Simple Log Service では、サードパーティ製ソフトウェア、さまざまなプログラミング言語のアプリケーション、クラウドサービス、およびストリームコンピューティングフレームワークが、Simple Log Service SDK を呼び出すことで、リアルタイムでデータを消費できます。ただし、SDK ベースの消費では、コンシューマー間のロードバランシングやフェールオーバーなど、特定の実装の詳細要件を満たすことができません。このような場合は、コンシューマーグループを作成して数秒以内にデータを消費できます。このトピックでは、コンシューマーグループを使用してデータを消費する方法について説明します。
概要
ログストアには複数のシャードがあります。Simple Log Service は、次のルールに基づいて、コンシューマーグループ内のコンシューマーにシャードを割り当てます。
新しいコンシューマーがコンシューマーグループに追加されると、コンシューマーグループ内のコンシューマーに割り当てられているシャードは、ロードバランシングのために各コンシューマーに再割り当てされます。シャードは、上記のルールに基づいて再割り当てされます。
用語
用語 | 説明 |
コンシューマーグループ | コンシューマーグループを使用して、Simple Log Service のデータを消費できます。コンシューマーグループは複数のコンシューマーで構成されます。コンシューマーグループ内のすべてのコンシューマーは、同じログストア内のデータを消費します。コンシューマーはデータを繰り返し消費しません。
重要 1 つのログストアにつき最大 30 のコンシューマーグループを作成できます。 |
コンシューマー | コンシューマーグループ内のコンシューマーがデータを消費します。
重要 コンシューマーグループ内のコンシューマーの名前は一意である必要があります。 |
ログストア | ログストアは、データの収集、保存、およびクエリに使用されます。詳細については、「ログストア」をご参照ください。 |
シャード | シャードは、ログストアの読み取りおよび書き込み容量を制御するために使用されます。Simple Log Service では、データはシャードに保存されます。詳細については、「シャード」をご参照ください。 |
チェックポイント | 消費チェックポイントは、プログラムがデータの消費を停止する位置です。プログラムが再起動されると、プログラムは最後の消費チェックポイントからデータを消費します。
説明 コンシューマーグループを使用してデータを消費する場合、プログラムでエラーが発生すると、Simple Log Service は消費チェックポイントを自動的に保存します。プログラムが回復した後、コンシューマーはデータを繰り返し消費することなく、消費チェックポイントからデータ消費を再開できます。 |
ステップ 1:コンシューマーグループを作成する
このセクションでは、Simple Log Service SDK、Simple Log Service API、および Simple Log Service CLI を使用してコンシューマーグループを作成する方法について説明します。
Simple Log Service SDK を使用する
サンプルコード:
CreateConsumerGroup.java
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.Client;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.ConsumerGroup;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.exception.LogException;
public class CreateConsumerGroup {
public static void main(String[] args) throws LogException {
// この例では、アクセスキー ID とアクセスキーシークレットは環境変数から取得されます。
String accessId = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
String accessKey = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// プロジェクトの名前。
String projectName = "ali-test-project";
// ログストアの名前。
String logstoreName = "ali-test-logstore";
// Simple Log Service エンドポイント。この例では、中国 (杭州) リージョンの Simple Log Service エンドポイントが使用されています。パラメータ値を実際のエンドポイントに置き換えてください。
String host = "https://cn-hangzhou.log.aliyuncs.com";
// Simple Log Service クライアントを作成します。
Client client = new Client(host, accessId, accessKey);
try {
// コンシューマーグループの名前。
String consumerGroupName = "ali-test-consumergroup2";
System.out.println("コンシューマーグループを作成する準備ができました");
ConsumerGroup consumerGroup = new ConsumerGroup(consumerGroupName, 300, true);
client.CreateConsumerGroup(projectName, logstoreName, consumerGroup);
System.out.println(String.format("コンシューマーグループ %s の作成に成功しました", consumerGroupName));
} catch (LogException e) {
System.out.println("LogException e :" + e.toString());
System.out.println("エラーコード :" + e.GetErrorCode());
System.out.println("エラーメッセージ :" + e.GetErrorMessage());
throw e;
}
}
}
コンシューマーグループの管理に使用されるサンプルコードの詳細については、「Java 用 Simple Log Service SDK を使用してコンシューマーグループを管理する」および「Python 用 Simple Log Service SDK を使用してコンシューマーグループを管理する」をご参照ください。
Simple Log Service API を使用する
Simple Log Service API を使用してコンシューマーグループを作成する方法の詳細については、「CreateConsumerGroup」をご参照ください。
コンシューマーグループが作成されているかどうかを確認する方法の詳細については、「ListConsumerGroup」をご参照ください。
ステップ 2:ログデータを消費する
仕組み
