By Lettie from Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch team
Index lifecycle management (ILM) refers to the management of the entire lifecycle from the setting, creating, opening, and closing to deleting Elasticsearch indexes. We can manage the lifecycle of the data stored in Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch in order to reduce index storage costs and improve cluster performance and execution efficiency.
Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch Version 6.6 and later provide the ILM feature and divide the index lifecycle into four stages: Hot, Warm, Cold, and Delete.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Hot | It mainly processes real-time writing of time series data. It depends on the number of indexed documents and the time of indexing to decide whether to call Rollover API to roll the index. |
| Warm | It is mainly used for queries, and indexes are no longer written. |
| Cold | Queries are few, the query speed is lower, and indexes are no longer updated. |
| Delete | Data is deleted. |
Note: Currently, the Rollover feature only supports three archiving policies: max_docs, max_size, and max_age. An index archiving is triggered if the conditions for any of these policies are met.
A large number of heartbeat-* time series indexes exist in service scenarios. The size of each new index every day is around 4 MB. The larger the data, the larger the number of shards, resulting in a higher cluster load. To prevent such situations, different Rollover policies need to be planned to roll the historical monitoring index at the beginning of heartbeat-*. This enables the contraction of shards and merging segments of the index in the Warm stage, moves data from the Hot nodes to the Cold or Warm nodes in the Cold stage, and deletes the index data on a regular basis.
For a seamless connection between the Heartbeat and ILM feature of Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch, define the Elasticsearch ILM feature in the Beat yml configuration. For more information about the configuration, see Set up index lifecycle management.
Download and decompress the Heartbeat installation package, and use the following commands to edit the Heartbeat.yml configuration to define the heartbeat.monitors, setup.kibana, and output.elasticsearch.
heartbeat.monitors:
- type: icmp
schedule: '*/5 * * * * * *'
hosts: ["47.111.169.233"]
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3
index.codec: best_compression
index.routing.allocation.require.box_type: "hot"
setup.kibana:
# Kibana Host
# Scheme and port can be left out and will be set to the default (http and 5601)
# In case you specify and additional path, the scheme is required: http://localhost:5601/path
# IPv6 addresses should always be defined as: https://[2001:db8::1]:5601
host: "https://es-cn-4591jumei000u1zp5.kibana.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:5601"
output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
hosts: ["es-cn-4591jumei000u1zp5.elasticsearch.aliyuncs.com:9200"]
ilm.enabled: true
setup.template.overwrite: true
ilm.rollover_alias: "heartbeat"
ilm.pattern: "{now/d}-000001"
# Enabled ilm (beta) to use index lifecycle management instead daily indices.
#ilm.enabled: false
# Optional protocol and basic auth credentials.
#protocol: "https"
username: "elastic"
password: "Elastic@363"1) index.number_of_shards: specifies the number of primary shards. The default value is 1.
2) index.routing.allocation.require.box_type: writes index data to a Hot node.
3) ilm.enabled: enables index lifecycle management when its value is set to true.
4) setup.template.overwrite overwrites the original template data. If an index template of the specified version has been loaded to Elasticsearch, Use this configuration to overwrite the data.
5) ilm.rollover_alias defines a rollover alias. The default value is heartbeat-{beat.version}. Use this parameter to specify the alias prefix.
6) ilm.pattern defines the pattern of the rolling index. The date math method is supported. The default value is {now/d}-000001. When the condition is triggered, the new index name increments by 1 to the last digit. For example, an index generated for the first roll operation is named heartbeat-2020.04.29-000001. When the roll operation is triggered based on one of the specified rollover parameters, a new index named heartbeat-2020.04.29-000002 is created.
Note: If you modify rollover_alias or pattern after the index template is loaded, you must set setup.template.overwrite to true to overwrite the template.
Heartbeat supports loading the default policy and writing it to Elasticsearch by using the ./heartbeat setup --ilm-policy command. The default policy can be printed on stdout through the ./heartbeat export ilm-policy command. Modify this command to create a policy manually. The following describes how to manually create a policy.
Configure the lifecycle policies for indexes by using API or Kibana. The following example shows how to create a Heartbeat policy by using the ILM policy API.
Note: Configure an index lifecycle Policy in Kibana> Management> Index lifecycle policies.
