By Mengyuan Pan
Canary release is a very effective and important release strategy in microservice development. In combination with reasonable traffic control and monitoring methods, canary release can greatly reduce risks during system release and achieve rapid iteration and efficient delivery. Canary release allows you to incrementally roll out new services or versions. For example, if you want to release a new version, you can first direct a portion of traffic to the version to test its functionality, and then increase traffic after the functionality is verified. Compared with other release modes, such as full release and blue-green release, the canary release offers advantages like resource optimization and high flexibility.
When services call each other, you may need to isolate environments and perform traffic shaping for the end-to-end service call chain when you perform a canary release. In other words, you must make sure that canary release traffic is sent to only the canary release versions of the services in the corresponding call chain. This way, different call chains are isolated from each other. This is called end-to-end canary release.
ASM provides lane functionality to isolate traffic for different versions. It also allows you to define a baseline version, which allows for automatically falling back to the baseline version when a service of another version fails to be called. This enables more flexible and stable traffic testing of canary release. You can use Kruise Rollout, a progressive delivery framework, to automatically manage the release status of new application versions, achieving end-to-end canary release throughout the lifecycle.
Alibaba Cloud Service Mesh (ASM) is a managed service mesh platform for unified traffic management of applications that use the microservices architecture. ASM is compatible with open-source Istio. ASM provides traffic control, mesh observation, and secure communication among services, which simplify service governance. In addition, ASM allows you to centrally manage services that run on heterogeneous computing infrastructure. You can add ACK clusters, serverless Kubernetes (ASK) clusters, Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances, and self-managed clusters to ASM instances. ASM builds managed and unified service mesh capabilities for hybrid cloud, multi-cloud, and multi-cluster scenarios.
ASM allows you to isolate a version or certain features of an application into an independent runtime environment (known as lane). Then, you can configure lane rules to route requests that meet the rules to the destination version or features of the application. Traffic lanes can be used together with custom routing resources, such as virtual services and destination rules, to implement end-to-end (E2E) traffic management in a centralized manner, fine-grained routing management, and simplified traffic processing.
Kruise Rollout is an open-source progressive rollout framework provided by OpenKruise. You can use Kruise Rollout to perform canary releases, blue-green deployments, and A/B testing. You can also use Kruise Rollout to control the canary traffic and pods. The release process can be automated in batches and paused based on Prometheus metrics. Kruise Rollout also provides seamless bypass connections and is compatible with various workloads such as Deployments, CloneSets, and StatefulSets. For more information, see Kruise Rollout.
Kruise Rollout is a bypass component. You need to only create a Rollout in your cluster to automate application releases and updates. Kruise Rollout supports seamless integration with Helm and PaaS platforms at low costs. The following figure shows how canary releases are performed by using Kruise Rollout.
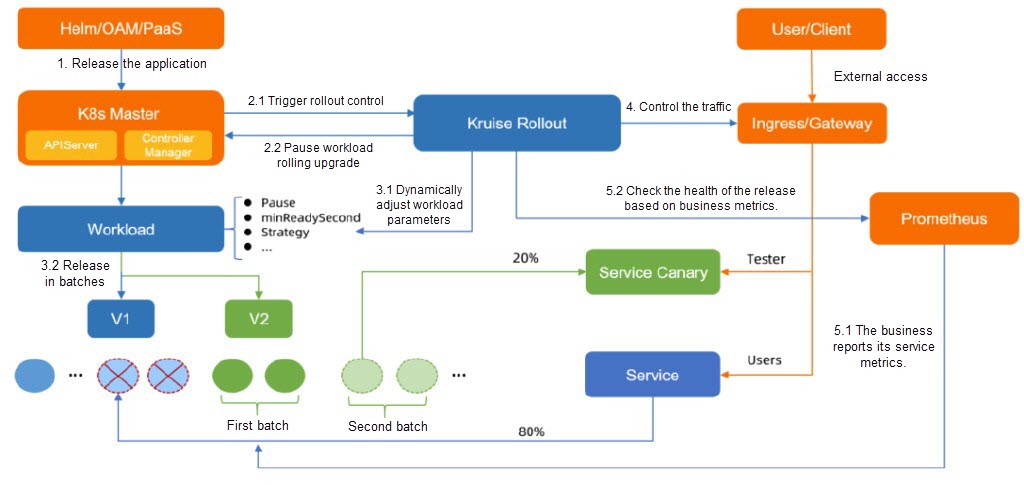
First, define an Istio gateway for traffic ingress. Use the following content to create an Istio gateway named ingressgateway in the istio-system namespace. For more information, see Manage Istio gateways.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: ingressgateway
namespace: istio-system
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- '*'Deploy three applications in the cluster: mocka, mockb, and mockc. The following figure shows the access relationship among them.

apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mocka
labels:
app: mocka
service: mocka
spec:
ports:
- port: 8000
name: http
selector:
app: mocka
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mockb
labels:
app: mockb
service: mockb
spec:
ports:
- port: 8000
name: http
selector:
app: mockb
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mockc
labels:
app: mockc
service: mockc
spec:
ports:
- port: 8000
name: http
selector:
app: mockc
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mocka-v1
labels:
app: mocka
version:
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mocka
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mocka
version: v1
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
spec:
containers:
- name: default
image: registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/aliacs-app-catalog/go-http-sample:1.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: version
value: v1
- name: app
value: mocka
- name: upstream_url
value: "http://mockb:8000/"
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mockb-v1
labels:
app: mockb
version: v1
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mockb
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mockb
version: v1
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
spec:
containers:
- name: default
image: registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/aliacs-app-catalog/go-http-sample:1.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: version
value: v1
- name: app
value: mockb
- name: upstream_url
value: "http://mockc.demo:8000/"
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mockc-v1
labels:
app: mockc
version: v1
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mockc
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mockc
version: v1
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
spec:
containers:
- name: default
image: registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/aliacs-app-catalog/go-http-sample:1.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: version
value: v1
- name: app
value: mockc
ports:
- containerPort: 8000Deploy a lane group and two lanes. The lane group defines three services, mocka, mockb, and mockc. The two lanes are the baseline lane and the canary release lane. The baseline lane contains applications with the ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base label, and the canary release lane contains applications with the ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary label.
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1
kind: ASMSwimLaneGroup
metadata:
name: rollout
spec:
ingress:
gateway:
name: ingressgateway
namespace: istio-system
type: ASM
ingressRouting:
ingressRoutingStrategy: rule_based
weightedRoutingRule:
hosts:
- '*'
requestMatches:
- uri:
exact: /mock
isPermissive: true
permissiveModeConfiguration:
fallbackTarget: base
routeHeader: x-asm-prefer-tag
traceHeader: my-request-id
autoUpdate: true
services:
- cluster:
id: c8f823ca6f5de404486e1b83d61b4e812
name: test
name: mockb
namespace: default
- cluster:
id: ce9724f7548914f9bbc0c09bbf0481623
name: test
name: mocka
namespace: default
- cluster:
id: ce9724f7548914f9bbc0c09bbf0481623
name: test
name: mockc
namespace: default
---
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1
kind: ASMSwimLane
metadata:
labels:
swimlane-group: rollout
name: base
spec:
ingressRules:
- hosts:
- '*'
match:
headers:
x-asm-prefer-tag:
exact: base
uri:
exact: /mock
name: base
online: true
route:
destination:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
ingressWeight:
destination: {}
labelSelector:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
services:
- cluster:
id: ce9724f7548914f9bbc0c09bbf0481623
name: test
name: mockb
namespace: default
- cluster:
id: ce9724f7548914f9bbc0c09bbf0481623
name: test
name: mocka
namespace: default
- cluster:
id: ce9724f7548914f9bbc0c09bbf0481623
name: test
name: mockc
namespace: default
---
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1
kind: ASMSwimLane
metadata:
labels:
swimlane-group: rollout
name: canary
spec:
ingressRules:
- hosts:
- '*'
match:
headers:
x-asm-prefer-tag:
exact: canary
uri:
exact: /mock
name: canary
online: true
route:
destination:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
labelSelector:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary
services: []After the deployment, ASM automatically creates VirtualService and DestinationRule based on the services and routing rules defined in the lane group and lanes. The routing rule means that:
• Traffic containing header x-asm-prefer-tag: base is routed to the baseline lane.
• Traffic containing header x-asm-prefer-tag: canary is routed to the canary lane.
• When a service call fails in the canary lane, traffic is routed to the baseline lane.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: swimlane-ingress-vs-rollout-base
namespace: istio-system
spec:
gateways:
- istio-system/ingressgateway
hosts:
- '*'
http:
- match:
- headers:
x-asm-prefer-tag:
exact: base
uri:
exact: /mock
name: base
route:
- destination:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: base
fallback:
target:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: base
headers:
request:
set:
x-asm-prefer-tag: base
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: swimlane-ingress-vs-rollout-canary
namespace: istio-system
spec:
gateways:
- istio-system/ingressgateway
hosts:
- '*'
http:
- match:
- headers:
x-asm-prefer-tag:
exact: canary
uri:
exact: /mock
name: canary
route:
- destination:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: canary
fallback:
target:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: base
headers:
request:
set:
x-asm-prefer-tag: canary
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-vs-rollout-default-mocka
namespace: istio-system
spec:
hosts:
- mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
http:
- name: default
route:
- destination:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: $asm-label
fallback:
target:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: base
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-vs-rollout-default-mockb
namespace: istio-system
spec:
hosts:
- mockb.default.svc.cluster.local
http:
- name: default
route:
- destination:
host: mockb.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: $asm-label
fallback:
target:
host: mockb.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: base
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-vs-rollout-default-mockc
namespace: istio-system
spec:
hosts:
- mockc.default.svc.cluster.local
http:
- name: default
route:
- destination:
host: mockc.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: $asm-label
fallback:
target:
host: mockc.default.svc.cluster.local
subset: baseapiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mocka
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockb
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockb.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockc
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockc.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
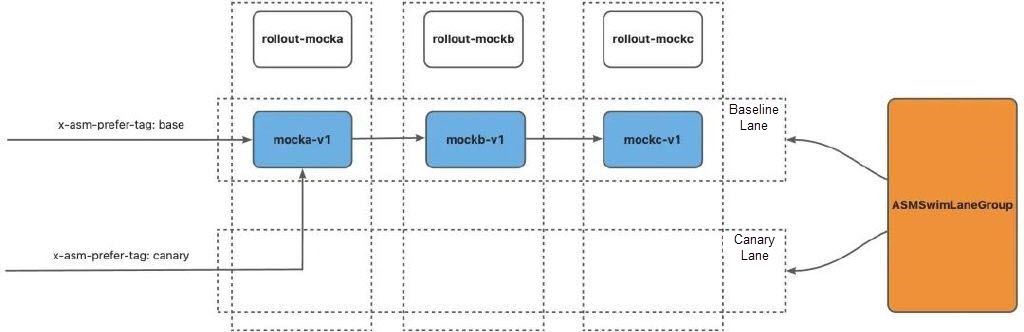
name: baseIn the initial state, the baseline lane contains three published baseline applications, while the canary lane does not contain any services. In this case, you can run the following command to access the baseline lane:
% curl ${ASM_GATEWAY}/mock -H 'x-asm-prefer-tag: base' -H 'my-request-id: 9999'
% -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.87)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.97)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.89)As the canary lane does not contain any applications, requests to the canary lane are also directed to the baseline lane.