Java 用 Simple Log Service SDK を初めて呼び出してコンシューマーを起動すると、コンシューマーが属するコンシューマーグループが見つからない場合、SDK はコンシューマーグループを作成します。コンシューマーグループが作成されると、SDK は消費開始チェックポイントを記録し、そのチェックポイントからデータの消費を開始します。消費開始チェックポイントは、初回の消費後に無効になります。コンシューマーが再起動されると、コンシューマーは Simple Log Service によって保存された最後の消費チェックポイントからデータ消費を再開します。消費チェックポイントの例:
例
Java、C++、Python、または Go 用 Simple Log Service SDK を使用して、コンシューマーグループを作成し、データを消費できます。この例では、Java 用 Simple Log Service SDK を使用します。
例 1:SDK を使用する
Maven の依存関係を追加します。
pom.xml ファイルを開き、次のコードを追加します。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.openservices</groupId>
<artifactId>loghub-client-lib</artifactId>
<version>0.6.50</version>
</dependency>
データ消費の実装ロジックを記述します。サンプルコード:
SampleLogHubProcessor.java
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.FastLog;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.FastLogContent;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.FastLogGroup;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.FastLogTag;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.LogGroupData;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.ILogHubCheckPointTracker;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.exceptions.LogHubCheckPointException;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.interfaces.ILogHubProcessor;
import java.util.List;
public class SampleLogHubProcessor implements ILogHubProcessor {
private int shardId;
// 最後の消費チェックポイントが保存された時刻。
private long mLastSaveTime = 0;
// プロセッサオブジェクトが初期化されるときに、initialize メソッドが 1 回呼び出されます。
public void initialize(int shardId) {
this.shardId = shardId;
}
// データ消費のメインロジック。データ消費中に発生する可能性のあるすべての例外を処理するコードを含める必要があります。
public String process(List<LogGroupData> logGroups, ILogHubCheckPointTracker checkPointTracker) {
// 取得したデータを表示します。
for (LogGroupData logGroup : logGroups) {
FastLogGroup fastLogGroup = logGroup.GetFastLogGroup();
System.out.println("タグ");
for (int i = 0; i < fastLogGroup.getLogTagsCount(); ++i) {
FastLogTag logTag = fastLogGroup.getLogTags(i);
System.out.printf("%s : %s\n", logTag.getKey(), logTag.getValue());
}
for (int i = 0; i < fastLogGroup.getLogsCount(); ++i) {
FastLog log = fastLogGroup.getLogs(i);
System.out.println("--------\nログ: " + i + ", 時刻: " + log.getTime() + ", GetContentCount: " + log.getContentsCount());
for (int j = 0; j < log.getContentsCount(); ++j) {
FastLogContent content = log.getContents(j);
System.out.println(content.getKey() + "\t:\t" + content.getValue());
}
}
}
long curTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 消費チェックポイントは 30 秒間隔で Simple Log Service に書き込まれます。ClientWorker インスタンスが 30 秒以内に予期せず停止した場合、新しく起動された ClientWorker インスタンスは最後の消費チェックポイントからデータを消費します。少量のデータが繰り返し消費される可能性があります。
try {
if (curTime - mLastSaveTime > 30 * 1000) {
// 値 true は、消費チェックポイントが Simple Log Service にすぐに更新されることを示します。デフォルトでは、メモリにキャッシュされた消費チェックポイントは 60 秒間隔で Simple Log Service に自動的に更新されます。
checkPointTracker.saveCheckPoint(true);
mLastSaveTime = curTime;
} else {
// 値 false は、消費チェックポイントがローカルにキャッシュされ、自動消費チェックポイント更新メカニズムを使用して Simple Log Service に更新できることを示します。
checkPointTracker.saveCheckPoint(false);
}
} catch (LogHubCheckPointException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// ClientWorker インスタンスのシャットダウン関数が呼び出されます。消費チェックポイントを管理できます。
public void shutdown(ILogHubCheckPointTracker checkPointTracker) {
// 消費チェックポイントを Simple Log Service にすぐに保存します。
try {
checkPointTracker.saveCheckPoint(true);
