シンプル アプリケーション サーバー上のデータ ディスクの空き容量が不足している場合は、ビジネス要件に基づいてデータ ディスクを拡張できます。このトピックでは、シンプル アプリケーション サーバー上のデータ ディスクを拡張する方法について説明します。
手順
ステップ 1:スナップショットの作成
データ ディスクを拡張すると、データが失われる可能性があります。データ ディスクを拡張する前に、スナップショットを作成してディスク データをバックアップすることをお勧めします。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバーコンソールの Servers ページに移動します。
[サーバー] ページで、スナップショットを作成するサーバーを見つけ、サーバーカードのサーバー ID をクリックします。
[ディスク] タブをクリックします。
データ ディスクの [アクション] 列で、[スナップショットの作成] をクリックします。
[スナップショットの作成] ダイアログ ボックスで、ディスク情報を確認し、スナップショットの名前を入力して、[確認] をクリックします。
ステップ 2:データ ディスクの拡張
シンプル アプリケーション サーバーコンソールの Servers ページに移動します。
データ ディスクを拡張するサーバーのカードで、サーバー ID をクリックします。
[ディスク] タブをクリックします。
表示されるページの左上隅にある [データ ディスクのスケールアップ] をクリックします。
[注意事項] ダイアログ ボックスで注意事項を読み、[データ ディスク操作] をクリックします。
ディスクの現在の構成と有効期限を確認し、[データ ディスク] の横にあるデータ ディスクサイズを選択します。
データ ディスクは最大 16,380 GB まで拡張できます。
重要データ ディスクは拡張のみ可能です。選択したデータ ディスクサイズの値は、元のデータ ディスクサイズの値よりも大きくなければなりません。
関連する契約を読み、確認して、[今すぐ購入] をクリックします。
画面の指示に従って支払いを完了します。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバーに接続して、データ ディスク上のパーティションとファイル システムを拡張します。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバーのオペレーティングシステムに基づいて、次の操作を実行します。
Linux サーバーのデータ ディスク上のパーティションとファイル システムの拡張
次の例では、データ ディスクが 40 GB から 60 GB に拡張されています。
説明シンプル アプリケーション サーバー上のデータ ディスクのデフォルトのデバイス名は
/dev/vdbです。Linux サーバーに接続します。
詳細については、「Linux サーバーへの接続」をご参照ください。
次のコマンドを実行して
rootユーザーに切り替えます。sudo su rootシンプル アプリケーション サーバーのディスクとパーティションを表示します。
次のコマンドを実行して、シンプル アプリケーション サーバーのディスクを表示します。
fdisk -luデータ ディスクの拡張は、システム ディスクのサイズには影響しません。次の図は、データ ディスク(
/dev/vdb)に関する情報のみを示しています。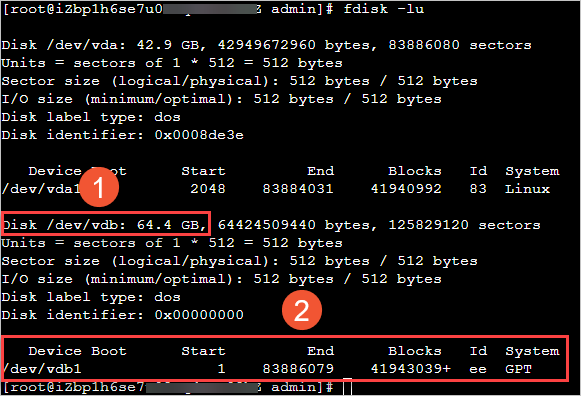 前の図の要素:
前の図の要素:① で示された四角形領域:
/dev/vdbデータ ディスクが拡張された後の新しいデータ ディスクサイズを示します。② で示された四角形領域:
Deviceの下の情報は、データ ディスクのパーティション名が/dev/vdb1であることを示し、Systemの下の情報は、データ ディスクのパーティションスタイルが GUID パーティションテーブル(GPT)であることを示します。
次のコマンドを実行して、パーティションに関する情報を表示します。
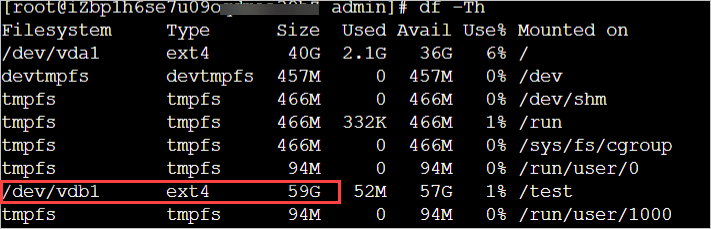
df -Th/dev/vdb1データディスクパーティションの Simple Application Server でのデフォルトのファイルシステムタイプは ext4 です。次の図はコマンド出力を示しており、データディスクパーティションのファイルシステムのサイズが 40 GB のままであることを示しています。データディスクを拡張するには、パーティションとファイルシステムを拡張する必要があります。
パーティションを拡張します。
次のコマンドを実行して、gdisk ユーティリティをインストールします。
パーティションが GPT 形式の場合は、この手順を実行する必要があります。パーティションがマスター ブートレコード(MBR)形式の場合は、この手順をスキップします。
yum install gdisk -y次のコマンドを実行して、growpart ユーティリティをインストールします。
growpart ユーティリティのインストールに使用するコマンドは、シンプル アプリケーション サーバーのオペレーティングシステムによって異なります。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバーで CentOS 7 以降が実行されている場合は、次のコマンドを実行します。