PUT /_ilm/policy/heartbeat-policy
{
"policy": {
"phases": {
"hot": {
"actions": {
"rollover": {
"max_size": "5mb",
"max_age": "1d",
"max_docs": 100
}
}
},
"warm": {
"min_age": "60s",
"actions": {
"forcemerge": {
"max_num_segments":1
},
"shrink": {
"number_of_shards":1
}
}
},
"cold": {
"min_age": "3m",
"actions": {
"allocate": {
"include": {
"box_type": "warm"
}
}
}
},
"delete": {
"min_age": "1h",
"actions": {
"delete": {}
}
}
}
}
}Different types of actions are supported for each stage. For more information, see Action.
After completing the preceding preparations, run the following command to start the Heartbeat service:
# sudo ./heartbeat -eGo to the Kibana index lifecycle policies page and associate the customized policies with the Heartbeat index template.
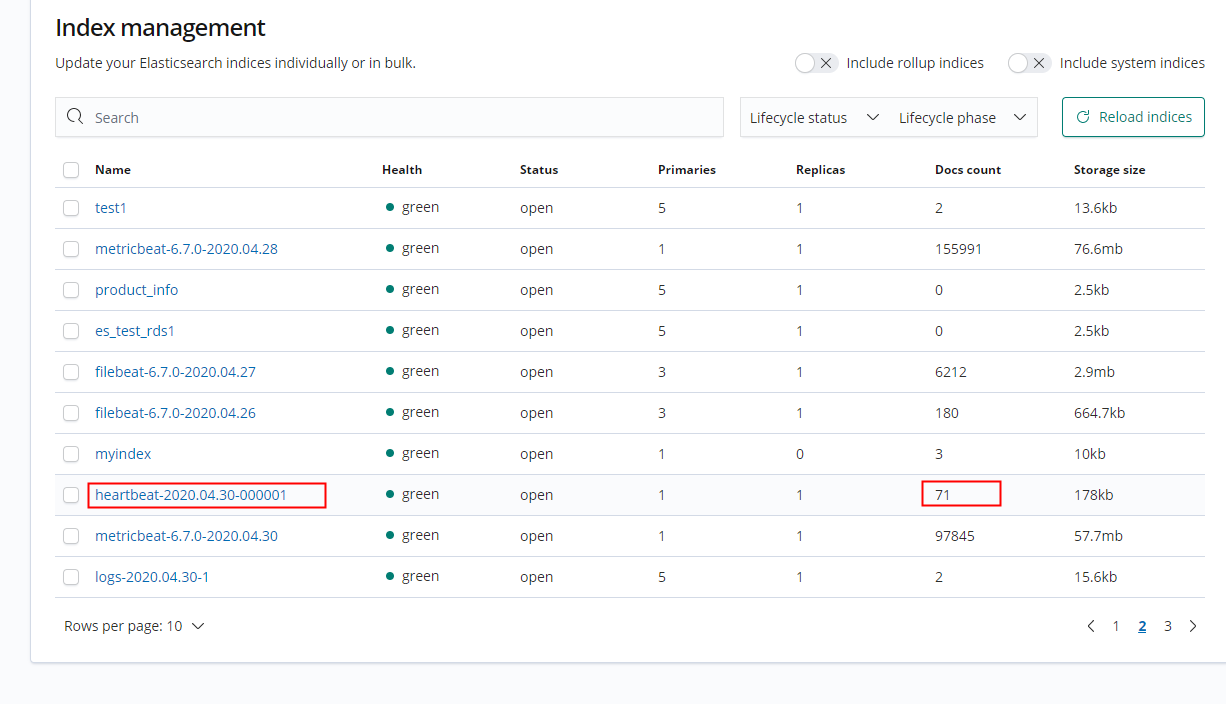
Go to the Index management page.