} catch (LogHubCheckPointException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
サンプルコードの詳細については、「aliyun-log-consumer-java」および「Aliyun LOG Go Consumer」をご参照ください。
コンシューマーエンティティを定義します。サンプルコード:
SampleLogHubProcessorFactory.java
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.interfaces.ILogHubProcessor;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.interfaces.ILogHubProcessorFactory;
class SampleLogHubProcessorFactory implements ILogHubProcessorFactory {
public ILogHubProcessor generatorProcessor() {
// コンシューマーを生成します。generatorProcessor メソッドが呼び出されるたびに、新しい SampleLogHubProcessor オブジェクトが期待どおりに返されます。
return new SampleLogHubProcessor();
}
}
コンシューマーグループを作成し、コンシューマースレッドを起動して、コンシューマーグループ内のコンシューマーが指定されたログストア内のデータを消費できるようにします。サンプルコード:
Main.java
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.ClientWorker;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.config.LogHubConfig;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.exceptions.LogHubClientWorkerException;
public class Main {
// Simple Log Service エンドポイント。ビジネス要件に基づいてエンドポイントを入力します。
private static String Endpoint = "cn-hangzhou.log.aliyuncs.com";
// Simple Log Service プロジェクトの名前。ビジネス要件に基づいて名前を入力します。既存のプロジェクトの名前を入力する必要があります。
private static String Project = "ali-test-project";
// ログストアの名前。ビジネス要件に基づいて名前を入力します。既存のログストアの名前を入力する必要があります。
private static String Logstore = "ali-test-logstore";
// コンシューマーグループの名前。ビジネス要件に基づいて名前を入力します。事前にコンシューマーグループを作成する必要はありません。プログラムの実行時にコンシューマーグループが自動的に作成されます。
private static String ConsumerGroup = "ali-test-consumergroup2";
// この例では、アクセスキー ID とアクセスキーシークレットは環境変数から取得されます。
private static String AccessKeyId= System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
private static String AccessKeySecret = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
public static void main(String[] args) throws LogHubClientWorkerException, InterruptedException {
// consumer_1 はコンシューマーの名前を指定します。コンシューマーグループ内の各コンシューマーの名前は一意である必要があります。異なるコンシューマーが異なるマシンでプロセスを起動してログストア内のデータを消費する場合、マシンの IP アドレスを使用して各コンシューマーを識別できます。
// maxFetchLogGroupSize は、Simple Log Service から一度に取得できるロググループの最大数を指定します。デフォルト値を保持します。config.setMaxFetchLogGroupSize(100); を使用して最大数を変更できます。有効な値:(0,1000]。
LogHubConfig config = new LogHubConfig(ConsumerGroup, "consumer_1", Endpoint, Project, Logstore, AccessKeyId, AccessKeySecret, LogHubConfig.ConsumePosition.BEGIN_CURSOR,1000);
ClientWorker worker = new ClientWorker(new SampleLogHubProcessorFactory(), config);
Thread thread = new Thread(worker);
// Thread インスタンスが実行されると、ClientWorker インスタンスが自動的に実行され、Runnable インターフェースが拡張されます。
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(60 * 60 * 1000);
// ClientWorker インスタンスの shutdown 関数が呼び出され、コンシューマーが終了します。Thread インスタンスは自動的に停止します。
worker.shutdown();
// ClientWorker インスタンスの実行中に複数の非同期タスクが生成されます。shutdown 後にすべての実行中タスクが安全に停止するように、Thread.sleep を 30 秒に設定することをお勧めします。
Thread.sleep(30 * 1000);
}
}
Main.java ファイルを実行します。
この例では、NGINX ログが消費され、消費結果が表示されます。
: GET
request_uri : /request/path-3/file-7
status : 200
body_bytes_sent : 3820
host : www.example.com
request_time : 43
request_length : 1987
http_user_agent : Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2228.0 Safari/537.36
http_referer : www.example.com
http_x_forwarded_for : 192.168.10.196
upstream_response_time : 0.02
--------
ログ: 158, 時刻: 1635629778, GetContentCount: 14
......