% curl ${ASM_GATEWAY}/mock -H 'x-asm-prefer-tag: canary' -H 'my-request-id: 10000'
% -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.87)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.97)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.89)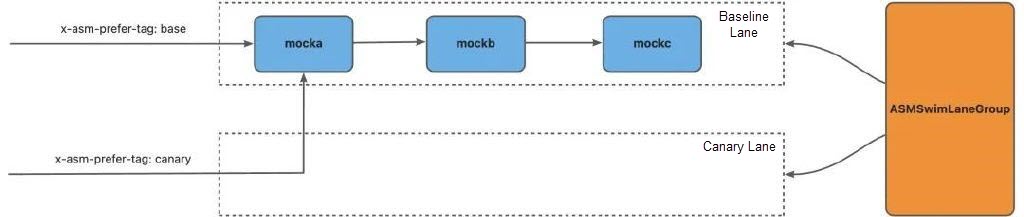
Deploy Kruise Rollout for the mocka, mockb, and mockc applications in the cluster and define the following release policies:
• Create a canary deployment to deploy the new version of the application.
• The release is completed in batches. A new version of the application is deployed in the first batch.
• The canary pod label contains ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary.
apiVersion: rollouts.kruise.io/v1beta1
kind: Rollout
metadata:
name: rollouts-mocka
spec:
workloadRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: mocka-v1
strategy:
canary:
# Create a deployment of the canary version.
enableExtraWorkloadForCanary: true
# One batch in total. Deploy one application in the first batch.
steps:
- replicas: 1
# Change the ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG label of the pod to canary.
patchPodTemplateMetadata:
labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary
---
apiVersion: rollouts.kruise.io/v1beta1
kind: Rollout
metadata:
name: rollouts-mockb
spec:
workloadRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: mockb-v1
strategy:
canary:
enableExtraWorkloadForCanary: true
steps:
- replicas: 1
patchPodTemplateMetadata:
labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary
---
apiVersion: rollouts.kruise.io/v1beta1
kind: Rollout
metadata:
name: rollouts-mockc
namespace: demo
spec:
workloadRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: mockc-v1
strategy:
canary:
enableExtraWorkloadForCanary: true
steps:
- replicas: 1
patchPodTemplateMetadata:
labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canaryRun the following command to modify the baseline application image and release the new version:
kubectl patch deployment mocka-v1\
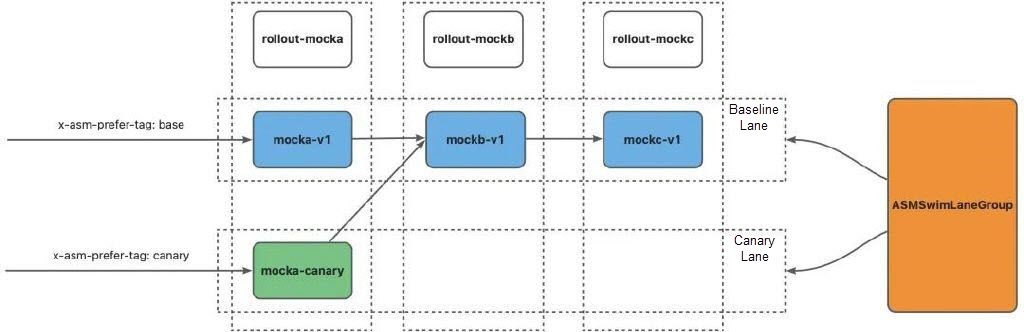
-p '{"spec": {"template": {"spec": {"containers": [{"name": "default", "image": "registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/aliacs-app-catalog/go-http-sample:2.0"}]}}}}}'Kruise Rollout automatically creates a canary deployment and deploys the new version of the pod in the canary lane. Run the following command to view the information about DestinationRule:
$ kubectl get destinationrule trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mocka -n istio-systemYou can find that a new version of the service has been added:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mocka
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
# Updated information about the new version of mocka.
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary
name: canary
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockb
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockb.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockc
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockc.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: baseRun the following command to access the canary lane:
% curl ${ASM_GATEWAY}/mock -H 'x-asm-prefer-tag: base' -H 'my-request-id: 10001'
% -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 172.16.0.88)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.97)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.89)Only the mocka service has the canary version. Therefore, both mockb and mockc traffic is routed to the baseline lane.
