
The blockchain technology plays different roles on many occasions, and its value has been unquestionably far beyond the concept of "crypto currency." From making a bet with friends while watching World Cup, to buying a house, the blockchain technology is transforming our world. From the decentralization and de-intermediary to the tamper-resistance of data, every feature of the blockchain serves as a perfect solution to everyday problems.
It's undeniable that blockchain technology has opened the door to a new world of technology possibilities. The main question being asked is exactly how blockchain technology will reshape our world and what are the extent of the changes it will bring to the tech sphere.
The Bitcoin is a kind of digital currency based on a smart encryption algorithm. Many wealthy tax-dodgers, anti-government activists as well as cyber criminals use it for illegal transactions.
The encryption technology that lays the foundation for Bitcoin is called the blockchain technology. The transaction system involved in blockchain technology is far beyond cash and currency. It provides a way through which individuals with little or no knowledge of each other can establish the assets records available to everyone. In a way, it is a truth defender.
The blockchain is a database that contains the records of each Bitcoin transaction. The technology allows copying of the distributed record in thousands of computers, namely Bitcoin "nodes," which are available to all the people throughout the world and are highly reliable. Many sophisticated mathematical algorithms and the powerful computing power of "mechanism for consensus" support its operations. During operation, the nodes will update each Bitcoin transaction through the blockchain.
The blockchain technology has extensive use in the modern world. According to blockchain.info, a website that tracks the dynamically changing blockchains, 'a daily average of approximately 120,000 transactions valuing $75,000,000 are written into blockchains.' There are 380,000 blocks now, and the ledgers occupy approximately 45 Gb. Massive enough, right? Let us see how blockchain originated to create such an impact.
Satoshi Nakamoto, although unknown to many people, is believed to be the Bitcoin founder and man behind the concept of the blockchain. In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto published a paper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System." The paper focuses on Nakamoto's vision of a decentralized system and ways to accomplish the same. It also addresses how banks need to avoid traditional payment systems to create a decentralized system truly and replace reliable third parties.
Blockchain technology has and continues to unlock new possibilities in different spheres and aspects of everyday life. Finance originally inspired Satoshi Nakamoto, so consequently, the first generation of enterprises to use blockchains were financial institutions. From its proven applications in finance, banking to smart property solutions to even rationalizing the stock market, the blockchain also plays a role in other fields. A report says that 'The Nasdaq will soon enable an equity transaction platform based on the blockchain technology to record the transactions of private companies.' In recent months, the technology has gained prominence within the domain of tamper-proof private blockchains. The reason is the technology developed by anti-government liberalists enables banks to meet the needs of governments well after knowing their clients and anti-money laundering rules. Following this, the Bank of England also acknowledged the significance of blockchain technology on the financial industry after remaining conservative for a long period.
In fact, during Paris OuiShare Fest conference (a global annual economic cooperation conference), the delegates discussed a more distant future of the blockchain, where the partners and leftists chewed over grassroots organizations and if they would shake massive databases like Facebook. The liberalists have been dreaming of the possibility of private contracts signed between individuals and contractors based on the blockchain technology can replace the increasing number of government regulations. Before going deeper into this discussion, let us see how blockchain emanated and rose to become a transformational technology.
Let us say; a person X has to pay service fees to a person Y for the leveraged work. They both have their Bitcoin "wallets," which are not browsers to connect web pages, but a software with blockchain access. Unfortunately, this system doesn't recognize users. As X enables the wallet and processes transaction, the changed blockchain shows the reduced balance in X's wallet and increased balance in Y's wallet. The network executes these changes through a multi-step process.
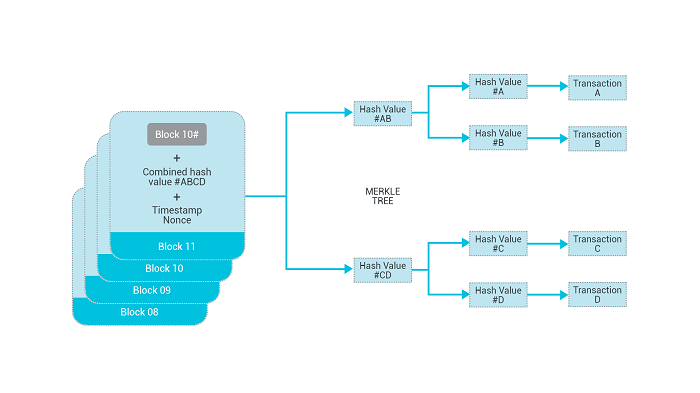
The above diagram represents the multi-step process using an example. During these changes in the network, each node will confirm whether X has spent these Bitcoins by continuously checking the ledger. If there is no error, the miners responsible for Bitcoin network maintenance will pack and write X's and other reliable transactions into a new block of the blockchain. For this purpose, the cryptographic hash function is required to break the block down into numeric strings with a given length to feed the data repeatedly.
Each transaction in the set that makes up a block goes through a program that creates an encrypted code known as the hash value. A further combination of the Hash values occurs in a system referred to as a Merkle Tree. The result of all this hashing along with a hash of the previous block's header and a timestamp goes into the block's header. The header then becomes part of the cryptographic puzzle solved by manipulating a number called the nonce. Upon finding a solution, the system adds the new block to the blockchain.
Like many other types of encryption, the hash calculation is unidirectional. It is easy to calculate identical hashes by data, while impossible to calculate the data by hash. Although there is no data in a hash, each hash is unique. It is possible to change the content written into a block in different ways, such as by changing a byte, the corresponding hash will change accordingly, and written into the generated header. The header will re-export the math problem that the hash function needs to solve by itself. Miners of the whole network may find the answer through trillions of trials. If one miner gets the correct answer, other nodes will soon check it (this process is unidirectional: hard to solve but easy to check), and each node that has confirmed the answer will update the corresponding blockchain. The hash of a header serves as the identifying string of a new block, which then becomes a part of ledgers. The block then writes and confirms X's payment to Y and other transactions. But we all wonder if these transactions are secured enough? Let's find out in the subsequent section.
To guarantee Bitcoin security, the problem-solving phase introduces three essential features:
First, occasionality: it is impossible to predict which miner will solve the problem and update the blockchain at any specified time. Instead, only hardworking miners rather than any random intruders can solve the problem.
Second, history: Each new block includes the hash of the previous block which contains the hash of the last block until the creation block is connected. It is precisely like the interconnection that strings the blocks as a blockchain. It is dead easy to re-export all blocks from the genesis block of a blockchain. However, any changes in the places, such as returning to some block in the very early phase, will modify the subsequent blocks. The implication is that the modified block together with the following blocks will become different. The previous ledger will no longer match the latest block identification, thus making its rejection easy.
Is there any way to turn that around?
Taking the same example, if the person X changes the idea of making payment to Y, X has to re-write the history to keep her Bitcoin in the wallet. If X is a competent miner, she has to create a blockchain while solving relevant hurdles which will make other nodes to extend the original blockchain continuously. Ideally, nodes always trust the longest blockchain, a rule integral to prevent the dilemma that arises when two miners solve a problem at the same time, avoids the temporary bifurcation of blockchains, and eliminates cheating. Therefore, this needs a blockchain version longer than the original one. It is impossible to control more than half of the computers in a short period, the so-called "51% attack" in the industry.
Currently, three trending blockchain-based products exist:
1: Transfer of different types of assets through blockchains.
A start-up company recently made a bet on this idea. The company has developed a mechanism that can adhere to extremely small Bitcoin transactions (the so-called "Bitcoin dust") and represent bonds, stocks or precious metal units by binding the "dust" with additional data.
2: Protection of land ownership
A blockchain-based app is considered to be a fact machine. The ledger lets you insert data about bitcoin transactions combined with other pieces of information into the ledger. A recent news says that Everledger uses the blockchain to protect valuables. For example, it "attaches" some distinct features to the blockchain data to provide an irrefutable identification. Many applications such as 'Onename' stores the personal information by setting passwords, or 'CoinSpark' which specializes in "notarization." It is noteworthy that although different from pure Bitcoin transactions, these applications still rely on the third-party service companies to store data.
3: A New Concept called Smart Contracts
One of the most ambitious applications of blockchain technology relates to its ability to execute "smart contracts" automatically in normal cases. Bitcoin is "programmable" and can play its role in certain conditions. One application of this capability is to pay the rewards to miners only after successful addition of more than 99 blocks - obtaining rewards after solving a problem is helpful to maintain the proper operation of blockchains.
Since blockchain is open and exciting, some people are skeptical regarding its security. They doubt that some security errors may occur leading to failures in extending the procedures. The developed Bitcoin and some small apps may not support thousands of services provided to tens of millions of users.
Although Satoshi Nakamoto's delicate design has proved impregnable by far, academic researchers have come up with a way to prevent some furtive miners with questionable motives from directly controlling 51% computing power, so that they can maintain the blockchain obediently. In this way, it is less likely to control a large part of network resources than before, hence ensuring security.
One of the major concerns here is the impact on the environment. The framework of Bitcoins forces miners to make such massive hard calculation, termed "workload proof mechanism." If miners do not mine, there will be no reward to ensure that all Bitcoin-related parts will be involved in this game. However, this process produces a lot of meaningless calculations. According to blockchain.info, miners of the whole network are carrying out 450,000 trillion calculations every second, and each calculation consumes energy.
Although miners keep all the details of the utilized hardware, it's hard to find out the actual electricity consumed by the network. Even after optimal usage of hardware, the annual electricity consumption is about two trillion watt-hours, which is more than that consumed by 15 million residents of Kings County in California's Silicon Valley.
Satoshi Nakamoto has set the upper limit of each block at 1 Mb, which can accommodate about 1,400 transactions, with about seven transactions processed every second.
The capacity of a block is expansible, but a larger block needs more time for broadcasting to the network, which may increase the risk of bifurcation. If there is a fundamental contradiction in the blockchain, it stores the unchangeable past and present in an encrypted manner, but in the end, it leads us to a different future.