category : null
source : 127.0.0.1
topic : nginx_access_log
machineUUID : null
タグ
__receive_time__ : 1635629815
--------
ログ: 0, 時刻: 1635629788, GetContentCount: 14
......
category : null
source : 127.0.0.1
topic : nginx_access_log
machineUUID : null
タグ
__receive_time__ : 1635629877
--------
......
例 2:SDK と SPL を使用する
Maven の依存関係を追加します。
pom.xml ファイルを開き、次のコードを追加します。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId>
<version>2.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.openservices</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-log</artifactId>
<version>0.6.114</version>
</dependency>
データ消費の実装ロジックを記述します。サンプルコード:
SPLLogHubProcessor.java
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.FastLog;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.FastLogContent;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.FastLogGroup;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.FastLogTag;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.LogGroupData;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.ILogHubCheckPointTracker;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.exceptions.LogHubCheckPointException;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.interfaces.ILogHubProcessor;
import java.util.List;
public class SPLLogHubProcessor implements ILogHubProcessor {
private int shardId;
// 最後の消費チェックポイントが保存された時刻。
private long mLastSaveTime = 0;
// プロセッサオブジェクトが初期化されるときに、initialize メソッドが 1 回呼び出されます。
public void initialize(int shardId) {
this.shardId = shardId;
}
// データ消費のメインロジック。データ消費中に発生する可能性のあるすべての例外を処理するコードを含める必要があります。
public String process(List<LogGroupData> logGroups, ILogHubCheckPointTracker checkPointTracker) {
// 取得したデータを表示します。
for (LogGroupData logGroup : logGroups) {
FastLogGroup fastLogGroup = logGroup.GetFastLogGroup();
System.out.println("タグ");
for (int i = 0; i < fastLogGroup.getLogTagsCount(); ++i) {
FastLogTag logTag = fastLogGroup.getLogTags(i);
System.out.printf("%s : %s\n", logTag.getKey(), logTag.getValue());
}
for (int i = 0; i < fastLogGroup.getLogsCount(); ++i) {
FastLog log = fastLogGroup.getLogs(i);
System.out.println("--------\nログ: " + i + ", 時刻: " + log.getTime() + ", GetContentCount: " + log.getContentsCount());
for (int j = 0; j < log.getContentsCount(); ++j) {
FastLogContent content = log.getContents(j);
System.out.println(content.getKey() + "\t:\t" + content.getValue());
}
}
}
long curTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 消費チェックポイントは 30 秒間隔で Simple Log Service に書き込まれます。ClientWorker インスタンスが 30 秒以内に予期せず停止した場合、新しく起動された ClientWorker インスタンスは最後の消費チェックポイントからデータを消費します。少量のデータが繰り返し消費される可能性があります。
try {
if (curTime - mLastSaveTime > 30 * 1000) {
// 値 true は、消費チェックポイントが Simple Log Service にすぐに更新されることを示します。デフォルトでは、メモリにキャッシュされた消費チェックポイントは 60 秒間隔で Simple Log Service に自動的に更新されます。
checkPointTracker.saveCheckPoint(true);
mLastSaveTime = curTime;
} else {
// 値 false は、消費チェックポイントがローカルにキャッシュされ、自動消費チェックポイント更新メカニズムを使用して Simple Log Service に更新できることを示します。
checkPointTracker.saveCheckPoint(false);
}
} catch (LogHubCheckPointException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// ClientWorker インスタンスのシャットダウン関数が呼び出されます。消費チェックポイントを管理できます。
public void shutdown(ILogHubCheckPointTracker checkPointTracker) {
// 消費チェックポイントを Simple Log Service にすぐに保存します。
try {
checkPointTracker.saveCheckPoint(true);
} catch (LogHubCheckPointException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
コンシューマーエンティティを定義します。サンプルコード:
SPLLogHubProcessorFactory.java
