本文介紹在邊界路由器VBR(Virtual border router)和私網IPsec-VPN串連使用BGP動態路由的情況下如何?物理專線私網流量加密傳輸。
背景資訊
開始操作前,建議您先瞭解加密物理專線私網流量原理。更多資訊,請參見加密物理專線私網流量。
情境樣本
本文以下圖情境為例。某企業在杭州擁有一個本機資料中心IDC(Internet Data Center),在阿里雲華東1(杭州)地區擁有一個VPC,VPC中使用Elastic Compute Service(Elastic Compute Service)部署了相關服務。因業務發展本地IDC需要串連上雲,基於一些安全合規要求企業需要使用物理專線和轉寄路由器實現本地IDC與VPC間的私網互連,同時為了降低資料泄露風險,防止企業機密資料被內部或外部人員竊取、篡改,企業希望通過物理專線傳輸的流量均加密後再傳輸至阿里雲。
在本地IDC與VPC實現私網互連的情況下,企業可以在本地網關裝置與轉寄路由器之間建立私網IPsec-VPN串連,私網IPsec-VPN串連可以加密經過物理專線的流量,滿足商業網路安全的高要求。
網路規劃
如果您需要自行為本地IDC和相關網路執行個體規劃網段,需確保要互連的網段之間沒有重疊。
路由機制說明
為實現物理專線私網流量加密傳輸,需要確保本地IDC和VPC之間的互訪流量優先通過私網IPsec-VPN串連傳輸,而非通過物理專線傳輸。本文通過控制路由來實現該目標:
流量從VPC去往本地IDC:
轉寄路由器可以分別通過VBR執行個體和私網IPsec-VPN串連學習到本地IDC的路由,根據轉寄路由器路由優先順序,預設通過VBR執行個體學習到的路由更優,此機制會導致VPC去往本地IDC的流量優先通過物理專線傳輸,無法實現加密。
本文通過宣告不同子網路遮罩的本地IDC網段來規避該問題。本地網關裝置向VBR執行個體宣告本地IDC網段時,需要宣告大網段(即子網路遮罩較短);向私網IPsec-VPN串連宣告本地IDC網段時,需要宣告小網段(即子網路遮罩較長)。
例如本地IDC的網段為192.168.0.0/16,本地IDC中與VPC互連的用戶端網段為192.168.20.0/24,則本地網關裝置向VBR執行個體宣告本地IDC網段192.168.0.0/16;向私網IPsec-VPN串連宣告具體的用戶端網段192.168.20.0/24。這樣可以保證式轉送路由器通過私網IPsec-VPN串連學習到路由更優,VPC訪問用戶端的流量優先通過私網IPsec-VPN串連加密傳輸。
流量從本地IDC去往VPC:
本地IDC可以同時通過VBR執行個體和私網IPsec-VPN串連學習到VPC執行個體的路由,本文在轉寄路由器側通過配置路由策略調整路由優先順序來確保本地IDC去往VPC的流量優先通過私網IPsec-VPN串連傳輸。
當前路由機制也可以確保私網IPsec-VPN串連中斷後,本地IDC與VPC依舊可以通過物理專線和轉寄路由器實現私網互連,只是流量不再被加密。
基礎網段規劃
配置目標 | 網段規劃 | IP地址 |
VPC |
|
|
