.
●The split cluster issue caused by network partitioning is resolved which in turn upgrades the reliability of data replication.
Although MGR is also known as the MySQL version of Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC), there are architectural differences between MGR and RAC. MGR shares nothing while Oracle RAC shares everything.
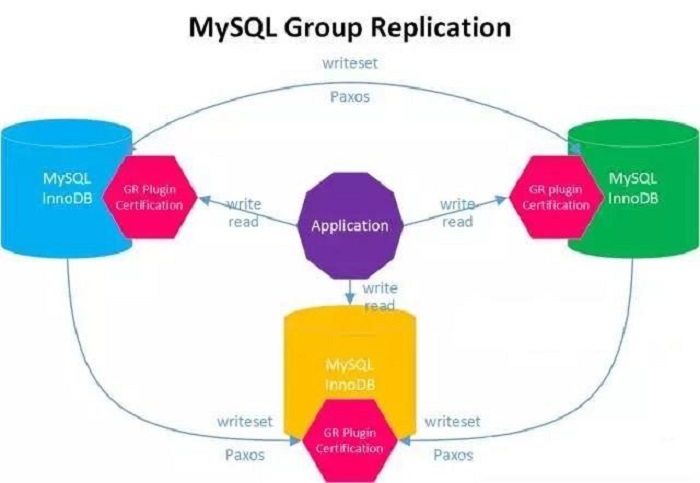
Galera is a multi-master cluster based on synchronous replication. It is an easy-to-use solution that offers scalability and data security.
Those familiar with Galera may see similarities between MGR and Galera. Some companies and banks have tried Galera's high availability solution for their production environments and have encountered severe problems. Compared with Galera, MGR's advantages are:
●MGR is an official product by MySQL with guaranteed product control and subsequent technical support.
●MGR works on the popular Paxos algorithm. This enables it to achieve optimal network performance and stability. The distributed peer-to-peer system of MGR also reduces overall latency. MGR supports nine nodes per group currently as compared to Galera which supports only three nodes.
●MGR supports multiple operating system platforms, while Galera only supports the Linux system.
First, let's look at MGR's performance improvement in a multi-master node environment, namely carrying out read/write tests at multiple nodes at the same time:
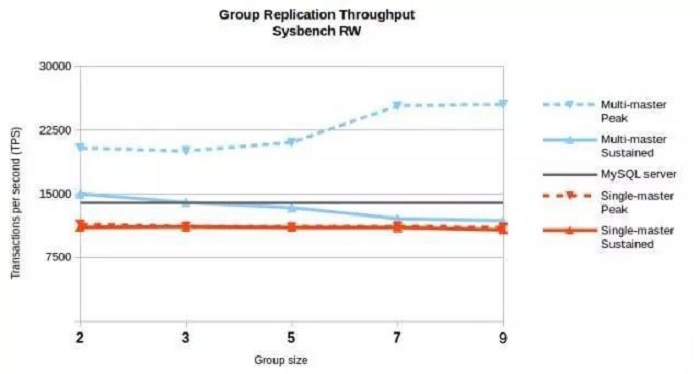
When the flow-control-mode parameter is disabled, i.e. when delay among cluster nodes is allowed, the MGR cluster performance can be elevated with the increase in the number of nodes. If it is configured to ensure reading consistency, the performance of an MGR cluster with five nodes is almost equivalent to that of a single MySQL instance.
The following figure compares MGR and Galera:
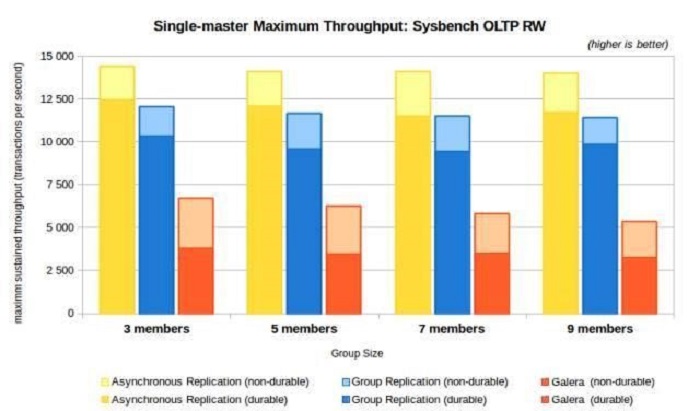
Group Replication delivers more than 80 percent of the throughput of asynchronous replication when durability is off. The impact of the use of durability on Galera results in a larger overhead. It only achieves 30 percent asynchronous replication throughput.
Although MySQL Group Replication provides high availability and a multi-master update everywhere in the replication solution, it still has few limitations.
●MGR only supports InnoDB tables, and each table must have a primary key for conflict detection of write sets.
●The global transaction identifier (GTID) feature must be enabled, and the binary log format must be set to ROW to select the master and write set.
●COMMIT may lead to a failure, which is similar to a snapshot failure scenario at the transaction isolation level.
●Currently, MGR supports a maximum of nine nodes.
●The foreign key and save point features are not supported and global constraint detection and partial rollback cannot be carried out.
●The binary log is not compatible with binlog event checksum.
According to Oracle's current development roadmap, a distributed document database cluster will be created in the future. InsideMySQL is hoping for the GA of InnoDB Cluster in the future. The development of MGR brings it one step closer. The more powerful MongoDB is a worthy rival for competition. In fact, it's worth waiting for a distributed document database based on MySQL, the most popular and stable option on the internet, which supports transactions, row level locks, MultiVersion Concurrency Control (MVCC), and high data consistency.
References
1.Zooming-in on Group Replication performance
2.Performance Evaluation: MySQL 5.7 Group Replication (GA Release)
3.InnoDB Cluster User Guide
4.http://galeracluster.com/products/
Original article: Galera to be phased out - MySQL Group Replication officially launched
Rest Assured - Ways to Avoid Security Issues When Using RESTful
Voiceprint Recognition – Not Just a Powerful Authentication Tool

2,593 posts | 792 followers
FollowApsaraDB - October 24, 2024
Alibaba Clouder - May 28, 2019
Alibaba System Software - August 30, 2018
Amber Wang - August 6, 2018
Alibaba System Software - August 30, 2018
ApsaraDB - May 17, 2023

2,593 posts | 792 followers
Follow ApsaraDB for MongoDB
ApsaraDB for MongoDB
A secure, reliable, and elastically scalable cloud database service for automatic monitoring, backup, and recovery by time point
Learn More AnalyticDB for MySQL
AnalyticDB for MySQL
AnalyticDB for MySQL is a real-time data warehousing service that can process petabytes of data with high concurrency and low latency.
Learn More PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn More ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
An on-demand database hosting service for MySQL with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder