By Wang Tantan (Si Ming)
Ordering systems are a type of general-purpose systems that are widely used in various industries, such as e-commerce orders, bank journal entries, and phone bills from communication service providers. Traditional practices for these systems have been established over decades of development. However, the development of Internet and increasing importance attached to data by enterprises lead to an increasing number of orders that need to be stored and persisted. The increasing data importance and data scale bring new challenges.
"E-commerce Platform A" needs to persist all the order data produced on this platform. Meanwhile, based on all the order data, the system needs to provide diversified query services targeting multiple roles: consumers, shop owners, and the platform. Consumers can query their historical orders, sellers can use statistics to find out best-selling products, and the platform can also analyze information such as user behaviors and platform transaction scale. The main query methods include multi-dimensional order retrieval, order data analysis, and statistics. The following are some examples:
Query targeting consumers: [consumer A] [recent year] [computers sold] order query;
Query targeting salespersons: [salesperson B] * [last month] sales orders;
In order scenarios, several technical factors need to be taken into consideration, including:
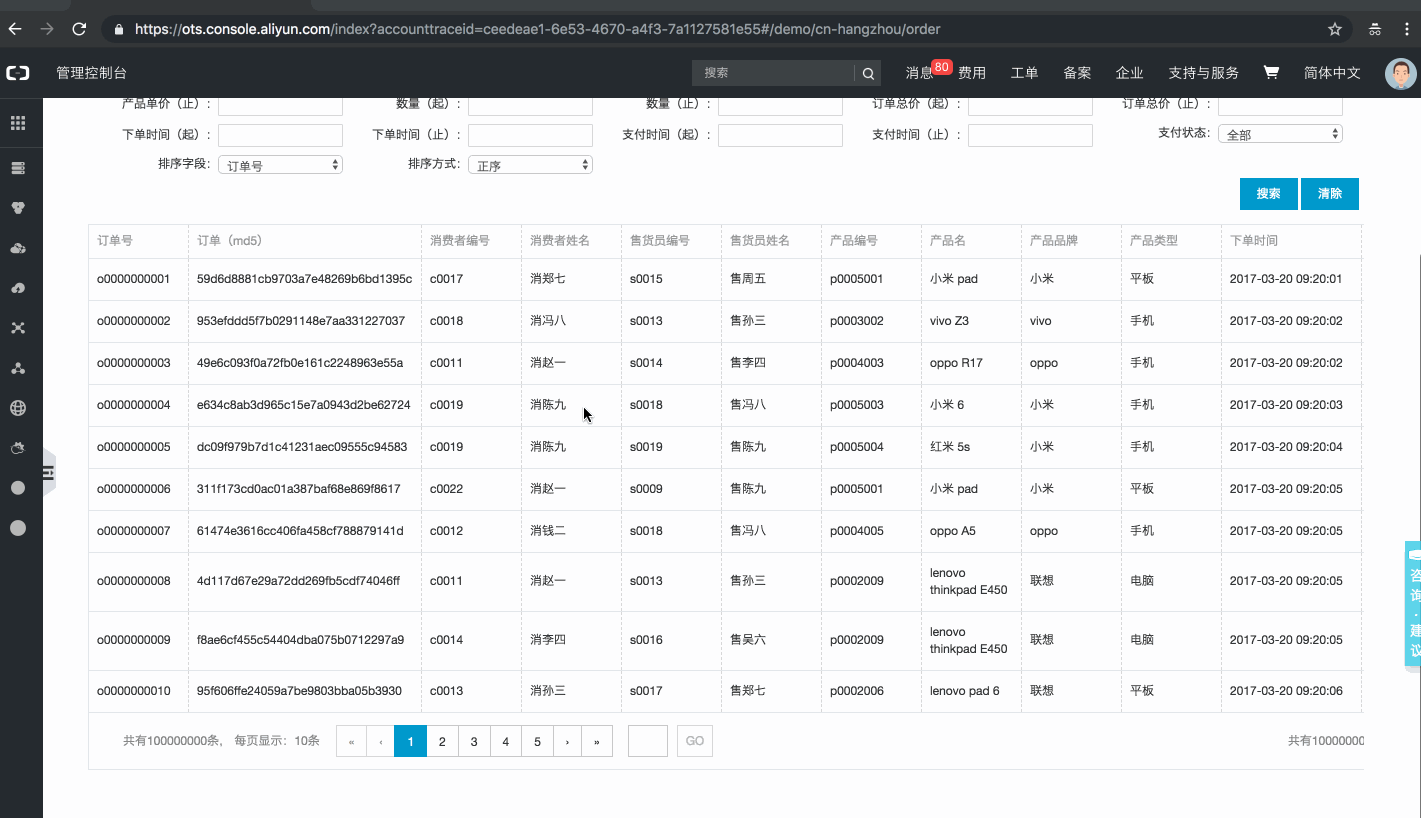
Multi-dimensional and real-time querying is a core feature of order management solutions. For more information, check Project Sample on the official console webpage.
In e-commerce, traditional MySQL solutions are usually used to meet requirements of order scenarios. The powerful query capability of the relational database allows users to implement multi-dimensional order query and data statistics directly by using SQL statements. Data expansion includes horizontal expansion and vertical expansion. Horizontal data expansion means that new field dimensions are constantly added in an iterative manner, and vertical data expansion refers to the increase in the total data storage volume. MySQL solutions alone gradually become difficult to deal with these two types of data expansion. The "SQL + NoSQL" combination solution (hereinafter referred to as "combination solution") is implemented and used to solve the needs in different scenarios by utilizing advantages of both the databases. However, the combination solution also causes new problems: The combination solution has higher storage costs and increases development work and the complexity of maintenance. Additional costs are incurred to ensure data consistency.
Let's look at the following ordinary solutions:
MySQL features powerful data query and analysis. Creating order systems based on MySQL can meet the requirements of multi-dimensional order data query and statistics. As the order data volume grows, users can adopt the pseudo-distributed database/table sharding solution to solve problems resulting from data expansion. However, once the data volume reaches the bottleneck, it is necessary to re-create larger database shards and perform full data migration, causing relentless troubles. The MySQL solution cannot solve the challenges brought by data iteration and expansion. The disadvantages of the traditional order solutions, which depend on MySQL, become increasingly obvious.
1) Vertical data expansion (data scale): For the database/table sharding solution, it is required to estimate the database scale when deploying MySQL. If the data volume reaches the upper limit, re-deployment and full data migration are required.
2) Horizontal data expansion (field dimension): It is required to pre-define schemas and iterating new fields becomes more complex. The database performance will affected when a certain number of dimensions are reached.
This dual-database solution is used to solve data expansion problems to some extent by storing real-time and historical data separately. This solution divides data to be stored into two parts: real-time data and historical data. In addition, this solution uses the data synchronization service to synchronize expired data to historical data.
1) Real-time orders (for example, orders over the last three months): Real-time orders are stored in the MySQL database. This limits the expansion speed of the total real-time order volume and ensures multi-dimensional query and analysis of real-time data.
2) Historical orders (for example, orders placed three months ago): Historical order data is stored in HBase. As a distributed NoSQL database, HBase can be used to efficiently solve data expansion challenges. This can also ensure the persistence of historical order data.
However, this solution assumes that historical data is extremely unlikely to be used and fails to provide much value of historical order data for consumers, shopowners, and the platform. Once historical order data is needed, a full table scan is required and this query is very slow with high I/O costs. In addition, maintaining data synchronization causes challenges such as data consistency and increased synchronization and maintenance cost.
Another combination solution is MySQL + ElasticSearch. This solution also divides data to be stored into two types to solve the problem of increased order index dimensions. Users maintain data synchronization services themselves to ensure the consistency of the two parts of data.
1) Full data: The full order data is stored in the MySQL database. Data other than order IDs is all stored as a field. The full data is persisted and also used for reverse lookup of non-indexed fields.
2) Query data: Only fields that need to be retrieved are stored into ElasticSearch (Lucene-based distributed index database). The indexing capability of Elasticsearch allows processing order data with increasing dimensions and performing reverse MySQL lookup to obtain complete order information.
This solution can solve the challenges from data dimension expansion. However, as the order volume increases continuously, the poor scalability of MySQL becomes obvious again. In the meantime, the solution of synchronizing data to ElasticSearch requires high development and maintenance costs. This solution itself has some disadvantages.
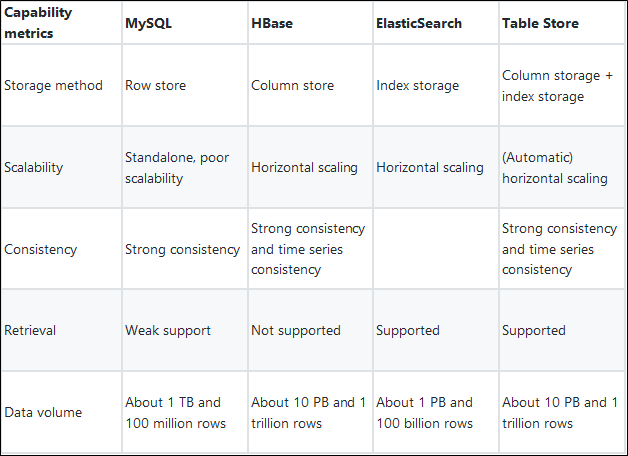
The SearchIndex solution from Table Store can perfectly support an order system holding 100 million orders. Table Store is out-of-the-box and pay-as-you-go. SearchIndex is an optimal solution for managing massive amounts of e-commerce order metadata and can be created at any time.
Table Store is a fully-hosted and distributed NoSQL data storage service from Alibaba Cloud that provides features such as storage of massive amounts of data, automatic sharding of hot data, and multi-dimensional retrieval of massive amounts of data. Table Store can efficiently solve the order data explosion challenge.
At the same time, SearchIndex provides multi-dimensional data search, statistics and other capabilities on the basis of ensuring high availability of user data. You can create multiple indexes for multiple scenarios to achieve retrieval in multiple modes. You can create and activate indexes as needed. Table Store ensures the consistency of data synchronization, greatly reducing the work required for your solution design, service maintenance, and code development.
The sample is integrated in the Table Store console. You can log on to the console to experiment with the system. (If you are a new Table Store user, you need to click Activate Now for a trial of this service. The service activation is free. Order data is stored in public instances. A trial doesn't consume storage, network traffic, or CUs.)
Note: This sample provides order data for about 100 million orders. Official console address: Project Sample
If you are satisfied with the order system for 100 million orders implemented based on Table Store and want to start to set up your own system, simply follow these steps:
Activate the Table Store service in the console. Table Store is out-of-the-box (post-paid) and billed on a pay-as-you-go basis. Table Store also provides a free quota that is sufficient for functional tests. For more information, visit Table Store Console and Free quota description.
Create a Table Store instance in the console and select a region that supports SearchIndex. (Currently the SearchIndex feature has not been commercialized and is supported in the following regions: Beijing, Shanghai, Hangzhou, and Shenzhen. This feature will be gradually available in other regions.)
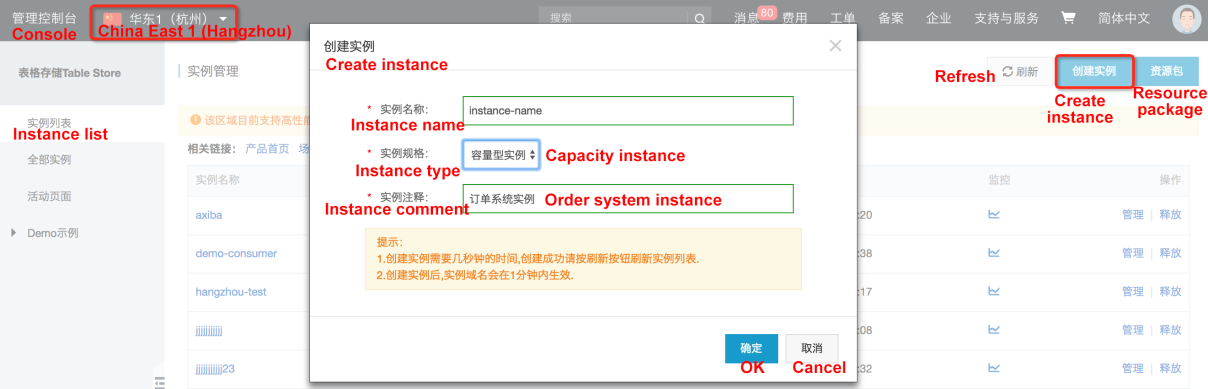
After the instance is created, open a ticket to apply for the SearchIndex beta test invitation. (After becoming commercialized, SearchIndex will be enabled by default. No fees will be incurred if the feature is not used.)
Use SDKs with SearchIndex (see the official website for more details). Currently, new functions are added for Java, Go, and Node.js SDKs.
Java-SDK
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.openservices</groupId>
<artifactId>tablestore</artifactId>
<version>4.8.0</version>
</dependency>Go-SDK
$ go get github.com/aliyun/aliyun-tablestore-go-sdkNodejs-SDK
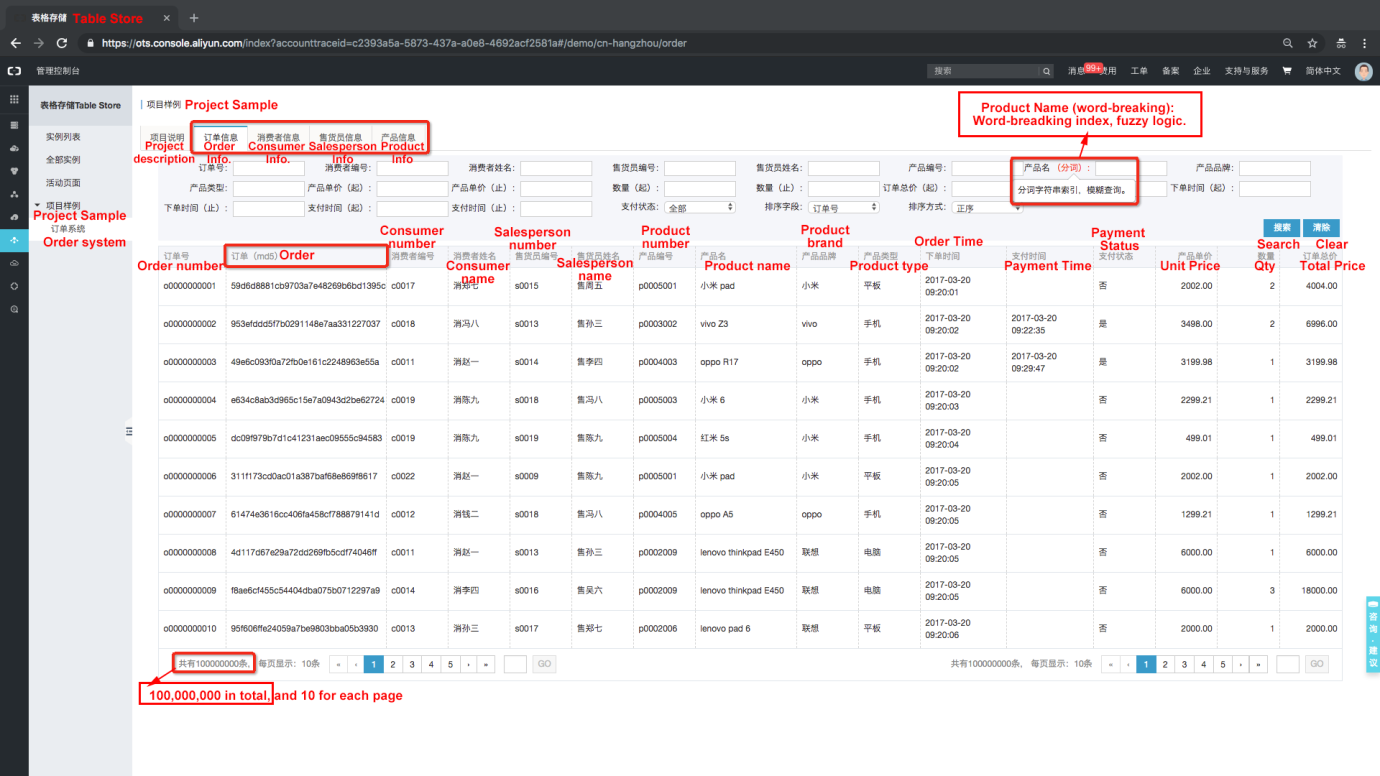
$ npm install tablestore@4.1.0An order system doesn't only include one order data table. An order system should include tables such as consumer tables, salesperson tables, product tables, supplier tables, transaction order tables, and payment order tables. The sample mainly uses four basic tables (consumer table, salesperson table, product table, and transaction order table). Let's take the order table for example:
Table name: order_contract
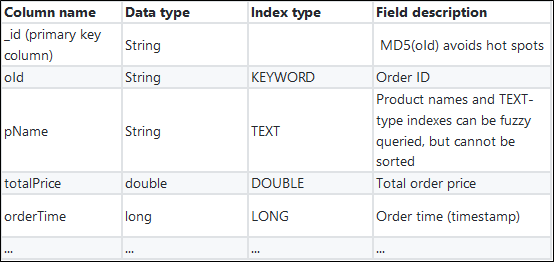
Four tables: Order Table, Consumer Table, Salesperson Table, and Product Table
Users only need to maintain one instance and create tables as follows: Create and manage data tables through the console (they can also directly create data tables through the SDK):
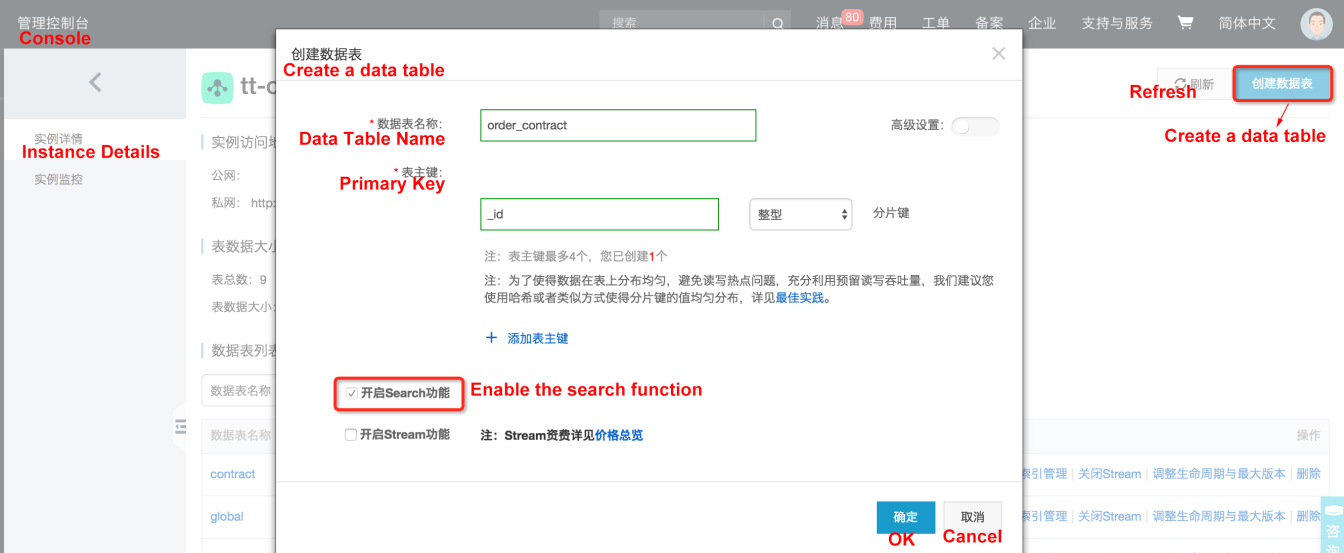
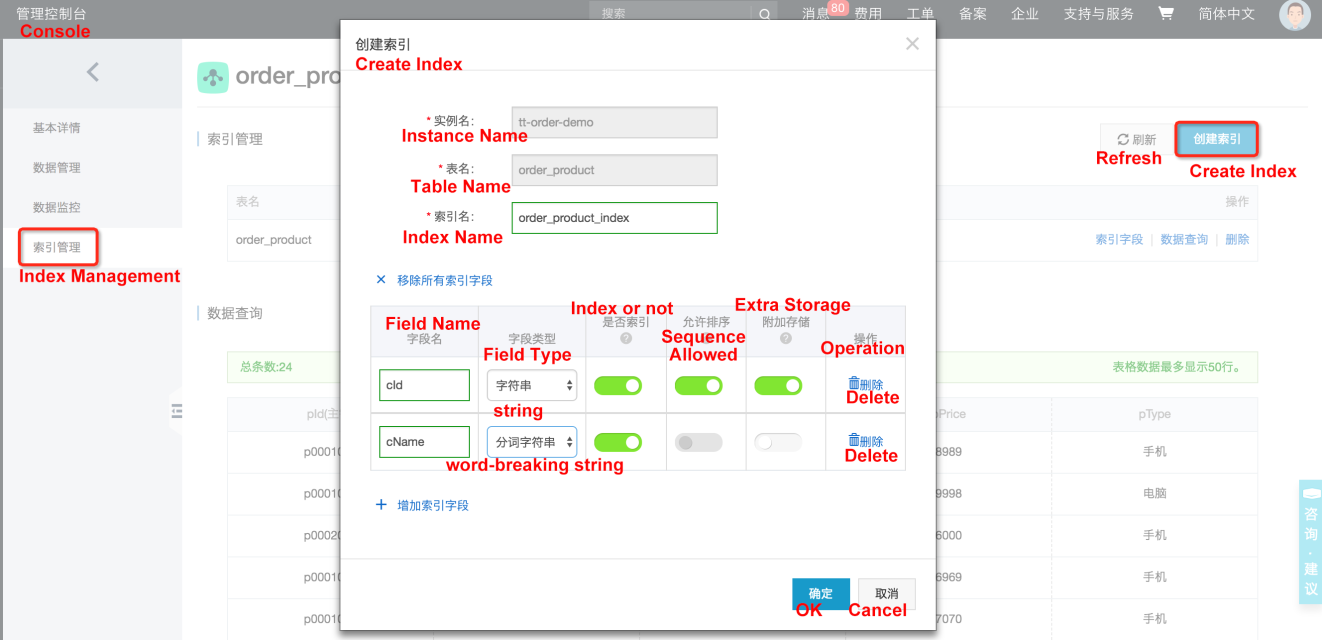
Table Store automatically synchronizes full and incremental index data: Users can create and manage SearchIndex through the console (or, they can also create it through the SDK):
Insert some test data (100 million entries of data are inserted into the console sample. Users can insert a small amount of test data on the console);
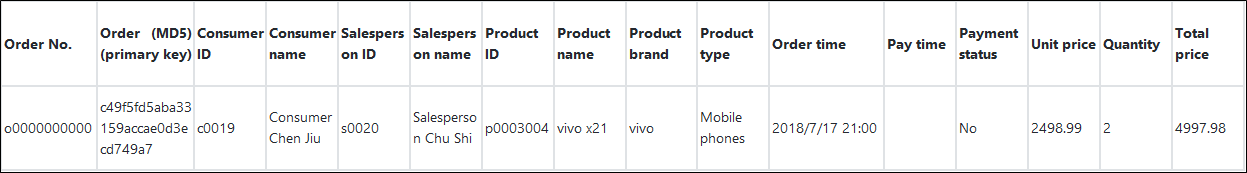
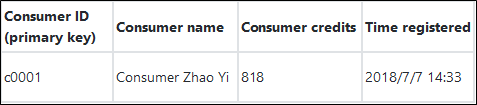
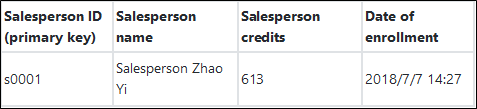
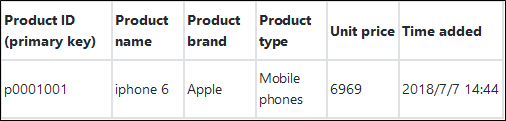
Data reading falls into two types:
1. Primary key reading
The primary key column is obtained based on the native Table Store: getRow, getRange, batchGetRow. Primary key reading is used for index (automatic) reverse lookup. Users can also provide a single query page for the primary key (Order MD5). And the query speed is extremely fast at the scale of 100 million entries of data. Multi-dimensional retrieval is not supported for the single primary key query;
2. Index reading
Query based on the new SearchIndex function: the search interface. Users can freely design multi-dimensional combination queries for index fields. By setting and selecting different query parameters, different query criteria and different sorting methods are built. Currently, exact query, range query, prefix query, match query, wildcard query, phrase match query, and word breaking string query are supported, and they are combined by boolean AND and OR.
For example, the combination of [orders of consumer c0001 with consumption above 99.99] is as follows:
List<Query> mustQueries = new ArrayList<Query>();
TermQuery termQuery = new TermQuery();
termQuery.setFieldName("cId");
termQuery.setTerm(ColumnValue.fromString("c0001"));
mustQueries.add(termQuery);
RangeQuery rangeQuery = new RangeQuery();
rangeQuery.setFieldName("totalPrice");
rangeQuery.setFrom(ColumnValue.fromDouble(99.99));
mustQueries.add(rangeQuery);
BoolQuery boolQuery = new BoolQuery();
boolQuery.setMustQueries(mustQueries);Implementing Tracking Management and Geo-Fencing on Table Store

57 posts | 12 followers
FollowApsaraDB - October 20, 2020
Hologres - July 1, 2021
ray - April 16, 2025
Hologres - July 24, 2020
francisndungu - December 12, 2018
ApsaraDB - November 28, 2022

57 posts | 12 followers
Follow Tablestore
Tablestore
A fully managed NoSQL cloud database service that enables storage of massive amount of structured and semi-structured data
Learn More ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase is a NoSQL database engine that is highly optimized and 100% compatible with the community edition of HBase.
Learn More Storage Capacity Unit
Storage Capacity Unit
Plan and optimize your storage budget with flexible storage services
Learn More Hybrid Cloud Storage
Hybrid Cloud Storage
A cost-effective, efficient and easy-to-manage hybrid cloud storage solution.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Storage