Run the following command to modify the baseline application images of mockb and mockc and release the new version:
$ kubectl patch deployment mockb-v1 \
-p '{"spec": {"template": {"spec": {"containers": [{"name": "default", "image": "registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/aliacs-app-catalog/go-http-sample:2.0"}]}}}}}'
$ kubectl patch deployment mockc-v1 \
-p '{"spec": {"template": {"spec": {"containers": [{"name": "default", "image": "registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/aliacs-app-catalog/go-http-sample:2.0"}]}}}}}'Run the following command to view the information about DestinationRule:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mocka
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary
name: canary
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockb
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockb.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary
name: canary
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockc
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockc.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary
name: canaryAs you can see, the canary version information is added to mockb and mockc. Run the following command to access the canary lane. It can be seen that the traffic is routed to the v2 application:
% curl ${ASM_GATEWAY}/mock -H 'x-asm-prefer-tag: canary' -H 'my-request-id: 10002'
% -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 172.16.0.88)-> mockb(version: v2, ip: 172.16.0.78)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 172.16.0.80)Run the following command to access the baseline lane. You can see that all traffic is routed to the v1 application:
% curl ${ASM_GATEWAY}/mock -H 'x-asm-prefer-tag: base' -H 'my-request-id: 10003'
% -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.87)-> mockb(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.97)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.89)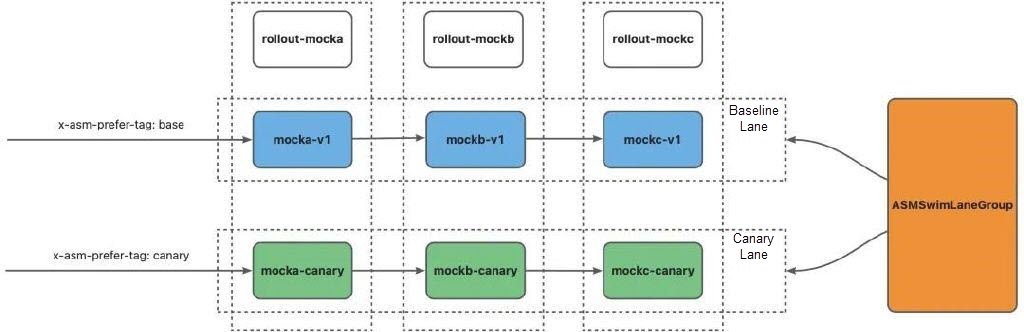
The new version of the mockb application has been tested. Run the following command to continue to release the new version of the mockb application and deploy the new version in the baseline.
% kubectl kruise rollout approve rollout/rollouts-mockbViewing the DestinationRule, you can see that the canary version of the mockb service is removed.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mocka
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary
name: canary
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockb
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockb.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
# The canary version is removed.
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockc
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockc.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: canary
name: canaryIn this case, running the following command to access the baseline lane, you can find that the new version of mockb has been deployed in the baseline environment.
% curl ${ASM_GATEWAY}/mock -H 'x-asm-prefer-tag: base' -H 'my-request-id: 10004'
% -> mocka(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.87)-> mockb(version: v2, ip: 172.16.0.236)-> mockc(version: v1, ip: 172.16.0.89)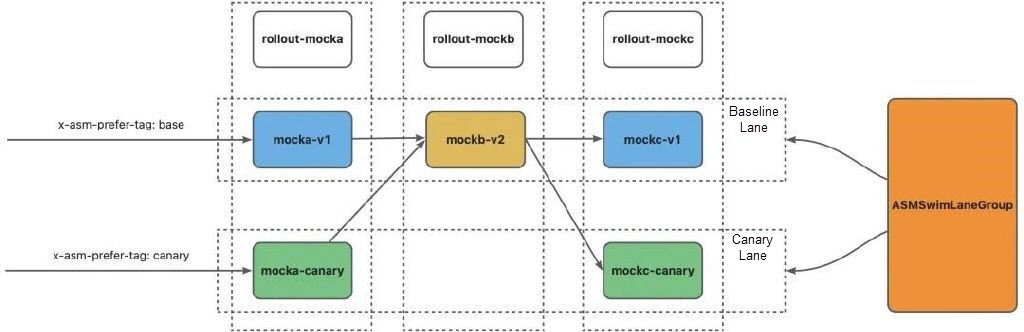
The new version of mocka and mockc applications are tested. Run the following command to continue to release the new version of the mocka and mockc applications and deploy the new versions in the baseline.