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.interfaces.ILogHubProcessor;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.interfaces.ILogHubProcessorFactory;
class SPLLogHubProcessorFactory implements ILogHubProcessorFactory {
public ILogHubProcessor generatorProcessor() {
// コンシューマーを生成します。generatorProcessor メソッドが呼び出されるたびに、新しい SPLLogHubProcessor オブジェクトが期待どおりに返されます。
return new SPLLogHubProcessor();
}
}
コンシューマーグループを作成し、コンシューマースレッドを起動して、コンシューマーグループ内のコンシューマーが指定されたログストア内のデータを消費できるようにします。サンプルコード:
Main.java
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.ClientWorker;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.config.LogHubConfig;
import com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.exceptions.LogHubClientWorkerException;
public class Main {
// Simple Log Service エンドポイント。ビジネス要件に基づいてエンドポイントを入力します。
private static String Endpoint = "cn-hangzhou.log.aliyuncs.com";
// Simple Log Service プロジェクトの名前。ビジネス要件に基づいて名前を入力します。既存のプロジェクトの名前を入力する必要があります。
private static String Project = "ali-test-project";
// ログストアの名前。ビジネス要件に基づいて名前を入力します。既存のログストアの名前を入力する必要があります。
private static String Logstore = "ali-test-logstore";
// コンシューマーグループの名前。ビジネス要件に基づいて名前を入力します。事前にコンシューマーグループを作成する必要はありません。プログラムの実行時にコンシューマーグループが自動的に作成されます。
private static String ConsumerGroup = "ali-test-consumergroup2";
// この例では、アクセスキー ID とアクセスキーシークレットは環境変数から取得されます。
private static String AccessKeyId = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
private static String AccessKeySecret = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
public static void main(String[] args) throws LogHubClientWorkerException, InterruptedException {
// consumer_1 はコンシューマーの名前を指定します。コンシューマーグループ内の各コンシューマーの名前は一意である必要があります。異なるコンシューマーが異なるマシンでプロセスを起動してログストア内のデータを消費する場合、マシンの IP アドレスを使用して各コンシューマーを識別できます。
// maxFetchLogGroupSize は、Simple Log Service から一度に取得できるロググループの最大数を指定します。デフォルト値を保持します。config.setMaxFetchLogGroupSize(100); を使用して最大数を変更できます。有効な値:(0,1000]。
LogHubConfig config = new LogHubConfig(ConsumerGroup, "consumer_1", Endpoint, Project, Logstore, AccessKeyId, AccessKeySecret, LogHubConfig.ConsumePosition.BEGIN_CURSOR, 1000);
// setQuery を使用して、データ消費用の Simple Log Service 処理言語 (SPL) ステートメントを指定できます。
config.setQuery("* | where cast(body_bytes_sent as bigint) > 14000");
ClientWorker worker = new ClientWorker(new SPLLogHubProcessorFactory(), config);
Thread thread = new Thread(worker);
// Thread インスタンスが実行されると、ClientWorker インスタンスが自動的に実行され、Runnable インターフェースが拡張されます。
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(60 * 60 * 1000);
// ClientWorker インスタンスの shutdown 関数が呼び出され、コンシューマーが終了します。Thread インスタンスは自動的に停止します。
worker.shutdown();
// ClientWorker インスタンスの実行中に複数の非同期タスクが生成されます。shutdown 後にすべての実行中タスクが安全に停止するように、Thread.sleep を 30 秒に設定することをお勧めします。
Thread.sleep(30 * 1000);
}
}
Main.java ファイルを実行します。
この例では、NGINX ログが消費され、消費結果が表示されます。
: GET
request_uri : /request/path-3/file-7
status : 200
body_bytes_sent : 3820
host : www.example.com
request_time : 43
request_length : 1987
http_user_agent : Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2228.0 Safari/537.36
http_referer : www.example.com
http_x_forwarded_for : 192.168.10.196
upstream_response_time : 0.02
--------
ログ: 158, 時刻: 1635629778, GetContentCount: 14
......
category : null
source : 127.0.0.1
topic : nginx_access_log
machineUUID : null
タグ
__receive_time__ : 1635629815
--------
ログ: 0, 時刻: 1635629788, GetContentCount: 14
......
category : null
source : 127.0.0.1
topic : nginx_access_log
machineUUID : null
タグ
__receive_time__ : 1635629877
--------
......
