By Musheng
Spring AI Alibaba RAG Example project source code address:https://github.com/springaialibaba/spring-ai-alibaba-examples/tree/main/spring-ai-alibaba-rag-example
● Spring AI: A Java AI development framework for the Spring ecosystem, providing a unified API for accessing large models, vector databases, and other AI infrastructure.
● Ollama: A local model running engine (similar to Docker) that supports quick deployment of open-source models.
● Spring AI Alibaba: An enhancement of Spring AI, integrating the DashScope model platform.
● Elasticsearch: A vector database that stores text vectorization data and supports semantic retrieval.
Docker Compose starts Ollama: (Simultaneously starts a model front-end system to interact with the Ollama model.)
services:
ollama:
container_name: ollama
image: ollama/ollama:latest
ports:
- 11434:11434
open-webui:
image: ghcr.io/open-webui/open-webui:main
container_name: open-webui
ports:
- 3005:8080
environment:
- 'OLLAMA_BASE_URL=http://host.docker.internal:11434'
# Allow the container to access the host network
extra_hosts:
- host.docker.internal:host-gatewayExecute the following commands:
docker exec -it ollama ollama pull deepseek-r1:8b
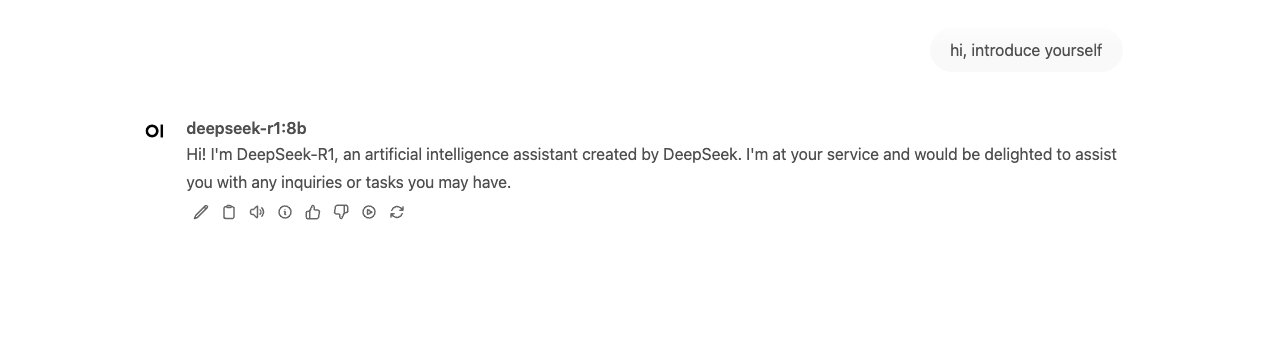
docker exec -it ollama ollama pull nomic-embed-text:latestInvoke the deepseek-r1:8b model in open-webui:
services:
elasticsearch:
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.16.1
container_name: elasticsearch
privileged: true
environment:
- "cluster.name=elasticsearch"
- "discovery.type=single-node"
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx1096m"
- bootstrap.memory_lock=true
volumes:
- ./config/es.yaml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
ports:
- "9200:9200"
- "9300:9300"
deploy:
resources:
limits:
cpus: "2"
memory: 1000M
reservations:
memory: 200MPrepare the configuration file for es startup:
cluster.name: docker-es
node.name: es-node-1
network.host: 0.0.0.0
network.publish_host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
# Disable authentication, default enabled in es 8.x
xpack.security.enabled: falseYou have completed all the environmental preparation steps needed to build a simple RAG application. Now, let's start setting up the project.
<!-- Spring Boot Web Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>3.3.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring AI Ollama Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-ollama-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-M5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Vector Storage -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-elasticsearch-store</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-M5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- PDF Parsing -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-pdf-document-reader</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-M5</version>
</dependency>spring:
ai:
# ollama configuration
ollama:
base-url: http://127.0.0.1:11434
chat:
model: deepseek-r1:8b
embedding:
model: nomic-embed-text:latest
# Vector database configuration
vectorstore:
elasticsearch:
index-name: ollama-rag-embedding-index
similarity: cosine
dimensions: 768
elasticsearch:
uris: http://127.0.0.1:9200Where:
● index-name is the es vector index name;
● dimensions is the vector dimension generated by the vector model (must match the vector dimension generated by the vector model, default is 1576);
● similarity defines the algorithm or metric used to measure the similarity between vectors; here cosine similarity is used with high-dimensional sparse vectors.
If you want to customize the instantiation configuration of es, you need to introduce spring-ai-elasticsearch-store:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-elasticsearch-store</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-M5</version>
</dependency>Implement in the project through custom configuration bean.
You are a MacOS expert. Please answer based on the following context:
---------------------
{question_answer_context}
---------------------
Please combine the given context and the provided historical information to answer in Chinese Markdown format; if the answer is not in the context, please make it clear.In Spring AI and Spring AI Alibaba, almost any data source can be used as a knowledge base source. In this example, PDF is used as the knowledge base document.
Spring AI Alibaba provides over 40 document-reader and parser plugins to load data into the RAG application.
public class KnowledgeInitializer implements ApplicationRunner {
// Inject the VectorStore instance, responsible for the increase and query operations of vectorized data
private final VectorStore vectorStore;
// Vector database client, using es here
private final ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient;
// .....
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) {
// 1. load pdf resources.
List<Resource> pdfResources = loadPdfResources();
// 2. parse pdf resources to Documents.
List<Document> documents = parsePdfResource(pdfResources);
// 3. import to ES.
importToES(documents);
}
private List<Document> parsePdfResource(List<Resource> pdfResources) {
// Split text according to specified policy and convert to Document resource objects
for (Resource springAiResource : pdfResources) {
// 1. parse document
DocumentReader reader = new PagePdfDocumentReader(springAiResource);
List<Document> documents = reader.get();
logger.info("{} documents loaded", documents.size());
// 2. split trunks
List<Document> splitDocuments = new TokenTextSplitter().apply(documents);
logger.info("{} documents split", splitDocuments.size());
// 3. add res list
resList.addAll(splitDocuments);
}
}
// ......
}Thus, the process of converting text data into vector data has been completed.
Next, we will use the Ollama Starter in Spring AI to interact with the model and build RAG applications.
AIRagService.java
@Service
public class AIRagService {
// Introduce system prompt template
@Value("classpath:/prompts/system-qa.st")
private Resource systemResource;
// Inject related bean instances
private final ChatModel ragChatModel;
private final VectorStore vectorStore;
// Text filtering to enhance vector retrieval accuracy
private static final String textField = "content";
// ......
public Flux<String> retrieve(String prompt) {
// Load prompt tmpl
String promptTemplate = getPromptTemplate(systemResource);
// Enable hybrid search including embedding and full-text search
SearchRequest searchRequest = SearchRequest.builder().
topK(4)
.similarityThresholdAll()
.build();
// build chatClient to call the large model service.
return ChatClient.builder(ragChatModel)
.build().prompt()
.advisors(new QuestionAnswerAdvisor(
vectorStore,
searchRequest,
promptTemplate)
).user(prompt)
.stream()
.content();
}
}Create a user request interface to handle user requests and call the service to obtain a large model response:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/rag/ai")
public class AIRagController {
@Resource
public AIRagService aiRagService;
@GetMapping("/chat/{prompt}")
public Flux<String> chat(
@PathVariable("prompt") String prompt,
HttpServletResponse response
) {
// Set response encoding to prevent garbled stream response.
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
if (!StringUtils.hasText(prompt)) {
return Flux.just("prompt is null.");
}
return aiRagService.retrieve(prompt);
}
}Here's an example: I am currently a Mac newbie, and I want to configure my Mac's trackpad to make it more usable. Do you have any suggestions? As shown in the example, you can see that the direct response from the model is relatively official and not very practical.

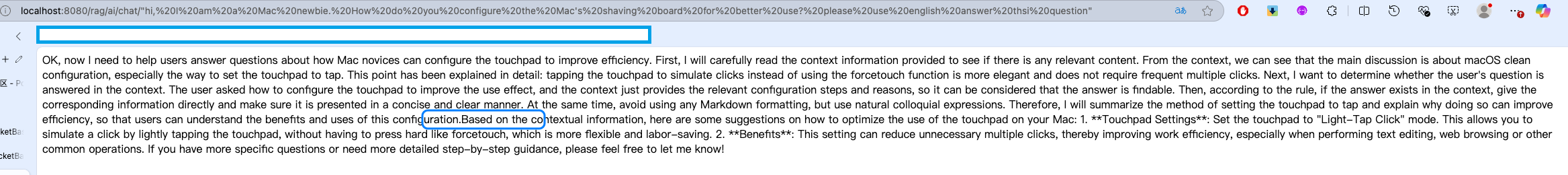
It can be seen that the output of the RAG application is more accurate and meets user needs.