VBR | 10.0.0.0/30 |
|
本地IDC | 用戶端網段:192.168.20.0/24 | 用戶端地址:192.168.20.6 |
本地網關裝置網段:
|
|
BGP網段規劃
BGP隧道網段需要是在169.254.0.0/16內的子網路遮罩為30的網段,且不能是169.254.0.0/30、169.254.1.0/30、169.254.2.0/30、169.254.3.0/30、169.254.4.0/30、169.254.5.0/30、169.254.6.0/30和169.254.169.252/30。一個IPsec串連下兩條隧道的隧道網段不能相同。
資源 | 隧道 | BGP隧道網段 | BGP IP地址 | BGP AS號(本端自治系統號) |
IPsec串連執行個體 | 隧道1 | 169.254.10.0/30 | 169.254.10.1 | 65534 |
隧道2 | 169.254.20.0/30 | 169.254.20.1 | ||
本地網關裝置 | 隧道1 | 169.254.10.0/30 | 169.254.10.2 | 65530 |
隧道2 | 169.254.20.0/30 | 169.254.20.2 |
準備工作
您已經在阿里雲華東1(杭州)地區建立了VPC並使用ECS部署了相關服務。具體操作,請參見搭建IPv4專用網路。
請檢查本地網關裝置,確保本地網關裝置支援標準的IKEv1和IKEv2協議,以便和阿里雲建立私網IPsec-VPN串連。關於本地網關裝置是否支援標準的IKEv1和IKEv2協議,請諮詢本地網關裝置廠商。
操作步驟
步驟一:通過物理專線和轉寄路由器實現IDC與VPC私網互連
第1步:部署物理專線
部署物理專線將本地IDC串連至阿里雲。
建立物理專線。
建立VBR執行個體。
在左側導覽列,單擊邊界路由器(VBR)。
在頂部功能表列,選擇華東1(杭州)地區。
VBR執行個體的地區需和物理專線所屬地區相同。
在邊界路由器(VBR)頁面,單擊建立邊界路由器。
在建立邊界路由器面板,根據以下資訊進行配置,然後單擊確定。
以下僅列舉本文強相關的配置項,其餘配置項保持預設狀態。更多資訊,請參見建立和管理邊界路由器。
配置項
說明
名稱
本文輸入VBR。
物理專線介面
本文選擇獨享專線類型,然後選擇已建立的物理專線介面。
VLAN ID
本文輸入0。
阿里雲側IPv4互聯IP
本文輸入10.0.0.1。
客戶側IPv4互聯IP
本文輸入10.0.0.2。
IPv4子網路遮罩
本文輸入255.255.255.252。
為VBR執行個體配置BGP組。
在邊界路由器(VBR)頁面,單擊VBR執行個體ID。
在邊界路由器執行個體詳情頁面,單擊BGP組頁簽。
在BGP組頁簽下,單擊建立BGP組,並根據以下資訊進行BGP組配置,然後單擊確定。
以下僅列舉本文強相關的配置項。更多資訊,請參見配置和管理BGP。
名稱:輸入VBR-BGP。
Peer AS號:輸入本地網關裝置的自治系統號65530。
本端AS號:輸入VBR執行個體使用的BGP AS號65534。