% kubectl kruise rollout approve rollout/rollouts-mocka
% kubectl kruise rollout approve rollout/rollouts-mockcViewing the DestinationRule, you can see that only the baseline version of the service exists.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mocka
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mocka.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockb
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockb.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: base
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
labels:
asm-system: "true"
provider: asm
swimlane-group: rollout
name: trafficlabel-dr-rollout-default-mockc
namespace: istio-system
spec:
host: mockc.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- labels:
ASM_TRAFFIC_TAG: base
name: baseRun the following command to access the baseline lane. The baseline environment is replaced by the new version.
% curl ${ASM_GATEWAY}/mock -H 'x-asm-prefer-tag: base' -H 'my-request-id: 10005'
% -> mocka(version: v2, ip: 172.16.0.97)-> mockb(version: v2, ip: 172.16.0.236)-> mockc(version: v2, ip: 172.16.0.78)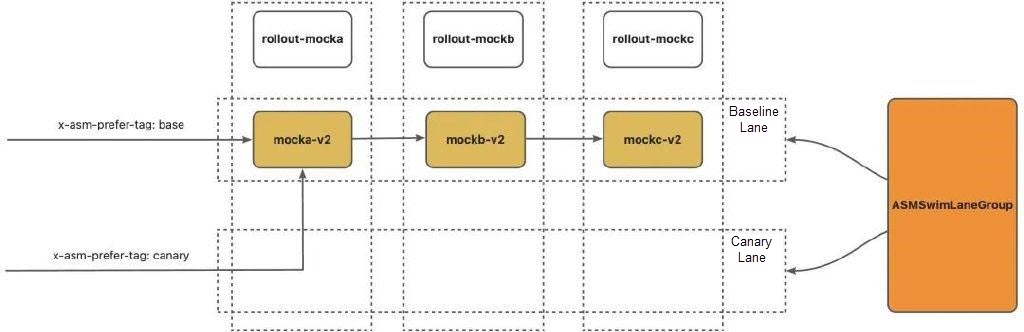
During the canary release, if you find an application exception, such as mocka not running as expected, you can run the following command to roll back the application and stop releasing the new version.
kubectl kruise rollout undo rollout/rollouts-mockaSo far, a complete release process has been completed. ASM and Kruise Rollout are used to help you better implement progressive releases. You can isolate different versions of applications in a single environment and route traffic. This way, you can implement end-to-end canary release testing in a more stable and cost-effective manner.
A Flexible Serverless Elasticity Solution for Workload-level Management
Kimi Large Model-based Massive Data Preprocessing Practice of Moonshot AI

193 posts | 33 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native Community - September 18, 2023
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - March 11, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native - January 18, 2024
Alibaba Container Service - January 14, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - November 22, 2023
Xi Ning Wang(王夕宁) - August 17, 2023

193 posts | 33 followers
Follow Container Service for Kubernetes
Container Service for Kubernetes
Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes is a fully managed cloud container management service that supports native Kubernetes and integrates with other Alibaba Cloud products.
Learn More Microservices Engine (MSE)
Microservices Engine (MSE)
MSE provides a fully managed registration and configuration center, and gateway and microservices governance capabilities.
Learn More ACK One
ACK One
Provides a control plane to allow users to manage Kubernetes clusters that run based on different infrastructure resources
Learn More Container Registry
Container Registry
A secure image hosting platform providing containerized image lifecycle management
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Container Service