When deploying model services with the local Ollama, the model's running speed is limited by local resource constraints, resulting in lengthy processing times. Therefore, we can enhance the user experience by utilizing models available on some cloud platforms.
Modify the application.yaml to:
spring:
application:
name: ollama-rag
ai:
dashscope:
api-key: ${AI_DASHSCOPE_API_KEY}
chat:
options:
model: deepseek-r1
embedding:
enabled: false
ollama:
base-url: http://127.0.0.1:11434
chat:
model: deepseek-r1:8b
enabled: false
embedding:
model: nomic-embed-text:latest
vectorstore:
elasticsearch:
index-name: ollama-rag-embedding-index
similarity: cosine
dimensions: 768
elasticsearch:
uris: http://127.0.0.1:9200This disables the Chat feature of Ollama and uses the DeepSeekR1 model on the DashScope platform through the Spring AI Alibaba Starter dependency.
Add dependency:
<!-- Spring AI Alibaba DashScope -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-alibaba-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-M6</version>
</dependency>Edit AIRAGService.java
public Flux<String> retrieve(String prompt) {
// Get the vector store prompt tmpl.
String promptTemplate = getPromptTemplate(systemResource);
// Enable hybrid search, both embedding and full text search
SearchRequest searchRequest = SearchRequest.builder().
topK(4)
.similarityThresholdAll()
.build();
// Build ChatClient with retrieval rerank advisor:
ChatClient runtimeChatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultAdvisors(new RetrievalRerankAdvisor(
vectorStore,
rerankModel,
searchRequest,
promptTemplate,
0.1)
).build();
// Spring AI RetrievalAugmentationAdvisor
Advisor retrievalAugmentationAdvisor = RetrievalAugmentationAdvisor.builder()
.queryTransformers(RewriteQueryTransformer.builder()
.chatClientBuilder(ChatClient.builder(ragChatModel).build().mutate())
.build())
.documentRetriever(VectorStoreDocumentRetriever.builder()
.similarityThreshold(0.50)
.vectorStore(vectorStore)
.build())
.build();
// Retrieve and llm generate
return ragClient.prompt()
.advisors(retrievalAugmentationAdvisor)
.user(prompt)
.stream()
.content();
}Spring AI RAG Documentation:https://docs.spring.io/spring-ai/reference/api/retrieval-augmented-generation.html
Spring AI Structured Documentation:https://java2ai.com/docs/1.0.0-M5.1/tutorials/rag/
When using Spring AI to build RAG applications, we can achieve optimal performance in retrieving vector data by setting personalized parameters when constructing the QuestionAnswerAdvisor.
During the data preprocessing phase, you can:
Q: Vector insertion failed
A: Check if the ES index dimensions match the model output
Q: Retrieval results are irrelevant
A: Check if the Embedding model matches the text type
Q: Response speed is slow
A: Adjust the computational resource configuration of Ollama
Q: Failed to pull spring-ai-alibaba-starter dependency
A: Configuration of mvn repository is needed
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<releases>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</releases>
</repository>
</repositories>The entire process of building a RAG application can be divided into the following three steps:
Through the RAG's retrieval enhancement, the model's responses can be more contextually relevant, ultimately improving the user experience.
Annotations for Nacos Configuration Center in Spring Cloud Applications

549 posts | 52 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Native - December 10, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - February 20, 2025
Alibaba Cloud Community - November 22, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Community - November 5, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - December 31, 2024
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - August 6, 2024

549 posts | 52 followers
Follow Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Cloud-Native Applications Management Solution
Accelerate and secure the development, deployment, and management of containerized applications cost-effectively.
Learn More AI Acceleration Solution
AI Acceleration Solution
Accelerate AI-driven business and AI model training and inference with Alibaba Cloud GPU technology
Learn More Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen)
Top-performance foundation models from Alibaba Cloud
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Native Community
Start building with 50+ products and up to 12 months usage for Elastic Compute Service
Get Started for Free Get Started for Free