ステップ 3:コンシューマーグループのステータスを表示する
このセクションでは、コンシューマーグループのステータスを表示するために使用できる方法について説明します。
Java 用 Simple Log Service SDK を使用する
各シャードの消費チェックポイントを表示します。サンプルコード:
ConsumerGroupTest.java
import java.util.List;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.Client;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.Consts.CursorMode;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.ConsumerGroup;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.common.ConsumerGroupShardCheckPoint;
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.exception.LogException;
public class ConsumerGroupTest {
static String endpoint = "cn-hangzhou.log.aliyuncs.com";
static String project = "ali-test-project";
static String logstore = "ali-test-logstore";
static String accesskeyId = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
static String accesskey = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
public static void main(String[] args) throws LogException {
Client client = new Client(endpoint, accesskeyId, accesskey);
// ログストアに作成されているすべてのコンシューマーグループを取得します。コンシューマーグループが存在しない場合は、空の文字列が返されます。
List<ConsumerGroup> consumerGroups = client.ListConsumerGroup(project, logstore).GetConsumerGroups();
for(ConsumerGroup c: consumerGroups){
// 各コンシューマーグループの属性 (名前、ハートビートタイムアウト期間、データが順番に消費されるかどうかなど) を表示します。
System.out.println("名前: " + c.getConsumerGroupName());
System.out.println("ハートビートタイムアウト期間: " + c.getTimeout());
System.out.println("順序付き消費: " + c.isInOrder());
for(ConsumerGroupShardCheckPoint cp: client.GetCheckPoint(project, logstore, c.getConsumerGroupName()).GetCheckPoints()){
System.out.println("シャード: " + cp.getShard());
// 時刻は long 整数で、マイクロ秒単位まで正確です。
System.out.println("消費チェックポイントが最後に更新された時刻: " + cp.getUpdateTime());
System.out.println("コンシューマー名: " + cp.getConsumer());
String consumerPrg = "";
if(cp.getCheckPoint().isEmpty())
consumerPrg = "消費が開始されていません";
else{
// UNIX タイムスタンプ。単位:秒。タイムスタンプの出力値を書式設定します。
try{
int prg = client.GetPrevCursorTime(project, logstore, cp.getShard(), cp.getCheckPoint()).GetCursorTime();
consumerPrg = "" + prg;
}
catch(LogException e){
if(e.GetErrorCode() == "InvalidCursor")
consumerPrg = "無効です。消費チェックポイントが最後に更新された時刻は、データの保存期間を超えています";
else{
// 内部サーバーエラー
throw e;
}
}
}
System.out.println("消費チェックポイント: " + consumerPrg);
String endCursor = client.GetCursor(project, logstore, cp.getShard(), CursorMode.END).GetCursor();
int endPrg = 0;
try{
endPrg = client.GetPrevCursorTime(project, logstore, cp.getShard(), endCursor).GetCursorTime();
}
catch(LogException e){
// 何もしません
}
// UNIX タイムスタンプ。単位:秒。タイムスタンプの出力値を書式設定します。
System.out.println("最後のデータレコードが受信された時刻: " + endPrg);
}
}
}
}
出力を表示します。例:
名前: ali-test-consumergroup2
ハートビートタイムアウト期間: 60
順序付き消費: false
シャード: 0
消費チェックポイントが最後に更新された時刻: 0
コンシューマー名: consumer_1
消費チェックポイント: 消費が開始されていません
最後のデータレコードが受信された時刻: 1729583617
シャード: 1
消費チェックポイントが最後に更新された時刻: 0
コンシューマー名: consumer_1
消費チェックポイント: 消費が開始されていません
最後のデータレコードが受信された時刻: 1729583738
プロセスは終了コード 0 で終了しました
Simple Log Service コンソールを使用する
Simple Log Service コンソール にログインします。
[プロジェクト] セクションで、管理するプロジェクトをクリックします。

タブで、管理するログストアの横にある  アイコンをクリックします。次に、
アイコンをクリックします。次に、 [データ消費] の横にある アイコンをクリックします。
[データ消費] の横にある アイコンをクリックします。
コンシューマーグループリストで、管理するコンシューマーグループをクリックします。
[コンシューマーグループのステータス] ページで、各シャードの消費チェックポイントを表示します。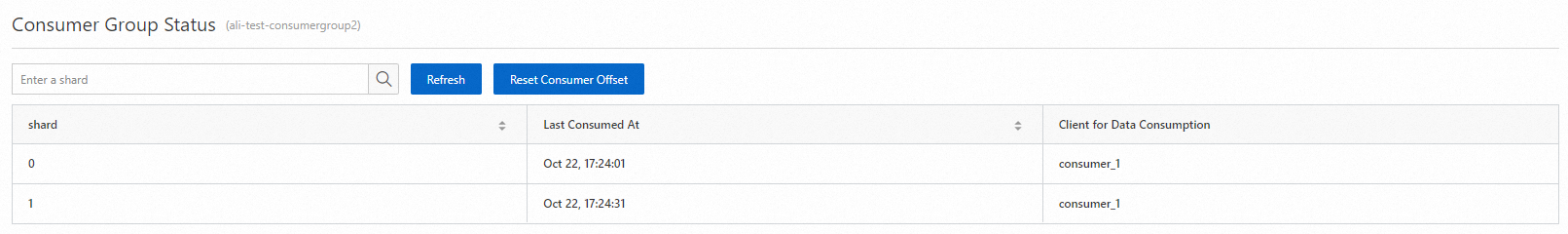
次のステップ
RAM ユーザーにコンシューマーグループに対する操作の実行を承認する
Resource Access Management (RAM) ユーザーがコンシューマーグループを管理できるようにするには、RAM ユーザーに必要な権限を付与する必要があります。詳細については、「RAM ユーザーを作成し、RAM ユーザーに Simple Log Service へのアクセスを承認する」をご参照ください。
次の表に、RAM ユーザーに実行を承認できる操作を示します。
操作 | 説明 | リソース |
log:GetCursorOrData(GetCursor) | ログが生成された時刻に基づいてカーソルをクエリします。 | acs:log:${regionName}:${projectOwnerAliUid}:project/${projectName}/logstore/${logstoreName} |
log:CreateConsumerGroup(CreateConsumerGroup) | ログストアのコンシューマーグループを作成します。 | acs:log:${regionName}:${projectOwnerAliUid}:project/${projectName}/logstore/${logstoreName}/consumergroup/${consumerGroupName} |
log:ListConsumerGroup(ListConsumerGroup) | ログストアのすべてのコンシューマーグループをクエリします。 | acs:log:${regionName}:${projectOwnerAliUid}:project/${projectName}/logstore/${logstoreName}/consumergroup/* |
log:ConsumerGroupUpdateCheckPoint(ConsumerGroupUpdateCheckPoint) | コンシューマーグループに割り当てられているシャードの消費チェックポイントを更新します。 | acs:log:${regionName}:${projectOwnerAliUid}:project/${projectName}/logstore/${logstoreName}/consumergroup/${consumerGroupName} |
log:ConsumerGroupHeartBeat(ConsumerGroupHeartBeat) | コンシューマーのハートビートメッセージを Simple Log Service に送信します。 | acs:log:${regionName}:${projectOwnerAliUid}:project/${projectName}/logstore/${logstoreName}/consumergroup/${consumerGroupName} |
log:UpdateConsumerGroup(UpdateConsumerGroup) | コンシューマーグループの属性を変更します。 | acs:log:${regionName}:${projectOwnerAliUid}:project/${projectName}/logstore/${logstoreName}/consumergroup/${consumerGroupName} |
log:GetConsumerGroupCheckPoint(GetCheckPoint) | コンシューマーグループに割り当てられている 1 つまたはすべてのシャードの消費チェックポイントをクエリします。 | acs:log:${regionName}:${projectOwnerAliUid}:project/${projectName}/logstore/${logstoreName}/consumergroup/${consumerGroupName} |
次のリストは、コンシューマーグループに関するリソース情報を示しています。RAM ユーザーがコンシューマーグループに対して操作を実行できるようにするには、次のコードを参照して、必要な権限を RAM ユーザーに付与します。
プロジェクトが属する Alibaba Cloud アカウントの ID:174649****602745
プロジェクトが存在するリージョンの ID:cn-hangzhou
プロジェクトの名前:project-test
ログストアの名前:logstore-test
コンシューマーグループの名前:consumergroup-test
サンプルコード:
{
"Version": "1",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"log:GetCursorOrData"
],
"Resource": "acs:log:cn-hangzhou:174649****602745:project/project-test/logstore/logstore-test"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"log:CreateConsumerGroup",
"log:ListConsumerGroup"
],