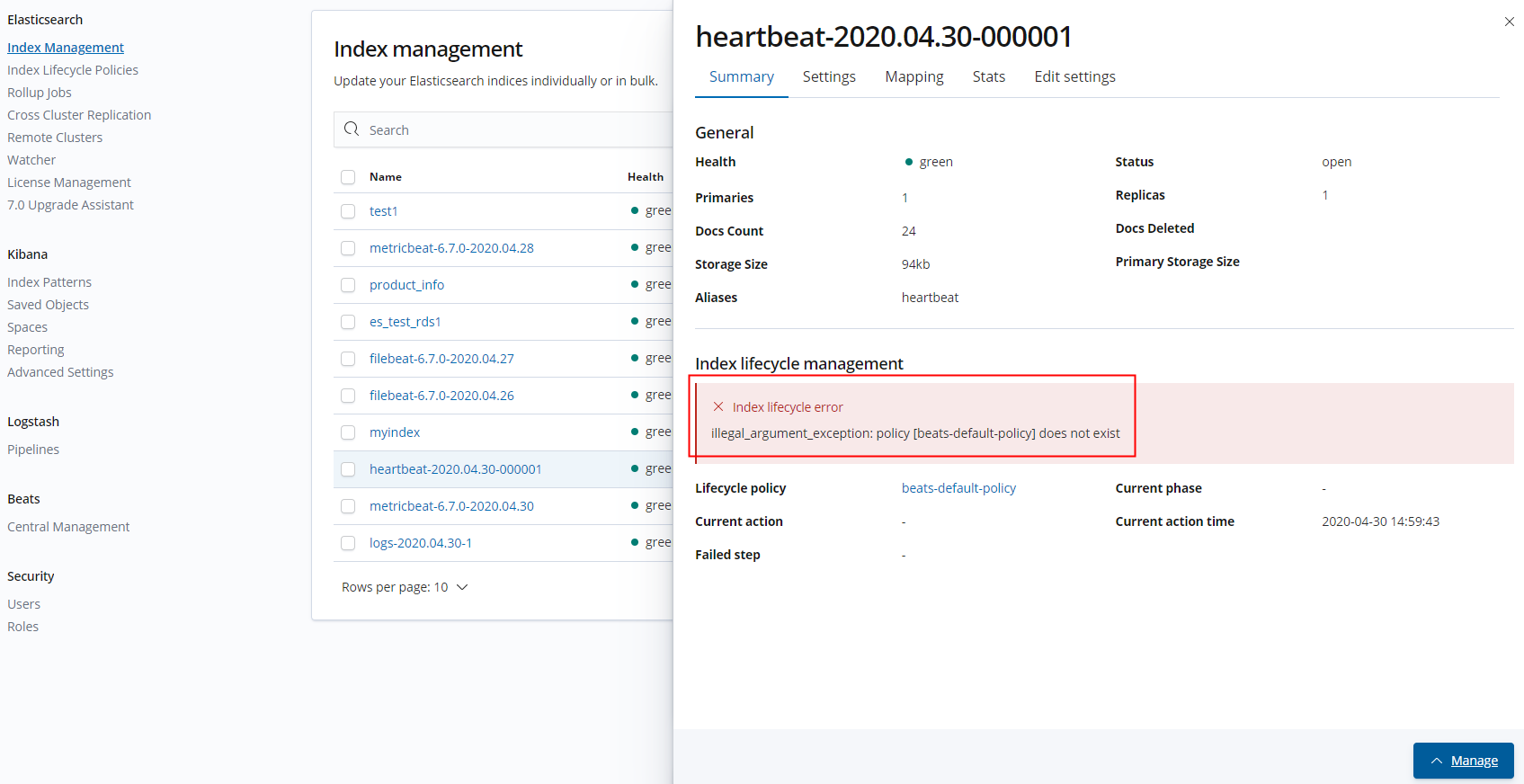
By default, this index is associated with a built-in Beat policy. If the default policy is not generated, specify a customized policy. Click "Manage", and remove the lifecycle policy.
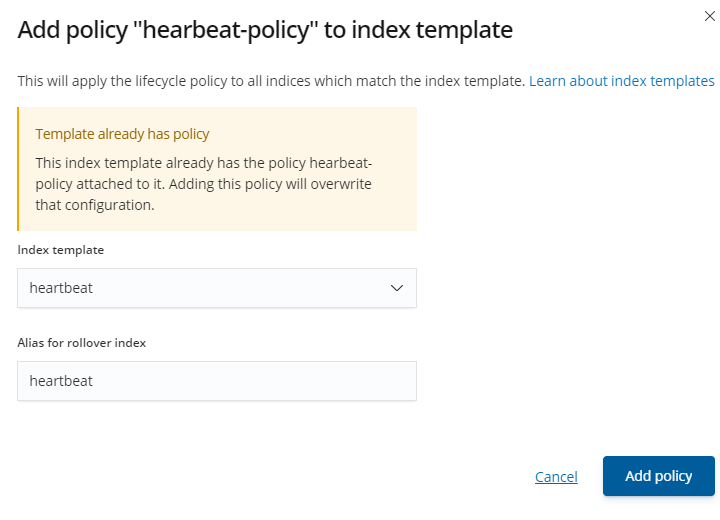
Then add a new policy to the index.