yum install -y cloud-utils-growpart説明CentOS 8 はサポート終了(EOL)に達しました。シンプル アプリケーション サーバーで CentOS 8 オペレーティングシステムが実行されている場合は、CentOS 8 リポジトリアドレスを変更します。Simple Application Server 詳細については、「CentOS 8 リポジトリ アドレスの変更」をご参照ください。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバーで Debian 9 以降、または Ubuntu 14 以降が実行されている場合は、次のコマンドを順番に実行します。
次のコマンドを実行して、ソフトウェア リポジトリを更新します。
apt-get update次のコマンドを実行して、cloud-guest-utils をインストールします。
apt-get install -y cloud-guest-utils
次のコマンドを実行して、パーティションを拡張します。
説明コマンド内の
/dev/vdbと1はスペースで区切ります。growpart /dev/vdb 1次のコマンド出力が返されます。
[root@iZbp1h6se7u09oqdmea**** admin]# growpart /dev/vdb 1 CHANGED: partition=1 start=2048 old: size=83881984 end=83884032 new: size=125827038 end=125829086コマンドの実行時にエラーが発生した場合は、問題のトラブルシューティングを行います。詳細については、「ステップ 1:ディスクのサイズ変更によるディスク容量の拡張」をご参照ください。
ファイル システムを拡張します。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバー上の
/dev/vdb1データ ディスクパーティションのデフォルトのファイル システムタイプは ext4 です。このステップでは、ext4 ファイル システムを拡張する方法について説明します。Simple Application Server次のコマンドを実行して、ファイル システムを拡張します。
resize2fs /dev/vdb1次のコマンドを実行して、ファイル システムが拡張されたかどうかを確認します。
df -Th次の図に示すように、ファイル システムのサイズが 60 GB の場合、ファイル システムは拡張されています。
 データ ディスクを拡張した後、データ ディスクの実際のサイズが想定どおりのサイズであるかどうかを確認します。
データ ディスクを拡張した後、データ ディスクの実際のサイズが想定どおりのサイズであるかどうかを確認します。シンプル アプリケーション サーバー上のビジネス プログラムが想定どおりに実行されている場合、データ ディスクは拡張されています。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバー上のビジネス プログラムが想定どおりに実行されていない場合、データ ディスクは拡張されていません。ステップ 1 で作成したスナップショットを使用して、ディスクをロールバックします。詳細については、「スナップショットの管理」トピックの「スナップショットの作成」セクションをご参照ください。
Windows サーバーのデータ ディスク上のファイル システムの拡張
次の例では、Windows Server 2012 R2 64 ビット オペレーティングシステムを実行するシンプル アプリケーション サーバーを使用しています。データ ディスクは 40 GB から 60 GB に拡張されています。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバーコンソールでデータ ディスクを拡張した Windows サーバーに接続します。
詳細については、「Windows サーバーへの接続」をご参照ください。
Windows デスクトップの左下隅で、
 アイコンを右クリックし、[ディスクの管理] をクリックします。
アイコンを右クリックし、[ディスクの管理] をクリックします。
[ディスクの管理] ダイアログ ボックスで、 を選択して、未割り当てディスクサイズを表示します。

ディスク 1 はデータ ディスクです。
[ディスク 1] セクションの空白部分を右クリックし、[ボリュームの拡張...] を選択します。

[ボリューム拡張ウィザード] ダイアログ ボックスで、デフォルト設定を使用してボリュームを拡張します。
次の図に示すように、新しいスペースが元のボリュームに自動的に追加されます。

データ ディスクを拡張した後、データ ディスクの実際のサイズが想定どおりのサイズであるかどうかを確認します。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバー上のビジネス プログラムが想定どおりに実行されている場合、データ ディスクは拡張されています。
シンプル アプリケーション サーバー上のビジネス プログラムが想定どおりに実行されていない場合、データ ディスクは拡張されていません。ステップ 1 で作成したスナップショットを使用して、ディスクをロールバックします。詳細については、「スナップショットの管理」トピックの「スナップショットの作成」セクションをご参照ください。