The computers used for mining can be made more energy saving to replace the workload proof mechanism. Developers are also developing "lightning network" for Bitcoins, which can deal with plenty of small transactions outside a blockchain. Such development would ensure faster connection to enable quicker broadcasting of larger blocks than before.
They can also get mining machine companies to install the new version of Bitcoin client which can support larger blocks. Although some miners have deployed the new version already, it still seems to be vulnerable to attacks by the Internet. Ideally, a large number of small transactions have pushed the system's limits, which essentially shows the necessity for upgrading.
In the current scenarios, when financial companies conduct business with each other, it takes several days to synchronize their internal ledgers, but this process will retain funds and increase risks. It will take a longer time for distributed ledgers to solve such problems, implement digital banking, and complete transactions within seconds or minutes. They may save a lot of expenses for banks: according to Banco Santander, such books can reduce bills of $20 billion annually by 2022. Suppliers still need to prove that these books can deal with transactions with a price much higher than that of Bitcoins, and some big banks have standardized these emerging technologies. Among them, UBS proposed to create a standard "settlement currency." UBS, jointly with Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, and other 22 banks, invested in establishing a blockchain start-up R3 CEV, which will be committed to developing a standard framework for private ledgers.
The problems faced by banks are not exclusive. It is hard to maintain the relationships with various companies and public institutions, in addition to the challenges of frequently incompatible databases and high costs of communicating with each other. Ethereum, the ambitious distributed ledger project, aims to solve these problems. The masterpiece Ethereum, developed by talented 21-year-old Vitalik Buterin from Canada, can deal with more data than Bitcoin. It comes with programming languages, which allow users to prepare more complicated smart contracts, create invoices upon receiving goods or automatically send dividends to stockholders when profit reaches a certain level. Buterin dreams of a "decentralized autonomous organization," a virtual company running on Ethereum blockchain. Before delving deeper into this, let us explore more about Ethereum.
Ethereum is a decentralized platform based on blockchain technology. It runs smart contracts, which are applications that run without any possibility of downtime, censorship, fraud or third party interference.
The usefulness of programmability provided in Ethereum is not just limited to track and record people's property, but also extends to many new aspects. One of them is the built-in car keys in Ethereum, which allow for the sale and release in agreement with relevant rules, producing a new P2P car leasing or the sharing mode. Besides, someone proposed to use this technology to make autonomous car become public resources. According to the predetermined rules, such cars can use the digital funds stored in their private keys to pay for fuel, maintenance, and parking.
Not surprisingly, some people think that this plan is too ambitious. The creation block of Ethereum, having commenced in August, only boasts a small number of start-ups currently working on this project. Also, Buterin admitted in a recent blog that he is short of funds at present. The specific details of the blockchain will not continue to arouse response, but this enthusiasm has been inspiring both start-ups and established magnates to continue exploring the potential of distributed ledgers. Although many have underestimated the ability of accountants all the time, the importance of ledgers remains self-evident.
Blockchain has a lot to offer even for scenarios related to the "Internet of Things" dealing with a network connected by billions of static everyday objects, such as refrigerators, snubs, and lawn sprinklers. A recent report titled "Device Democratization" of IBM indicates that it is almost impossible to make centralized tracking and management of billions of devices. Hence, it is unwise to attempt as it may make the overall management process vulnerable to hacker attacks and government monitoring. For such cases, distributed ledger system seems to be a feasible and tangible solution.
Principally, this blog highlighted the fundamentals of bitcoins and blockchain technology, their evolution, applications in various fields, and their future. Besides, it focuses on the technicalities behind a single bitcoin transaction and clarifies basics about the hash value and hash calculations. Additionally, it talks about the disadvantages of the Bitcoins including the security aspects and ways to address these problems. Every technology has an inception cycle while growing from an idea into the maturity. Whether you are a software engineer, a financial analyst or a legal person, blockchain technology offers promising technological revolution worthy of the future. Let's aim at unlocking its hidden potential to change our lives and influence our future and the world.
Original link: https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/60564
References:
http://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=9c2bf3f5-42d5-4136-a6b2-2a646176ab30
http://www.economist.com/news/briefing/21677228-technology-behind-bitcoin-lets-people-who-do-not-know-or-trust-each-other-build-dependable
http://ouisharefest.com/
https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
https://www.ethereum.org/
https://blockchain.info/charts
Private vs. Public Cloud: Which one is right for your business?

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - December 6, 2016
Alibaba Clouder - July 26, 2021
vic - August 30, 2019
Wei Kuo - August 30, 2019
Iain Ferguson - January 21, 2022
Alibaba Clouder - July 11, 2018

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow LedgerDB
LedgerDB
A ledger database that provides powerful data audit capabilities.
Learn More Blockchain as a Service
Blockchain as a Service
BaaS provides an enterprise-level platform service based on leading blockchain technologies, which helps you build a trusted cloud infrastructure.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder
Raja_KT March 12, 2019 at 4:42 am
Hashing and hashing and hashing....how much CPU , infra ...usage? mining for a long chain.....whaw. Tangle -IOTA?