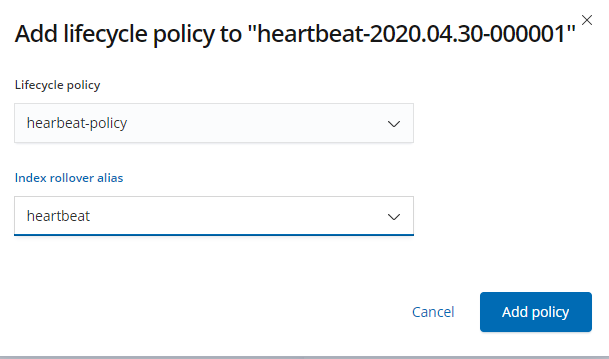
The following association is successful.
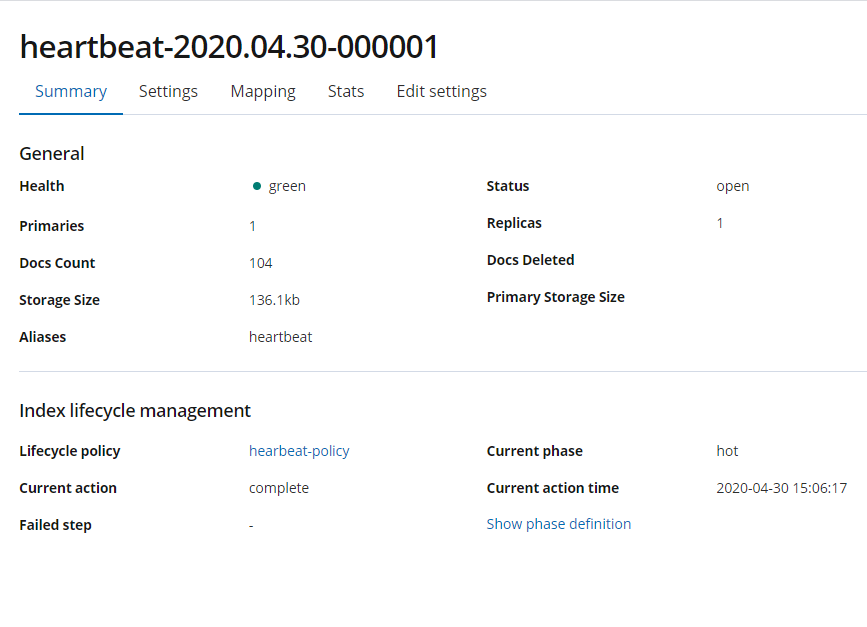
Filter the rolling indexes in the Hot stage.
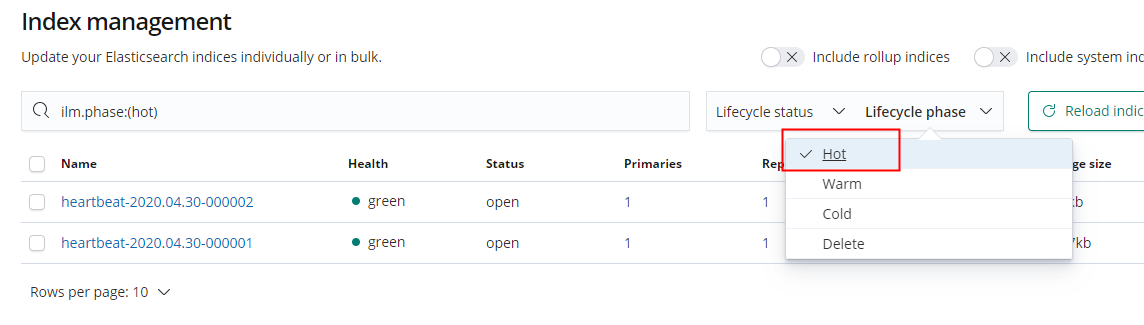
Filter the indexes in the Warm stage.