"Resource": "acs:log:cn-hangzhou:174649****602745:project/project-test/logstore/logstore-test/consumergroup/*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"log:ConsumerGroupUpdateCheckPoint",
"log:ConsumerGroupHeartBeat",
"log:UpdateConsumerGroup",
"log:GetConsumerGroupCheckPoint"
],
"Resource": "acs:log:cn-hangzhou:174649****602745:project/project-test/logstore/logstore-test/consumergroup/consumergroup-test"
}
]
}
トラブルシューティング用に Log4j を構成する。
コンシューマーグループで例外が発生した場合にエラーメッセージを表示するために、コンシューマープログラム用に Log4j を構成することをお勧めします。これは、エラーのトラブルシューティングに役立ちます。次のコードは、一般的な log4j.properties 構成ファイルを示しています。
log4j.rootLogger = info,stdout
log4j.appender.stdout = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.Target = System.out
log4j.appender.stdout.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern = [%-5p] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS} method:%l%n%m%n
Log4j を構成すると、コンシューマープログラムの実行時にエラーメッセージを受信できます。次の例は、エラーメッセージを示しています。
[WARN ] 2018-03-14 12:01:52,747 method:com.aliyun.openservices.loghub.client.LogHubConsumer.sampleLogError(LogHubConsumer.java:159)
com.aliyun.openservices.log.exception.LogException: 無効なロググループ数、(0,1000]
コンシューマーグループを使用して、特定の時点以降に生成されたデータを消費する
// consumerStartTimeInSeconds は特定の時点を指定します。その時点以降に生成されたデータが消費されます。
public LogHubConfig(String consumerGroupName,
String consumerName,
String loghubEndPoint,
String project, String logStore,
String accessId, String accessKey,
int consumerStartTimeInSeconds);
// position は列挙変数です。LogHubConfig.ConsumePosition.BEGIN_CURSOR は、最も古いデータから消費が開始されることを指定します。LogHubConfig.ConsumePosition.END_CURSOR は、最新のデータから消費が開始されることを指定します。
public LogHubConfig(String consumerGroupName,
String consumerName,
String loghubEndPoint,
String project, String logStore,
String accessId, String accessKey,
ConsumePosition position);
説明 ビジネス要件に基づいて、さまざまなコンストラクタを使用できます。
Simple Log Service に消費チェックポイントが保存されている場合、データ消費はそのチェックポイントから開始されます。
Simple Log Service がデータを消費する場合、消費チェックポイントが優先的に使用されてデータ消費が開始されます。Simple Log Service がデータ消費を開始する時点を指定する場合は、consumerStartTimeInSeconds の値が生存時間 (TTL) 期間内にあることを確認してください。そうでない場合、Simple Log Service は構成に基づいてデータを消費できません。
消費チェックポイントをリセットする
public static void updateCheckpoint() throws Exception {
Client client = new Client(host, accessId, accessKey);
// 秒単位で正確な UNIX タイムスタンプを指定します。ミリ秒単位のタイムスタンプを指定する場合は、タイムスタンプを 1000 で除算します。例:
long timestamp = Timestamp.valueOf("2017-11-15 00:00:00").getTime() / 1000;
ListShardResponse response = client.ListShard(new ListShardRequest(project, logStore));
for (Shard shard : response.GetShards()) {
int shardId = shard.GetShardId();
String cursor = client.GetCursor(project, logStore, shardId, timestamp).GetCursor();
client.UpdateCheckPoint(project, logStore, consumerGroup, shardId, cursor);
}
}

 アイコンをクリックします。次に、
アイコンをクリックします。次に、 [データ消費] の横にある アイコンをクリックします。
[データ消費] の横にある アイコンをクリックします。