為VBR執行個體配置BGP鄰居。
在邊界路由器執行個體詳情頁面,單擊BGP鄰居頁簽。
在BGP鄰居頁簽下,單擊建立BGP鄰居。
在建立BGP鄰居面板,配置BGP鄰居資訊,然後單擊確定。
BGP組:選擇VBR-BGP。
BGP鄰居IP:輸入BGP鄰居的IP地址。本文輸入本地網關裝置串連物理專線的介面的IP地址10.0.0.1。
在本地網關裝置配置BGP路由。
說明本文以思科防火牆ASA(軟體版本9.19.1)作為配置樣本。不同軟體版本的配置命令可能會有所差異,操作時請根據您的實際環境查詢對應文檔或諮詢相關廠商。更多本地網關裝置配置樣本,請參見本地網關裝置配置樣本。
以下內容包含的第三方產品資訊僅供參考。阿里雲對第三方產品的效能、可靠性以及操作可能帶來的潛在影響,不做任何暗示或其他形式的承諾。
ciscoasa> enable Password: ******** #輸入進入enable模式的密碼。 ciscoasa# configure terminal #進入配置模式。 ciscoasa(config)# #思科防火牆已完成了介面配置,並已開啟介面。以下為本文的介面配置樣本。 ciscoasa(config)# show running-config interface ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 #串連VBR的介面。 nameif VBR #GigabitEthernet0/0介面名稱。 security-level 0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.252 #GigabitEthernet0/0介面配置的IP地址。 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 #串連本地IDC的介面。 nameif private #GigabitEthernet0/2介面名稱。 security-level 100 #指定串連本地IDC的介面的security-level低於對接阿里雲的介面。 ip address 192.168.50.215 255.255.255.0 #GigabitEthernet0/2介面配置的IP地址。 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/3 #對接私網IPsec-VPN隧道1的介面 nameif VPN-IP1 #GigabitEthernet0/3介面名稱。 security-level 0 ip address 192.168.10.136 255.255.255.0 #GigabitEthernet0/3介面配置的私網IP地址。 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/4 #對接私網IPsec-VPN隧道2的介面 nameif VPN-IP2 #GigabitEthernet0/4介面名稱。 security-level 0 ip address 192.168.40.159 255.255.255.0 #GigabitEthernet0/4介面配置的私網IP地址。 ! #配置prefix-list和route-map prefix-list VBR permit 192.168.0.0/16 route-map VBR permit 10 match ip address prefix-list VBR #配置BGP路由 router bgp 65530 #開啟BGP路由協議,並配置本地IDC的自治系統號。本文為65530。 bgp router-id 10.0.0.1 #BGP路由器ID,本文設定為10.0.0.1。 address-family ipv4 unicast neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 65534 #與VBR執行個體建立BGP鄰居關係。 neighbor 10.0.0.2 activate #啟用BGP鄰居。 neighbor 10.0.0.2 route-map VBR out #對VBR僅宣告大段路由。 network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 #宣告本地IDC的網段,建議宣告大網段。 exit-address-family ! #配置去往本地IDC用戶端的路由。 route private 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 192.168.50.216重要對VBR執行個體宣告本地IDC網段時,建議宣告大網段,以確保後續轉寄路由器通過私網IPsec-VPN串連學習的本地IDC網段比當前宣告的網段更明細,路由優先順序更高。
第2步:配置轉寄路由器
本地IDC通過物理專線串連至阿里雲後,開始配置轉寄路由器,通過轉寄路由器實現本地IDC與VPC間的私網互連。
在建立雲企業網執行個體對話方塊選擇單獨建立,然後自訂雲企業網執行個體名稱,其餘配置項保持預設狀態。
在華東1(杭州)地區建立一個轉寄路由器執行個體,用於串連VBR執行個體和VPC執行個體。其餘配置項保持預設狀態。
建立VPC串連。
在雲企業網執行個體詳情頁面的頁簽,找到華東1(杭州)地區的轉寄路由器執行個體,在操作列單擊建立網路執行個體串連。
在串連網路執行個體頁面,根據以下資訊進行配置,然後單擊確定建立,將VPC執行個體串連至轉寄路由器。
以下僅列舉本文強相關的配置項,其餘配置項保持預設狀態。更多資訊,請參見使用企業版轉寄路由器建立VPC串連。
配置項
說明
執行個體類型
選擇Virtual Private Cloud。
地區
選擇華東1(杭州)。
串連名稱
自訂名稱為VPC-Attachment。
網路執行個體
選擇VPC。
交換器
在轉寄路由器支援的可用性區域選擇交換器執行個體。
本文選擇交換器2和交換器3。在支援多可用性區域的地區,需在至少2個可用性區域中各選擇一個交換器執行個體。推薦使用未承載業務的交換器建立VPC串連。
進階配置
使用預設路由配置,即開啟三種進階配置。
單擊繼續建立串連,返回串連網路執行個體頁面。
建立VBR串連。
在串連網路執行個體頁面,根據以下資訊進行配置,然後單擊確定建立,將VBR執行個體串連至轉寄路由器。以下僅列舉本文強相關的配置項,其餘配置項保持預設狀態。更多資訊,請參見使用企業版轉寄路由器建立VBR串連。
配置項
配置項說明
執行個體類型
選擇邊界路由器(VBR)。
地區
選擇華東1(杭州)。
串連名稱
自訂名稱為VBR-Attachment。
網路執行個體
選擇VBR。
進階配置
使用預設路由配置,即開啟三種進階配置。
第3步:測試私網連通性
完成上述配置後,本地IDC與VPC間已經實現私網互連,您可以通過以下步驟測試私網連通性。
登入VPC中的ECS1執行個體。具體操作,請參見ECS遠端連線操作指南。
執行ping命令,訪問本地IDC網段下的任意一台用戶端。
ping <本地IDC用戶端IP地址>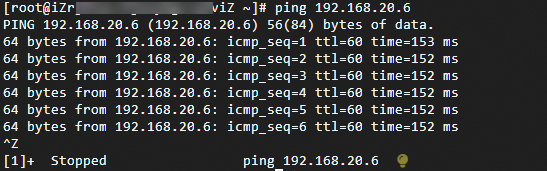
如上圖所示,如果ECS1可以收到響應報文,則表示本地IDC與VPC間已實現私網互連。
步驟二:加密物理專線私網流量
本地IDC與VPC實現私網互連後,您可以在本地網關裝置與轉寄路由器間建立私網網路類型的IPsec-VPN串連,然後通過路由配置,引導本地IDC與VPC之間的流量通過私網IPsec-VPN串連進行傳輸,實現加密物理專線私網流量。
第1步:建立私網IPsec-VPN串連
為轉寄路由器添加轉寄路由器位址區段10.10.10.0/24。具體操作,請參見建立轉寄路由器後添加位址區段。
轉寄路由器位址區段用於為IPsec串連分配網關IP地址,以便建立私網IPsec-VPN串連。轉寄路由器位址區段不能與本地IDC、VPC中要參與網路互連的網段衝突。
建立2個使用者網關,將本地網關裝置的2個VPN IP地址和BGP AS號註冊至阿里雲。
- 登入VPN網關管理主控台。
在左側導覽列,選擇。
在使用者網關頁面,單擊建立使用者網關。
在建立使用者網關面板,根據以下資訊進行配置,然後單擊確定。
以下僅列舉本文強相關的配置項,其餘配置項保持預設狀態。更多資訊,請參見建立和系統管理使用者網關。
使用者網關1
名稱:定義使用者網關名稱為Customer-Gateway1。
IP地址:輸入本地網關裝置的VPN IP地址1192.168.10.136。
自治系統號:輸入本地網關裝置的BGP AS號65530。
使用者網關2
名稱:定義使用者網關名稱為Customer-Gateway2。
IP地址:輸入本地網關裝置的VPN IP地址2192.168.40.159。
自治系統號:輸入本地網關裝置的BGP AS號65530。
建立IPsec串連。
在左側導覽列,選擇。
在IPsec串連頁面,單擊綁定雲企業網。
在建立IPsec串連(CEN)頁面,根據以下資訊配置IPsec串連,然後單擊確定。
以下內容僅列舉本文強相關的配置項,其餘配置項保持預設狀態。更多資訊,請參見建立和管理IPsec串連(雙隧道模式)。
配置項
IPsec串連
IPsec串連名稱
定義為IPsec串連。
地區
選擇待綁定的轉寄路由器所屬的地區。
IPsec串連建立完成後所屬地區與轉寄路由器地區相同。
網關類型
選擇私網。
綁定雲企業網
選擇本帳號綁定。
Cloud Enterprise Network執行個體ID
選擇已建立的雲企業網執行個體。
系統將會一併展示雲企業網執行個體在該地區建立的轉寄路由器執行個體ID和轉寄路由器位址區段,IPsec串連將會被綁定至該轉寄路由器。
路由模式
本文使用目的路由模式,後續通過路由控制傳輸的流量。
啟用BGP
開啟BGP功能。
本端自治系統號
輸入IPsec串連的BGP AS號65534。
Tunnel 1
使用者網關
關聯Customer-Gateway1。
預先共用金鑰
fddsFF111****。
重要IPsec串連及其對端網關裝置配置的預先共用金鑰需一致,否則系統無法正常建立IPsec-VPN串連。
加密配置
除以下參數外,其餘配置項保持預設值。
IKE配置的DH分組(完美向前加密 PFS)選擇group14。
IPsec配置的DH分組(完美向前加密 PFS)選擇group14。
說明您需要根據本地網關裝置的支援情況選擇加密配置參數,確保IPsec串連和本地網關裝置的加密配置保持一致。
BGP配置
隧道網段:輸入169.254.10.0/30。
本端BGP地址:輸入169.254.10.1。
Tunnel 2
使用者網關
關聯Customer-Gateway2。
預先共用金鑰
fddsFF222****。
加密配置
除以下參數外,其餘配置項保持預設值。
IKE配置的DH分組(完美向前加密 PFS)選擇group14。
IPsec配置的DH分組(完美向前加密 PFS)選擇group14。
說明您需要根據本地網關裝置的支援情況選擇加密配置參數,確保IPsec串連和本地網關裝置的加密配置保持一致。
BGP配置
隧道網段:輸入169.254.20.0/30。
本端BGP地址:輸入169.254.20.1。
高級配置(包含自動關聯路由表、配置轉寄路由等配置)
使用預設路由配置,即開啟所有進階配置選項。
IPsec串連建立完成後,您可以在IPsec串連詳情頁面查看IPsec串連的網關IP地址,IPsec串連將使用這2個網關IP地址與本地網關裝置建立私網IPsec-VPN串連。
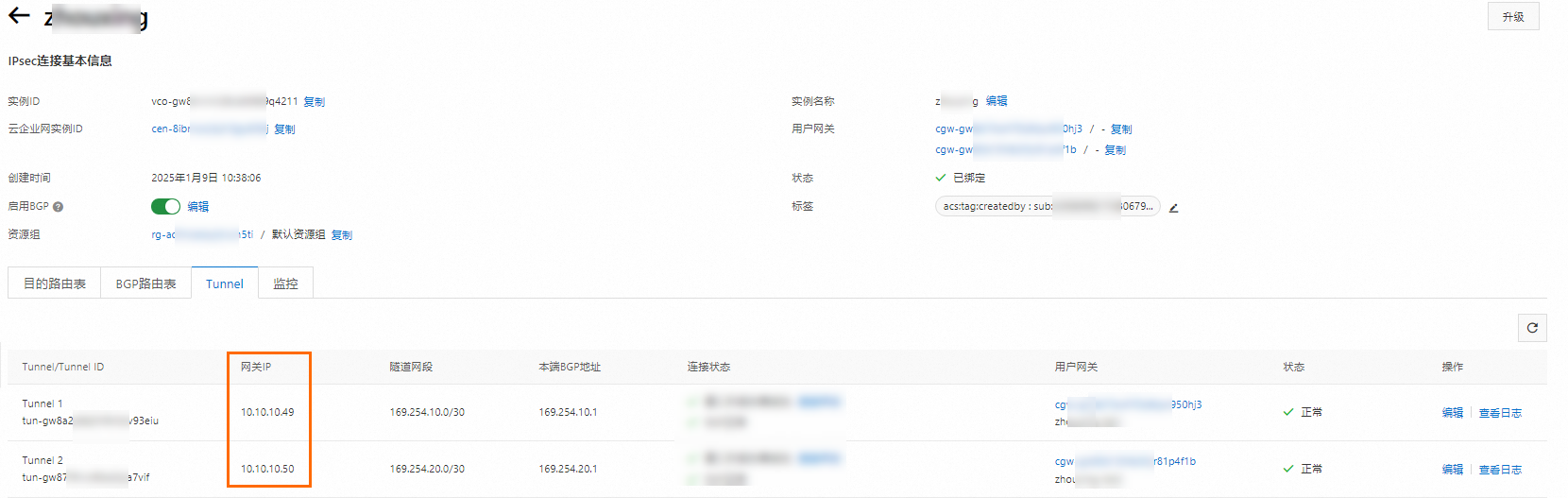
返回IPsec串連頁面,找到建立的IPsec串連,在操作列單擊產生對端配置。
對端配置是指需要在IPsec串連對端添加的VPN配置。本文情境中您需要將這些配置添加在本地網關裝置上。
在IPsec串連配置對話方塊,複製配置並儲存在您的本地,用於後續配置本地網關裝置。
配置本地網關裝置。
建立IPsec串連後,您需要在本地網關裝置上添加VPN配置,使本地網關裝置與阿里雲之間成功建立私網IPsec-VPN串連。
完成上述配置後,本地網關裝置已經可以與阿里雲成功建立私網IPsec-VPN串連,但BGP鄰居尚未建立成功。您可以在阿里雲IPsec串連執行個體詳情頁面查看私網IPsec-VPN串連狀態。如果您的環境中未成功建立私網IPsec-VPN串連,請嘗試自助排查問題。具體操作,請參見IPsec-VPN自助診斷。
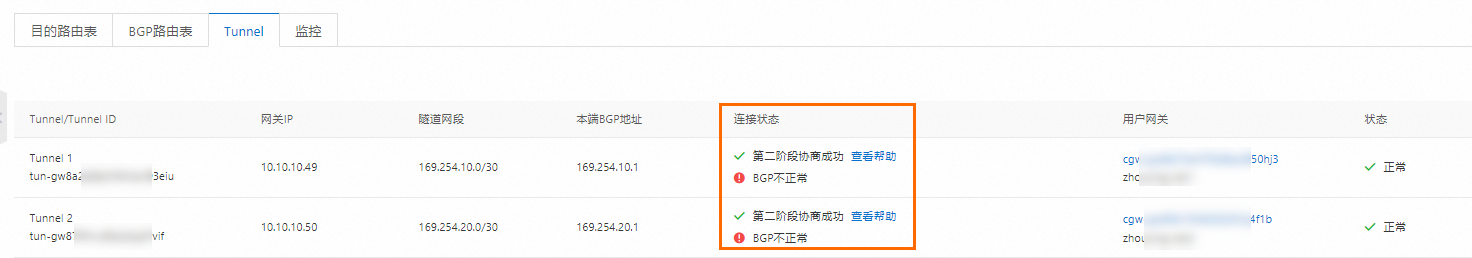
第2步:配置路由
私網IPsec-VPN串連建立完成後,本地IDC與VPC之間的流量依舊是通過物理專線傳輸,還未進行加密。需要添加相關路由使本地IDC與VPC之間的流量通過私網IPsec-VPN串連進行傳輸。
在本地網關裝置上添加BGP路由配置。
#配置prefix-list和route-map prefix-list VPN permit 192.168.10.0/16 prefix-list VPN permit 192.168.20.0/16 prefix-list VPN permit 192.168.40.0/16 route-map VPN permit 10 match ip address prefix-list VPN #添加BGP配置,使本地網關裝置與IPsec串連建立BGP鄰居關係 router bgp 65530 address-family ipv4 unicast neighbor 169.254.10.1 remote-as 65534 #指定BGP鄰居,即阿里雲側隧道1的IP地址。 neighbor 169.254.10.1 activate #啟用BGP鄰居。 neighbor 169.254.10.1 route-map VPN out #對隧道1僅宣告明細路由。 neighbor 169.254.20.1 remote-as 65534 #指定BGP鄰居,即阿里雲側隧道2的IP地址。 neighbor 169.254.20.1 activate #啟用BGP鄰居。 neighbor 169.254.20.1 route-map VPN out #對隧道2僅宣告明細路由。 maximum-paths 5 #提升BGP ECMP等價路由條目數量。 network 192.168.10.0 mask 255.255.255.0 #宣告本地IDC的網段,該網段需比對VBR執行個體宣告的網段更明細。 network 192.168.20.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 192.168.40.0 mask 255.255.255.0 exit-address-family重要對私網IPsec-VPN串連宣告本地IDC網段時,需確保該網段比對VBR執行個體宣告的本地IDC網段更明細,以保證式轉送路由器通過私網IPsec-VPN串連學習到的本地IDC的路由更優。
為轉寄路由器添加自訂路由條目。
上述路由配置完成後,私網IPsec-VPN串連會中斷,需要在轉寄路由器路由表中添加去往本地網關裝置VPN IP地址的明細路由,下一跳指向VBR執行個體,重建立立私網IPsec-VPN串連。
保持在转发路由器路由表頁簽,單擊路由條目頁簽,然後單擊建立路由條目。
在添加路由條目對話方塊,配置路由條目資訊,然後單擊確定。
配置項
網段1
網段2
目的地址CIDR
輸入本地網關裝置VPN IP地址1192.168.10.136/32。
輸入本地網關裝置VPN IP地址2192.168.40.159/32。
是否為黑洞路由
選擇否。
下一跳串連
選擇VBR-Attachment。
在轉寄路由器路由表下添加第1個路由策略。
本地IDC將通過VBR執行個體和私網IPsec-VPN串連同時學習到VPC的網段,為確保雲下去往雲上的流量優先通過私網IPsec-VPN串連進入VPC,您需要在轉寄路由器中配置路由策略,使VBR執行個體向本地IDC發布的VPC的網段的優先順序低於私網IPsec-VPN串連向本地IDC發布的VPC網段的優先順序。
登入雲企業網管理主控台。
在雲企業網執行個體頁面,找到已建立的雲企業網執行個體,單擊目標執行個體ID。
在雲企業網執行個體詳情頁面,單擊華東1(杭州)地區的轉寄路由器ID。
在轉寄路由器詳情頁面,單擊轉寄路由器路由表頁簽,然後單擊路由策略。
在路由策略頁簽,單擊添加路由策略。根據以下資訊配置路由策略,然後單擊確定。
以下內容僅列舉本文強相關的配置項,其餘配置項保持預設狀態。更多資訊,請參見路由策略。

配置項
路由策略
策略優先順序
輸入30。
關聯路由表
保持預設值。
生效方向
選擇出地區網關。
匹配條件
目的執行個體ID列表:VBR執行個體ID。
路由首碼:輸入172.16.10.0/24和172.16.20.0/24,並選擇精確匹配。
策略行為
選擇允許。
添加策略值
本文選擇追加AS Path,並輸入65525、65526、65527,降低VBR執行個體向本地IDC發布的VPC網段的優先順序。
在轉寄路由器路由表下添加第2個路由策略,拒絕私網IPsec-VPN串連向本地IDC傳播本地網關裝置VPN IP地址的路由,防止路由環路。
策略優先順序:本文輸入40。
關聯路由表:保持預設值。
生效方向:選擇出地區網關。
匹配條件:
目的執行個體ID列表:IPsec串連執行個體ID。
路由首碼:選擇精確匹配,輸入本地網關裝置VPN IP地址192.168.10.136/32、192.168.40.159/32。
策略行為:選擇拒絕。
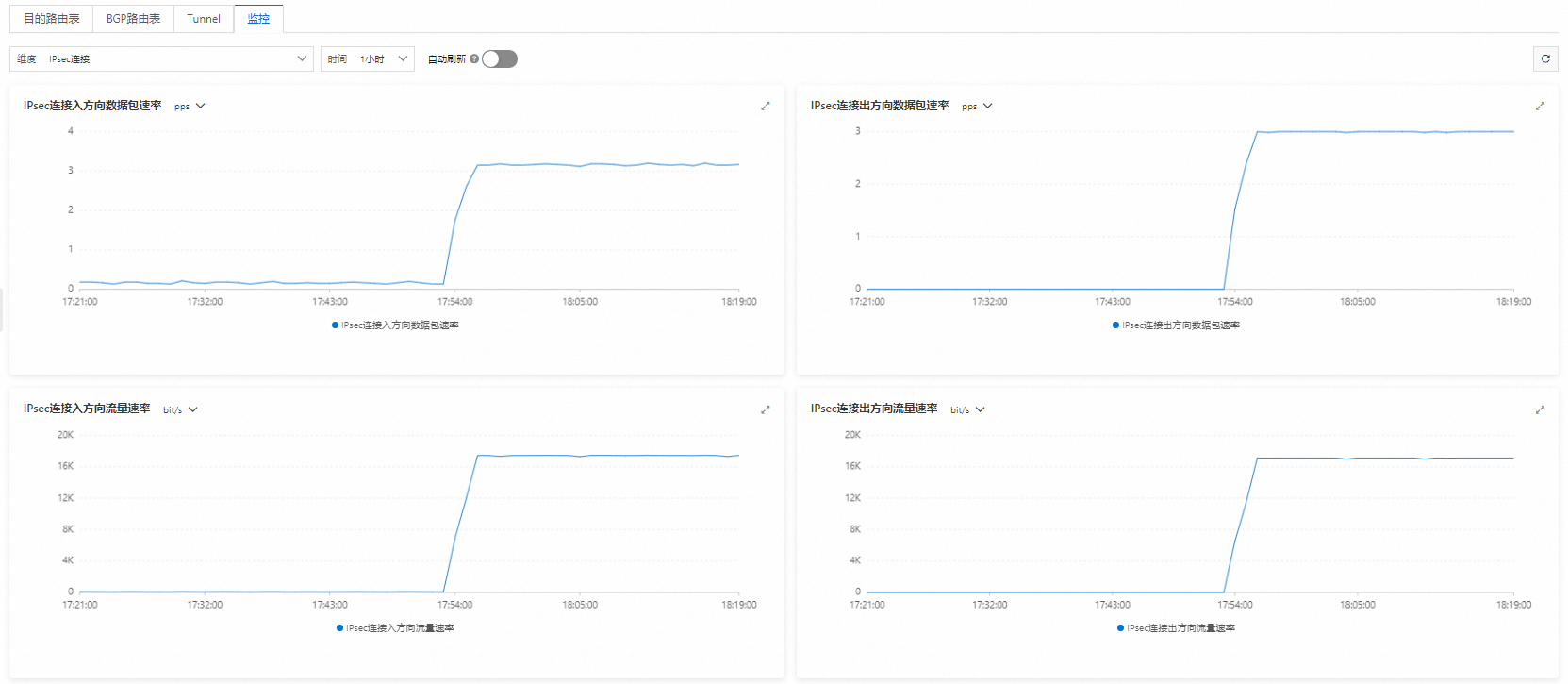
步驟三:驗證加密效果
完成上述配置後,如果您可以在IPsec串連詳情頁面查看到流量傳輸監控資料,則證明物理專線的私網流量已經過加密處理。
登入VPC中的ECS1執行個體。執行ping命令,持續訪問本地IDC網段下的任意一台用戶端。
ping <本地IDC用戶端IP地址> -s 1000 -c 10000-s 1000:指定發送1000位元組的資料包。-c 10000:持續發送10000個請求包。
登入VPN網關管理主控台。
在頂部狀態列處,選擇華東1(杭州)地區。
在左側導覽列,選擇。
在IPsec串連頁面,找到已建立的IPsec串連,單擊IPsec串連ID。
在IPsec串連詳情頁面查看流量傳輸監控資料。