
Blockchain is a distributed peer-to-peer network without any central control points. It uses distributed unified operation to achieve a set of tamper-resistant and trusted database technical solutions. It also features decentralized storage and highly transparent information with superior security against data tampering. Simply put, Blockchain is a "large open ledger" that records the entire transaction information across a network using computer programs.
While Blockchain V1.0, mainly applies to Bitcoin and large financial ledgers, Blockchain 2.0 is gaining momentum and investment across industries and applications. However, the evolution of Blockchain from 1.0 to Blockchain 2.0 is not a simple process. The complexities and challenges of this transformation are summarized in the 3-tier phases described below:
I. Registration Phase: We must first address the problems related to registration. Blockchain is trustable and traceable because it adopts the "proof of work algorithm" and other commonly recognized rules to ensure that only legal blocks can be added. Once a block is linked to Blockchain after thorough verification, it will be stored permanently. The native ledger chain databases on the internet can never be destroyed, and the recorded information field is matched to the generation time. All information in the trustable ledger chain is unique and tamper-resistant. As a result, Blockchain can be used to record various types of information.
II. Verification Phase: The second area of improvement is accurate verification. Being open-source and shareable, Blockchain allows various organizations and individuals into the functioning of the entire system. Every node participating in maintenance receives a full copy of the entire database so that the information ownership can be confirmed. Blockchain is an ideal solution for storing permanent records such as authenticity verification, land ownership, equity transaction, and other applications.
III. Management Phase: This brings us to the third phase. Here, it is imperative to focus on smart management. Fans of Blockchain believe that Blockchain's core contribution is to solve any credibility issue during multi-point information interaction. This issue or challenge has been coined as "The Byzantine Generals' Problem".
In our case of Blockchain, given the geographical disassociation of the sources, we would need to ascertain their reliability to ensure accuracy.
Blockchain as a technology has evolved rapidly in the past decade. Let us discuss a few major innovations that have revolutionized this field.
Blockchain requires legal support to increase the pace of its development. A positive progress in this area, the introduction of "Legal Chain" took place on August 16, 2016. "Legal Chain" is the world's first electronic certificate Blockchain Alliance, which is an evidence recording and storing system, built and run jointly by Onchain, Microsoft (China) and fadada.com among other organizations. It is an open Blockchain alliance that facilitates participation of multiple parties.
The participating organizations in "Legal Chain" contribute in different areas to create an open ecosystem. Onchain provides the underlying Blockchain technology while fadada.com provides e-contracts, with both systems successfully achieving "in-depth integration."
All information is broadcasted on various storage nodes and is accessible by all members of the "Legal Chain." This information includes signing time, signing parties, and digital and fingerprint information such as file hash values of each e-contract. The system synchronizes and stores file hash value information in a national center for electronic data with authoritative judicial expertise. The restrictions imposed by "Legal Chain" to some extent prevent fabrication of information, addressing concerns of several netizens regarding the crisis of confidence during transactions.
Blockchain technology has the potential to meet requirements for e-evidences for judicial needs. This has been further validated by the newly-revised Law of Civil Procedure officially implemented from January 1, 2013. The law stipulates the admissibility of electronic data as evidence. However, in actual implementation, electronic evidence usually has low credibility due to its vulnerability to falsifications. By using Blockchain technology, no party can tamper with e-evidence once stored. Also, the e-evidence will aid every participant in removing obstacles, making it an effective judicial evidence.
Similar to its predecessors, Blockchain 3.0 still focuses on the application and norms in its derivative fields. The differentiating feature of Blockchain 3.0 is the introduction of a decentralized domain name system - Namecoin. A brief description of Namecoin and its features along with its challenges and applications is described below:
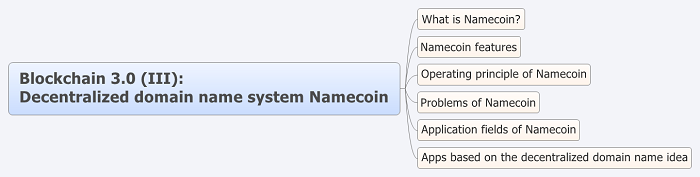
Figure 1.
Apps based on the decentralized domain name idea Namecoin, are one of the first batch of apps that apply Blockchain technology into the non-currency field. These apps boast of a high research value. Several restrictions prevent them from becoming popular for now, although the ideology can be applied to various fields. For example, did you know that the digital identity authentication service "KeyID" draws some reference to Namecoin?
The anonymity, low cost, and the immunity towards censorship make Namecoin vulnerable to misuse. Users can use .bit to host illegal content or businesses without being subjected to legal consequences.
In addition, websites in China have to be filed for record. Since .bit websites cannot be recorded in China, they are unusable within the country.
The financial services industry is expected to see many potential benefits of Blockchain. However, there would be various strategic and legal challenges which will increase complexity of its application. Despite all this, the future looks more secure and transparent with Blockchain. With its broad application, will Blockchain boost our digital innovations and habits? For that, we might have to wait a little bit longer to find out.

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - July 26, 2021
PM - C2C_Yuan - July 16, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - March 6, 2017
Alibaba Clouder - January 4, 2021
Alibaba Cloud Community - May 30, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Community - December 15, 2022

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow LedgerDB
LedgerDB
A ledger database that provides powerful data audit capabilities.
Learn More Blockchain as a Service
Blockchain as a Service
BaaS provides an enterprise-level platform service based on leading blockchain technologies, which helps you build a trusted cloud infrastructure.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder
Raja_KT March 12, 2019 at 4:34 am
Good but I think of Tangle , IOTA....