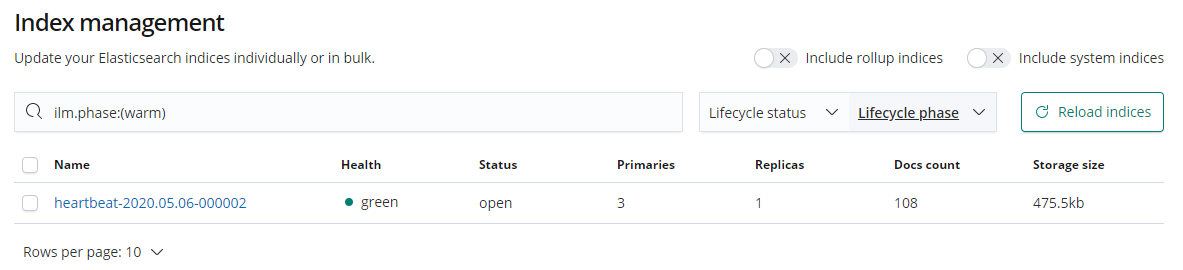
Filter the indexes in the Cold stage.
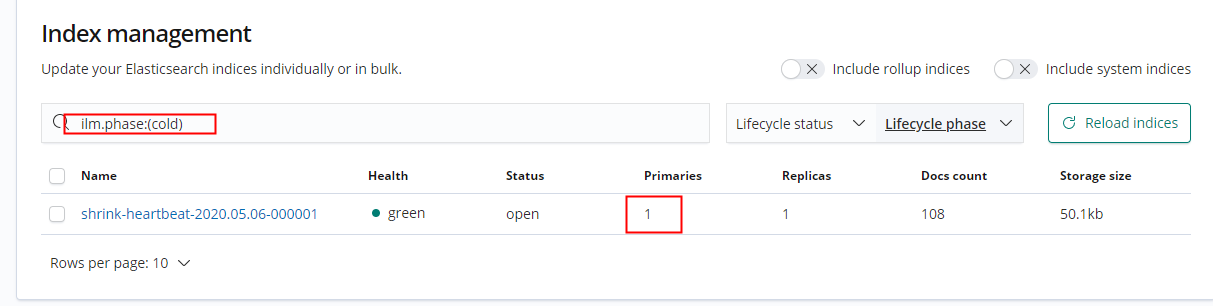
Note that the max_doc value specified in the strategy is 100. However, it's critical to understand why do the indexes roll only after the document number reaches more than 100?
By default, the lifecycle policy of indexes checks for indexes that meet the policy every 10 minutes. Therefore, the number of indexes may exceed the specified threshold. Modify indices.lifecycle.poll_interval to control the checking frequency.
Modify the parameter with caution to avoid unnecessary loads on the node due to a short checking interval. In this test, change the time interval to one minute.
PUT _cluster/settings
{
"transient": {
"indices.lifecycle.poll_interval":"1m"
}
}Define both "template" and "alias" for the index before configuring the index lifecycle policy.
There are two ways to add an index lifecycle policy:
1) Add a Management Template in the Lifecycle: The policy can be applied to all indexes covered by the alias.
2) Add an Index Lifecycle Policy for a Single Index: Only the current index is involved, and new rolling indexes are not affected by the lifecycle policy.
After modifying the index rollover policy, the new policy takes effect on the next rolling index.
The Alibaba Cloud Elastic Stack is completely compatible with open-source Elasticsearch and has nine unique capabilities

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowData Geek - May 10, 2024
Data Geek - May 21, 2024
Alibaba Clouder - January 4, 2021
Alibaba Clouder - May 31, 2018
Alibaba Clouder - December 29, 2020
Data Geek - February 17, 2025

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Alibaba Cloud provides big data consulting services to help enterprises leverage advanced data technology.
Learn More Vector Retrieval Service for Milvus
Vector Retrieval Service for Milvus
A cloud-native vector search engine that is 100% compatible with open-source Milvus, extensively optimized in performance, stability, availability, and management capabilities.
Learn More Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Alibaba Cloud experts provide retailers with a lightweight and customized big data consulting service to help you assess your big data maturity and plan your big data journey.
Learn More Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch
Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch
Alibaba Cloud Elasticsearch helps users easy to build AI-powered search applications seamlessly integrated with large language models, and featuring for the enterprise: robust access control, security monitoring, and automatic updates.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder